|
Incan Animal Husbandry
Inca animal husbandry refers to how in the pre-Hispanic andes, camelids played a truly important role in the economy. In particular, the Lama glama, llama and Vicugna pacos, alpaca—the only camelids domesticated by Andean people— which were raised in large-scale houses and used for different purposes within the production system of the Incas. Likewise, two other species of undomesticated camelids were used: the Vicugna vicugna, ''vicuña'' and the Lama guanicoe, ''guanaco''. The guanacos were hunted by means of ''chacos'' (collective hunts). The Inca people used tools such as: stones, knives or Tumi, ''tumis'', axes that, according to chroniclers, were made of stone and bronze, and ropes that were made by them in their leisure time. Many of these tools were used to shear the camelids, which were then set free; in this way, they ensured that their numbers were maintained. Guanacos, on the other hand, were hunted for their meat, which was highly prized. Camelid raising The Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lama3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene. Function Laminins are basement membrane components thought to mediate the attachment, migration and organization of cells into tissues during embryonic development by interacting with other extracellular matrix components. The protein encoded by this gene is the alpha-3 chain of laminin 5, which is a complex glycoprotein composed of three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. Laminin 5 is thought to be involved in cell adhesion, signal transduction and differentiation of keratinocytes. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene have been identified as the cause of Herlitz type Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (medicine), junctional epidermolysis bullosa. It may be associated with Laryngoonychocutaneous syndrome. Interactions Laminin, alpha 3 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
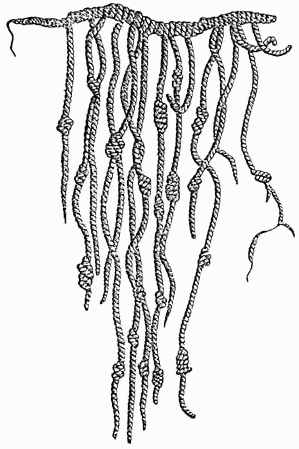
Quipu
''Quipu'' ( ), also spelled ''khipu'', are record keeping devices fashioned from knotted cords. They were historically used by various cultures in the central Andes of South America, most prominently by the Inca Empire. A ''quipu'' usually consists of cotton or camelid fiber cords, and contains categorized information based on dimensions like color, order and number. The Inca, in particular, used knots tied in a decimal positional system to store numbers and other values in ''quipu'' cords. Depending on its use and the amount of information it stored, a given ''quipu'' may have anywhere from a few to several thousand cords. Objects which can unambiguously be identified as ''quipus'' first appear in the archaeological record during 1st millennium CE,Urton, Gary. (2011). "Tying the Archive in Knots, or: Dying to Get into the Archive in Ancient Peru likely attributable to the Wari Empire. ''Quipus'' subsequently played a key part in the administration of the Kingdom of Cusco of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chucuito
Chucuito is a village in the Chucuito District, Puno Province, Peru. It is from the city of Puno. It sits at above sea level. The population is 7,913. The town was important in pre-Inca The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ... times and described by Pedro De Cieza De Leon, who was told by the locals that Chucuito was the oldest site in the region and continued to be held as a sacred site by the Inca. The town previously consisted of large buildings and was a major center of power. Gallery File:The church in Chucuito.jpg, The church in Chucuito File:Chucuito-1.jpg, In front of the Church of the Assumption in Chucuito File:Chucuito-2.jpg, Beheaded colonial sculptures File:Chucuito-3.jpg, Church in Chucuito File:Chucuito-4.jpg, The interior of the church in Chucuito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedro Cieza De León
Pedro Cieza de León ( Llerena, Spain c. 1518 or 1520 – Seville, Spain July 2, 1554) was a Spanish conquistador and chronicler of Peru and Popayán. He is known primarily for his extensive work, ''Crónicas del Perú'' (The Chronicle of Peru), which has been a source of knowledge for centuries for different disciplines such as history, philology, geography, biology, anthropology, botany and zoology. He wrote this book in four parts, but only the first was published during his lifetime; the remaining sections were not published until the 19th and 20th centuries. Early life His father, Lope de León, was a shopkeeper in the town, and his mother, Leonor de Cazalla, was a native of Llerena. There is scant documentary evidence of the young Cieza de León’s childhood, and little is known of his early life before his voyage to the Americas. Given the fact that he left home at 13, it is unlikely that Cieza de León received more than a rudimentary education. In 1536, in Córdoba, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isla Grande De Tierra Del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego ( English: ''Big Island of the Land of Fire'') also formerly ''Isla de Xátiva'' is an island near the southern tip of South America from which it is separated by the Strait of Magellan. The western portion (61.4%) of the island () is in Chile ( Province of Tierra del Fuego and Antártica Chilena Province), while the eastern portion (38.6%, ) is in Argentina ( Tierra del Fuego Province). It forms the major landmass in an extended group of islands or archipelago also known as Tierra del Fuego. The island has an area of , making it the largest island in South America and the 29th largest island in the world. Its two biggest towns are Ushuaia and Río Grande, both in Argentina. Other towns are Tolhuin, Porvenir, Camerón, and Cerro Sombrero. The Argentine side, Tierra del Fuego Province, has 190,641 inhabitants (2022), whereas the Chilean side has only 6,656 (2012), almost all located in the Tierra del Fuego Province. Its highest point is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arequipa - Canyon De Colca 199 - Copie Vigogne
Arequipa (; Aymara and ), also known by its nicknames of ''Ciudad Blanca'' (Spanish for "White City") and ''León del Sur'' (Spanish for "South's Lion"), is a city in Peru and the capital of the eponymous province and department. It is the seat of the Constitutional Court of Peru and often dubbed the "legal capital of Peru". It is the second most populated city in Peru, after the capital Lima, with an urban population of 1,296,278 inhabitants according to the 2017 national census. known for its colonial architecture and volcanic stone buildings, it is a major cultural and economic center. Its metropolitan area integrates twenty-one districts, including the foundational central area, which it is the seat of the city government. The city had a nominal GDP of US$9,445 million, equivalent to US$10,277 per capita (US$18,610 per capita PPP) in 2015, making Arequipa the city with the second-highest economic activity in Peru. Arequipa is also an important industrial and commercial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayllu
The ''ayllu'', a family clan, is the traditional form of a community in the Andes, especially among Quechuas and Aymaras. They are an indigenous local government model across the Andes region of South America, particularly in Bolivia and Peru. Ayllus functioned prior to Inca conquest, during the Inca and Spanish colonial period, and continue to exist to the present day – such as the Andean community Ocra. Membership gave individual families more variation and security on the land that they farmed. Ayllus had defined territories and were essentially extended family or kin groups, but could include non-related members. Their primary function was to solve subsistence issues, and issues of how to get along in family, and the larger community. Ayllus descended from stars in the Inca cosmogony, and just like stars had unique celestial locations, each ayllu had a terrestrial location defined by the paqarina, the mythical point of emergence of the lineage huaca. Current practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Types of pasture Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or swine. The vegetation of tended pasture, forage, consists mainly of grasses, with an interspersion of legumes and other forbs (non-grass herbaceous plants). Pasture is typically grazed throughout the summer, in contrast to meadow which is ungrazed or used for grazing only after being mown to make hay for animal fodder. Pasture in a wider sense additionally includes rangelands, other unenclosed pastoral systems, and land types used by wild animals for grazing or browsing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are distinguished from rangelands by being managed through more intensive agricultural practices of seeding, irrigation, and the use of fertilizers, while rangelands grow primarily native vegetation, managed with e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish language, Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechuan languages, Quechua and Aymara language, Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla people, Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north–south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau many towns and several cities, including El Alto and Oruro, Bolivia, Oruro in Bolivia, Juliaca and Puno in Peru. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several Salt pan (geology), salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had complet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for transportation (e.g. riding horses and camels), while others are service animals trained to execute certain specialized tasks (e.g. hunting and guide dogs, messenger pigeons, and fishing cormorants). They may also be used for milking or herding. Some, at the end of their working lives, may also be used for meat or leather. The history of working animals may predate agriculture as dogs were used by hunter-gatherer ancestors; around the world, millions of animals work in relationship with their owners. Domesticated species are often bred for different uses and conditions, especially horses and working dogs. Working animals are usually raised on farms, though some are still captured from the wild, such as dolphins and some Asian elephants. People have found uses for a wide variety of abili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
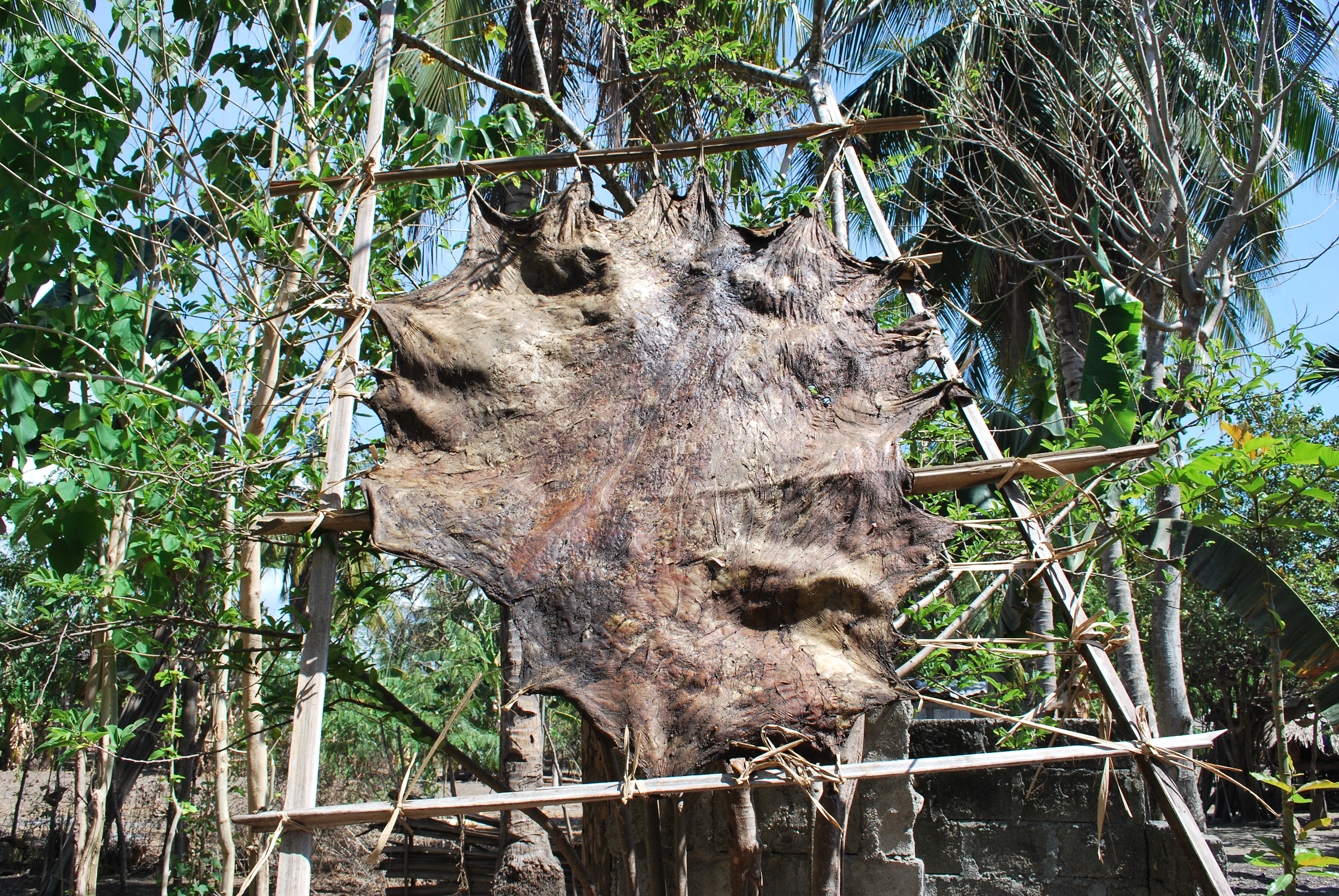
Leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning (leather), tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, ostriches, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in unsustainable practices that pose health hazards to the people and the environment near them. Production processes The leather manufacturing process is divided into three fundamental subprocesses: preparatory stages, tanning, and crusting. A further subprocess, finishing, can be added into the leather process sequence, but not all leathers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
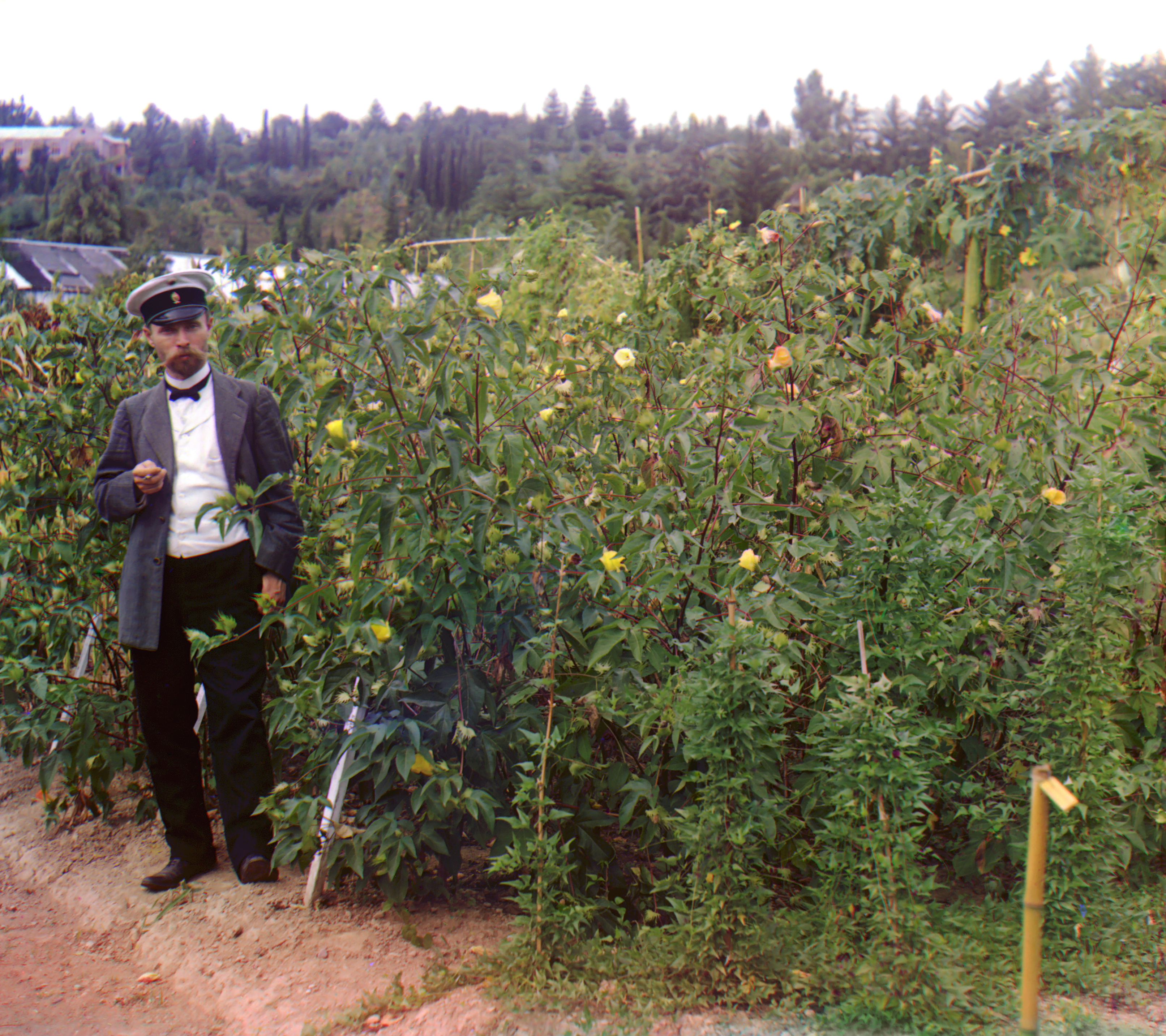
Gossypium
''Gossypium'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Gossypieae of the Malva, mallow family, Malvaceae, from which cotton is harvested. It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Old World, Old and New Worlds. There are about 50 ''Gossypium'' species, making it the largest genus in the tribe Gossypieae, and new species continue to be discovered. The name of the genus is derived from the Arabic word ''goz'', which refers to a soft substance. Cotton is the primary natural fibre used by humans today, amounting to about 80% of world natural fibre production. Where cotton is cultivated, it is a major oilseed crop and a main protein source for animal feed. Cotton is thus of great importance for agriculture, industry and trade, especially for tropical and subtropical countries in Africa, South America and Asia. Consequently, the genus ''Gossypium'' has long attracted the attention of scientists. The origin of the genus ''Gossypium'' is dated to around 5–10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |