 A computer virus is a type of
A computer virus is a type of malware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to caus ...
that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es.
Computer viruses generally require a host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. By contrast, a computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks.
Virus writers use social engineering deception
Deception is the act of convincing of one or many recipients of untrue information. The person creating the deception knows it to be false while the receiver of the information does not. It is often done for personal gain or advantage.
Tort of ...
s and exploit detailed knowledge of security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems and to spread the virus. Viruses use complex anti-detection/stealth strategies to evade antivirus software. Motives for creating viruses can include seeking profit (e.g., with ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that Encryption, encrypts the victim's personal data until a ransom is paid. Difficult-to-trace Digital currency, digital currencies such as paysafecard or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency, cryptocurrencies are com ...
), desire to send a political message, personal amusement, to demonstrate that a vulnerability exists in software, for sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, government, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, demoralization (warfare), demoralization, destabilization, divide and rule, division, social disruption, disrupti ...
and denial of service, or simply because they wish to explore cybersecurity issues, artificial life and evolutionary algorithm
Evolutionary algorithms (EA) reproduce essential elements of the biological evolution in a computer algorithm in order to solve "difficult" problems, at least Approximation, approximately, for which no exact or satisfactory solution methods are k ...
s.
As of 2013, computer viruses caused billions of dollars' worth of economic damage each year. In response, an industry of antivirus software has cropped up, selling or freely distributing virus protection to users of various operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s.
History
The first academic work on the theory of self-replicating computer programs was done in 1949 byJohn von Neumann
John von Neumann ( ; ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian and American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist and engineer. Von Neumann had perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time, in ...
who gave lectures at the University of Illinois about the "Theory and Organization of Complicated Automata". The work of von Neumann was later published as the "Theory of self-reproducing automata". In his essay von Neumann described how a computer program could be designed to reproduce itself. Von Neumann's design for a self-reproducing computer program is considered the world's first computer virus, and he is considered to be the theoretical "father" of computer virology.
In 1972, Veith Risak directly building on von Neumann's work on self-replication, published his article "Selbstreproduzierende Automaten mit minimaler Informationsübertragung" (Self-reproducing automata with minimal information exchange). The article describes a fully functional virus written in assembler programming language for a SIEMENS 4004/35 computer system. In 1980, Jürgen Kraus wrote his '' Diplom'' thesis "Selbstreproduktion bei Programmen" (Self-reproduction of programs) at the University of Dortmund. In his work Kraus postulated that computer programs can behave in a way similar to biological viruses.
 The Creeper virus was first detected on
The Creeper virus was first detected on ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first computer networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the tec ...
, the forerunner of the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
, in the early 1970s. Creeper was an experimental self-replicating program written by Bob Thomas at BBN Technologies in 1971. Creeper used the ARPANET to infect DEC PDP-10
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)'s PDP-10, later marketed as the DECsystem-10, is a mainframe computer family manufactured beginning in 1966 and discontinued in 1983. 1970s models and beyond were marketed under the DECsystem-10 name, especi ...
computers running the TENEX operating system. Creeper gained access via the ARPANET and copied itself to the remote system where the message, "I'M THE CREEPER. CATCH ME IF YOU CAN!" was displayed. The ''Reaper'' program was created to delete Creeper.
In 1982, a program called " Elk Cloner" was the first personal computer virus to appear "in the wild"—that is, outside the single computer or computer lab where it was created. Written in 1981 by Richard Skrenta, a ninth grader at Mount Lebanon High School near Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
, it attached itself to the Apple DOS 3.3 operating system and spread via floppy disk. On its 50th use the Elk Cloner virus would be activated, infecting the personal computer and displaying a short poem beginning "Elk Cloner: The program with a personality."
In 1984, Fred Cohen from the University of Southern California
The University of Southern California (USC, SC, or Southern Cal) is a Private university, private research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Founded in 1880 by Robert M. Widney, it is the oldest private research university in ...
wrote his paper "Computer Viruses – Theory and Experiments". It was the first paper to explicitly call a self-reproducing program a "virus", a term introduced by Cohen's mentor Leonard Adleman. In 1987, Cohen published a demonstration that there is no algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
that can perfectly detect all possible viruses.Cohen, Fred, , 1987, IBM Cohen's theoretical compression virus was an example of a virus which was not malicious software (malware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to caus ...
), but was putatively benevolent (well-intentioned). However, antivirus
Antivirus software (abbreviated to AV software), also known as anti-malware, is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware.
Antivirus software was originally developed to detect and remove computer viruses, hence the name ...
professionals do not accept the concept of "benevolent viruses", as any desired function can be implemented without involving a virus (automatic compression, for instance, is available under Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
at the choice of the user). Any virus will by definition make unauthorised changes to a computer, which is undesirable even if no damage is done or intended. The first page of ''Dr Solomon's Virus Encyclopaedia'' explains the undesirability of viruses, even those that do nothing but reproduce.
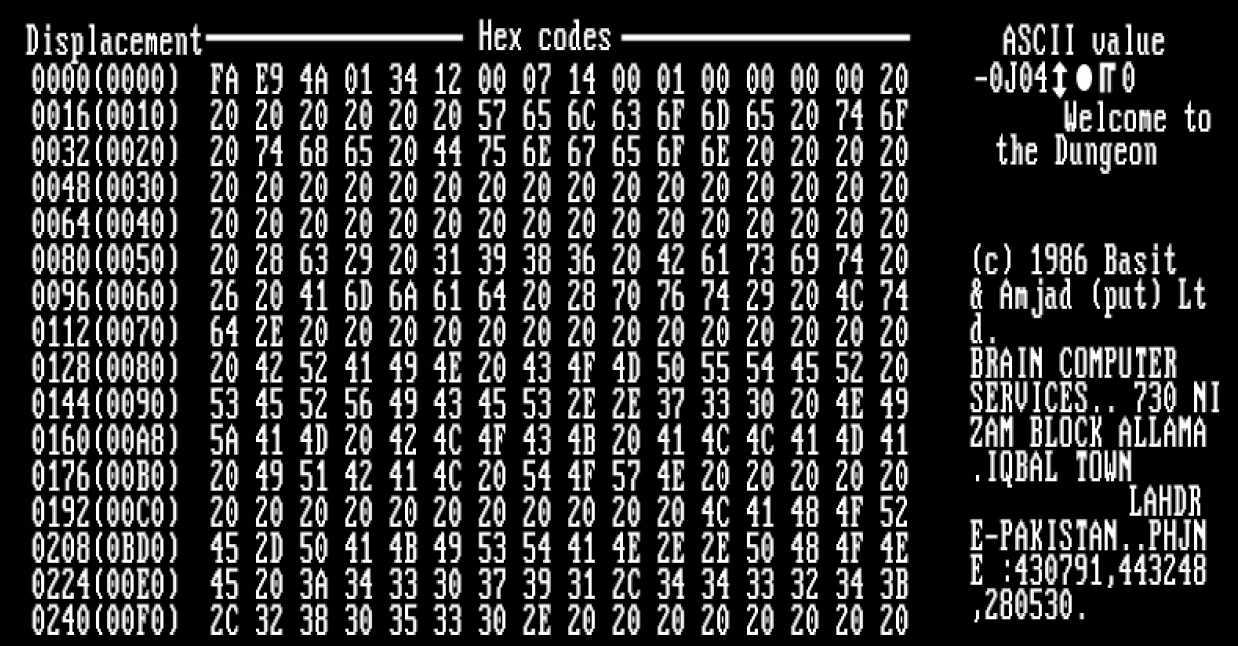
An article that describes "useful virus functionalities" was published by J. B. Gunn under the title "Use of virus functions to provide a virtual APL interpreter under user control" in 1984. The first IBM PC compatible virus in the "wild" was a boot sector virus dubbed (c)Brain, created in 1986 and was released in 1987 by Amjad Farooq Alvi and Basit Farooq Alvi in Lahore, Pakistan, reportedly to deter unauthorized copying of the software they had written.
The first virus to specifically target Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
, WinVir was discovered in April 1992, two years after the release of Windows 3.0. The virus did not contain any Windows API calls, instead relying on DOS interrupts. A few years later, in February 1996, Australian hackers from the virus-writing crew VLAD created the Bizatch virus (also known as "Boza" virus), which was the first known virus to specifically target Windows 95. This virus attacked the new portable executable (PE) files introduced in Windows 95. In late 1997 the encrypted, memory-resident stealth virus Win32.Cabanas was released—the first known virus that targeted Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
(it was also able to infect Windows 3.0 and Windows 9x hosts).
Even home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
s were affected by viruses. The first one to appear on the Amiga was a boot sector virus called SCA virus, which was detected in November 1987. By 1988, one sysop reportedly found that viruses infected 15% of the software available for download on his BBS.
Design
Parts
A computer virus generally contains three parts: the infection mechanism, which finds and infects new files, the payload, which is the malicious code to execute, and the trigger, which determines when to activate the payload. ; Infection mechanism: Also called the infection vector, this is how the virus spreads. Some viruses have a search routine, which locate and infect files on disk. Other viruses infect files as they are run, such as the Jerusalem DOS virus. ; Trigger: Also known as a logic bomb, this is the part of the virus that determines the condition for which the payload is activated. This condition may be a particular date, time, presence of another program, size on disk exceeding a threshold, or opening a specific file. ; Payload: The payload is the body of the virus that executes the malicious activity. Examples of malicious activities include damaging files, theft of confidential information or spying on the infected system. Payload activity is sometimes noticeable as it can cause the system to slow down or "freeze". Sometimes payloads are non-destructive and their main purpose is to spread a message to as many people as possible. This is called a virus hoax.Phases
Virus phases is the life cycle of the computer virus, described by using an analogy tobiology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
. This life cycle can be divided into four phases:
; Dormant phase: The virus program is idle during this stage. The virus program has managed to access the target user's computer or software, but during this stage, the virus does not take any action. The virus will eventually be activated by the "trigger" which states which event will execute the virus. Not all viruses have this stage.
; Propagation phase: The virus starts propagating, which is multiplying and replicating itself. The virus places a copy of itself into other programs or into certain system areas on the disk. The copy may not be identical to the propagating version; viruses often "morph" or change to evade detection by IT professionals and anti-virus software. Each infected program will now contain a clone of the virus, which will itself enter a propagation phase.
; Triggering phase: A dormant virus moves into this phase when it is activated, and will now perform the function for which it was intended. The triggering phase can be caused by a variety of system events, including a count of the number of times that this copy of the virus has made copies of itself. The trigger may occur when an employee is terminated from their employment or after a set period of time has elapsed, in order to reduce suspicion.
; Execution phase: This is the actual work of the virus, where the "payload" will be released. It can be destructive such as deleting files on disk, crashing the system, or corrupting files or relatively harmless such as popping up humorous or political messages on screen.
Targets and replication
Computer viruses infect a variety of different subsystems on their host computers and software. One manner of classifying viruses is to analyze whether they reside in binary executables (such as .EXE or .COM files), data files (such asMicrosoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor program, word processing program developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platf ...
documents or PDF files), or in the boot sector of the host's hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
(or some combination of all of these).
A ''memory-resident virus'' (or simply "resident virus") installs itself as part of the operating system when executed, after which it remains in RAM from the time the computer is booted up to when it is shut down. Resident viruses overwrite interrupt handling code or other functions, and when the operating system attempts to access the target file or disk sector, the virus code intercepts the request and redirects the control flow to the replication module, infecting the target. In contrast, a ''non-memory-resident virus'' (or "non-resident virus"), when executed, scans the disk for targets, infects them, and then exits (i.e. it does not remain in memory after it is done executing).
Many common applications, such as Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook is a personal information manager software system from Microsoft, available as a part of the Microsoft 365 software suites. Primarily popular as an email client for businesses, Outlook also includes functions such as Calendari ...
and Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor program, word processing program developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platf ...
, allow macro programs to be embedded in documents or emails, so that the programs may be run automatically when the document is opened. A ''macro virus'' (or "document virus") is a virus that is written in a macro language and embedded into these documents so that when users open the file, the virus code is executed, and can infect the user's computer. This is one of the reasons that it is dangerous to open unexpected or suspicious attachments in e-mails. While not opening attachments in e-mails from unknown persons or organizations can help to reduce the likelihood of contracting a virus, in some cases, the virus is designed so that the e-mail appears to be from a reputable organization (e.g., a major bank or credit card company).
''Boot sector viruses'' specifically target the boot sector and/or the Master Boot Record
A master boot record (MBR) is a type of boot sector in the first block of disk partitioning, partitioned computer mass storage devices like fixed disks or removable drives intended for use with IBM PC-compatible systems and beyond. The concept ...
(MBR) of the host's hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
, solid-state drive, or removable storage media ( flash drives, floppy disks, etc.).
The most common way of transmission of computer viruses in boot sector is physical media. When reading the VBR of the drive, the infected floppy disk or USB flash drive connected to the computer will transfer data, and then modify or replace the existing boot code. The next time a user tries to start the desktop, the virus will immediately load and run as part of the master boot record.
Email viruses are viruses that intentionally, rather than accidentally, use the email system to spread. While virus infected files may be accidentally sent as email attachments, email viruses are aware of email system functions. They generally target a specific type of email system (Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook is a personal information manager software system from Microsoft, available as a part of the Microsoft 365 software suites. Primarily popular as an email client for businesses, Outlook also includes functions such as Calendari ...
is the most commonly used), harvest email addresses from various sources, and may append copies of themselves to all email sent, or may generate email messages containing copies of themselves as attachments.
Detection
To avoid detection by users, some viruses employ different kinds ofdeception
Deception is the act of convincing of one or many recipients of untrue information. The person creating the deception knows it to be false while the receiver of the information does not. It is often done for personal gain or advantage.
Tort of ...
. Some old viruses, especially on the DOS platform, make sure that the "last modified" date of a host file stays the same when the file is infected by the virus. This approach does not fool antivirus software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, however, especially those which maintain and date cyclic redundancy checks on file changes. Some viruses can infect files without increasing their sizes or damaging the files. They accomplish this by overwriting unused areas of executable files. These are called ''cavity viruses''. For example, the CIH virus, or Chernobyl Virus, infects Portable Executable
The Portable Executable (PE) format is a file format for executables, object file, object code, Dynamic-link library, dynamic-link-libraries (DLLs), and binary files used on 32-bit and 64-bit Microsoft Windows, Windows operating systems, as well ...
files. Because those files have many empty gaps, the virus, which was 1 KB in length, did not add to the size of the file. Some viruses try to avoid detection by killing the tasks associated with antivirus software before it can detect them (for example, Conficker). A Virus may also hide its presence using a rootkit by not showing itself on the list of system processes or by disguising itself within a trusted process. In the 2010s, as computers and operating systems grow larger and more complex, old hiding techniques need to be updated or replaced. Defending a computer against viruses may demand that a file system migrate towards detailed and explicit permission for every kind of file access. In addition, only a small fraction of known viruses actually cause real incidents, primarily because many viruses remain below the theoretical epidemic threshold.
Read request intercepts
While some kinds of antivirus software employ various techniques to counter stealth mechanisms, once the infection occurs any recourse to "clean" the system is unreliable. In Microsoft Windows operating systems, the NTFS file system is proprietary. This leaves antivirus software little alternative but to send a "read" request to Windows files that handle such requests. Some viruses trick antivirus software by intercepting its requests to the operating system. A virus can hide by intercepting the request to read the infected file, handling the request itself, and returning an uninfected version of the file to the antivirus software. The interception can occur by code injection of the actual operating system files that would handle the read request. Thus, an antivirus software attempting to detect the virus will either not be permitted to read the infected file, or, the "read" request will be served with the uninfected version of the same file. The only reliable method to avoid "stealth" viruses is to boot from a medium that is known to be "clear". Security software can then be used to check the dormant operating system files. Most security software relies on virus signatures, or they employ heuristics. Security software may also use a database of file " hashes" for Windows OS files, so the security software can identify altered files, and request Windows installation media to replace them with authentic versions. In older versions of Windows, file cryptographic hash functions of Windows OS files stored in Windows—to allow file integrity/authenticity to be checked—could be overwritten so that the System File Checker would report that altered system files are authentic, so using file hashes to scan for altered files would not always guarantee finding an infection.Self-modification
Most modern antivirus programs try to find virus-patterns inside ordinary programs by scanning them for so-called ''virus signatures''. Different antivirus programs will employ different search methods when identifying viruses. If a virus scanner finds such a pattern in a file, it will perform other checks to make sure that it has found the virus, and not merely a coincidental sequence in an innocent file, before it notifies the user that the file is infected. The user can then delete, or (in some cases) "clean" or "heal" the infected file. Some viruses employ techniques that make detection by means of signatures difficult but probably not impossible. These viruses modify their code on each infection. That is, each infected file contains a different variant of the virus. One method of evading signature detection is to use simpleencryption
In Cryptography law, cryptography, encryption (more specifically, Code, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the inf ...
to encipher (encode) the body of the virus, leaving only the encryption module and a static cryptographic key in cleartext which does not change from one infection to the next. In this case, the virus consists of a small decrypting module and an encrypted copy of the virus code. If the virus is encrypted with a different key for each infected file, the only part of the virus that remains constant is the decrypting module, which would (for example) be appended to the end. In this case, a virus scanner cannot directly detect the virus using signatures, but it can still detect the decrypting module, which still makes indirect detection of the virus possible. Since these would be symmetric keys, stored on the infected host, it is entirely possible to decrypt the final virus, but this is probably not required, since self-modifying code
In computer science, self-modifying code (SMC or SMoC) is source code, code that alters its own instruction (computer science), instructions while it is execution (computing), executing – usually to reduce the instruction path length and imp ...
is such a rarity that finding some may be reason enough for virus scanners to at least "flag" the file as suspicious. An old but compact way will be the use of arithmetic operation like addition or subtraction and the use of logical conditions such as XORing, where each byte in a virus is with a constant so that the exclusive-or operation had only to be repeated for decryption. It is suspicious for a code to modify itself, so the code to do the encryption/decryption may be part of the signature in many virus definitions. A simpler older approach did not use a key, where the encryption consisted only of operations with no parameters, like incrementing and decrementing, bitwise rotation, arithmetic negation, and logical NOT. Some viruses, called polymorphic viruses, will employ a means of encryption inside an executable in which the virus is encrypted under certain events, such as the virus scanner being disabled for updates or the computer being rebooted. This is called cryptovirology.
Polymorphic code was the first technique that posed a serious threat to virus scanners. Just like regular encrypted viruses, a polymorphic virus infects files with an encrypted copy of itself, which is decoded by a decryption module. In the case of polymorphic viruses, however, this decryption module is also modified on each infection. A well-written polymorphic virus therefore has no parts which remain identical between infections, making it very difficult to detect directly using "signatures". Antivirus software can detect it by decrypting the viruses using an emulator, or by statistical pattern analysis of the encrypted virus body. To enable polymorphic code, the virus has to have a polymorphic engine (also called "mutating engine" or "mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
engine") somewhere in its encrypted body. See polymorphic code for technical detail on how such engines operate.
Some viruses employ polymorphic code in a way that constrains the mutation rate of the virus significantly. For example, a virus can be programmed to mutate only slightly over time, or it can be programmed to refrain from mutating when it infects a file on a computer that already contains copies of the virus. The advantage of using such slow polymorphic code is that it makes it more difficult for antivirus professionals and investigators to obtain representative samples of the virus, because "bait" files that are infected in one run will typically contain identical or similar samples of the virus. This will make it more likely that the detection by the virus scanner will be unreliable, and that some instances of the virus may be able to avoid detection.
To avoid being detected by emulation, some viruses rewrite themselves completely each time they are to infect new executables. Viruses that utilize this technique are said to be in metamorphic code. To enable metamorphism, a "metamorphic engine" is needed. A metamorphic virus is usually very large and complex. For example, W32/Simile consisted of over 14,000 lines of assembly language code, 90% of which is part of the metamorphic engine.
Effects
Damage is due to causing system failure, corrupting data, wasting computer resources, increasing maintenance costs or stealing personal information. Even though no antivirus software can uncover all computer viruses (especially new ones), computer security researchers are actively searching for new ways to enable antivirus solutions to more effectively detect emerging viruses, before they become widely distributed. A ''power virus'' is a computer program that executes specific machine code to reach the maximum CPU power dissipation (thermal energy
The term "thermal energy" is often used ambiguously in physics and engineering. It can denote several different physical concepts, including:
* Internal energy: The energy contained within a body of matter or radiation, excluding the potential en ...
output for the central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
s). Computer cooling apparatus are designed to dissipate power up to the thermal design power, rather than maximum power, and a power virus could cause the system to overheat if it does not have logic to stop the processor. This may cause permanent physical damage. Power viruses can be malicious, but are often suites of test software used for integration testing and thermal testing of computer components during the design phase of a product, or for product benchmarking
Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other companies. Dimensions typically measured are Project management triangle, quality, time and cost.
Benchmarking is ...
.
Stability test applications are similar programs which have the same effect as power viruses (high CPU usage) but stay under the user's control. They are used for testing CPUs, for example, when overclocking. Spinlock in a poorly written program may cause similar symptoms, if it lasts sufficiently long.
Different micro-architectures typically require different machine code to hit their maximum power. Examples of such machine code do not appear to be distributed in CPU reference materials.
Infection vectors
As software is often designed with security features to prevent unauthorized use of system resources, many viruses must exploit and manipulate security bugs, which are security defects in a system or application software, to spread themselves and infect other computers.Software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
strategies that produce large numbers of "bugs" will generally also produce potential exploitable "holes" or "entrances" for the virus.
To replicate itself, a virus must be permitted to execute code and write to memory. For this reason, many viruses attach themselves to executable files that may be part of legitimate programs (see code injection). If a user attempts to launch an infected program, the virus' code may be executed simultaneously. In operating systems that use file extensions to determine program associations (such as Microsoft Windows), the extensions may be hidden from the user by default. This makes it possible to create a file that is of a different type than it appears to the user. For example, an executable may be created and named "picture.png.exe", in which the user sees only "picture.png" and therefore assumes that this file is a digital image and most likely is safe, yet when opened, it runs the executable on the client machine. Viruses may be installed on removable media, such as flash drives. The drives may be left in a parking lot of a government building or other target, with the hopes that curious users will insert the drive into a computer. In a 2015 experiment, researchers at the University of Michigan found that 45–98 percent of users would plug in a flash drive of unknown origin.
The vast majority of viruses target systems running Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
. This is due to Microsoft's large market share of desktop computer
A desktop computer, often abbreviated as desktop, is a personal computer designed for regular use at a stationary location on or near a desk (as opposed to a portable computer) due to its size and power requirements. The most common configuratio ...
users. The diversity of software systems on a network limits the destructive potential of viruses and malware. Open-source operating systems such as Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
allow users to choose from a variety of desktop environments
A desktop traditionally refers to:
* The surface of a desk (often to distinguish office appliances that fit on a desk, such as photocopiers and printers, from larger equipment covering its own area on the floor)
Desktop may refer to various compu ...
, packaging tools, etc., which means that malicious code targeting any of these systems will only affect a subset of all users. Many Windows users are running the same set of applications, enabling viruses to rapidly spread among Microsoft Windows systems by targeting the same exploits on large numbers of hosts.
While Linux and Unix in general have always natively prevented normal users from making changes to the operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
environment without permission, Windows users are generally not prevented from making these changes, meaning that viruses can easily gain control of the entire system on Windows hosts. This difference has continued partly due to the widespread use of administrator accounts in contemporary versions like Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
. In 1997, researchers created and released a virus for Linux—known as " Bliss". Bliss, however, requires that the user run it explicitly, and it can only infect programs that the user has the access to modify. Unlike Windows users, most Unix users do not log in as an administrator, or "root user", except to install or configure software; as a result, even if a user ran the virus, it could not harm their operating system. The Bliss virus never became widespread, and remains chiefly a research curiosity. Its creator later posted the source code to Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Elli ...
, allowing researchers to see how it worked.
Before computer networks became widespread, most viruses spread on removable media
In computing, a removable media is a data storage media that is designed to be readily inserted and removed from a system. Most early removable media, such as floppy disks and optical discs, require a dedicated read/write device (i.e. a drive) ...
, particularly floppy disks. In the early days of the personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
, many users regularly exchanged information and programs on floppies. Some viruses spread by infecting programs stored on these disks, while others installed themselves into the disk boot sector, ensuring that they would be run when the user booted the computer from the disk, usually inadvertently. Personal computers of the era would attempt to boot first from a floppy if one had been left in the drive. Until floppy disks fell out of use, this was the most successful infection strategy and boot sector viruses were the most common in the "wild" for many years. Traditional computer viruses emerged in the 1980s, driven by the spread of personal computers and the resultant increase in bulletin board system
A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), is a computer server running list of BBS software, software that allows users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user perfor ...
(BBS), modem use, and software sharing. Bulletin board–driven software sharing contributed directly to the spread of Trojan horse
In Greek mythology, the Trojan Horse () was a wooden horse said to have been used by the Greeks during the Trojan War to enter the city of Troy and win the war. The Trojan Horse is not mentioned in Homer, Homer's ''Iliad'', with the poem ending ...
programs, and viruses were written to infect popularly traded software. Shareware and bootleg software were equally common vectors for viruses on BBSs. Viruses can increase their chances of spreading to other computers by infecting files on a network file system or a file system that is accessed by other computers.
Macro viruses have become common since the mid-1990s. Most of these viruses are written in the scripting languages for Microsoft programs such as Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor program, word processing program developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platf ...
and Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet editor developed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows, Windows, macOS, Android (operating system), Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a ...
and spread throughout Microsoft Office by infecting documents and spreadsheets. Since Word and Excel were also available for Mac OS, most could also spread to Macintosh computers. Although most of these viruses did not have the ability to send infected email messages, those viruses which did take advantage of the Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook is a personal information manager software system from Microsoft, available as a part of the Microsoft 365 software suites. Primarily popular as an email client for businesses, Outlook also includes functions such as Calendari ...
Component Object Model (COM) interface. Some old versions of Microsoft Word allow macros to replicate themselves with additional blank lines. If two macro viruses simultaneously infect a document, the combination of the two, if also self-replicating, can appear as a "mating" of the two and would likely be detected as a virus unique from the "parents".
A virus may also send a web address link as an instant message to all the contacts (e.g., friends and colleagues' e-mail addresses) stored on an infected machine. If the recipient, thinking the link is from a friend (a trusted source) follows the link to the website, the virus hosted at the site may be able to infect this new computer and continue propagating. Viruses that spread using cross-site scripting were first reported in 2002, and were academically demonstrated in 2005. There have been multiple instances of the cross-site scripting viruses in the "wild", exploiting websites such as MySpace (with the Samy worm) and Yahoo!
Yahoo (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web portal that provides the search engine Yahoo Search and related services including My Yahoo, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports, y!entertainment, yahoo!life, and its a ...
.
Countermeasures
 In 1989 The '' ADAPSO Software Industry Division'' published ''Dealing With Electronic Vandalism'', in which they followed the risk of data loss by "the added risk of losing customer confidence."
Many users install antivirus software that can detect and eliminate known viruses when the computer attempts to
In 1989 The '' ADAPSO Software Industry Division'' published ''Dealing With Electronic Vandalism'', in which they followed the risk of data loss by "the added risk of losing customer confidence."
Many users install antivirus software that can detect and eliminate known viruses when the computer attempts to download
In computer networks, download means to ''receive'' data from a remote system, typically a server such as a web server, an FTP server, an email server, or other similar systems. This contrasts with uploading, where data is ''sent to'' a remote ...
or run the executable file (which may be distributed as an email attachment, or on USB flash drives, for example). Some antivirus software blocks known malicious websites that attempt to install malware. Antivirus software does not change the underlying capability of hosts to transmit viruses. Users must update their software regularly to patch security vulnerabilities ("holes"). Antivirus software also needs to be regularly updated to recognize the latest threats. This is because malicious hacker
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who achieves goals and solves problems by non-standard means. The term has become associated in popular culture with a security hackersomeone with knowledge of bug (computing), bugs or exp ...
s and other individuals are always creating new viruses. The German AV-TEST Institute publishes evaluations of antivirus software for Windows and Android.
Examples of Microsoft Windows anti virus and anti-malware software include the optional Microsoft Security Essentials (for Windows XP, Vista and Windows 7) for real-time protection, the Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool (now included with Windows (Security) Updates on " Patch Tuesday", the second Tuesday of each month), and Windows Defender (an optional download in the case of Windows XP). Additionally, several capable antivirus software programs are available for free download from the Internet (usually restricted to non-commercial use). Some such free programs are almost as good as commercial
competitors. Common security vulnerabilities are assigned CVE IDs and listed in the US National Vulnerability Database. Secunia PSI is an example of software, free for personal use, that will check a PC for vulnerable out-of-date software, and attempt to update it. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that Encryption, encrypts the victim's personal data until a ransom is paid. Difficult-to-trace Digital currency, digital currencies such as paysafecard or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency, cryptocurrencies are com ...
and phishing scam
A scam, or a confidence trick, is an attempt to defraud a person or group after first gaining their Trust (emotion), trust. Confidence tricks exploit victims using a combination of the victim's credulity, naivety, compassion, vanity, confidence ...
alerts appear as press releases on the Internet Crime Complaint Center noticeboard. Ransomware is a virus that posts a message on the user's screen saying that the screen or system will remain locked or unusable until a ransom payment is made. Phishing is a deception in which the malicious individual pretends to be a friend, computer security expert, or other benevolent individual, with the goal of convincing the targeted individual to reveal passwords or other personal information.
Other commonly used preventive measures include timely operating system updates, software updates, careful Internet browsing (avoiding shady websites), and installation of only trusted software. Certain browsers flag sites that have been reported to Google and that have been confirmed as hosting malware by Google.
There are two common methods that an antivirus software application uses to detect viruses, as described in the antivirus software article. The first, and by far the most common method of virus detection is using a list of virus signature definitions. This works by examining the content of the computer's memory (its Random Access Memory (RAM), and boot sectors) and the files stored on fixed or removable drives (hard drives, floppy drives, or USB flash drives), and comparing those files against a database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
of known virus "signatures". Virus signatures are just strings of code that are used to identify individual viruses; for each virus, the antivirus designer tries to choose a unique signature string that will not be found in a legitimate program. Different antivirus programs use different "signatures" to identify viruses. The disadvantage of this detection method is that users are only protected from viruses that are detected by signatures in their most recent virus definition update, and not protected from new viruses (see " zero-day attack").
A second method to find viruses is to use a heuristic algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
based on common virus behaviors. This method can detect new viruses for which antivirus security firms have yet to define a "signature", but it also gives rise to more false positives than using signatures. False positives can be disruptive, especially in a commercial environment, because it may lead to a company instructing staff not to use the company computer system until IT services have checked the system for viruses. This can slow down productivity for regular workers.
Recovery strategies and methods
One may reduce the damage done by viruses by making regularbackup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
s of data (and the operating systems) on different media, that are either kept unconnected to the system (most of the time, as in a hard drive), read-only or not accessible for other reasons, such as using different file systems. This way, if data is lost through a virus, one can start again using the backup (which will hopefully be recent). If a backup session on optical media like CD and DVD is closed, it becomes read-only and can no longer be affected by a virus (so long as a virus or infected file was not copied onto the CD/ DVD). Likewise, an operating system on a bootable CD can be used to start the computer if the installed operating systems become unusable. Backups on removable media must be carefully inspected before restoration. The Gammima virus, for example, propagates via removable flash drives.
Many websites run by antivirus software companies provide free online virus scanning, with limited "cleaning" facilities (after all, the purpose of the websites is to sell antivirus products and services). Some websites—like Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
subsidiary VirusTotal.com—allow users to upload one or more suspicious files to be scanned and checked by one or more antivirus programs in one operation. Additionally, several capable antivirus software programs are available for free download from the Internet (usually restricted to non-commercial use). Microsoft offers an optional free antivirus utility called Microsoft Security Essentials, a Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool that is updated as part of the regular Windows update regime, and an older optional anti-malware (malware removal) tool Windows Defender that has been upgraded to an antivirus product in Windows 8.
Some viruses disable System Restore and other important Windows tools such as Task Manager and CMD. An example of a virus that does this is CiaDoor. Many such viruses can be removed by rebooting the computer, entering Windows " safe mode" with networking, and then using system tools or Microsoft Safety Scanner. System Restore on Windows Me, Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
, Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
and Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
can restore the registry and critical system files to a previous checkpoint. Often a virus will cause a system to "hang" or "freeze", and a subsequent hard reboot will render a system restore point from the same day corrupted. Restore points from previous days should work, provided the virus is not designed to corrupt the restore files and does not exist in previous restore points.
Microsoft's System File Checker (improved in Windows 7 and later) can be used to check for, and repair, corrupted system files. Restoring an earlier "clean" (virus-free) copy of the entire partition from a cloned disk, a disk image, or a backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back ...
copy is one solution—restoring an earlier backup disk "image" is relatively simple to do, usually removes any malware, and may be faster than "disinfecting" the computer—or reinstalling and reconfiguring the operating system and programs from scratch, as described below, then restoring user preferences. Reinstalling the operating system is another approach to virus removal. It may be possible to recover copies of essential user data by booting from a live CD, or connecting the hard drive to another computer and booting from the second computer's operating system, taking great care not to infect that computer by executing any infected programs on the original drive. The original hard drive can then be reformatted and the OS and all programs installed from original media. Once the system has been restored, precautions must be taken to avoid reinfection from any restored executable files.
Popular culture
The first known description of a self-reproducing program in fiction is in the 1970 short story ''The Scarred Man'' by Gregory Benford which describes a computer program called VIRUS which, when installed on a computer with telephone modem dialing capability, randomly dials phone numbers until it hits a modem that is answered by another computer, and then attempts to program the answering computer with its own program, so that the second computer will also begin dialing random numbers, in search of yet another computer to program. The program rapidly spreads exponentially through susceptible computers and can only be countered by a second program called VACCINE. His story was based on an actual computer virus written in FORTRAN that Benford had created and run on the lab computer in the 1960s, as a proof-of-concept, and whiche told John Brunner about
in 1970. The idea was explored further in two 1972 novels, '' When HARLIE Was One'' by David Gerrold and '' The Terminal Man'' by Michael Crichton, and became a major theme of the 1975 novel '' The Shockwave Rider'' by John Brunner. The 1973 Michael Crichton sci-fi film '' Westworld'' made an early mention of the concept of a computer virus, being a central plot theme that causes androids to run amok.
Alan Oppenheimer
Alan Oppenheimer (born April 23, 1930) is an American actor. He has performed numerous roles on live action television since the 1960s and has had an active career doing voice work since the 1970s.
Early life
Oppenheimer was born in New York ...
's character summarizes the problem by stating that "...there's a clear pattern here which suggests an analogy to an infectious disease process, spreading from one...area to the next." To which the replies are stated: "Perhaps there are superficial similarities to disease" and, "I must confess I find it difficult to believe in a disease of machinery."
In 2016, Jussi Parikka announced the creation of The Malware Museum of Art: a collection of malware programs, usually viruses, distributed in the 1980s and 1990s on home computers. Malware Museum of Art is hosted at The Internet Archive and is curated by Mikko Hyppönen from Helsinki
Helsinki () is the Capital city, capital and most populous List of cities and towns in Finland, city in Finland. It is on the shore of the Gulf of Finland and is the seat of southern Finland's Uusimaa region. About people live in the municipali ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
. The collection allows anyone with a computer to experience virus infection of decades ago with safety.The Malware Museum of Art
Other malware
The term "virus" is also misused by extension to refer to other types ofmalware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to caus ...
. "Malware" encompasses computer viruses along with many other forms of malicious software, such as computer worm, computer "worms", ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that Encryption, encrypts the victim's personal data until a ransom is paid. Difficult-to-trace Digital currency, digital currencies such as paysafecard or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency, cryptocurrencies are com ...
, spyware
Spyware (a portmanteau for spying software) is any malware that aims to gather information about a person or organization and send it to another entity in a way that harms the user by violating their privacy, endangering their device's securit ...
, adware, trojan horses, keyloggers, rootkits, bootkits, malicious Browser Helper Object (BHOs), and other malicious software. The majority of active malware threats are trojan horse programs or computer worms rather than computer viruses. The term computer virus, coined by Fred Cohen in 1985, is a misnomer. Viruses often perform some type of harmful activity on infected host computers, such as acquisition of hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
space or central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU) time, accessing and stealing private information (e.g., credit card numbers, debit card
A debit card, also known as a check card or bank card, is a payment card that can be used in place of cash to make purchases. The card usually consists of the bank's name, a card number, the cardholder's name, and an expiration date, on either ...
numbers, phone numbers, names, email addresses, passwords, bank information, house addresses, etc.), corrupting data, displaying political, humorous or threatening messages on the user's screen, spamming their e-mail contacts, logging their keystrokes, or even rendering the computer useless. However, not all viruses carry a destructive " payload" and attempt to hide themselves—the defining characteristic of viruses is that they are self-replicating computer programs that modify other software without user consent by injecting themselves into the said programs, similar to a biological virus which replicates within living cells.
See also
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
'Computer Viruses – Theory and Experiments'
nbsp;– The original paper by Fred Cohen, 1984
Hacking Away at the Counterculture
by Andrew Ross (On hacking, 1990) {{pp-move
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
Internet security
Deception
Security breaches
Types of malware