menarche on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Menarche ( ; ) is the first
September 2020 The timing of menarche is influenced by female
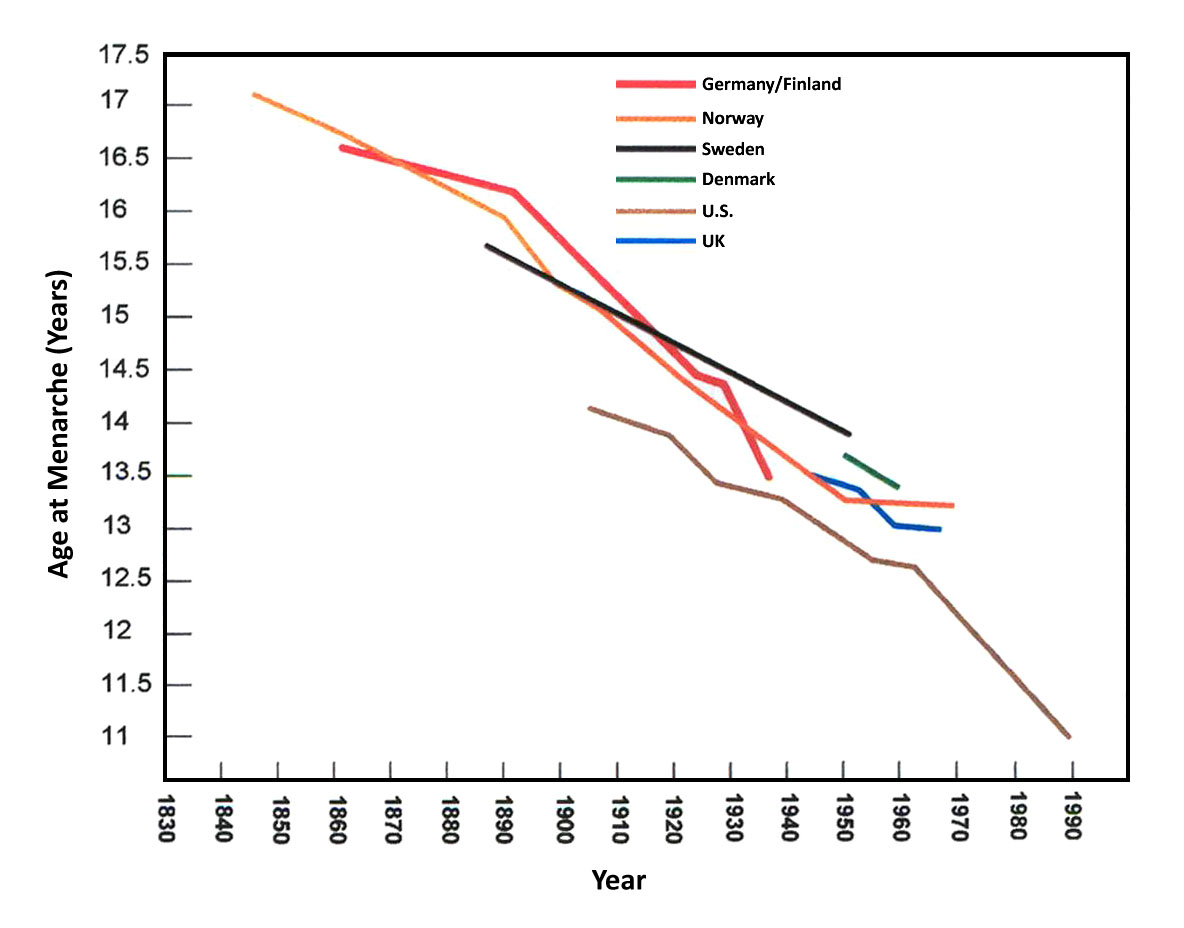 There were few systematic studies of timing of menarche before the second half of the 20th century. Most older estimates of average onset of menarche were based on observation of a small, homogeneous, non-representative sample of the larger population, or based on recall by adult women, which is susceptible to error. Most sources agree that the average age of menarche in girls in modern societies has declined, though the reasons and the degree remain subjects of study.
From the sixth to the 15th centuries in Europe, most women reached menarche at about 14, between the ages of 12 and 15. The average age of menarche dropped from 14-15 years in the early 20th century to 12-13 years in the present, but girls in the 19th century had a later age of menarche (16 to 18 years) compared to girls in earlier centuries. A large North American survey reported a 2–3 month decline from the mid-1970s to the mid-1990s. A 2011 study found that each 1 kg/m2 increase in childhood
There were few systematic studies of timing of menarche before the second half of the 20th century. Most older estimates of average onset of menarche were based on observation of a small, homogeneous, non-representative sample of the larger population, or based on recall by adult women, which is susceptible to error. Most sources agree that the average age of menarche in girls in modern societies has declined, though the reasons and the degree remain subjects of study.
From the sixth to the 15th centuries in Europe, most women reached menarche at about 14, between the ages of 12 and 15. The average age of menarche dropped from 14-15 years in the early 20th century to 12-13 years in the present, but girls in the 19th century had a later age of menarche (16 to 18 years) compared to girls in earlier centuries. A large North American survey reported a 2–3 month decline from the mid-1970s to the mid-1990s. A 2011 study found that each 1 kg/m2 increase in childhood
 Some cultures have observed rites of passage such as a party or other celebration, for a girl experiencing menarche, in the past and the present.
Some cultures have observed rites of passage such as a party or other celebration, for a girl experiencing menarche, in the past and the present.
Discusses some of the social influences
{{Authority control Developmental biology Developmental stages Menstrual cycle Pediatrics Puberty Sexuality and age Human female endocrine system ja:月経#初潮
menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eg ...
, or first menstrual bleeding, in female human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, as it signals the possibility of fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
. Girls experience menarche at different ages, but the most common age is 12. Having menarche occur between the ages of 9–14 in the West is considered normal.US National Health Statistics ReportSeptember 2020 The timing of menarche is influenced by female
biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
, as well as genetic, environmental factor
An environmental factor, ecological factor or eco factor is any factor, abiotic or biotic, that influences living organisms. Abiotic factors include ambient temperature, amount of sunlight, air, soil, water and pH of the water soil in which an ...
s, and nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- ...
al factors. The mean age of menarche has declined over the last century, but the magnitude of the decline and the factors responsible remain subjects of contention. The worldwide average age of menarche is very difficult to estimate accurately, and it varies significantly by geographical region, race, ethnicity and other characteristics, and occurs mostly during a span of ages from 8 to 16, with a small percentage of girls having menarche by age 10, and the vast majority having it by the time they were 14.
There is a later age of onset in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
n populations compared to the West, but it too is changing with time. For example a Korean study in 2011 showed an overall average age of 12.7, with around 20% before age 12, and more than 90% by age 14. A Chinese study from 2014 published in '' Acta Paediatrica'' showed similar results (overall average of age 12.8 in 2005 down to age 12.3 in 2014) and a similar trend in time, but also similar findings about ethnic, cultural, and environmental effects. The average age of menarche was about 12.7 years in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
in 2001, and 12.9 in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. A study of girls in Istanbul
Istanbul is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, constituting the country's economic, cultural, and historical heart. With Demographics of Istanbul, a population over , it is home to 18% of the Demographics ...
, Turkey, in 2011 found the median age at menarche to be 12.7 years. In the United States, an analysis of 10,590 women aged 15–44 taken from the 2013–2017 round of the CDC's National Survey of Family Growth
found a median age of 11.9 years (down from 12.1 in 1995), with a mean of 12.5 years (down from 12.6).
Physiology
Puberty
Menarche is the culmination of a series ofphysiological
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
and anatomic processes of puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
:
* Attainment of a sufficient body fat percentage
The body fat percentage of an organism is the total mass of its fat divided by its total body mass, multiplied by 100; body fat includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive fu ...
(typically around 17% of total body mass).
* Disinhibition of the GnRH
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released ...
pulse generator in the arcuate nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARH), or ARC, is also known as the infundibular nucleus to distinguish it from the arcuate nucleus of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The arcuate nucleus is an aggregation of neurons in the medio ...
of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
.
* Secretion of estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
by the ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
in response to pituitary
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of th ...
hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s.
* Over an interval of about 2 to 3 years, estrogen stimulates growth of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
and breasts
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is ...
, as well as an increase in height, widening of the pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
, and increased regional adipose tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
.
* Estrogen stimulates growth and vascularity of the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The funct ...
, the lining of the uterus.
* Fluctuations of hormone levels can result in changes of adequacy of blood supply to parts of the endometrium.
* Death of some of the endometrial tissue from these hormone or blood supply fluctuations leads to ''deciduation'', a sloughing off of part of the lining with some blood, which together flows from the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
, i.e. menstrual flow.
Menarche tends to be painless and occurs without warning.
The ''menstruum'', or ''flow'', consists of a combination of fresh and clotted blood with endometrial tissue. Flow may be scanty in amount and might be as little as a single instance of "spotting". Like other menses
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized ...
, menarche may be accompanied by lower abdominal cramps.
Relation to fertility
For most girls, menarche does not mean thatovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and ...
has occurred. In post-menarchal girls, about 80% of the cycles are anovulatory
Anovulation is when the ovaries do not release an oocyte during a menstrual cycle. Therefore, ovulation does not take place. However, a woman who does not ovulate at each menstrual cycle is not necessarily going through menopause. Chronic anovul ...
in the first year after menarche, 50% in the third, and 10% in the sixth year. Regular ovulation is usually indicated by predictable and consistent intervals between menses, and predictable and consistent patterns of flow (e.g., heaviness or cramping). Continuing ovulation typically requires a body fat percentage
The body fat percentage of an organism is the total mass of its fat divided by its total body mass, multiplied by 100; body fat includes essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive fu ...
of at least 22%.
Not every girl follows the typical pattern. Some girls ovulate prior to their first menstruation
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and Mucous membrane, mucosal tissue from the endometrium, inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized ...
. Although unlikely, it is possible for a girl who has engaged in sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
shortly before her menarche to conceive and become pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
(delaying her menarche until after the end of her pregnancy, if she carries to full term).
Younger age of menarche is not correlated with a younger age of first sexual intercourse.
Onset
When menarche occurs, it confirms that the girl has had a gradualestrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
-induced growth of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, especially the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The funct ...
, and that the "outflow tract" from the uterus, through the cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time ...
to the vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
, is open.
When experiencing menarche, the blood flow (colloquially described as having one's "period") can vary from a slow and spotty discharge to a consistent blood flow for 3–7 days. The color of the blood ranges from bright red to brown in color; this is normal. Periods may be light or heavy.
In very rare instances, menarche may occur at an unusually early age, preceding thelarche
Thelarche, also known as breast budding, is the onset of secondary breast development, often representing the beginning of pubertal development. It is the stage at which male and female breasts differentiate due to variance in hormone levels; howe ...
and other signs of puberty. This is termed ''isolated premature menarche'', but other causes of vaginal bleeding must be investigated and excluded. Isolated premature menarche is rarely the first manifestation of precocious puberty
In medicine, precocious puberty is puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most cases, the process is normal in every aspect except the unusually early age and simply represents a variation of normal development. There is early developm ...
.
When menarche has failed to occur for more than three years after thelarche, or beyond 15 years of age, the delay is referred to as primary amenorrhea.
Timing
Chronic illness
Certain systemic or chronic illness can delay menarche, such asdiabetes mellitus type 1
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system destroys pancreatic cells (beta cells). In healthy persons, beta cells produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone required ...
, cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, inflammatory diseases, and untreated celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, among others. Sometimes, lab tests do not return determinative results, so that underlying pathologies are not identified and the girl is diagnosed with constitutional growth delay
Constitutional delay of growth and puberty (CDGP) is a term describing a temporary delay in the skeletal growth and thus height of a child with no physical abnormalities causing the delay. Short stature may be the result of a growth pattern inhe ...
.
Conditions and disease states
Studies have been conducted to observe the association of the timing of menarche with various conditions and diseases. Some studies have shown that there may be an association between early or late-age menarche andcardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumati ...
, although the mechanism of the association is not well understood. A systematic review has concluded that early onset of menarche is a risk factor for insulin resistance and breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
risk.
There is conflicting evidence regarding the association between obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
and timing of menarche; a meta-analysis and systematic review has determined that more studies must be conducted to make any definitive conclusions about this association.
Effects of stress and social environment
Some of the aspects of family structure and function reported to be independently associated with earlier menarche ntenatal and early childhood* Being non-white (in the UK) * Having experienced pre-eclampsia in the womb * Being a singleton, i.e. not a twin or triplet * Low birthweight * Not having been breast-fed * Exposure to smoking * High-conflict family relationships * Lack of exercise in childhood Other research has focused on the effect of childhood stress on timing of puberty, especially female. Stress is a vague term and studies have examined conditions ranging from family tensions or conflict to wartime refugee status with threat to physical survival. The more dire social conditions have been found to be associated with delay of maturation, an effect that is compounded by inadequate diet and nutrition. There is mixed evidence if milder degrees of stress can accelerate puberty in girls as would be predicted bylife history theory
Life history theory (LHT) is an analytical frameworkVitzthum, V. (2008). Evolutionary models of women's reproductive functioning. ''Annual Review of Anthropology'', ''37'', 53-73 designed to study the diversity of life history strategies used by d ...
and demonstrated in non-human mammals.
The understanding of these environmental effects is incomplete and the following cautions are relevant:
* Most of these "effects" are statistical associations revealed by epidemiologic surveys. Statistical associations are not necessarily causal, and secondary variables and alternative explanations can be possible instead. Effects of small size studies can never be confirmed or refuted for any individual child.
* Despite the small magnitude of effect, interpretations of the studies are politically controversial because this type of research is often be used for political advocacy. Accusations of bias based on political agenda sometimes accompany scientific criticism.
* Correlation does not imply causation
The phrase "correlation does not imply causation" refers to the inability to legitimately deduce a cause-and-effect relationship between two events or variables solely on the basis of an observed association or correlation between them. The id ...
. While correlation can be objectively measured, causation is statistically inferred. For example, some suggest that childhood stress is caused by precocious puberty recognized later, rather than being the cause of it.
Changes in time of average age
 There were few systematic studies of timing of menarche before the second half of the 20th century. Most older estimates of average onset of menarche were based on observation of a small, homogeneous, non-representative sample of the larger population, or based on recall by adult women, which is susceptible to error. Most sources agree that the average age of menarche in girls in modern societies has declined, though the reasons and the degree remain subjects of study.
From the sixth to the 15th centuries in Europe, most women reached menarche at about 14, between the ages of 12 and 15. The average age of menarche dropped from 14-15 years in the early 20th century to 12-13 years in the present, but girls in the 19th century had a later age of menarche (16 to 18 years) compared to girls in earlier centuries. A large North American survey reported a 2–3 month decline from the mid-1970s to the mid-1990s. A 2011 study found that each 1 kg/m2 increase in childhood
There were few systematic studies of timing of menarche before the second half of the 20th century. Most older estimates of average onset of menarche were based on observation of a small, homogeneous, non-representative sample of the larger population, or based on recall by adult women, which is susceptible to error. Most sources agree that the average age of menarche in girls in modern societies has declined, though the reasons and the degree remain subjects of study.
From the sixth to the 15th centuries in Europe, most women reached menarche at about 14, between the ages of 12 and 15. The average age of menarche dropped from 14-15 years in the early 20th century to 12-13 years in the present, but girls in the 19th century had a later age of menarche (16 to 18 years) compared to girls in earlier centuries. A large North American survey reported a 2–3 month decline from the mid-1970s to the mid-1990s. A 2011 study found that each 1 kg/m2 increase in childhood body-mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) an ...
(BMI) can be expected to result in a 6.5% higher absolute risk of early menarche (before age 12 years). This is called the secular trend.
In 2002, fewer than 10% of U.S. girls started to menstruate before 11 years of age, and 90% of all U.S. girls were menstruating by 13.75 years of age, with a median age of 12.43 years. This age at menarche is not much different (0.3 years earlier) than that reported for U.S. girls in 1973. Age at menarche for non-Hispanic black girls was significantly earlier than that of white girls, whereas non-white Mexican American girls were only slightly earlier than white girls.
Society and culture
Menstruation is a cultural as well as scientific phenomenon as many societies have rituals, social norms, and religious laws associated with it. These typically begin at menarche and may be enacted during each menstruation cycle. The menarches are important in determining a status change for the girls. Upon menarche and completion of the ritual, they have become a woman as defined by their culture. Canadian psychological researcher Niva Piran claims that menarche or the perceived average age of puberty is used in many cultures to separate girls from activity with boys, and to begin transition into womanhood. For example, post-menarche, young women compete in field hockey while young men play ice hockey.Celebratory ceremonies
 Some cultures have observed rites of passage such as a party or other celebration, for a girl experiencing menarche, in the past and the present.
Some cultures have observed rites of passage such as a party or other celebration, for a girl experiencing menarche, in the past and the present.
Past
In ancient Japan, when a Japanese girl had her first period, the family sometimes celebrated by eating red-colored rice and beans ''(sekihan
Red bean rice, called ''patbap'' () in Korean language, Korean, ''sekihan'' () in Japanese language, Japanese, and ''hóngdòu fàn'' () in Chinese language, Chinese, is an East Asian rice dish consisting of cooked rice, rice cooked with adzuki ...
)''. Although both blood and sekihan rice are red, this was not of symbolic significance. All rice in ancient Japan was red; it was also rare and precious. (At most other times, millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
was eaten instead.) The celebration was kept a secret from extended family until the rice was served.
Present
In South Indian Hindu communities, young women are given a special menarche ceremony called Ruthu Sadangu; at that time, they begin to wear two-piece saris. InMorocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, the girl is thrown a celebration. All of her family members are invited and the girl is showered with money and gifts. Quinceañera
In Mexico, Mexican and other Latin American cultures, it is customary to celebrate a girl's 15th birthday. In Spanish language, Spanish, the girl celebrating her 15th birthday is called a ; in English language, English, primarily in the Unite ...
in Latin America, is similar, except that the specific age of 15 marks the transition rather than menarche.
The Mescalero
Mescalero or Mescalero Apache () is an Apache tribe of Southern Athabaskan–speaking Native Americans. The tribe is federally recognized as the Mescalero Apache Tribe of the Mescalero Apache Reservation, located in south-central New Mexico.
In ...
Apaches place high importance on their menarche ceremony and it is regarded as the most important ritual in their tribe. Each year, there is an eight-day event celebrating all of the girls who have menstruated in the past year. The days are split between feasting and private ceremonies reflecting on their new womanly status.
In the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, public schools have a sex education
Sex education, also known as sexual education, sexuality education or sex ed, is the instruction of issues relating to human sexuality, including human sexual anatomy, Human sexual activity, sexual activity, sexual reproduction, safe sex, birth ...
program that teaches girls about menstruation and what to expect at the onset of menarche; this takes place between the fifth and eight grades. Like most of the modern industrialized world, menstruation is a private matter and a girl's menarche is not a community phenomenon.
Rituals of purification
TheUlithi
Ulithi (, , or ; pronounced roughly as YOU-li-thee) is an atoll in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, about east of Yap, within Yap State.
Name
The name of the island goes back to Chuukic languages, Proto-Chuukic ''*úlú-diw ...
tribe of Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of approximately 2,000 small islands in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: Maritime Southeast Asia to the west, Poly ...
call a girl's menarche ''kufar''. She goes to a menstrual house, where the women bathe her and recite spells. She will have to return to the menstruation hut every time she menstruates. Her parents build her a private hut that she will live in until she is married.
In Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, an astrologer
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
is contacted to study the alignment of stars when the girl experiences menarche because it is believed that her future can be predicted. The women of the family then gather in her home and scrub her in a ritual bathing ceremony. Her family then throws a familial party at which the girl wears white and may receive gifts.
In Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, Beta Jewish women were separated from male society and sent to menstruation huts during menarche and every menstruation following as the blood associated with menstruation in the Beta Jewish culture was believed to be impure. The Beta Jews built their villages surrounding and near bodies of water specifically for their women to have a place to clean themselves. The menstruation huts were built close to these bodies of water.
In India, purdah
Pardah or purdah (from Hindi-Urdu , , meaning "curtain") is a religious and social practice of sex segregation prevalent among some Muslim, Zoroastrian and Hindu communities. The purdah garment is the same as a burqa, or yashmak, i.e a veil ...
is practiced by some Hindu and Muslim communities. Women, starting at menarche and continuing with each subsequent period, are separated from men, and also wear different garments to conceal their skin during menstruation.
In Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, the Aboriginals treat a girl to "love magic". She is taught the ways of womanhood by the other women in her tribe. Her mother builds her a menstruation hut to which she confines herself for the remainder of her menses. The hut is burned and she is bathed in the river at the end of menstruation. When she returns to the village, she is paired with a man who will be her husband.
In Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, the Tiv ethnic group cut four lines into the abdomen of their girls during menarche. The lines are supposed to represent fertility.
Rituals of strength
TheNavajo
The Navajo or Diné are an Indigenous people of the Southwestern United States. Their traditional language is Diné bizaad, a Southern Athabascan language.
The states with the largest Diné populations are Arizona (140,263) and New Mexico (1 ...
have a celebration called ''kinaalda'' (kinn-all-duh). Girls are expected to demonstrate their strength through footraces. The girls make a cornmeal pudding for the tribe to taste. The girls who experience menarche wear special clothes and style their hair like the Navajo goddess " Changing Woman".
The Nuu-chah-nulth
The Nuu-chah-nulth ( ; ), also formerly referred to as the Nootka, Nutka, Aht, Nuuchahnulth or Tahkaht, are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast in Canada. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifteen related tri ...
(also known as the Nootka) believe that physical endurance is the most important quality in young women. At menarche the girl is taken out to sea and left there to swim back.
Movies, TV, and novels
Girls experiencing their first periods are part of many movies, particularly ones that includecoming-of-age
Coming of age is a young person's transition from being a child to being an adult. The specific age at which this transition takes place varies between societies, as does the nature of the change. It can be a simple legal convention or can b ...
plot lines, such as '' The Blue Lagoon'' (1980), '' The Company of Wolves'' (1984), '' An Angel at My Table'' (1990), '' My Girl'' (1991), '' Return to the Blue Lagoon'' (1991), '' Eve’s Bayou'' (1997), and '' A Walk on the Moon'' (1999). Menarche is also discussed in an episode of the animated series ''Baymax!
''Baymax!'' is an American animated superhero science fiction comedy television series created by Don Hall that premiered on Disney+ on June 29, 2022, featuring the Marvel Comics character of the same name. The series is a spin-off of the a ...
'' (2022) in which the eponymous healthcare robot helps a girl deal with her first period.
In the horror movie '' Carrie'' (1976), an adaptation of the Stephen King
Stephen Edwin King (born September 21, 1947) is an American author. Dubbed the "King of Horror", he is widely known for his horror novels and has also explored other genres, among them Thriller (genre), suspense, crime fiction, crime, scienc ...
novel of the same name, protagonist Carrie White experiences menarche as she showers after the school gym class. Unaware of what is happening to her, she panics and pleads for help, but the other girls respond by bullying her. Menarche unleashes Carrie's telekinetic powers which are key to her wild transformation that causes death and destruction. This theme is common to horror movies, another example being the Canadian horror movie '' Ginger Snaps'' (2000), where the protagonist's first period is central to her gradual transformation into a werewolf
In folklore, a werewolf (), or occasionally lycanthrope (from Ancient Greek ), is an individual who can shapeshifting, shapeshift into a wolf, or especially in modern film, a Shapeshifting, therianthropic Hybrid beasts in folklore, hybrid wol ...
. The theme of transformation around menarche is similarly present in '' Turning Red'' (2022), although the film also explores other aspects of puberty and the protagonist does not yet have her first period.
One of the better-known middle reader (8 to 12 year old) novels in the U.S. and Canada about the year leading up to menarche in the 1970s to 1990s is " Are You There God? It's Me, Margaret" (1970) by Judy Blume.
See also
*Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
* Gonadarche
* Thelarche
Thelarche, also known as breast budding, is the onset of secondary breast development, often representing the beginning of pubertal development. It is the stage at which male and female breasts differentiate due to variance in hormone levels; howe ...
* Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 5 ...
, the equivalent opposite change at the end of the child-bearing years
* Delayed puberty
Delayed puberty is when a person lacks or has incomplete development of specific sexual characteristics past the usual age of onset of puberty. The person may have no physical or hormone, hormonal signs that puberty has begun. In the United States ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Discusses some of the social influences
{{Authority control Developmental biology Developmental stages Menstrual cycle Pediatrics Puberty Sexuality and age Human female endocrine system ja:月経#初潮