|
Bramo SAM 22
The Siemens-Halske Sh 22 (also known as SAM 22) was a nine-cylinder aircraft radial engine manufactured by Siemens & Halske in Germany in the 1930s. Following the reorganization of its manufacturer and change in military nomenclature, the engine became known as the Bramo 322. It was a result of a series of modifications to the original Bristol Jupiter IV design, which Siemens licensed in 1929. The first modifications were to "Germanize" the dimensions, producing the Sh.20 and Sh.21. The design was then bored out to produce the 950 hp (708 kW) Sh.22 in 1930. Like the Jupiter, the Sh.22 featured a rather "old" looking arrangement with rather prominent valve pushrods on the front of the engine. In the mid-1930s the Reich Air Ministry (RLM) rationalized engine naming, and Bramo was given the 300-block of numbers, the Sh.14 and Sh.22 becoming the Bramo 314 and 322 respectively. The 322 never matured and remained unreliable. It became a base for the more successful Bramo 323. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings around the edge of the master rod. Extra "rows" of radial cylinders can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Air-cooled Radial Piston Engines
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicyclic Gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gears mesh so that their pitch circles roll without slip. A point on the pitch circle of the planet gear traces an epicycloid curve. In this simplified case, the sun gear is fixed and the planetary gear(s) roll around the sun gear. An epicyclic gear train can be assembled so the planet gear rolls on the inside of the pitch circle of a fixed, outer gear ring, or ring gear, sometimes called an ''annular gear''. In this case, the curve traced by a point on the pitch circle of the planet is a hypocycloid. The combination of epicycle gear trains with a planet engaging both a sun gear and a ring gear is called a ''planetary gear train''.J. J. Uicker, G. R. Pennock and J. E. Shigley, 2003, ''Theory of Machines and Mechanisms,'' Oxford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farman Aviation Works
Farman Aviation Works (french: Avions Farman) was a French aircraft company founded and run by the brothers Richard, Henri, and Maurice Farman. They designed and constructed aircraft and engines from 1908 until 1936; during the French nationalization and rationalization of its aeronautical industry, Farman's assets were assigned to the ''Société Nationale de Constructions Aéronautiques du Centre'' (SNCAC). In 1941 the Farman brothers reestablished the firm as the "''Société Anonyme des Usines Farman''" (SAUF), but only three years later it was absorbed by Sud-Ouest. Maurice's son, Marcel Farman, reestablished the SAUF in 1952, but his effort proved unsuccessful and the firm was dissolved in 1956. The Farman brothers designed and built more than 200 types of aircraft between 1908 and 1941. They also built cars until 1931 and boats until 1930. Background In 1907, Henri Farman bought his first aircraft from Gabriel Voisin and soon began to improve the design of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. On average, U.S. refineries produce, from a barrel of crude oil, about 19 to 20 gallons of gasoline; 11 to 13 gallons of distillate fuel (most of which is sold as diesel fuel); and 3 to 4 gallons of jet fuel. The product ratio depends on the processing in an oil refinery and the crude oil assay. A barrel of oil is defined as holding 42 US gallons, which is about 159 liters or 35 imperial gallons. The characteristic of a particular gasoline blend to resist igniting too early (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating, which is produced in several grades. Tetraethyl lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
87 Octane
An octane rating, or octane number, is a standard measure of a fuel's ability to withstand compression in an internal combustion engine without detonating. The higher the octane number, the more compression the fuel can withstand before detonating. Octane rating does not relate directly to the power output or the energy content of the fuel per unit mass or volume, but simply indicates gasoline's capability against compression. Whether or not a higher octane fuel improves or impairs an engine's performance depends on the design of the engine. In broad terms, fuels with a higher octane rating are used in higher-compression gasoline engines, which may yield higher power for these engines. Such higher power comes from the fuel's higher compression by the engine design, and not directly from the gasoline. In contrast, fuels with lower octane (but higher cetane numbers) are ideal for diesel engines because diesel engines (also called compression-ignition engines) do not compress th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
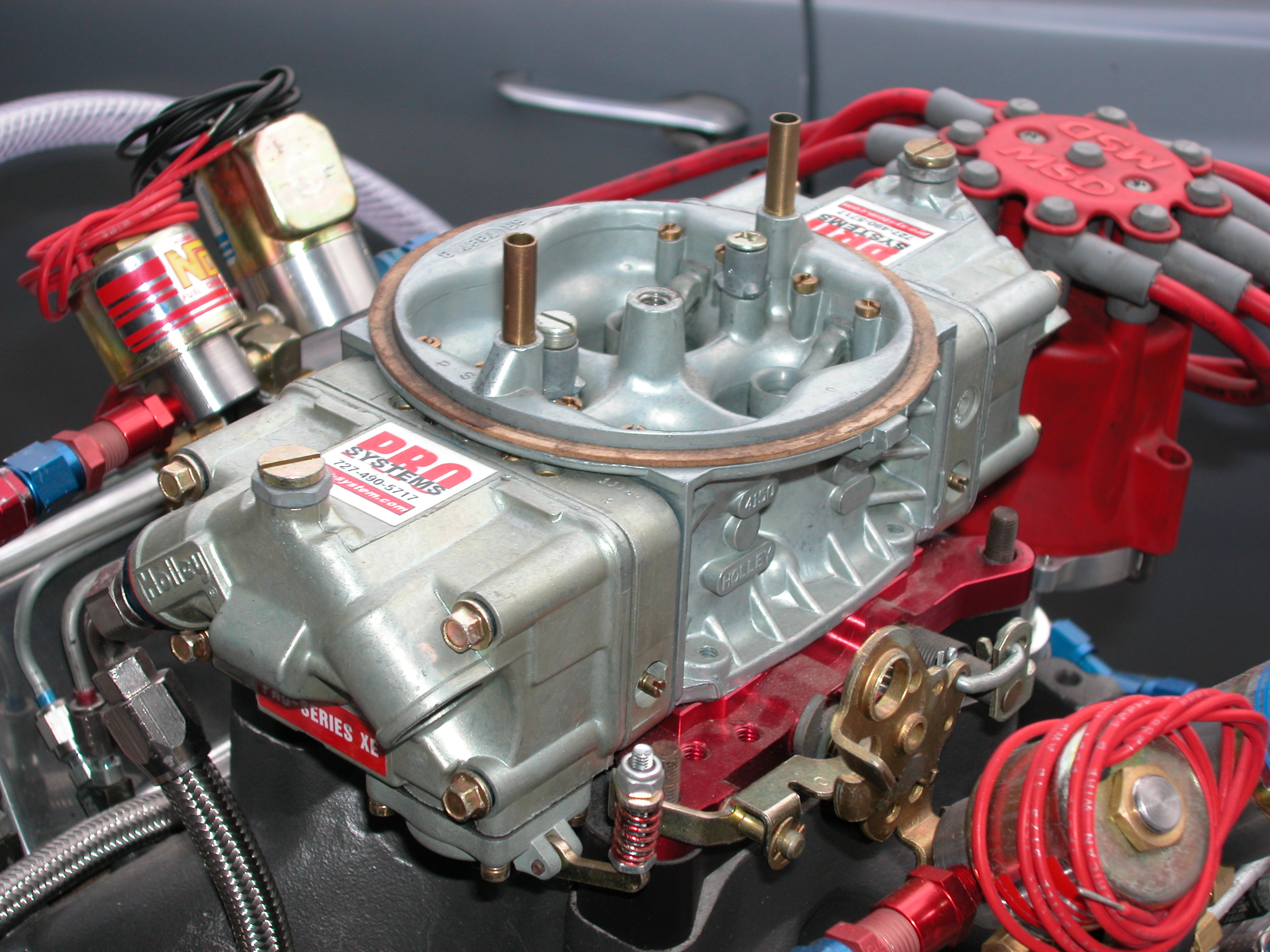
Carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Type Supercharger
A centrifugal supercharger is a specialized type of supercharger that makes use of centrifugal force in order to increase the manifold air pressure, MAP. An increased MAP allows the engine to burn more fuel, which results in an increased power output. Centrifugal superchargers are generally attached to the front of the engine via a belt-drive or gear-drive from the engine's crankshaft. Types of centrifugal superchargers The centrifugal supercharger is used in many applications including, but not limited to, automotive, truck, marine, aircraft, motorcycles and UTV's. Of these applications, they are most commonly utilized for increasing horsepower in street vehicles and race applications. While the first practical centrifugal compressor was designed in 1899, centrifugal superchargers evolved during World War II with their use in aircraft, where they were frequently paired with their exhaust driven counterpart, the turbosupercharger. This term refers to the fact that turbochargers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Valve
An overhead valve (OHV) engine, sometimes called a ''pushrod engine'', is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier flathead engines, where the valves were located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. Although an overhead camshaft (OHC) engine also has overhead valves, the common usage of the term "overhead valve engine" is limited to engines where the camshaft is located in the engine block. In these traditional OHV engines, the motion of the camshaft is transferred using pushrods (hence the term "pushrod engine") and rocker arms to operate the valves at the top of the engine. Some early intake-over-exhaust engines used a hybrid design combining elements of both side-valves and overhead valves. History Predecessors The first internal combustion engines were based on steam engines and therefore used slide valves. This was the case for the first Otto engine, which was first s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million residents within the city limits, over 17 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in the metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's largest cities; being the most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest urban and metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow grew to become a prosperous and powerful city that served as the capital of the Grand Duchy that bears its name. When the Grand Duchy of Moscow evolved into the Tsardom of Russia, Moscow remained the political and economic center for most of the Tsardom's history. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
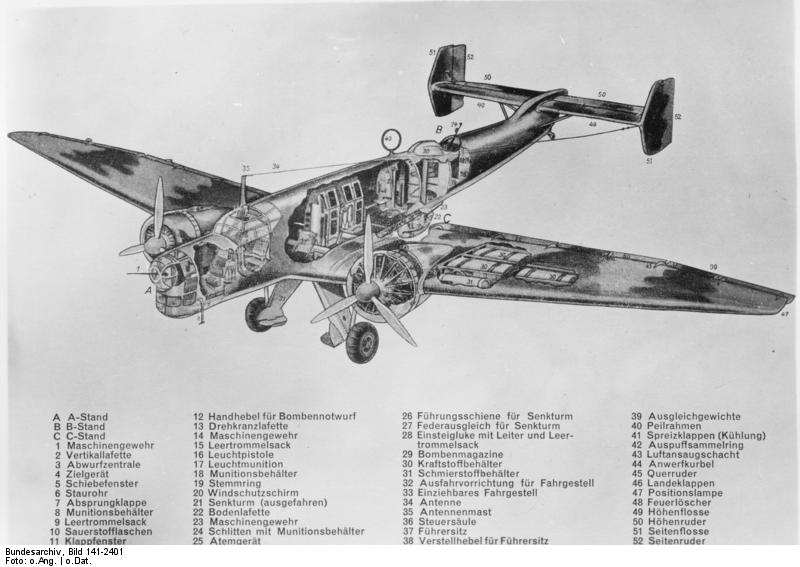
Junkers Ju 86
The Junkers Ju 86 was a German monoplane bomber and civilian airliner designed in the early 1930s, and employed by various air forces on both sides during World War II. The civilian model Ju 86B could carry ten passengers. Two were delivered to Swissair and five to Deutsche Luft Hansa. In addition a single civilian Ju 86Z was delivered to Sweden's AB Aerotransport. Design and development In 1934, a specification for a modern twin-engined aircraft, capable of operating both as a high-speed airliner for the German airline Luft Hansa and as a medium bomber for the nascent Luftwaffe, was issued to both Junkers and Heinkel. Five prototypes were ordered from each company; the Junkers Ju 86 and Heinkel He 111.Green and Swanborough 1982, p. 15. Junkers' design was a low-winged twin-engined monoplane, of all-metal stressed skin construction. Unlike most of Junkers' previous designs, it discarded the typical corrugated skinning in favour of smooth metal skinning which helped to reduce drag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |