|
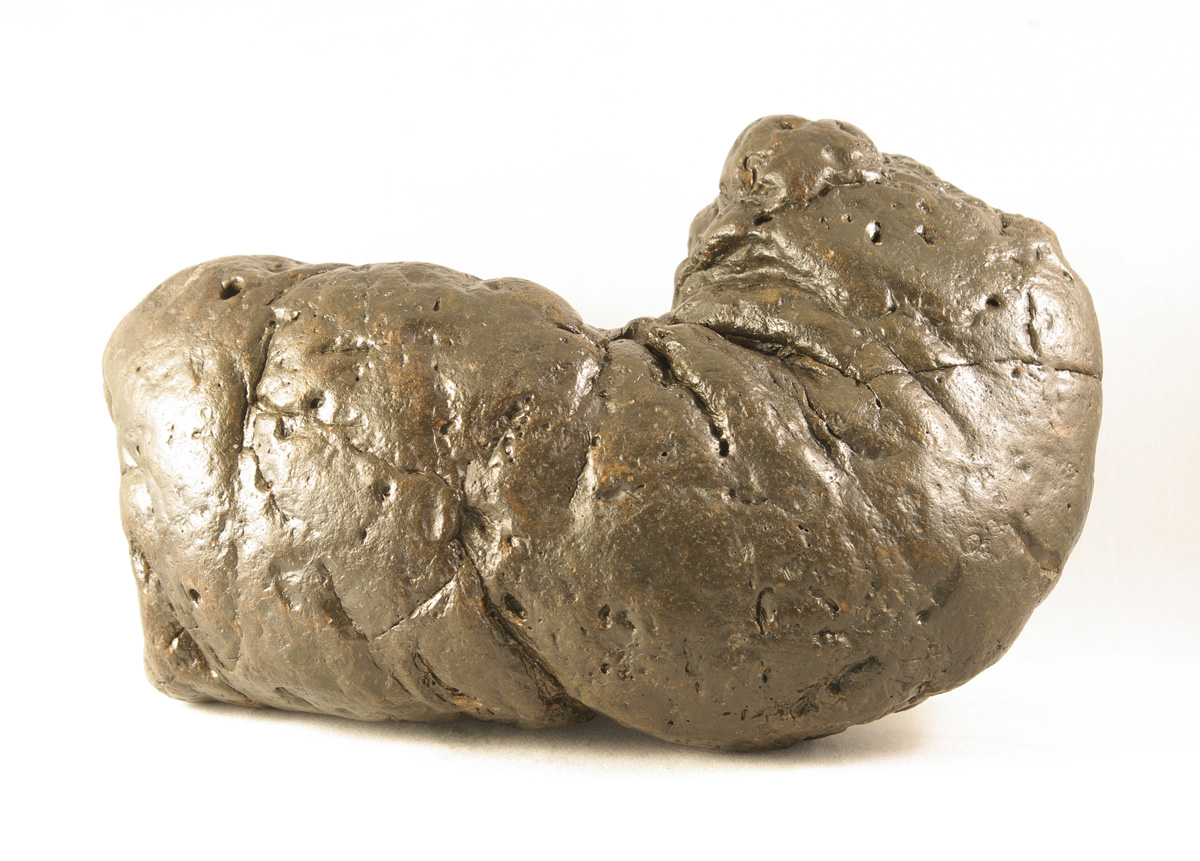
Coprolite
A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than morphology. The name is derived from the Greek words κόπρος (''kopros'', meaning "dung") and λίθος (''lithos'', meaning "stone"). They were first described by William Buckland in 1829. Before this, they were known as "fossil fir cones" and "bezoar stones". They serve a valuable purpose in paleontology because they provide direct evidence of the predation and diet of extinct organisms. Coprolites may range in size from a few millimetres to over 60 centimetres. Coprolites, distinct from '' paleofeces'', are fossilized animal dung. Like other fossils, coprolites have had much of their original composition replaced by mineral deposits such as silicates and calcium carbonates. Paleofeces, on the other hand, retain much of their original organic compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coprolites 1
A coprolite (also known as a coprolith) is fossilized feces. Coprolites are classified as trace fossils as opposed to body fossils, as they give evidence for the animal's behaviour (in this case, diet) rather than Morphology (biology), morphology. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words κόπρος (''kopros'', meaning "dung") and λίθος (''lithos'', meaning "stone"). They were first described by William Buckland in 1829. Before this, they were known as "fossil conifer cone#Pinaceae cones, fir cones" and "bezoar stones". They serve a valuable purpose in paleontology because they provide direct evidence of the predation and diet of extinct organisms. Coprolites may range in size from a few millimetres to over 60 centimetres. Coprolites, distinct from ''paleofeces'', are fossilized animal dung. Like other fossils, coprolites have had much of their original composition replaced by mineral deposits such as silicates and calcium carbonates. Paleofeces, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paleofeces
Paleofeces (or palaeofaeces in British English) are ancient human feces, often found as part of archaeological excavations or surveys. The term coprolite is often used interchangeably, although coprolite can also refer to fossilized animal feces. Intact feces of ancient people may be found in caves in arid climates and in other locations with suitable preservation conditions. They are studied to determine the diet and health of the people who produced them through the analysis of seeds, small bones, and parasite eggs found inside. The feces can contain information about the person excreting the material as well as information about the material itself. They can also be chemically analyzed for more in-depth information on the individual who excreted them, using lipid analysis and ancient DNA analysis. The success rate of usable DNA extraction is relatively high in paleofeces, making it more reliable than skeletal DNA retrieval. The reason this analysis is possible at all i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
William Buckland
William Buckland Doctor of Divinity, DD, Royal Society, FRS (12 March 1784 – 14 August 1856) was an English theologian, geologist and paleontology, palaeontologist. His work in the early 1820s proved that Kirkdale Cave in North Yorkshire had been a prehistoric hyena den, for which he was awarded the Copley Medal. It was praised as an example of how scientific analysis could reconstruct events in the distant past. He pioneered the use of fossilised Feces, faeces in reconstructing ecosystems, coining the term coprolites. Buckland also wrote the first full account of a fossil dinosaur, which he named ''Megalosaurus'' in 1824. Buckland followed the Gap creationism, Gap Theory in interpreting the biblical account of ''Genesis'' as two widely separated episodes of creation. It had emerged as a way to reconcile the scriptural account with discoveries in geology suggesting the earth was very old. Early in his career Buckland believed he had found evidence of the Deluge myth, bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides. Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurians were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods, until they were replaced as the top aquatic predators by another marine reptilian group, the Plesiosauria, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially-altered bilirubin and dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. Feces are discharged through the anus or cloaca during defecation. Feces can be used as fertilizer or soil conditioner in agriculture. They can also be burned as dry animal dung fuel, fuel or dried and used for wattle and daub, construction. Some medicinal uses have been found. In the case of human feces, fecal transplants or fecal bacteriotherapy are in use. Urine and feces together are called excretion, excreta. Characteristics The distinctive odor of feces is due to skatole, and thiols (sulfur-containing compounds), as well as amines and carboxylic acids. Sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tyrannosaurus Rex Coprolite Poozeum
''Tyrannosaurus'' () is a genus of large theropod dinosaur. The type species ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' ( meaning 'king' in Latin), often shortened to ''T. rex'' or colloquially t-rex, is one of the best represented theropods. It lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. ''Tyrannosaurus'' had a much wider range than other tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of geological formations dating to the latest Campanian-Maastrichtian ages of the late Cretaceous period, 72.7 to 66 million years ago, with isolated specimens possibly indicating an earlier origin in the middle Campanian. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids and among the last non- avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Like other tyrannosaurids, ''Tyrannosaurus'' was a bipedal carnivore with a massive skull balanced by a long, heavy tail. Relative to its large and powerful hind limbs, the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silesaurus
''Silesaurus'' is a genus of silesaurid dinosauriform from the Late Triassic, of what is now Poland. Discovery and naming The Krasiejów claypit near Opole, Poland, was first discovered as a fossil locality in the 1980s after quarrying for a nearby cement plant reached the fossil layer, though scientific excavations began in 1993 with the discovery of an almost complete phytosaur skull by Polish paleontologist Jerzy Dzik. Preliminary investigations identified Krasiejów as a diverse vertebrate assemblage, named the "'' Paleorhinus'' fauna", preserving partially articulated skeletons of amphibians and reptiles, including possible early dinosaurs from the middle to late Carnian. Following these preliminary reports, extensive excavations of Krasiejów were undertaken from 2000 to 2002, collecting numerous skulls, partially articulated skeletons, and isolated remains. An area with dense skeletons was left intact to construct a museum exhibit of the University of Opole around, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Michiko Chiura
Michiko Chiura, also Michiko Mori-Chiura, Japanese: 千浦美智子 (1947/48 - 1982) was a Japanese archaeologist, who was an early proponent of archaeological flotation in Japan. In the 1970s she pioneered the study of coprolites in Japan, with particular focus on those from the Torihama shell mound in Fukui Prefecture. Chiura studied for her undergraduate degree at the University of Toronto, then subsequently worked at the International Christian University is a non-denominational private university located in Mitaka, Tokyo. With the efforts of Prince Takamatsu, General Douglas MacArthur, and Bank of Japan, BOJ Governor Hisato Ichimada, ICU was established in 1949 as the first liberal arts coll ... in Tokyo. She died aged 35 in 1982. Her death from cancer, and attitude to life, was written about by Shigeaki Hinohara, who was her physician. Selected works * 千浦美智子. "環境復原とフロテーション その植物利用範囲." ''季刊どるめん'' 13 (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trace Fossil
A trace fossil, also called an ichnofossil (; ), is a fossil record of biological activity by lifeforms, but not the preserved remains of the organism itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, which are the fossilized remains of parts of organisms' bodies, usually altered by later chemical activity or by mineralization. The study of such trace fossils is ichnology - the work of ichnologists. Trace fossils may consist of physical impressions made on or in the substrate by an organism. For example, burrows, borings ( bioerosion), urolites (erosion caused by evacuation of liquid wastes), footprints, feeding marks, and root cavities may all be trace fossils. The term in its broadest sense also includes the remains of other organic material produced by an organism; for example coprolites (fossilized droppings) or chemical markers (sedimentological structures produced by biological means; for example, the formation of stromatolites). However, most sedimentary struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |