history of agriculture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Early people began altering communities of
Early people began altering communities of  Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe and included a diverse range of taxa. At least 11 separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. Some of the earliest known domestications were of animals.
Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe and included a diverse range of taxa. At least 11 separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. Some of the earliest known domestications were of animals.  It was not until after 9500 BC that the eight so-called
It was not until after 9500 BC that the eight so-called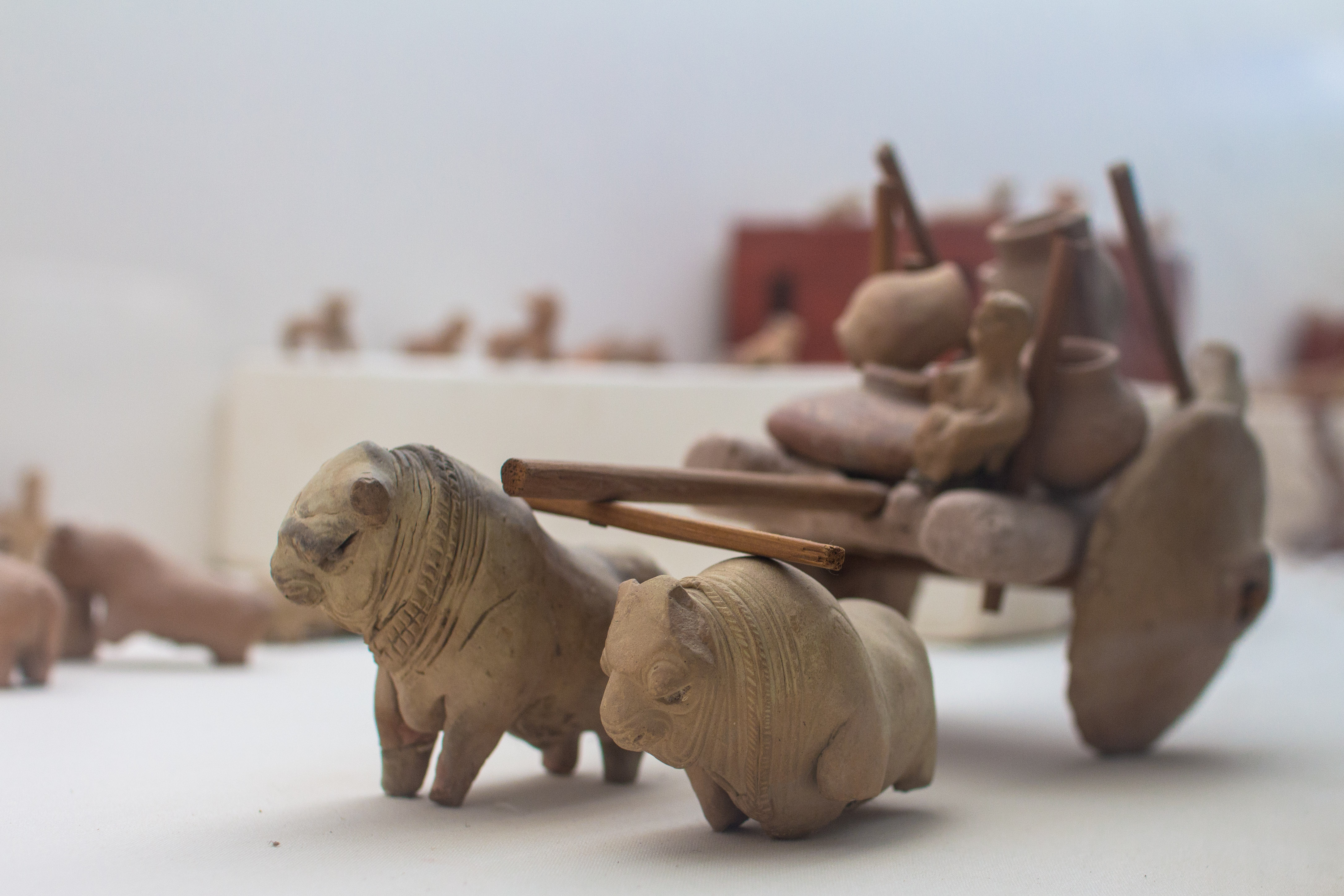  In northern
In northern  In southern China, rice was domesticated in the
In southern China, rice was domesticated in the

 Records from the
Records from the 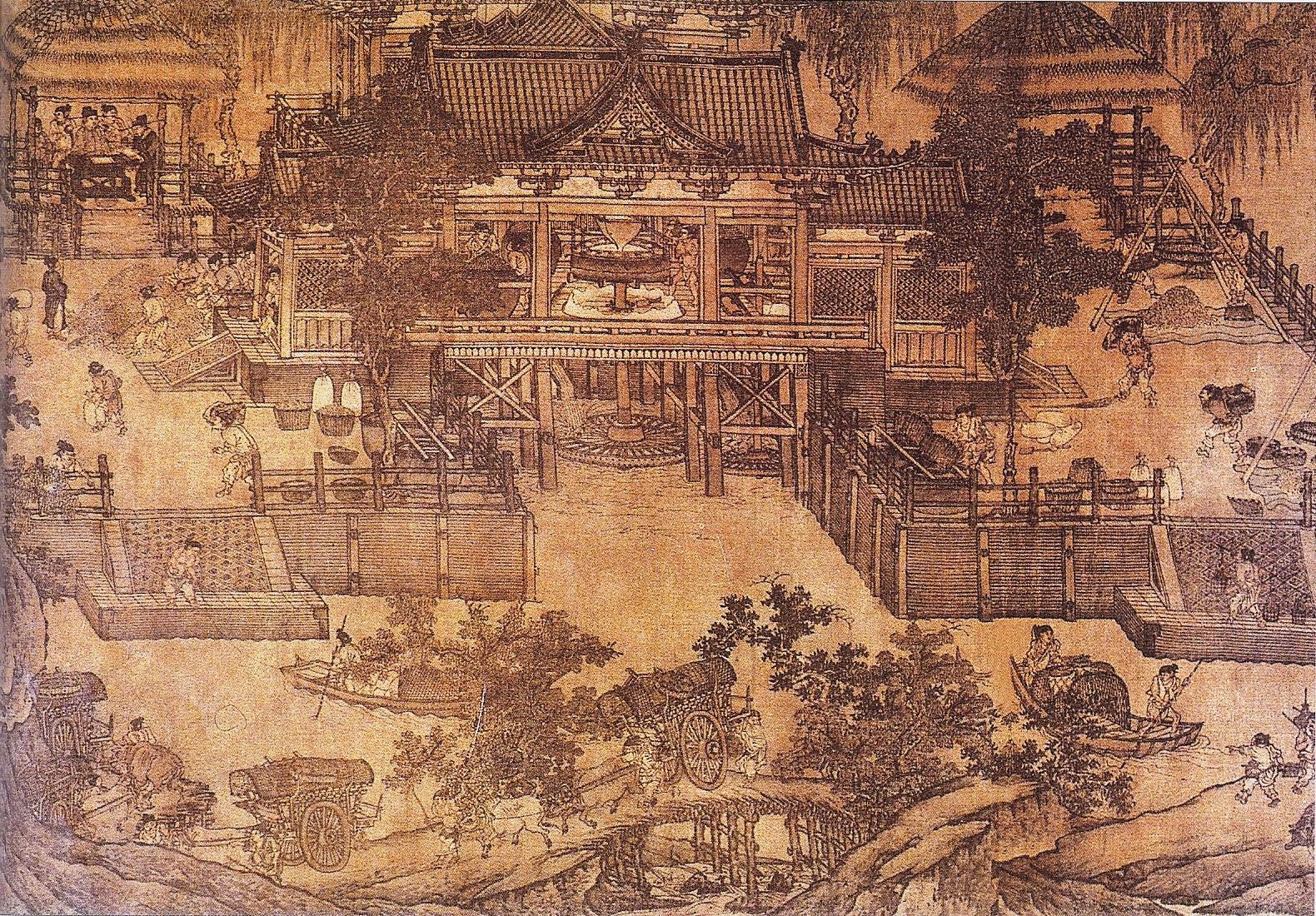 For agricultural purposes, the Chinese had innovated the
For agricultural purposes, the Chinese had innovated the

 The earliest known areas of possible agriculture in the Americas dating to about 9000 BC are in
The earliest known areas of possible agriculture in the Americas dating to about 9000 BC are in
 In Mesoamerica, wild
In Mesoamerica, wild
 The indigenous people of the Eastern U.S. domesticated numerous crops. Sunflowers,
The indigenous people of the Eastern U.S. domesticated numerous crops. Sunflowers,
 In the Sahel region, civilizations such as the
In the Sahel region, civilizations such as the
 By AD 900, developments in
By AD 900, developments in
 Maize and cassava were introduced from Brazil into Africa by Portuguese traders in the 16th century, becoming staple foods, replacing native African crops. After its introduction from South America to Spain in the late 1500s, the potato became a staple crop throughout Europe by the late 1700s. The potato allowed farmers to produce more food, and initially added variety to the European diet. The increased supply of food reduced disease, increased births and reduced mortality, causing a population boom throughout the
Maize and cassava were introduced from Brazil into Africa by Portuguese traders in the 16th century, becoming staple foods, replacing native African crops. After its introduction from South America to Spain in the late 1500s, the potato became a staple crop throughout Europe by the late 1700s. The potato allowed farmers to produce more food, and initially added variety to the European diet. The increased supply of food reduced disease, increased births and reduced mortality, causing a population boom throughout the
 The Haber-Bosch method for synthesizing
The Haber-Bosch method for synthesizing
 The Green Revolution was a series of research, development, and
The Green Revolution was a series of research, development, and 
excerpt
* Federico, Giovanni. ''Feeding the World: An Economic History of Agriculture 1800–2000'' (Princeton UP, 2005) highly quantitative * Grew, Raymond
''Food in Global History''
(1999) * Heiser, Charles B. ''Seed to Civilization: The Story of Food'' (W.H. Freeman, 1990) * Herr, Richard, ed. ''Themes in Rural History of the Western World'' (Iowa State UP, 1993) * Kiple, Kenneth F., and Kriemhild Coneè Ornelas, eds. ''The Cambridge world history of food'' (2 vol Cambridge University Press, 2000
online
* Mazoyer, Marcel, and Laurence Roudart. ''A History of World Agriculture: From the Neolithic Age to the Current Crisis'' (Monthly Review Press, 2006) Marxist perspective. * Pilcher, Jeffrey M. ''Food in world history'' (Routledge, 2023). * Prentice, E. Parmalee
''Hunger and History: The Influence of Hunger on Human History''
(Harper, 1939) * Tauger, Mark. ''Agriculture in World History'' (Routledge, 2008) * Toussaint-Samat, Maguelonne. ''A history of food'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2009), 800+ pp
online
* ; covers historiographical traditions within geographic regions across the world.
The economic history of china: with special reference to agriculture
' (Columbia University, 1921) * Murray, Jacqueline. ''The First European Agriculture'' (Edinburgh UP, 1970) * Oka, H-I. ''Origin of Cultivated Rice'' (Elsevier, 2012) * Price, T.D. and A. Gebauer, eds. ''Last Hunters – First Farmers: New Perspectives on the Prehistoric Transition to Agriculture'' (1995) * Srivastava, Vinod Chandra, ed. ''History of Agriculture in India'' (5 vols., 2014). From 2000 BC to present. * Stevens, C.E. "Agriculture and Rural Life in the Later Roman Empire" in ''Cambridge Economic History of Europe, Vol. I, The Agrarian Life of the Middle Ages'' (Cambridge UP, 1971) * * Yasuda, Y., ed. ''The Origins of Pottery and Agriculture'' (SAB, 2003)
New Cambridge History of India: An Agrarian History of South Asia
'' (Cambridge, 1999). * * * Mintz, Sidney. ''Sweetness and Power: The Place of Sugar in Modern History'' (Penguin, 1986) * Reader, John. ''Propitious Esculent: The Potato in World History'' (Heinemann, 2008) a standard scholarly history * Salaman, Redcliffe N. ''The History and Social Influence of the Potato'' (Cambridge, 2010)
A history of agriculture in Europe and America
' (Crofts, 1925) * Harvey, Nigel. ''The Industrial Archaeology of Farming in England and Wales'' (HarperCollins, 1980) * Hoffman, Philip T. ''Growth in a Traditional Society: The French Countryside, 1450–1815'' (Princeton UP, 1996) * Hoyle, Richard W., ed. ''The Farmer in England, 1650–1980'' (Routledge, 2013
online review
* Kussmaul, Ann. ''A General View of the Rural Economy of England, 1538–1840'' (Cambridge University Press, 1990) * Langdon, John. ''Horses, Oxen and Technological Innovation: The Use of Draught Animals in English Farming from 1066 to 1500'' (Cambridge UP, 1986) * * Moon, David. ''The Plough that Broke the Steppes: Agriculture and Environment on Russia's Grasslands, 1700–1914'' (Oxford UP, 2014) * Slicher van Bath, B.H. ''The Agrarian History of Western Europe, AD 500–1850'' (Edward Arnold, reprint, 1963) * Thirsk, Joan, et al. ''The Agrarian History of England and Wales'' (Cambridge University Press, 8 vols., 1978) * Williamson, Tom. ''Transformation of Rural England: Farming and the Landscape 1700–1870'' (Liverpool UP, 2002) * Zweiniger-Bargielowska, Ina, Rachel Duffett, and Alain Drouard, eds. ''Food and war in twentieth century Europe'' (Ashgate, 2011)
online
* Cochrane, Willard W. ''The Development of American Agriculture: A Historical Analysis'' (University of Minnesota P, 1993) * * Gras, Norman.
A History of Agriculture in Europe and America
'' (F.S. Crofts, 1925) * Gray, L.C. ''History of Agriculture in the Southern United States to 1860'' (P. Smith, 1933
Volume I onlineVol. 2
* Hart, John Fraser. ''The Changing Scale of American Agriculture''. (University of Virginia Press, 2004) * Hurt, R. Douglas. ''American Agriculture: A Brief History'' (Purdue UP, 2002) * * O'Sullivan, Robin. ''American Organic: A Cultural History of Farming, Gardening, Shopping, and Eating'' (University Press of Kansas, 2015) * Rasmussen, Wayne D., ed. ''Readings in the history of American agriculture'' (University of Illinois Press, 1960) * Robert, Joseph C.
The story of tobacco in America
' (University of North Carolina Press, 1949) * Russell, Howard. ''A Long Deep Furrow: Three Centuries of Farming In New England'' (UP of New England, 1981) * Russell, Peter A. ''How Agriculture Made Canada: Farming in the Nineteenth Century'' (McGill-Queen's UP, 2012) * Schafer, Joseph.
The social history of American agriculture
' (Da Capo, 1970 936 * Schlebecker John T. ''Whereby we thrive: A history of American farming, 1607–1972'' (Iowa State UP, 1972) * Weeden, William Babcock.
Economic and Social History of New England, 1620–1789
' (Houghton, Mifflin, 1891)
"The Core Historical Literature of Agriculture"
from

Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
. At least eleven separate regions of the Old and New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
were involved as independent centers of origin.
The development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans lived. They switched from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to permanent settlements and farming.
Wild grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
were collected and eaten from at least 104,000 years ago. However, domestication did not occur until much later. The earliest evidence of small-scale cultivation of edible grasses is from around 21,000 BC with the Ohalo II people on the shores of the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee (, Judeo-Aramaic languages, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ), also called Lake Tiberias, Genezareth Lake or Kinneret, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest freshwater lake on Earth ...
. By around 9500 BC, the eight Neolithic founder crops
The founder crops or primary domesticates are a group of flowering plants that were Domestication, domesticated by early farming communities in Southwest Asia and went on to form the basis of agriculture, agricultural economies across Eurasia. As ...
– emmer wheat, einkorn wheat, hulled barley, pea
Pea (''pisum'' in Latin) is a pulse or fodder crop, but the word often refers to the seed or sometimes the pod of this flowering plant species. Peas are eaten as a vegetable. Carl Linnaeus gave the species the scientific name ''Pisum sativum' ...
s, lentil
The lentil (''Vicia lens'' or ''Lens culinaris'') is an annual plant, annual legume grown for its Lens (geometry), lens-shaped edible seeds or ''pulses'', also called ''lentils''. It is about tall, and the seeds grow in Legume, pods, usually w ...
s, bitter vetch, chickpea
The chickpea or chick pea (''Cicer arietinum'') is an annual plant, annual legume of the family (biology), family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, cultivated for its edible seeds. Its different types are variously known as gram," Bengal gram, ga ...
s, and flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
– were cultivated in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
. Rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
may have been cultivated earlier, but this claim remains controversial. Regardless, rye's spread from Southwest Asia to the Atlantic was independent of the Neolithic founder crop package. Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
was domesticated in China by 6200 BC with earliest known cultivation from 5700 BC, followed by mung, soy and azuki beans. Rice was also independently domesticated in West Africa and cultivated by 1000 BC. Pigs were domesticated in Mesopotamia around 11,000 years ago, followed by sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
. Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
were domesticated from the wild aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
in the areas of modern Turkey and India around 8500 BC. Camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
s were domesticated late, perhaps around 3000 BC.
In subsaharan Africa, sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
was domesticated in the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
region of Africa by 3000 BC, along with pearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
by 2000 BC. Yams were domesticated in several distinct locations, including West Africa (unknown date), and cowpea
The cowpea (''Vigna unguiculata'') is an annual herbaceous legume from the genus '' Vigna''. Its tolerance for sandy soil and low rainfall have made it an important crop in the semiarid regions across Africa and Asia. It requires very few inpu ...
s by 2500 BC. Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
( African rice) was also independently domesticated in West Africa and cultivated by 1000 BC. Teff and likely finger millet
Finger millet (''Eleusine coracana'') is an Annual plant, annual herbaceous plant widely grown as a cereal crop in the arid and Semi-arid climate, semiarid areas in Africa and Asia. It is a tetraploid and Self-pollination, self-pollinating speci ...
were domesticated in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
by 3000 BC, along with noog, ensete
''Ensete'' is a genus of monocarpic flowering plants native plant, native to tropical regions of Africa and Asia. It is one of the three genera in the banana family, Musaceae, and includes the false banana or enset (''Ensete ventricosum, E. vent ...
, and coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
. Other plant foods domesticated in Africa include watermelon
The watermelon (''Citrullus lanatus'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Cucurbitaceae, that has a large, edible fruit. It is a Glossary of botanical terms#scandent, scrambling and trailing vine-like plant, and is plant breeding ...
, okra
Okra (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the Malvaceae, mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions aro ...
, tamarind
Tamarind (''Tamarindus indica'') is a Legume, leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is indigenous to tropical Africa and naturalized in Asia. The genus ''Tamarindus'' is monotypic taxon, monotypic, meaning that it contains only this spe ...
and black eyed peas
The Black Eyed Peas are an American musical group formed in Los Angeles in 1995, composed of rappers will.i.am, apl.de.ap and Taboo (rapper), Taboo. Fergie (singer), Fergie was a member during the height of their popularity in the 2000s, and ...
, along with tree crops such as the kola nut and oil palm
''Elaeis'' () is a genus of palms, called oil palms, containing two species, native to Africa and the Americas. They are used in commercial agriculture in the production of palm oil.
Description
Mature palms are single-stemmed, and can gro ...
. Plantains were cultivated in Africa by 3000 BC and banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
s by 1500 BC. The helmeted guineafowl
Guinea fowl () (or guineahen) are birds of the family Numididae in the order Galliformes. They are endemic to Africa and rank among the oldest of the gallinaceous birds. Phylogenetically, they branched off from the core Galliformes after the C ...
was domesticated in West Africa. Sanga cattle was likely also domesticated in North-East Africa, around 7000 BC, and later crossbred with other species.
In South America, agriculture began as early as 9000 BC, starting with the cultivation of several species of plants that later became only minor crops. In the Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
of South America, the potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
was domesticated between 8000 BC and 5000 BC, along with beans
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are tradition ...
, squash, tomatoes
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originated from and was d ...
, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
s, coca
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine. Coca leaves contain cocaine which acts as a mild stimulant when chewed or ...
, llama
The llama (; or ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with ...
s, alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. Traditionally, alpacas were kept in herds that grazed on the level heights of the Andes of Southern Peru, Western Bolivia, Ecuador, and Northern Chile. More recentl ...
s, and guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy ( ), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus ''Cavia'', family Caviidae. Animal fancy, Breeders tend to use the name "cavy" for the ani ...
s. Cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
was domesticated in the Amazon Basin no later than 7000 BC. Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
(''Zea mays'') found its way to South America from Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
, where wild teosinte
''Zea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the Poaceae, grass family. The best-known species is ''Z. mays'' (variously called maize, corn, or Indian corn), one of the most important crops for human societies throughout much of the world. The four ...
was domesticated about 7000 BC and selectively bred to become domestic maize. Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
was domesticated in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
by 4200 BC; another species of cotton was domesticated in Mesoamerica and became by far the most important species of cotton in the textile industry in modern times. Evidence of agriculture in the Eastern United States dates to about 3000 BCE. Several plants were cultivated, later to be replaced by the Three Sisters cultivation of maize, squash, and beans.
Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
and some root vegetables
Root vegetables are underground plant parts eaten by humans or animals as food. In agricultural and culinary terminology, the term applies to true roots, such as taproots and tuberous root, root tubers, as well as non-roots such as bulbs, corms, ...
were domesticated in New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
around 7000 BC. Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
s were cultivated and hybridized in the same period in Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
. In Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, agriculture was invented at a currently unspecified period, with the oldest eel traps of Budj Bim
Budj Bim, also known as Mount Eccles, is a dormant volcano near Macarthur in southwestern Victoria, Australia. It lies within the geologically-defined area known as the Newer Volcanics Province, which is the youngest volcanic area in Austra ...
dating to 6,600 BC and the deployment of several crops ranging from yamsGammage, Bill (October 2011). The Biggest Estate on Earth: How Aborigines made Australia. Allen & Unwin. pp. 281–304. . to bananas.
The Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, from , witnessed the intensification of agriculture in civilizations such as Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
n Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
, ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, ancient Sudan, the Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, and ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
. From 100 BC to 1600 AD, world population continued to grow along with land use, as evidenced by the rapid increase in methane emissions
Increasing methane emissions are a major contributor to the rising concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere, and are responsible for up to one-third of near-term global heating. During 2019, about 60% (360 million tons) of methane r ...
from cattle and the cultivation of rice. During the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
and era of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
, the expansion of ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, both the Republic and then the Empire, throughout the ancient Mediterranean and Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
built upon existing systems of agriculture while also establishing the manorial system that became a bedrock of medieval agriculture. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, both in Europe and in the Islamic world, agriculture was transformed with improved techniques and the diffusion of crop plants, including the introduction of sugar, rice, cotton and fruit trees such as the orange to Europe by way of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
. After the voyages of Christopher Columbus
Between 1492 and 1504, the Italian explorer and navigator Christopher Columbus led four transatlantic maritime expeditions in the name of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain to the Caribbean and to Central and South America. These voyages led to t ...
in 1492, the Columbian exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the New World (the Americas) in the Western Hemisphere, and the Old World (Afro-Eurasia) in the Eastern Hemis ...
brought New World crops such as maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es, sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of ...
es, and manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
to Europe, and Old World crops such as wheat, barley, rice, and turnips, and livestock including horses, cattle, sheep, and goats to the Americas.
Irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
, crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. This practice reduces the reliance of crops on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, along with the pro ...
, and fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
s were introduced soon after the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
and developed much further in the past 200 years, starting with the British Agricultural Revolution
The British Agricultural Revolution, or Second Agricultural Revolution, was an unprecedented increase in agricultural production in Britain arising from increases in labor and land productivity between the mid-17th and late 19th centuries. Agricu ...
. Since 1900, agriculture in the developed nations, and to a lesser extent in the developing world, has seen large rises in productivity as human labour has been replaced by mechanization
Mechanization (or mechanisation) is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text, a machine is defined as follows:
In every fields, mechan ...
, and assisted by synthetic fertilizers, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, and selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
. The Haber-Bosch process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely di ...
allowed the synthesis of ammonium nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, but does not form hydrates. It is predominantly us ...
fertilizer on an industrial scale, greatly increasing crop yields. Modern agriculture has raised social, political, and environmental issues including overpopulation, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from Biomass (energy), biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels such as oil. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricu ...
s, genetically modified organism
A genetically modified organism (GMO) is any organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. The exact definition of a genetically modified organism and what constitutes genetic engineering varies, with ...
s, tariff
A tariff or import tax is a duty (tax), duty imposed by a national Government, government, customs territory, or supranational union on imports of goods and is paid by the importer. Exceptionally, an export tax may be levied on exports of goods ...
s and farm subsidies. In response, organic farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of ...
developed in the twentieth century as an alternative to the use of synthetic pesticides.
Origins
Origin hypotheses
Scholars have developed a number of hypotheses to explain the historical origins of agriculture. Studies of the transition fromhunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
to agricultural societies indicate an antecedent period of intensification and increasing sedentism
In anthropology, sedentism (sometimes called sedentariness; compare sedentarism) is the practice of living in one place for a long time. As of , the large majority of people belong to sedentary cultures. In evolutionary anthropology and arch ...
; examples are the Natufian culture
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even befor ...
in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and the Early Chinese Neolithic in China. Current models indicate that wild stands that had been harvested previously started to be planted, but were not immediately domesticated.
Localised climate change is the favoured explanation for the origins of agriculture in the Levant. When major climate change took place after the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
(c. 11,000 BC), much of the earth became subject to long dry seasons. These conditions favoured annual plant
An annual plant is a plant that completes its life cycle, from germination to the production of seeds, within one growing season, and then dies. Globally, 6% of all plant species and 15% of herbaceous plants (excluding trees and shrubs) are ...
s which die off in the long dry season, leaving a dormant seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
or tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure that plants use as storage organs for nutrients, derived from stems or roots. Tubers help plants perennate (survive winter or dry months), provide energy and nutrients, and are a means of asexual reproduc ...
. An abundance of readily storable wild grains and pulses enabled hunter-gatherers in some areas to form the first settled villages at this time. Across Western Eurasia it was not until approximately 4,000 BC that farming societies completely replaced hunter-gatherers. These technologically advanced societies expanded faster in areas with less forest, pushing hunter-gatherers into denser woodlands. Only the middle-late Bronze Age and Iron Age societies were able to fully replace hunter-gatherers in their final stronghold located in the most densely forested areas. Unlike their Bronze and Iron Age counterparts, Neolithic societies couldn't establish themselves in dense forests, and Copper Age societies had only limited success.
Early development
 Early people began altering communities of
Early people began altering communities of flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
and fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
for their own benefit through means such as fire-stick farming and forest gardening very early.
Wild grains
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit ( caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and le ...
have been collected and eaten from at least 105,000 years ago, and possibly much longer. Exact dates are hard to determine, as people collected and ate seeds before domesticating them, and plant characteristics may have changed during this period without human selection. An example is the semi-tough rachis
In biology, a rachis (from the [], "backbone, spine") is a main axis or "shaft".
In zoology and microbiology
In vertebrates, ''rachis'' can refer to the series of articulated vertebrae, which encase the spinal cord. In this case the ''rachi ...
and larger seeds of cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s from just after the Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (YD, Greenland Stadial GS-1) was a period in Earth's geologic history that occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years Before Present (BP). It is primarily known for the sudden or "abrupt" cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, when the ...
(about 9500 BC) in the early Holocene
The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ...
in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
region of the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent () is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, and Syria, together with northern Kuwait, south-eastern Turkey, and western Iran. Some authors also include ...
. Monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
characteristics were attained without any human intervention, implying that apparent domestication of the cereal rachis
In biology, a rachis (from the [], "backbone, spine") is a main axis or "shaft".
In zoology and microbiology
In vertebrates, ''rachis'' can refer to the series of articulated vertebrae, which encase the spinal cord. In this case the ''rachi ...
could have occurred quite naturally.
 Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe and included a diverse range of taxa. At least 11 separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. Some of the earliest known domestications were of animals.
Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe and included a diverse range of taxa. At least 11 separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. Some of the earliest known domestications were of animals. Domestic pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s had multiple centres of origin in Eurasia, including Europe, East Asia and Southwest Asia, where wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
were first domesticated about 10,500 years ago. Sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
were domesticated in Mesopotamia between 11,000 BC and 9000 BC. Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
were domesticated from the wild aurochs
The aurochs (''Bos primigenius''; or ; pl.: aurochs or aurochsen) is an extinct species of Bovini, bovine, considered to be the wild ancestor of modern domestic cattle. With a shoulder height of up to in bulls and in cows, it was one of t ...
in the areas of modern Turkey and India around 8500 BC. Camels were domesticated relatively late, perhaps around 3000 BC.
 It was not until after 9500 BC that the eight so-called
It was not until after 9500 BC that the eight so-called founder crops
The founder crops or primary domesticates are a group of flowering plants that were domesticated by early farming communities in Southwest Asia and went on to form the basis of agricultural economies across Eurasia. As originally defined by Dan ...
of agriculture appear: first emmer and einkorn wheat, then hulled barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, pea
Pea (''pisum'' in Latin) is a pulse or fodder crop, but the word often refers to the seed or sometimes the pod of this flowering plant species. Peas are eaten as a vegetable. Carl Linnaeus gave the species the scientific name ''Pisum sativum' ...
s, lentil
The lentil (''Vicia lens'' or ''Lens culinaris'') is an annual plant, annual legume grown for its Lens (geometry), lens-shaped edible seeds or ''pulses'', also called ''lentils''. It is about tall, and the seeds grow in Legume, pods, usually w ...
s, bitter vetch, chick pea
The chickpea or chick pea (''Cicer arietinum'') is an annual legume of the family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, cultivated for its edible seeds. Its different types are variously known as gram," Bengal gram, garbanzo, garbanzo bean, or Egypt ...
s and flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
. These eight crops occur more or less simultaneously on Pre-Pottery Neolithic B ( PPNB) sites in the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
, although wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
was the first to be grown and harvested on a significant scale. At around the same time (9400 BC), parthenocarpic fig trees were domesticated.
Domesticated rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
occurs in small quantities at some Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
sites in (Asia Minor) Turkey, such as the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B
Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BC. It was Type site, typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon ...
(c. 7600 – c. 6000 BC) Can Hasan III near Çatalhöyük, but is otherwise absent until the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
of central Europe, c. 1800–1500 BC. Claims of much earlier cultivation of rye, at the Epipalaeolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
site of Tell Abu Hureyra in the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
valley of northern Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, remain controversial. Critics point to inconsistencies in the radiocarbon dates, and identifications based solely on grain, rather than on chaff
Chaff (; ) is dry, scale-like plant material such as the protective seed casings of cereal grains, the scale-like parts of flowers, or finely chopped straw. Chaff cannot be digested by humans, but it may be fed to livestock, ploughed into soil ...
.
By 8000 BC, farming was entrenched on the banks of the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
. About this time, agriculture was developed independently in the Far East, probably in China, with rice rather than wheat as the primary crop. Maize was domesticated from the wild grass teosinte
''Zea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the Poaceae, grass family. The best-known species is ''Z. mays'' (variously called maize, corn, or Indian corn), one of the most important crops for human societies throughout much of the world. The four ...
in southern Mexico by 6700 BC.
The potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
(8000 BC), tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
, pepper (4000 BC), squash (8000 BC) and several varieties of bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
(8000 BC onwards) were domesticated in the New World.
Agriculture was independently developed on the island of New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
. Banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
cultivation of ''Musa acuminata
''Musa acuminata'' is a species of banana native to South Asia, Southern Asia, its range comprising the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Many of the modern edible dessert bananas are derived from this species, although some are hybrids wi ...
'', including hybridization, dates back to 5000 BC, and possibly to 8000 BC, in Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
.
Bees were kept for honey in the Middle East around 7000 BC. Archaeological evidence from various sites on the Iberian peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
suggest the domestication of plants and animals between 6000 and 4500 BC. The Céide Fields, located in Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
consist of extensive tracts of land enclosed by stone walls, these walls date to 3500 BC and is the oldest known field systems in europe. The horse was domesticated in the Pontic steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from n ...
around 4000 BC In Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
. Cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
was in use in China in Neolithic times and may have been domesticated there; it was in use both as a fibre for ropemaking and as a medicine in Ancient Egypt by about 2350 BC.
 In northern
In northern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
was domesticated by early Sino-Tibetan speakers at around 8000 to 6000 BC, becoming the main crop of the Yellow River
The Yellow River, also known as Huanghe, is the second-longest river in China and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system on Earth, with an estimated length of and a Drainage basin, watershed of . Beginning in the Bayan H ...
basin by 5500 BC. They were followed by mung, soy and azuki beans.
Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
basin at around 11,500 to 6200 BC, along with the development of wetland agriculture, by early Austronesian and Hmong-Mien-speakers. Other food plants were also harvested, including acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s, water chestnuts, and foxnuts. Rice cultivation was later spread to Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as ...
by the Austronesian expansion
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
, starting at around 3,500 to 2,000 BC. This migration event also saw the introduction of cultivated and domesticated food plants from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as ...
, and New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
into the Pacific Islands
The Pacific islands are a group of islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of several ...
as canoe plants. Contact with Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
by Austronesian sailors also led to an exchange of food plants which later became the origin of the valuable spice trade
The spice trade involved historical civilizations in Asia, Northeast Africa and Europe. Spices, such as cinnamon, cassia, cardamom, ginger, pepper, nutmeg, star anise, clove, and turmeric, were known and used in antiquity and traded in t ...
. In the 1st millennium AD, Austronesian sailors also settled Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
and the Comoros
The Comoros, officially the Union of the Comoros, is an archipelagic country made up of three islands in Southeastern Africa, located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city is Moroni, ...
, bringing Southeast Asian and South Asian food plants with them to the East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
n coast, including bananas and rice. Rice was also spread southwards into Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to th ...
by around 2000 to 1500 BC by the migrations of the early Austroasiatic and Kra-Dai-speakers.
In the Sahel
The Sahel region (; ), or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a Biogeography, biogeographical region in Africa. It is the Ecotone, transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a ...
region of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
was domesticated by 3000 BC in Sudan and pearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
by 2500 BC in Mali. Kola nut and coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
were also domesticated in Africa. In New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
, ancient Papuan people Papuans may refer to:
* Indonesian Papuans – the Native Indonesians of Papua-origin
* Papua New Guineans – the nationals of Papua New Guinea
* Indigenous people of New Guinea
{{Disambiguation
Language and nationality disambiguation page ...
s began practicing agriculture around 7000 BC, domesticating sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
and taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a ...
. In the Indus Valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
from the eighth millennium BC onwards at Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh is a Neolithic archaeological site situated on the Kacchi Plain of Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan in Pakistan. It is located near the Bolan Pass, to the west of the Indus River and between the modern-day Pakistani cities of Quetta, ...
, 2-row and 6-row barley were cultivated, along with einkorn, emmer, and durum wheats, and dates. In the earliest levels of Merhgarh, wild game such as gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . There are also seven species included in two further genera; '' Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third former subgenus, ' ...
, swamp deer, blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is a medium-sized antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources.
It stands up to high at the sh ...
, chital, wild ass, wild goat, wild sheep, boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
, and nilgai
The nilgai (''Boselaphus tragocamelus'') (, literally meaning "blue cow") is the largest antelope of Asia, and is ubiquitous across the northern Indian subcontinent. It is the sole member of the genus (biology), genus ''Boselaphus'', which was ...
were all hunted for food. These are successively replaced by domesticated sheep, goats, and humped zebu
The zebu (; ''Bos indicus''), also known as indicine cattle and humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of Bos taurus, domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump ...
cattle by the fifth millennium BC, indicating the gradual transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture.
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
and squash were domesticated in Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
; potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es in South America, and sunflower
The common sunflower (''Helianthus annuus'') is a species of large annual forb of the daisy family Asteraceae. The common sunflower is harvested for its edible oily seeds, which are often eaten as a snack food. They are also used in the pr ...
s in the Eastern Woodlands of North America.
Civilizations
Sumer

Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian farmers grew the cereals barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
and wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, starting to live in villages from about 8000 BC. Given the low rainfall of the region, agriculture relied on the Tigris
The Tigris ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian Desert, Syrian and Arabia ...
and Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
rivers. Irrigation canals leading from the rivers permitted the growth of cereals in large enough quantities to support cities. The first ploughs appear in pictograph
A pictogram (also pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto) is a graphical symbol that conveys meaning through its visual resemblance to a physical object. Pictograms are used in systems of writing and visual communication. A pictography is a wri ...
s from Uruk around 3000 BC; seed-ploughs that funneled seed into the ploughed furrow appear on seals around 2300 BC. Vegetable crops included chickpea
The chickpea or chick pea (''Cicer arietinum'') is an annual plant, annual legume of the family (biology), family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, cultivated for its edible seeds. Its different types are variously known as gram," Bengal gram, ga ...
s, lentil
The lentil (''Vicia lens'' or ''Lens culinaris'') is an annual plant, annual legume grown for its Lens (geometry), lens-shaped edible seeds or ''pulses'', also called ''lentils''. It is about tall, and the seeds grow in Legume, pods, usually w ...
s, peas, beans, onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' , from Latin ), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion which was classifie ...
s, garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plants in the genus '' Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chives, Welsh onion, and Chinese onion. Garlic is native to central and south Asia, str ...
, lettuce
Lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'') is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae mostly grown as a leaf vegetable. The leaves are most often used raw in Green salad, green salads, although lettuce is also seen in other kinds of food, such as sandwiche ...
, leek
A leek is a vegetable, a cultivar of ''Allium ampeloprasum'', the broadleaf wild leek (synonym (taxonomy), syn. ''Allium porrum''). The edible part of the plant is a bundle of Leaf sheath, leaf sheaths that is sometimes erroneously called a "s ...
s and mustard. They grew fruits including dates, grapes, apples, melons, and figs. Alongside their farming, Sumerians also caught fish and hunted fowl
Fowl are birds belonging to one of two biological orders, namely the gamefowl or landfowl ( Galliformes) and the waterfowl ( Anseriformes). Anatomical and molecular similarities suggest these two groups are close evolutionary relatives; toget ...
and gazelle
A gazelle is one of many antelope species in the genus ''Gazella'' . There are also seven species included in two further genera; '' Eudorcas'' and '' Nanger'', which were formerly considered subgenera of ''Gazella''. A third former subgenus, ' ...
. The meat of sheep, goats, cows and poultry was eaten, mainly by the elite. Fish was preserved by drying, salting and smoking.
Ancient Egypt
The civilization ofAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
was indebted to the Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
and its dependable seasonal flooding. The river's predictability and the fertile soil allowed the Egyptians to build an empire on the basis of great agricultural wealth. Egyptians were among the first peoples to practice agriculture on a large scale, starting in the pre-dynastic period from the end of the Paleolithic into the Neolithic, between around 10,000 BC and 4000 BC. This was made possible with the development of basin irrigation. Their staple food crops were grains such as wheat and barley, alongside industrial crops such as flax
Flax, also known as common flax or linseed, is a flowering plant, ''Linum usitatissimum'', in the family Linaceae. It is cultivated as a food and fiber crop in regions of the world with temperate climates. In 2022, France produced 75% of t ...
and papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
. Archaeological evidence also suggests that the spread of agriculture in Egypt was facilitated by farming communities associated with the playa lakes of the Sahara some 6,500 years ago.
Indian Subcontinent
Jujube was domesticated in theIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
by 9000 BC. Barley and wheat cultivation – along with the domestication of cattle, primarily sheep and goats – followed in Mehrgarh culture by 8000–6000 BC. This period also saw the first domestication of the elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
. Pastoral farming in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
included threshing, planting crops in rows – either of two or of six – and storing grain in granaries.Possehl, Gregory L. (1996). ''Mehrgarh'' in ''Oxford Companion to Archaeology'', edited by Brian Fagan. Oxford University Press. Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
was cultivated by the 5th–4th millennium BC. By the 5th millennium BC, agricultural communities became widespread in Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
. Irrigation was developed in the Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
by around 4500 BC. The size and prosperity of the Indus civilization grew as a result of this innovation, leading to more thoroughly planned settlements which used drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of a surface's water and sub-surface water from an area with excess water. The internal drainage of most agricultural soils can prevent severe waterlogging (anaerobic conditions that harm root gro ...
and sewers. Archeological evidence of an animal-drawn plough
A plough or ( US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden ...
dates back to 2500 BC in the Indus Valley Civilization.
Ancient China
 Records from the
Records from the Warring States
The Warring States period in Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and struggles for gre ...
, Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng enga ...
, and Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
provide a picture of early Chinese agriculture from the 5th century BC to 2nd century AD which included a nationwide granary
A granary, also known as a grain house and historically as a granarium in Latin, is a post-harvest storage building primarily for grains or seeds. Granaries are typically built above the ground to prevent spoilage and protect the stored grains o ...
system and widespread use of sericulture
Sericulture, or silk farming, is the cultivation of silkworms to produce silk. Although there are several commercial species of silkworms, the caterpillar of the Bombyx mori, domestic silkmoth is the most widely used and intensively studied silkwo ...
. An important early Chinese book on agriculture is the Qimin Yaoshu of AD 535, written by Jia Sixie. Needham, Joseph (1986). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 6, Part 2''. Taipei: Caves Books Ltd. pp. 55–56. Jia's writing style was straightforward and lucid relative to the elaborate and allusive writing typical of the time. Jia's book was also very long, with over one hundred thousand written Chinese characters
Chinese characters are logographs used Written Chinese, to write the Chinese languages and others from regions historically influenced by Chinese culture. Of the four independently invented writing systems accepted by scholars, they represe ...
, and it quoted many other Chinese books that were written previously, but no longer survive. The contents of Jia's 6th century book include sections on land preparation, seeding, cultivation, orchard management, forestry, and animal husbandry. The book also includes peripherally related content covering trade and culinary uses for crops.Needham, Volume 6, Part 2, 57. The work and the style in which it was written proved influential on later Chinese agronomist
An agriculturist, agriculturalist, agrologist, or agronomist (abbreviated as agr.) is a professional in the science, practice, and management of agriculture and agribusiness. It is a regulated profession in Canada, India, the Philippines, the Uni ...
s, such as Wang Zhen and his groundbreaking ''Nong Shu'' of 1313.Needham, Volume 6, Part 2, 56.
hydraulic
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
-powered trip hammer
Trip may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
Fictional characters
* Trip (Pokémon), Trip (''Pokémon''), a ''Pokémon'' character
* Trip (Power Rangers), in the American television series ''Time Force Power Rangers''
* Trip, in the 2013 film ...
by the 1st century BC.Needham, Joseph (1986). ''Science and Civilization in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology, Part 2, Mechanical Engineering''. Taipei: Caves Books, Ltd. p. 184 Although it found other purposes, its main function to pound, decorticate, and polish grain that otherwise would have been done manually. The Chinese also began using the square-pallet chain pump by the 1st century AD, powered by a waterwheel or oxen
An ox (: oxen), also known as a bullock (in BrE, British, AusE, Australian, and IndE, Indian English), is a large bovine, trained and used as a draft animal. Oxen are commonly castration, castrated adult male cattle, because castration i ...
pulling an on a system of mechanical wheels.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 89, 110. Although the chain pump found use in public works
Public works are a broad category of infrastructure projects, financed and procured by a government body for recreational, employment, and health and safety uses in the greater community. They include public buildings ( municipal buildings, ...
of providing water for urban and palatial pipe systems,Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 33. it was used largely to lift water from a lower to higher elevation in filling irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
s and channels for farmland
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous with bot ...
.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 110. By the end of the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
in the late 2nd century, heavy ploughs had been developed with iron ploughshares and mouldboards.Robert Greenberger, ''The Technology of Ancient China'', Rosen Publishing Group, 2006, pp. 11–12. These slowly spread west, revolutionizing farming in Northern Europe by the 10th century. ( Thomas Glick, however, argues for a development of the Chinese plough as late as the 9th century, implying its spread east from similar designs known in Italy by the 7th century.)
Asian rice was domesticated 8,200–13,500 years ago in China, with a single genetic origin from the wild rice '' Oryza rufipogon'', in the Pearl River valley region of China. Rice cultivation then spread to South and Southeast Asia.
Ancient Greece and Hellenistic world
The major cereal crops of the ancient Mediterranean region were wheat, emmer, and barley, while common vegetables included peas, beans,fava
''Vicia faba'', commonly known as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of vetch, a flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption, and also as a cover crop. Vari ...
, and olives, dairy products came mostly from sheep and goats, and meat, which was consumed on rare occasion for most people, usually consisted of pork, beef, and lamb.Koester, Helmut (1995), ''History, Culture, and Religion of the Hellenistic Age'', 2nd edition, New York: Walter de Gruyter, , pp. 76–77. Agriculture in ancient Greece was hindered by the topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the landforms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sci ...
of mainland Greece
Greece is a country in Southeastern Europe, on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered to the north by Albania, North Macedonia and Bulgaria; to the east by Turkey, and is surrounded to the east by the Aegean Sea, to the south by the Cret ...
that only allowed for roughly 10% of the land to be cultivated properly, necessitating the specialised exportation of oil and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
and importation of grains from Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
(centered in what is now Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
) and the Greek colonies
Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ages ...
of Pontic Greeks
The Pontic Greeks (; or ; , , ), also Pontian Greeks or simply Pontians, are an ethnically Greek group indigenous to the region of Pontus, in northeastern Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). They share a common Pontic Greek culture that is di ...
near the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
. During the Hellenistic period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
, the Ptolemaic Empire controlled Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
, and Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika (, , after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between the 16th and 25th meridians east, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, als ...
, major grain-producing regions that mainland Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
depended on for subsistence, while the Ptolemaic grain market
The grain trade refers to the local and international trade in cereals such as wheat, barley, maize, rice, and other food grains. Grain is an important trade item because it is easily stored and transported with limited spoilage, unlike other agri ...
also played a critical role in the rise of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
. In the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire ( ) was a Greek state in West Asia during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 312 BC by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire founded by Alexander the Great ...
, Mesopotamia was a crucial area for the production of wheat, while nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, animal fiber, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising ...
was also practiced in other parts.Helmut Koester (1995), ''History, Culture, and Religion of the Hellenistic Age'', 2nd edition, New York: Walter de Gruyter, , p. 77.
Roman Empire
In theGreco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world , also Greco-Roman civilization, Greco-Roman culture or Greco-Latin culture (spelled Græco-Roman or Graeco-Roman in British English), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and co ...
of Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
, Roman agriculture was built on techniques originally pioneered by the Sumerians, transmitted to them by subsequent cultures, with a specific emphasis on the cultivation of crops for trade and export. The Romans laid the groundwork for the manorial economic system, involving serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
, which flourished in the Middle Ages. The farm sizes in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
can be divided into three categories. Small farms were from 18 to 88 iugera (one iugerum is equal to about 0.65 acre). Medium-sized farms were from 80 to 500 iugera (singular iugerum). Large estates (called latifundia
A ''latifundium'' (Latin: ''latus'', "spacious", and ''fundus'', "farm", "estate") was originally the term used by ancient Romans for great landed estates specialising in agriculture destined for sale: grain, olive oil, or wine. They were charac ...
) were over 500 iugera. The Romans had four systems of farm management: direct work by the owner and his family; slaves doing work under the supervision of slave managers; tenant farming
A tenant farmer is a farmer or farmworker who resides and works on land owned by a landlord, while tenant farming is an Agrarian system, agricultural production system in which landowners contribute their land and often a measure of operating Ca ...
or sharecropping
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement in which a landowner allows a tenant (sharecropper) to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land. Sharecropping is not to be conflated with tenant farming, providing the tenant a ...
in which the owner and a tenant divide up a farm's produce; and situations in which a farm was leased to a tenant.White, K. D. (1970), ''Roman Farming'' (Cornell University Press)
The Americas
Agricultural history took a different path from theOld World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
as the Americas lacked large-seeded, easily domesticated grains (such as wheat and barley) and large domestic animals that could be used for agricultural labor. Rather than the practice which developed in the Old World of sowing a field with a single crop, pre-historic American agriculture usually consisted of cultivating many crops close to each other utilizing only hand labor. Moreover, agricultural areas in the Americas lacked the uniformity of the east–west area of Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of se ...
s in southern Europe and southwestern Asia, but instead had a north–south pattern with a variety of different climatic zones in close proximity to each other. This fostered the domestication of many different plants.
At the time of first contact between the Europeans and the Americans, the Europeans practiced "extensive agriculture, based on the plough and draught animals," with tenants under landlords, but also forced labor or slavery, while the Indigenous peoples of the Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
practiced "intensive agriculture, based on human labour." Europeans wanted control of land for the grazing of their livestock and property rights for the control of production. Though they were impressed with the productivity of traditional farming techniques, they saw no connection to their system and were dismissive of Native American practices as "gardening" rather than a commercializable enterprise. Due to several thousand years of selective breeding, maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, the hemisphere's most important crop, was more productive than Old World grain crops. Maize produced two and one-half times more calories per acre than wheat and barley.
South America

 The earliest known areas of possible agriculture in the Americas dating to about 9000 BC are in
The earliest known areas of possible agriculture in the Americas dating to about 9000 BC are in Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
, near present-day Pereira, and by the Las Vegas
Las Vegas, colloquially referred to as Vegas, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Nevada and the county seat of Clark County. The Las Vegas Valley metropolitan area is the largest within the greater Mojave Desert, and second-l ...
culture in Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
on the Santa Elena peninsula. The plants cultivated (or manipulated by humans) were lerén (''Calathea allouia''), arrowroot
Arrowroot is a starch obtained from the rhizomes (rootstock) of several tropical plants, traditionally ''Maranta arundinacea'', but also Florida arrowroot from ''Zamia integrifolia'', and tapioca from cassava (''Manihot esculenta''), which is of ...
(''Maranta arundinacea''), squash (''Cucurbita'' species), and bottle gourd
Calabash (; ''Lagenaria siceraria''), also known as bottle gourd, white-flowered gourd, long melon, birdhouse gourd, New Guinea bean, New Guinea butter bean, Tasmania bean, and opo squash, is a vine grown for its fruit. It can be either harvest ...
(''Lagenaria siceraria''). All are plants of humid climates and their existence at this time on the semi-arid Santa Elena peninsula may be evidence that they were transplanted there from more humid environments. In another study, this area of South America was identified as one of the four oldest places of origin for agriculture, along with the Fertile Crescent, China, and Mesoamerica, dated between 6200 BC and 10000 BC. (To facilitate comprehension by readers, Radiocarbon calibrated BP dates in the above sources have been converted to BC.)
In the Andes region, with civilizations including the Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
, the major crop was the potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
, domesticated between 8000 and 5000 BC. Coca
Coca is any of the four cultivated plants in the family Erythroxylaceae, native to western South America. Coca is known worldwide for its psychoactive alkaloid, cocaine. Coca leaves contain cocaine which acts as a mild stimulant when chewed or ...
, still a major crop to this day, was domesticated in the Andes, as were the peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), goober pea, pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics by small and large ...
, tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, and pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a Tropical vegetation, tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae.
The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been culti ...
. Cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
was domesticated in Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
by 4200 BC. Animals were also domesticated, including llama
The llama (; or ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with ...
s, alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. Traditionally, alpacas were kept in herds that grazed on the level heights of the Andes of Southern Peru, Western Bolivia, Ecuador, and Northern Chile. More recentl ...
s, and guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy ( ), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus ''Cavia'', family Caviidae. Animal fancy, Breeders tend to use the name "cavy" for the ani ...
s. The people of the Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
of South America grew large surpluses of food which they stored in buildings called Qullqas.
The most important crop domesticated in the Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries ...
and tropical lowlands was probably cassava
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
( Manihot esculenta), which was domesticated before 7000 BCE, likely in the Rondônia
Rondônia () is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northern subdivision of the country (central-western part). It is bordered by Acre (state), Acre in the west,
Amazonas, Brazil, Amazonas in the north, Mato Grosso in the east, and Bo ...
and Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – ) is one of the states of Brazil, the List of Brazilian states by area, third largest by area, located in the Central-West Region, Brazil, Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible ...
states of Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. The Guaitecas Archipelago in modern Chile was the southern limit of Pre-Hispanic agriculture near 44° South latitude, as noted by the mention of the cultivation of Chiloé potatoes by a Spanish expedition in 1557.
Mesoamerica
 In Mesoamerica, wild
In Mesoamerica, wild teosinte
''Zea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the Poaceae, grass family. The best-known species is ''Z. mays'' (variously called maize, corn, or Indian corn), one of the most important crops for human societies throughout much of the world. The four ...
was transformed through human selection into the ancestor of modern maize, about 7,000 BC. It gradually spread across North America and to South America and was the most important crop of Native Americans at the time of European exploration. Other Mesoamerican crops include hundreds of varieties of locally domesticated squash and bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, while cocoa, also domesticated in the region, was a major crop. The turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, one of the most important poultry birds, was probably domesticated in Mexico or the U.S. Southwest.
In Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El S ...
, the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
s were active farmers and had an agriculturally focused economy. The land around Lake Texcoco was fertile, but not large enough to produce the amount of food needed for the population of their expanding empire. The Aztecs developed irrigation systems, formed terraced hillsides, fertilized their soil, and developed chinampa
Chinampa ( ) is a technique used in Agriculture in Mesoamerica, Mesoamerican agriculture which relies on small, rectangle, rectangular areas of fertility (soil), fertile arable land to grow agriculture, crops on the shallow lake beds in the Va ...
s or artificial islands, also known as "floating gardens". The Mayas
Maya () are an ethnolinguistic group of Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical region. Today ...
between 400 BC to 900 AD used extensive canal and raised field systems to farm swampland on the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula ( , ; ) is a large peninsula in southeast Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north and west of the peninsula from the C ...
.
North America
 The indigenous people of the Eastern U.S. domesticated numerous crops. Sunflowers,
The indigenous people of the Eastern U.S. domesticated numerous crops. Sunflowers, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, varieties of squash and '' Chenopodium'', as well as crops no longer grown, including marsh elder and little barley. Wild foods including wild rice and maple sugar
Maple sugar is a traditional sweetener in Canada and the Northeastern United States, prepared from the sap of the maple tree ("maple syrup, maple sap").
Sources
Three species of maple trees in the genus ''Acer (plant), Acer'' are predomina ...
were harvested. The domesticated strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit ...
is a hybrid of a Chilean and a North American species, developed by breeding in Europe and North America. Two major crops, pecan
The pecan ( , , ; ''Carya illinoinensis'') is a species of hickory native to the Southern United States and northern Mexico in the region of the Mississippi River.
The tree is cultivated for its seed primarily in the U.S. states of Georgia ( ...
s and Concord grapes, were used extensively in prehistoric times but do not appear to have been domesticated until the 19th century.
The indigenous people in what is now California and the Pacific Northwest practiced various forms of forest gardening and fire-stick farming in the forests, grasslands, mixed woodlands, and wetlands, ensuring that desired food and medicine plants continued to be available. The natives controlled fire on a regional scale to create a low-intensity fire ecology
Fire ecology is a scientific discipline concerned with the effects of fire on natural ecosystems. Many ecosystems, particularly prairie, savanna, chaparral and coniferous forests, have evolved with fire as an essential contributor to habitat vit ...
which prevented larger, catastrophic fires and sustained a low-density agriculture in loose rotation; a sort of "wild" permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to land management and settlement design that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using Systems theory, whole-systems thinking. It applies t ...
.
A system of companion planting
Companion planting in gardening and agriculture is the planting of different crops in proximity for any of a number of different reasons, including Weed control, weed suppression, pest control, pollination, providing habitat for beneficial ins ...
called the Three Sisters was developed in North America. Three crops that complemented each other were planted together: winter squash
Winter squash is an annual fruit representing several squash species within the genus '' Cucurbita''. Late-growing, less symmetrical, odd-shaped, rough or warty varieties, small to medium in size, but with long-keeping qualities and hard rinds, ...
, maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
(corn), and climbing bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s (typically tepary beans or common beans). The maize provides a structure for the beans to climb, eliminating the need for poles. The beans provide the nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
to the soil that the other plants use, and the squash spreads along the ground, blocking the sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
, helping prevent the establishment of weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, growing where it conflicts with human preferences, needs, or goals.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. Pla ...
s. The squash leaves also act as a "living mulch
A mulch is a layer of material applied to the surface of soil. Reasons for applying mulch include conservation of soil moisture, improving soil fertility, fertility and health of the soil, reducing Weed control, weed growth, and enhancing the v ...
".
Sub-Saharan Africa
 In the Sahel region, civilizations such as the
In the Sahel region, civilizations such as the Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
and Songhai empires cultivated sorghum
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a species in the Poaceae, grass genus ''Sorghum (genus), Sorghum'' cultivated for its grain. The grain i ...
and pearl millet
Pearl millet (''Cenchrus americanus'', commonly known as the synonym ''Pennisetum glaucum'') is the most widely grown type of millet. It has been grown in Africa and the Indian subcontinent since prehistoric times. The center of diversity, and ...
, which were domesticated between 3000 and 2500 BC. The donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
was domesticated in Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
at approximately 5000 BC. Archaeological evidence suggests that Sanga cattle may have been independently domesticated in East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
at around 1600 BC.
In the tropical region of West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
, crops such as black-eyed peas, Sea Island red peas, yams, kola nuts, Jollof rice and kokoro were domesticated between 3000 and 1000 BC. The coastal region of West Africa is often referred to as the "Yam Belt", due to its high production of yams. The guineafowl
Guinea fowl () (or guineahen) are birds of the family Numididae in the order Galliformes. They are endemic to Africa and rank among the oldest of the gallinaceous birds. Phylogenetically, they branched off from the core Galliformes after the C ...
is a poultry bird that was domesticated in West Africa, and while the time of the guineafowl's domestication remains unclear, there is evidence that it was present in Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
during the 5th century BC.
Several species of coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
were also domesticated throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, with ''Coffea arabica
''Coffea arabica'' (), also known as the Arabica coffee, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee and madder family Rubiaceae. It is believed to be the first species of coffee to have been cultivated and is the dominant cultivar, represe ...
'' originating in Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
and serving as the main production of modern-day coffee since the late 15th century.
Oceania
Australia

Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of contemporary Australia prior to History of Australia (1788–1850), British colonisation. The ...
were predominately nomadic hunter-gatherers
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, especially w ...
. Due to the policy of ''terra nullius
''Terra nullius'' (, plural ''terrae nullius'') is a Latin expression meaning " nobody's land".
Since the nineteenth century it has occasionally been used in international law as a principle to justify claims that territory may be acquired ...
'', Aboriginals were regarded as not having been capable of sustained agriculture. However, the current consensus is that various agricultural methods were employed by the indigenous people.
In two regions of Central Australia, the central west coast and eastern central Australia, forms of agriculture were practiced. People living in permanent settlements of over 200 residents sowed or planted on a large scale and stored the harvested food. The Nhanda and Amangu of the central west coast grew yams ('' Dioscorea hastifolia''), while various groups in eastern central Australia (the Corners Region) planted and harvested bush onions (''yaua'' – '' Cyperus bulbosus''), native millet (''cooly, tindil'' – '' Panicum decompositum'') and a sporocarp, ''ngardu'' ('' Marsilea drummondii'').
Indigenous Australians used systematic burning, fire-stick farming, to enhance natural productivity. In the 1970s and 1980s archaeological research in south west Victoria established that the Gunditjmara and other groups had developed sophisticated eel farming and fish trapping systems over a period of nearly 5,000 years. The archaeologist Harry Lourandos suggested in the 1980s that there was evidence of 'intensification' in progress across Australia, a process that appeared to have continued through the preceding 5,000 years. These concepts led the historian Bill Gammage to argue that in effect the whole continent was a managed landscape.
Torres Strait Islanders are now known to have planted banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
s.
Pacific Islands
InNew Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
, archaeological evidence suggests that agriculture independently emerged around 7,000 years ago with the domestication of crops such as bananas and taro
Taro (; ''Colocasia esculenta'') is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, stems and Petiole (botany), petioles. Taro corms are a ...
. Pigs and chickens were imported to New Guinea, which were later innovated by other Pacific Island nations, such as those in Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
.
Middle Ages and Early Modern period
Europe
TheMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
saw further improvements in agriculture. Monasteries
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone ( hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which m ...
spread throughout Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and became important centers for the collection of knowledge related to agriculture and forestry. The manorial system allowed large landowners to control their land and its laborers, in the form of peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasan ...
s or serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
s. During the medieval period, the Arab world
The Arab world ( '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in ...
was critical in the exchange of crops and technology between the European, Asia and African continents. Besides transporting numerous crops, they introduced the concept of summer irrigation to Europe and developed the beginnings of the plantation
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tob ...
system of sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
growing through the use of slaves for intensive cultivation.
 By AD 900, developments in
By AD 900, developments in iron smelting
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron, copper, silver, tin, lead and zinc ...
allowed for increased production in Europe, leading to developments in the production of agricultural implements such as plough
A plough or ( US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden ...
s, hand tool
A hand tool is any tool that is powered manual labour, by hand rather than a motor. Categories of hand tools include wrenches, pliers, cutter (disambiguation), cutters, File (tool), files, hammer, striking tools, chisel, struck or hammered tools, ...
s and horse shoes. The carruca heavy plough improved on the earlier scratch plough, with the adoption of the Chinese mouldboard plough to turn over the heavy, wet soils of northern Europe. This led to the clearing of northern European forests and an increase in agricultural production, which in turn led to an increase in population. At the same time, some farmers in Europe moved from a two field crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. This practice reduces the reliance of crops on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, along with the pro ...
to a three-field crop rotation in which one field of three was left fallow every year. This resulted in increased productivity and nutrition, as the change in rotations permitted nitrogen-fixing
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
legumes
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consu ...
such as peas, lentils and beans. Improved horse harness
A horse harness is a device that connects a horse to a horse-drawn vehicle or another type of load to pull. There are two main designs of horse harness: (1) the Breastplate (tack)#Harness, breast collar or breaststrap, and (2) the Horse collar, ...
es and the whippletree further improved cultivation.
Watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as mill (grinding), milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in ...
s were introduced by the Romans, but were improved throughout the Middle Ages, along with windmill
A windmill is a machine operated by the force of wind acting on vanes or sails to mill grain (gristmills), pump water, generate electricity, or drive other machinery.
Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern period ...
s, and used to grind grains into flour, to cut wood and to process flax and wool.
Crops included wheat, rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
, barley and oats
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural). Oats appear to have been domesticated as a secondary crop, as their seed ...
. Peas, beans, and vetches became common from the 13th century onward as a fodder crop for animals and also for their nitrogen-fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiologically in chemical industries. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is catalyzed by en ...
fertilizing properties. Crop yields peaked in the 13th century, and stayed more or less steady until the 18th century. Though the limitations of medieval farming were once thought to have provided a ceiling for the population growth in the Middle Ages, recent studies have shown that the technology of medieval agriculture was always sufficient for the needs of the people under normal circumstances, and that it was only during exceptionally harsh times, such as the terrible weather of 1315–17, that the needs of the population could not be met.
Arab world
From the 8th century to the 14th century, theIslamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
underwent a transformation in agricultural practice, described by the historian Andrew Watson as the Arab agricultural revolution
The Arab Agricultural Revolution was the transformation in agriculture in the Old World during the Islamic Golden Age (8th to 13th centuries). The agronomic literature of the time, with major books by Ibn Bassal and Ibn al-'Awwam, demonstrates t ...
. This transformation was driven by a number of factors including the diffusion of many crops and plants along Muslim trade routes, the spread of more advanced farming techniques, and an agricultural-economic system which promoted increased yields and efficiency. The shift in agricultural practice changed the economy, population distribution
Species distribution, or species dispersion, is the manner in which a biological taxon is spatially arranged. The geographic limits of a particular taxon's distribution is its range, often represented as shaded areas on a map. Patterns of distr ...
, vegetation cover, agricultural production, population levels, urban growth, the distribution of the labour force, cooking, diet, and clothing across the Islamic world. Muslim traders covered much of the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
, and trade enabled the diffusion of many crops, plants and farming techniques across the region, as well as the adaptation of crops, plants and techniques from beyond the Islamic world. This diffusion introduced major crops to Europe by way of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
, along with the techniques for their cultivation and cuisine. Sugar cane, rice, and cotton were among the major crops transferred, along with citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes.
''Citrus'' is nativ ...
and other fruit trees, nut trees, vegetables such as aubergine, spinach
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to Central Asia, Central and Western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common vegetable consumed eit ...
and chard
Chard (; '' Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'', Cicla Group and Flavescens Group) is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, or Swiss chard, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf b ...
, and the use of imported spices such as cumin, coriander
Coriander (), whose leaves are known as cilantro () in the U.S. and parts of Canada, and dhania in parts of South Asia and Africa, is an annual plant, annual herb (''Coriandrum sativum'') in the family Apiaceae.
Most people perceive the ...
, nutmeg
Nutmeg is the seed, or the ground spice derived from the seed, of several tree species of the genus '' Myristica''; fragrant nutmeg or true nutmeg ('' M. fragrans'') is a dark-leaved evergreen tree cultivated for two spices derived from its fru ...
and cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, b ...
. Intensive irrigation, crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. This practice reduces the reliance of crops on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, along with the pro ...
, and agricultural manuals were widely adopted. Irrigation, partly based on Roman technology, made use of noria water wheels, water mill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the production ...
s, dams and reservoirs.
Columbian exchange
After 1492, a global exchange of previously local crops and livestock breeds occurred. Maize, potatoes,sweet potatoes
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant in the morning glory family, Convolvulaceae. Its sizeable, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a root vegetable, which is a staple food in parts of the ...
and manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', common name, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America, from Brazil, Paraguay and parts of the Andes. Although ...
were the key crops that spread from the New World to the Old, while varieties of wheat, barley, rice and turnips traveled from the Old World to the New. There had been few livestock species in the New World, with horses, cattle, sheep and goats being completely unknown before their arrival with Old World settlers. Crops moving in both directions across the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
caused population growth around the world and a lasting effect on many cultures in the Early Modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
.  Maize and cassava were introduced from Brazil into Africa by Portuguese traders in the 16th century, becoming staple foods, replacing native African crops. After its introduction from South America to Spain in the late 1500s, the potato became a staple crop throughout Europe by the late 1700s. The potato allowed farmers to produce more food, and initially added variety to the European diet. The increased supply of food reduced disease, increased births and reduced mortality, causing a population boom throughout the
Maize and cassava were introduced from Brazil into Africa by Portuguese traders in the 16th century, becoming staple foods, replacing native African crops. After its introduction from South America to Spain in the late 1500s, the potato became a staple crop throughout Europe by the late 1700s. The potato allowed farmers to produce more food, and initially added variety to the European diet. The increased supply of food reduced disease, increased births and reduced mortality, causing a population boom throughout the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
, the US and Europe. The introduction of the potato also brought about the first intensive use of fertilizer, in the form of guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a le ...
imported to Europe from Peru, and the first artificial pesticide, in the form of an arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
compound used to fight Colorado potato beetles. Before the adoption of the potato as a major crop, the dependence on grain had caused repetitive regional and national famines when the crops failed, including 17 major famines in England between 1523 and 1623. The resulting dependence on the potato however caused the European Potato Failure, a disastrous crop failure from disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
that resulted in widespread famine and the death of over one million people in Ireland alone. Adapted from ''1493: Uncovering the New World Columbus Created'', by Charles C. Mann.
Modern agriculture
British agricultural revolution
Between the 17th century and the mid-19th century, Britain saw a large increase in agricultural productivity and net output. New agricultural practices likeenclosure
Enclosure or inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or "common land", enclosing it, and by doing so depriving commoners of their traditional rights of access and usage. Agreements to enc ...
, mechanization, four-field crop rotation to maintain soil nutrients, and selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
enabled an unprecedented population growth to 5.7 million in 1750, freeing up a significant percentage of the workforce, and thereby helped drive the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
. The productivity of wheat went up from per acre
The acre ( ) is a Unit of measurement, unit of land area used in the Imperial units, British imperial and the United States customary units#Area, United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), ch ...
in 1720 to around by 1840, marking a major turning point in history.
Advice on more productive techniques for farming began to appear in England in the mid-17th century, from writers such as Samuel Hartlib, Walter Blith and others. The main problem in sustaining agriculture in one place for a long time was the depletion of nutrients, most importantly nitrogen levels, in the soil. To allow the soil to regenerate, productive land was often let fallow and, in some places, crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. This practice reduces the reliance of crops on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, along with the pro ...
was used. The Dutch four-field rotation system was popularised by the British agriculturist Charles Townshend
Charles Townshend (27 August 1725 – 4 September 1767) was a British politician who held various titles in the Parliament of Great Britain. His establishment of the controversial Townshend Acts is considered one of the key causes of the Amer ...
in the 18th century. The system (wheat, turnips, barley and clover) opened up a fodder crop and grazing crop allowing livestock to be bred year-round. The use of clover was especially important as the legume roots replenished soil nitrates.
The mechanisation and rationalisation of agriculture was another important factor. Robert Bakewell and Thomas Coke introduced selective breeding
Selective breeding (also called artificial selection) is the process by which humans use animal breeding and plant breeding to selectively develop particular phenotypic traits (characteristics) by choosing which typically animal or plant m ...
and initiated a process of inbreeding to maximise desirable traits from the mid 18th century, such as the New Leicester sheep. Machines were invented to improve the efficiency of various agricultural operation, such as Jethro Tull's seed drill
file:7263 Canterbury Agricultural College farm.jpg, Filling a feed-box of a seed drill, Lincoln University (New Zealand), Canterbury Agricultural College farm, 1948
A seed drill is a device used in agriculture that sowing, sows seeds for crops by ...
of 1701 that mechanised seeding at the correct depth and spacing and Andrew Meikle's threshing machine
A threshing machine or a thresher is a piece of agricultural machinery, farm equipment that separates grain seed from the plant stem, stalks and husks. It does so by beating the plant to make the seeds fall out. Before such machines were developed ...
of 1784. Ploughs were steadily improved, from Joseph Foljambe's Rotherham iron plough in 1730 to James Small's improved "Scots Plough" metal in 1763. In 1789 Ransomes, Sims & Jefferies was producing 86 plough models for different soils. Powered farm machinery began with Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He ...
's stationary steam engine
Stationary steam engines are fixed steam engines used for pumping or driving mills and factories, and for power generation. They are distinct from locomotive engines used on railways, traction engines for heavy steam haulage on roads, steam car ...
, used to drive a threshing machine, in 1812. Mechanisation spread to additional farm uses throughout the 19th century. The first petrol-driven tractor
A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a Trailer (vehicle), trailer or machinery such as that used in agriculture, mining or constructio ...
was built in America by John Froelich in 1892.
John Bennet Lawes began the scientific investigation of fertilization at the Rothamsted Experimental Station
Rothamsted Research, previously known as the Rothamsted Experimental Station and then the Institute of Arable Crops Research, is one of the oldest agricultural research institutions in the world, having been founded in 1843. It is located at Harp ...
in 1843. He investigated the impact of inorganic and organic fertilizers on crop yield and founded one of the first artificial fertilizer manufacturing factories in 1842. Fertilizer, in the shape of sodium nitrate
Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula . This alkali metal nitrate salt (chemistry), salt is also known as Chile saltpeter (large deposits of which were historically mined in Chile) to distinguish it from ordi ...
deposits in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, was imported to Britain by John Thomas North as well as guano
Guano (Spanish from ) is the accumulated excrement of seabirds or bats. Guano is a highly effective fertiliser due to the high content of nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium, all key nutrients essential for plant growth. Guano was also, to a le ...
(birds droppings). The first commercial process for fertilizer production was the obtaining of phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
from the dissolution of coprolite
A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. The name ...
s in sulphuric acid.
20th century
Dan Albone constructed the first commercially successful gasoline-powered general-purpose tractor in 1901, and the 1923International Harvester
The International Harvester Company (often abbreviated IH or International) was an American manufacturer of agricultural and construction equipment, automobiles, commercial trucks, lawn and garden products, household equipment, and more. It wa ...
Farmall tractor marked a major point in the replacement of draft animals (particularly horses) with machines. Since that time, self-propelled mechanical harvesters ( combines), planters, transplanters and other equipment have been developed, further revolutionizing agriculture. These inventions allowed farming tasks to be done with a speed and on a scale previously impossible, leading modern farms to output much greater volumes of high-quality produce per land unit.
 The Haber-Bosch method for synthesizing
The Haber-Bosch method for synthesizing ammonium nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, but does not form hydrates. It is predominantly us ...
represented a major breakthrough and allowed crop yields to overcome previous constraints. It was first patented by German chemist Fritz Haber
Fritz Jakob Haber (; 9 December 1868 – 29 January 1934) was a German chemist who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his invention of the Haber process, a method used in industry to synthesize ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrog ...
. In 1910 Carl Bosch, while working for German chemical company BASF
BASF SE (), an initialism of its original name , is a European Multinational corporation, multinational company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters are located in Ludwigshafen, Ge ...
, successfully commercialized the process and secured further patents. In the years after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the use of synthetic fertilizer increased rapidly, in sync with the increasing world population.
Collective farming
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-o ...
was widely practiced in the Soviet Union, the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries, China, and Vietnam, starting in the 1930s in the Soviet Union; one result was the Soviet famine of 1932–33. Another consequence occurred during the Great Leap Forward
The Great Leap Forward was an industrialization campaign within China from 1958 to 1962, led by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). Party Chairman Mao Zedong launched the campaign to transform the country from an agrarian society into an indu ...
in China initiated by Mao Tse-tung that resulted in the Great Chinese Famine from 1959 to 1961 and ultimately reshaped the thinking of Deng Xiaoping
Deng Xiaoping also Romanization of Chinese, romanised as Teng Hsiao-p'ing; born Xiansheng (). (22 August 190419 February 1997) was a Chinese statesman, revolutionary, and political theorist who served as the paramount leader of the People's R ...
.
In the past century agriculture has been characterized by increased productivity, the substitution of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides for labour, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, and farm subsidies. Other applications of scientific research since 1950 in agriculture include gene manipulation,Weasel, Lisa H. 2009. ''Food Fray.'' Amacom Publishing hydroponics
Hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of #Passive sub-irrigation, hydroculture which involves growing plants, usually crops or medicinal plants, without soil, by using water-based mineral Plant nutrition, nutrient Solution (chemi ...
,Douglas, James S., ''Hydroponics,'' 5th ed. Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 1975. 1–3 and the development of economically viable biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from Biomass (energy), biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels such as oil. Biofuel can be produced from plants or from agricu ...
s such as ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
.
The number of people involved in farming in industrial countries fell radically from 24 percent of the American population to 1.5 percent in 2002. The number of farms also decreased, and their ownership became more concentrated; for example, between 1967 and 2002, one million pig farms in America consolidated into 114,000, with 80 percent of the production on factory farms. According to the Worldwatch Institute
The Worldwatch Institute was a globally focused environmental research organization based in Washington, D.C., founded by Lester R. Brown. Worldwatch was named as one of the top ten sustainable development research organizations by Globescan S ...
, 74 percent of the world's poultry, 43 percent of beef, and 68 percent of eggs are produced this way.
Famines however continued to sweep the globe through the 20th century. Through the effects of climatic events, government policy, war and crop failure, millions of people died in each of at least ten famines between the 1920s and the 1990s.
Green Revolution
 The Green Revolution was a series of research, development, and
The Green Revolution was a series of research, development, and technology transfer
Technology transfer (TT), also called transfer of technology (TOT), is the process of transferring (disseminating) technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, in an attempt to transform invent ...
initiatives between the 1940s and the late 1970s. It increased agriculture production around the world, especially from the late 1960s. The initiatives, led by Norman Borlaug and credited with saving over a billion people from starvation, involved the development of high-yielding varieties of cereal grains, expansion of irrigation infrastructure, modernization of management techniques, distribution of hybridized seeds, synthetic fertilizers, and pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s to farmers.
Synthetic nitrogen, mined rock phosphate, pesticides, and mechanization have greatly increased crop yields in the early 20th century. Increased supply of grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
s has also led to cheaper livestock. Further, global yield increases were experienced later in the 20th century when high-yield varieties of common staple grains such as rice, wheat, and corn were introduced as a part of the Green Revolution. The Green Revolution exported the technologies (including pesticides and synthetic nitrogen) of the developed world to the developing world. Thomas Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English economist, cleric, and scholar influential in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
famously predicted that the Earth would not be able to support its growing population. Still, technologies such as the Green Revolution have allowed the world to produce a food surplus.
Although the Green Revolution significantly increased rice yields in Asia, yield leveled off. The genetic "yield potential" has increased for wheat, but the yield potential for rice has not increased since 1966, and the yield potential for maize has "barely increased in 35 years". It takes only a decade or two for herbicide-resistant weeds to emerge, and insects become resistant to insecticides within about a decade, delayed somewhat by crop rotation.

Organic agriculture
For most of its history, agriculture has been organic, without synthetic fertilisers orpesticides
Pesticides are substances that are used to pest control, control pest (organism), pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for a ...
, and without GMOs. With the advent of chemical agriculture, Rudolf Steiner
Rudolf Joseph Lorenz Steiner (; 27 or 25 February 1861 – 30 March 1925) was an Austrian occultist, social reformer, architect, esotericist, and claimed clairvoyant. Steiner gained initial recognition at the end of the nineteenth century ...
called for farming without synthetic pesticides, and his Agriculture Course of 1924 laid the foundation for biodynamic agriculture
Biodynamic agriculture is a form of alternative agriculture based on pseudoscientific and esoteric concepts initially developed in 1924 by Rudolf Steiner (1861–1925). It was the first of the organic farming movements. It treats soil fertility, ...
. Lord Northbourne
Baron Northbourne, of Betteshanger in the County of Kent, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created in 1884 for Walter James, 1st Baron Northbourne, Sir Walter James, 2nd Baronet, who had earlier represented Kingston upon H ...
developed these ideas and presented his manifesto of organic farming
Organic farming, also known as organic agriculture or ecological farming or biological farming,Labelling, article 30 o''Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2024 on organic production and labelling of ...
in 1940. This became a worldwide movement, and organic farming is now practiced in many countries.
See also
*Agricultural expansion
Agricultural expansion describes the growth of agricultural land ( arable land, pastures, etc.) especially in the 20th and 21st centuries.
The agricultural expansion is often explained as a direct consequence of the global increase in food and e ...
* Effects of climate change on agriculture
There are numerous effects of climate change on agriculture, many of which are making it harder for agricultural activities to provide global food security. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns often result in lower crop yields du ...
* Farming/language dispersal hypothesis
* Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
* Historical hydroculture
* History of cotton
* History of fertilizer
* History of gardening
* History of sugar
The history of sugar has five main phases:
# The extraction of sugar cane juice from the sugarcane plant, and the subsequent domestication of the plant in tropical India and Southeast Asia sometime around 4,000 Anno Domini, BC.
# The invention o ...
* History of the potato
* Rural history
In historiography, rural history is a field of study focusing on the history of societies in rural areas. At its inception, the field was based on the economic history of agriculture. Since the 1980s it has become increasingly influenced by socia ...
References
Further reading
Surveys
* Civitello, Linda. ''Cuisine and Culture: A History of Food and People'' (Wiley, 2011excerpt
* Federico, Giovanni. ''Feeding the World: An Economic History of Agriculture 1800–2000'' (Princeton UP, 2005) highly quantitative * Grew, Raymond
''Food in Global History''
(1999) * Heiser, Charles B. ''Seed to Civilization: The Story of Food'' (W.H. Freeman, 1990) * Herr, Richard, ed. ''Themes in Rural History of the Western World'' (Iowa State UP, 1993) * Kiple, Kenneth F., and Kriemhild Coneè Ornelas, eds. ''The Cambridge world history of food'' (2 vol Cambridge University Press, 2000
online
* Mazoyer, Marcel, and Laurence Roudart. ''A History of World Agriculture: From the Neolithic Age to the Current Crisis'' (Monthly Review Press, 2006) Marxist perspective. * Pilcher, Jeffrey M. ''Food in world history'' (Routledge, 2023). * Prentice, E. Parmalee
''Hunger and History: The Influence of Hunger on Human History''
(Harper, 1939) * Tauger, Mark. ''Agriculture in World History'' (Routledge, 2008) * Toussaint-Samat, Maguelonne. ''A history of food'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2009), 800+ pp
online
* ; covers historiographical traditions within geographic regions across the world.
Premodern
* Bakels, C.C. ''The Western European Loess Belt: Agrarian History, 5300 BC – AD 1000'' (Springer, 2009) * Barker, Graeme, and Candice Goucher, eds. ''The Cambridge World History: Volume 2, A World with Agriculture, 12000 BCE–500 CE''. (Cambridge UP, 2015) * Bowman, Alan K. and Rogan, Eugene, eds. ''Agriculture in Egypt: From Pharaonic to Modern Times'' (Oxford UP, 1999) * Cohen, M.N. ''The Food Crisis in Prehistory: Overpopulation and the Origins of Agriculture'' (Yale UP, 1977) * Crummey, Donald and Stewart, C.C., eds. ''Modes of Production in Africa: The Precolonial Era'' (Sagem 1981) * Diamond, Jared. ''Guns, Germs, and Steel
''Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies'' (subtitled ''A Short History of Everybody for the Last 13,000 Years'' in Britain) is a 1997 transdisciplinary nonfiction book by the American author Jared Diamond. The book attempts to ...
'' (W.W. Norton, 1997)
* Duncan-Jones, Richard. ''Economy of the Roman Empire'' (Cambridge UP, 1982)
* Habib, Irfan. ''Agrarian System of Mughal India'' (Oxford UP, 3rd ed. 2013)
* Harris, D.R., ed. ''The Origins and Spread of Agriculture and Pastoralism in Eurasia'', (Routledge, 1996)
* Isager, Signe and Jens Erik Skydsgaard. ''Ancient Greek Agriculture: An Introduction'' (Routledge, 1995)
* Lee, Mabel Ping-hua. The economic history of china: with special reference to agriculture
' (Columbia University, 1921) * Murray, Jacqueline. ''The First European Agriculture'' (Edinburgh UP, 1970) * Oka, H-I. ''Origin of Cultivated Rice'' (Elsevier, 2012) * Price, T.D. and A. Gebauer, eds. ''Last Hunters – First Farmers: New Perspectives on the Prehistoric Transition to Agriculture'' (1995) * Srivastava, Vinod Chandra, ed. ''History of Agriculture in India'' (5 vols., 2014). From 2000 BC to present. * Stevens, C.E. "Agriculture and Rural Life in the Later Roman Empire" in ''Cambridge Economic History of Europe, Vol. I, The Agrarian Life of the Middle Ages'' (Cambridge UP, 1971) * * Yasuda, Y., ed. ''The Origins of Pottery and Agriculture'' (SAB, 2003)
Modern
* Collingham, E.M. ''The Taste of War: World War Two and the Battle for Food'' (Penguin, 2012) * Kerridge, Erik. "The Agricultural Revolution Reconsidered." ''Agricultural History'' (1969) 43:4, 463–475. , in Britain, 1750–1850 * Ludden, David, ed.New Cambridge History of India: An Agrarian History of South Asia
'' (Cambridge, 1999). * * * Mintz, Sidney. ''Sweetness and Power: The Place of Sugar in Modern History'' (Penguin, 1986) * Reader, John. ''Propitious Esculent: The Potato in World History'' (Heinemann, 2008) a standard scholarly history * Salaman, Redcliffe N. ''The History and Social Influence of the Potato'' (Cambridge, 2010)
Europe
* Ambrosoli, Mauro. ''The Wild and the Sown: Botany and Agriculture in Western Europe, 1350–1850'' (Cambridge UP, 1997) * Brassley, Paul, Yves Segers, and Leen Van Molle, eds. ''War, Agriculture, and Food: Rural Europe from the 1930s to the 1950s'' (Routledge, 2012) * Brown, Jonathan. ''Agriculture in England: A Survey of Farming, 1870–1947'' (Manchester UP, 1987) * * Dovring, Folke, ed. ''Land and labor in Europe in the twentieth century: a comparative survey of recent agrarian history'' (Springer, 1965) * Gras, Norman.A history of agriculture in Europe and America
' (Crofts, 1925) * Harvey, Nigel. ''The Industrial Archaeology of Farming in England and Wales'' (HarperCollins, 1980) * Hoffman, Philip T. ''Growth in a Traditional Society: The French Countryside, 1450–1815'' (Princeton UP, 1996) * Hoyle, Richard W., ed. ''The Farmer in England, 1650–1980'' (Routledge, 2013
online review
* Kussmaul, Ann. ''A General View of the Rural Economy of England, 1538–1840'' (Cambridge University Press, 1990) * Langdon, John. ''Horses, Oxen and Technological Innovation: The Use of Draught Animals in English Farming from 1066 to 1500'' (Cambridge UP, 1986) * * Moon, David. ''The Plough that Broke the Steppes: Agriculture and Environment on Russia's Grasslands, 1700–1914'' (Oxford UP, 2014) * Slicher van Bath, B.H. ''The Agrarian History of Western Europe, AD 500–1850'' (Edward Arnold, reprint, 1963) * Thirsk, Joan, et al. ''The Agrarian History of England and Wales'' (Cambridge University Press, 8 vols., 1978) * Williamson, Tom. ''Transformation of Rural England: Farming and the Landscape 1700–1870'' (Liverpool UP, 2002) * Zweiniger-Bargielowska, Ina, Rachel Duffett, and Alain Drouard, eds. ''Food and war in twentieth century Europe'' (Ashgate, 2011)
North America
* Bidwell, Percy Wells, and John I. Falconer. ''History of agriculture in the northern United States, 1620–1860'' (1925), massive scholarly historyonline
* Cochrane, Willard W. ''The Development of American Agriculture: A Historical Analysis'' (University of Minnesota P, 1993) * * Gras, Norman.
A History of Agriculture in Europe and America
'' (F.S. Crofts, 1925) * Gray, L.C. ''History of Agriculture in the Southern United States to 1860'' (P. Smith, 1933
Volume I online
* Hart, John Fraser. ''The Changing Scale of American Agriculture''. (University of Virginia Press, 2004) * Hurt, R. Douglas. ''American Agriculture: A Brief History'' (Purdue UP, 2002) * * O'Sullivan, Robin. ''American Organic: A Cultural History of Farming, Gardening, Shopping, and Eating'' (University Press of Kansas, 2015) * Rasmussen, Wayne D., ed. ''Readings in the history of American agriculture'' (University of Illinois Press, 1960) * Robert, Joseph C.
The story of tobacco in America
' (University of North Carolina Press, 1949) * Russell, Howard. ''A Long Deep Furrow: Three Centuries of Farming In New England'' (UP of New England, 1981) * Russell, Peter A. ''How Agriculture Made Canada: Farming in the Nineteenth Century'' (McGill-Queen's UP, 2012) * Schafer, Joseph.
The social history of American agriculture
' (Da Capo, 1970 936 * Schlebecker John T. ''Whereby we thrive: A history of American farming, 1607–1972'' (Iowa State UP, 1972) * Weeden, William Babcock.
Economic and Social History of New England, 1620–1789
' (Houghton, Mifflin, 1891)
External links
"The Core Historical Literature of Agriculture"
from
Cornell University Library
The Cornell University Library is the library system of Cornell University. As of 2014, it holds over eight million printed volumes and over a million ebooks. More than 90 percent of its current 120,000 Periodical literature, periodical ti ...
{{History of biology
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
History by topic