|
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance can be improved or reversed with lifestyle approaches, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from ''endocrine system, endocrine'' + ''wikt:-logy#Suffix, -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, human development (biology), growth and development, tissue (biology), tissue function, sleep, digestion, Respiration (physiology), respiration, excretion, mood (psychology), mood, Stress (physiology), stress, lactation, Motor coordination, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology. The endocrine system consists of several glands, all in different parts of the body, that secrete hormones directly into the blood rather than into a Duct (anatomy), duct system. Therefore, endocrine glands are regarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glucose Clamp Technique
__NOTOC__ Glucose clamp technique is a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. It is used to measure either how well an individual metabolizes glucose or how sensitive an individual is to insulin. Procedure Two types of clamp are quite commonly used. The hyperglycemic clamp, which requires maintaining a high blood sugar level by perfusion or infusion with glucose, is a way to quantify how fast beta-cells respond to glucose. The hyperinsulinemic clamp, which requires maintaining a high insulin level by perfusion or infusion with insulin, is a way to quantify how sensitive the tissue is to insulin. The hyperinsulinemic clamp is also called ''euglycemic clamp'', meaning a normal blood sugar level is maintained. Hyperglycemic clamp technique: The plasma glucose concentration is acutely raised to 125 mg/dl above basal levels by a continuous infusion of glucose. This hyperglycemic plateau is maintained by adjustment of a variable glucose infusion, based on the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
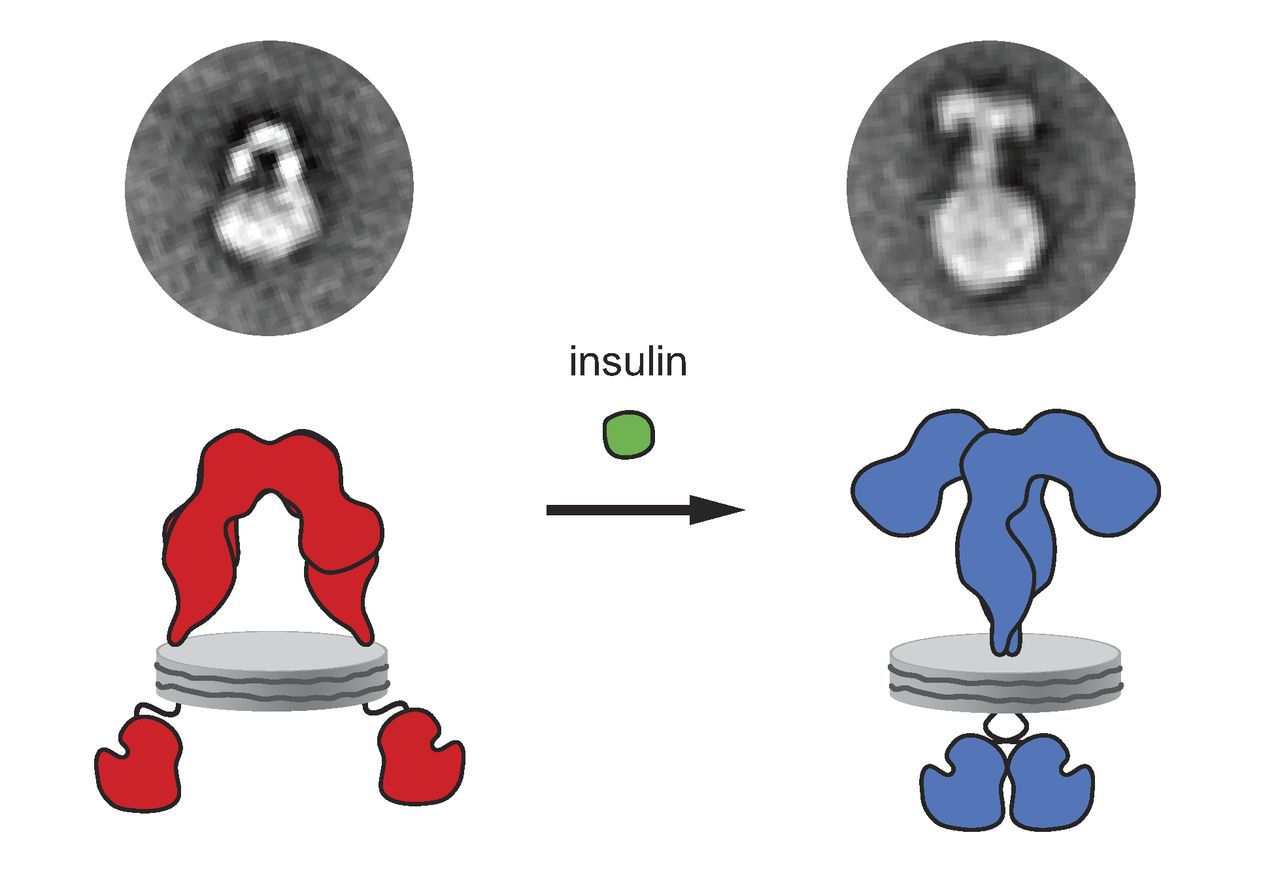
Insulin Receptor
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis; a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene , from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Downregulation
In biochemistry, in the biology, biological context of organisms' regulation of gene expression and production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell (biology), cell decreases the production and quantities of its cellular components, such as RNA and proteins, in response to an external stimulus. The complementary process that involves increase in quantities of cellular components is called upregulation. An example of downregulation is the cellular decrease in the expression of a specific Receptor (biochemistry), receptor in response to its increased activation by a molecule, such as a hormone or neurotransmitter, which reduces the cell's sensitivity to the molecule. This is an example of a locally acting (negative feedback) mechanism. An example of upregulation is the response of liver cells exposed to such xenobiotic molecules as Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, dioxin. In this situation, the cells increase their production of cytochrome P450, cytochrome P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pathological
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psychological conditions (such as ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a component of metabolic syndrome and is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall below the threshold to diagnose diabetes mellitus. It usually does not cause symptoms, but people with prediabetes often have obesity (especially abdominal or visceral obesity), dyslipidemia with high triglycerides and/or low HDL cholesterol, and hypertension. It is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Prediabetes is more accurately considered an early stage of diabetes, as health complications associated with type 2 diabetes often occur before the diagnosis of diabetes. Prediabetes can be diagnosed by measuring hemoglobin A1c, fasting glucose, or glucose tolerance test. Many people may be diagnosed through routine screening tests. The primary treatment approach includes lifestyle changes such as exercise and dietary adjustments. Some medications can be used to reduce the risks associated with prediabetes. There is a high rate of pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or polycystic ovarian syndrome, (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The name is a misnomer, as not all women with this condition develop cysts on their ovaries. The name originated from the observation of cysts which form on the ovaries of some women with this condition. However, this is not a universal symptom and is not the underlying cause of the disorder. The primary characteristics of PCOS include hyperandrogenism, anovulation, insulin resistance, and neuroendocrinology, neuroendocrine disruption. Women may also experience Abnormal uterine bleeding, irregular menstrual periods, Menorrhagia, heavy periods, hirsutism, excess hair, acne, pelvic pain, infertility, difficulty getting pregnant, and patches of acanthosis nigricans, darker skin. Beyond its reproductive implications, PCOS is increasingly recognized as a multifactorial metabolic condition with significant long-term health consequences, including an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prothrombotic
Thrombosis () is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus. Thrombosis can cause serious conditions such as stroke and heart attack. Thrombosis may occur in veins (venous thrombosis) or in arteries (arterial thrombosis). Venous thrombosis (sometimes called DVT, deep vein thrombosis) leads to a blood clot in the affected part of the body, while arterial thrombosis (and, rarely, severe venous thrombosis) affects the blood supply and leads to damage of the tissue supplied by that artery (ischemia and necrosis). A piece of either an arterial or a venous thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Endothelial Dysfunction
In blood vessel diseases, endothelial dysfunction is an unhealthy state of the the cells that line the blood vessels (endothelium). The main cause of endothelial dysfunction is impaired bioavailability of nitric oxide. In addition to acting as a semipermeable membrane, the endothelium is responsible for maintaining vascular tone and regulating oxidative stress by releasing mediators, such as nitric oxide, prostacyclin and endothelin, and by controlling local angiotensin-II activity. Dysfunctional endothelium is characterized by constricted blood vessels, increased ability of chemicals to flow through blood vessel walls, blood clots, and inflammation. This pathological state is often associated with elevated levels of biomarkers such as prothrombin time, D-dimer, von Willebrand factor, fibrin degradation products, C-reactive protein (CRP), ferritin, Interleukin 6 (IL-6), and plasma creatinine. The result of this endothelial dysregulation is a cascade of harmful effects, inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inflammatory Markers
Acute-phase proteins (APPs) are a class of proteins whose concentrations in blood plasma either increase (positive acute-phase proteins) or decrease (negative acute-phase proteins) in response to inflammation. This response is called the ''acute-phase reaction'' (also called ''acute-phase response''). The acute-phase reaction characteristically involves fever, acceleration of peripheral leukocytes, circulating neutrophils and their precursors. The terms ''acute-phase protein'' and ''acute-phase reactant'' (APR) are often used synonymously, although some APRs are (strictly speaking) polypeptides rather than proteins. In response to injury, local inflammatory cells (neutrophil granulocytes and macrophages) secrete a number of cytokines into the bloodstream, most notable of which are the interleukins IL1, and IL6, and TNF-α. The liver responds by producing many acute-phase reactants. At the same time, the production of a number of other proteins is reduced; these proteins are, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hyperuricemia
Hyperuricaemia or hyperuricemia is an abnormally high level of uric acid in the blood. In the pH conditions of body fluid, uric acid exists largely as urate, the ion form. Serum uric acid concentrations greater than 6 mg/dL for females, 7 mg/dL for males, and 5.5 mg/dL for youth (under 18 years old) are defined as hyperuricemia. The amount of urate in the body depends on the balance between the amount of purines eaten in food, the amount of urate synthesised within the body (e.g., through cell turnover), and the amount of urate that is excreted in urine or through the gastrointestinal tract. Hyperuricemia may be the result of increased production of uric acid, decreased excretion of uric acid, or both increased production and reduced excretion. Signs and symptoms Unless high blood levels of uric acid are determined in a clinical laboratory, hyperuricemia may not cause noticeable symptoms in most people. Development of gout which is a painful, short-term d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |