delta wave on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Delta waves are high amplitude neural oscillations with a frequency between 0.5 and 4 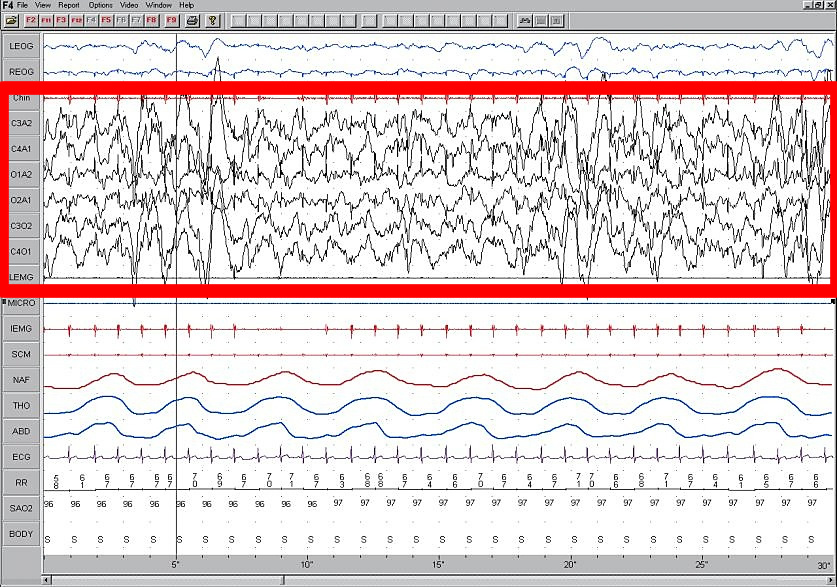
hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
. Delta waves, like other brain waves, can be recorded with electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in ...
(EEG) and are usually associated with the deep stage 3 of NREM sleep, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS), and aid in characterizing the depth of sleep. Suppression of delta waves leads to inability of body rejuvenation, brain revitalization and poor sleep.

Background and history
"Delta waves" were first described in the 1930s by W. Grey Walter, who improved upon Hans Berger's electroencephalograph machine (EEG) to detect alpha and delta waves. Delta waves can be quantified using quantitative electroencephalography.Classification and features
Delta waves, like all brain waves, can be detected byelectroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG)
is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in ...
(EEG). Delta waves were originally defined as having a frequency between 1 and 4 Hz, although more recent classifications put the boundaries at between 0.5 and 2 Hz. They are the slowest and highest amplitude classically described brainwaves, although recent studies have described slower (<0.1 Hz) oscillations Delta waves begin to appear in stage 3 sleep, but by stage 4 nearly all spectral activity is dominated by delta waves. Stage 3 sleep is defined as having less than 50% delta wave activity, while stage 4 sleep has more than 50% delta wave activity. These stages have recently been combined and are now collectively referred to as stage N3 slow-wave sleep. During N3 SWS, delta waves account for 20% or more of the EEG record during this stage. Delta waves occur in all mammals, and potentially all animals as well.
Delta waves are often associated with another EEG phenomenon, the K-complex. K-Complexes have been shown to immediately precede delta waves in slow wave sleep.
Delta waves have also been classified according to the location of the activity into frontal (FIRDA), temporal (TIRDA), and occipital (OIRDA) intermittent delta activity.
Neurophysiology
Sex differences
Females have been shown to have more delta wave activity, and this is true across most mammal species. This discrepancy does not become apparent until early adulthood (in the 30s or 40s in humans), with males showing greater age-related reductions in delta wave activity than females.Brain localization and biochemistry
Delta waves can arise either in the thalamus or in the cortex. When associated with the thalamus, they are thought to arise in coordination with the reticular formation. In the cortex, the suprachiasmatic nuclei have been shown to regulate delta waves, as lesions to this area have been shown to cause disruptions in delta wave activity. In addition, delta waves show a lateralization, with right hemisphere dominance during sleep. Delta waves have been shown to be mediated in part by T-type calcium channels. During delta wave sleep, neurons are globally inhibited bygamma-aminobutyric acid
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
(GABA).Hobson, J., & Pace-Schott, E. (2002). The Cognitive Neuroscience of Sleep: Neuronal Systems, Consciousness and Learning. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(9), 679-693.
Delta activity stimulates the release of several hormones, including growth hormone releasing hormone GHRH and prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secr ...
(PRL). GHRH is released from the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, which in turn stimulates release of growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary. The secretion of (PRL), which is closely related to (GH), is also regulated by the pituitary. The release of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), is decreased in response to delta-wave signaling.
Development
Infants have been shown to spend a great deal of time in slow-wave sleep, and thus have more delta wave activity. In fact, delta-waves are the predominant waveforms of infants. Analysis of the waking EEG of anewborn
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
infant indicates that delta wave activity is predominant in that age, and still appears in a waking EEG of five-year-olds. Delta wave activity during slow-wave sleep declines during adolescence, with a drop of around 25% reported between the ages of 11 and 14 years. Delta waves have been shown to decrease across the lifespan, with most of the decline seen in the mid-forties. By the age of about 75, stage four sleep and delta waves may be entirely absent.
In addition to a decrease in the incidence of delta waves during slow-wave sleep in the elderly, the incidence of temporal delta wave activity is commonly seen in older adults, and incidences also increase with age.
Disruptions and disorders
Regional delta wave activity not associated with NREM sleep was first described by W. Grey Walter, who studiedcerebral hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
tumors. Disruptions in delta wave activity and slow wave sleep are seen in a wide array of disorders. In some cases there may be increases or decreases in delta wave activity, while others may manifest as disruptions in delta wave activity, such as alpha waves presenting in the EEG spectrum. Delta wave disruptions may present as a result of physiological damage, changes in nutrient metabolism, chemical alteration, or may also be idiopathic.
Disruptions in delta activity is seen in adults during states of intoxication or delirium and in those diagnosed with various neurological disorders such as dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
or schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, f ...
.
Temporal low-voltage irregular delta wave
Temporal low-voltage irregular delta wave activity has been commonly detected in patients with ischemic brain diseases, particularly in association with small ischemic lesions and is seen to be indicative of early-stage cerebrovascular damage.Parasomnias
Parasomnias, a category of sleep disorders, are often associated with disruptions in slow wave sleep. Sleep walking and sleep talking most often occur during periods of high delta wave activity. Sleep walkers have also been shown to have more hypersynchronous delta activity (HSD) compared to total time spent in stages 2, 3, and 4 sleep relative to healthy controls. HSD refers to the presence of continuous, high-voltage (> 150 μV) delta waves seen in sleep EEGs.Pilon M; Zadra A; Joncas S et al. Hypersynchronous delta waves and somnambulism: brain topography and effect of sleep deprivation. SLEEP 2006;29(1): 77–84. Parasomnias which occur deep in NREM sleep also include sleep terrors and confusional arousals.Sleep deprivation
Total sleep deprivation has been shown to increase delta wave activity during sleep recovery, and has also been shown to increase hypersynchronous delta activity.Parkinson's disease
Sleep disturbances, as well asdementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
, are common features of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, and patients with this disease show disrupted brain wave activity. The drug Rotigotine, developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, has been shown to increase delta power and slow-wave sleep.
Schizophrenia
People with schizophrenia have shown disrupted EEG patterns, and there is a close association of reduced delta waves during deep sleep and negative symptoms associated with schizophrenia. During slow wave sleep (stages 3 and 4), people with schizophrenia have been shown to have reduced delta wave activity, although delta waves have also been shown to be increased during waking hours in more severe forms of schizophrenia. A recent study has shown that the right frontal and central delta wave dominance, seen in healthy individuals, is absent in patients with schizophrenia. In addition, the negative correlation between delta wave activity and age is also not observed in those with schizophrenia.Diabetes and insulin resistance
Disruptions in slow wave (delta) sleep have been shown to increase risk for development of Type II diabetes, potentially due to disruptions in the growth hormone secreted by the pituitary. In addition, hypoglycemia occurring during sleep may also disrupt delta-wave activity. Low-voltage irregular delta waves, have also been found in the left temporal lobe of diabetic patients, at a rate of 56% (compared to 14% in healthy controls).Fibromyalgia
Patients with fibromyalgia often report unrefreshing sleep. A study conducted in 1975 by Moldovsky ''et al.'' showed that the delta wave activity of these patients in stages 3 and 4 sleep were often interrupted byalpha wave
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent ( in phase or constructive) neocortical neuronal electrical activity possibly involving thala ...
s. They later showed that depriving the body of delta wave sleep activity also induced musculoskeletal pain and fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
.
Alcoholism
Alcoholism has been shown to produce sleep with less slow wave sleep and less delta power, while increasing stage 1 and REM incidence in both men and women. In long-term alcohol abuse, the influences of alcohol on sleep architecture and reductions in delta activity have been shown to persist even after long periods of abstinence.Temporal lobe epilepsy
Slow waves, including delta waves, are associated with seizure-like activity within the brain. W. Grey Walter was the first person to use delta waves from an EEG to locate brain tumors and lesions causing temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurofeedback has been suggested as a treatment for temporal lobe epilepsy, and theoretically acts to reduce inappropriate delta wave intrusion, although there has been limited clinical research in this area.Other disorders
Other disorders frequently associated with disrupted delta-wave activity include: * Narcolepsy * Depression *Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
* Obsessive–compulsive disorder
Obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental disorder in which an individual has intrusive thoughts (an ''obsession'') and feels the need to perform certain routines (''Compulsive behavior, compulsions'') repeatedly to relieve the dis ...
* Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple con ...
(ADHD) and its three subtypes.
* Juvenile chronic arthritis
*Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a condition characterized by an abnormally large increase in heart rate upon sitting up or standing. POTS is a disorder of the autonomic nervous system that can lead to a variety of symptoms, ...
(PoTS)
* Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
*Angelman Syndrome
Angelman syndrome (AS) is a genetic disorder that affects approximately 1 in 15,000 individuals. AS impairs the function of the nervous system, producing symptoms, such as severe intellectual disability, developmental disability, limited to no ...
Consciousness and dreaming
Initially, dreaming was thought to only occur in rapid eye movement sleep, though it is now known that dreaming may also occur during slow-wave sleep. Delta waves and delta wave activity are marked, in most people, by an apparently unconscious state, and the loss of physical awareness as well as the "iteration of information". Delta wave activity has also been purported to aid in declarative and explicit memory formation.Pharmacology
While most drugs that affect sleep do so by stimulating sleep onset, or disrupting REM sleep, a number of chemicals and drugs have been shown to alter delta wave activity. * Delta sleep-inducing peptide, as the name suggests, induces delta wave EEG activity. * Alcohol reduces SWS delta wave activity, thereby restricting the release of growth hormone (GH) by the pituitary. * The muramyl peptide, muramyl dipeptide (MDP, N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine) has been shown to increase delta wave activity during slow wave sleep. * The drug Gabapentin, a drug used to control epileptic seizures, increases delta-wave activity and slow wave sleep in adults. * While hypnotics like zolpidem increase slow wave sleep, they do not increase delta wave activity, and instead increase spindle activity during slow wave sleep.D'haenen, H. A. H., Johan A. Den Boer, and Paul Willner. Biological Psychiatry. Chichester: Wiley, 2002. Print. * Gamma-hydroxy butyrate (GHB) increases delta slow-wave sleep as well as sleep-related growth hormone (GH). * Administration of high-dosenitrous oxide
Nitrous oxide (dinitrogen oxide or dinitrogen monoxide), commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or factitious air, among others, is a chemical compound, an Nitrogen oxide, oxide of nitrogen with the Chemical formula, formula . At room te ...
is associated with transient, large amplitude slow-delta oscillations.
Effects of diet
Diets very low in carbohydrates, such as a ketogenic diet, have been shown to increase the amount of delta activity and slow wave sleep in healthy individuals.Afaghi, A., O'Connor, H., & Chow, C. (2008). Acute Effects of the Very Low Carbohydrate Diet on Sleep Indices. Nutritional Neuroscience, 11(4), 146-154.See also
* * * * * *Brain waves
* Delta wave – (0.1 – 4 Hz) * Theta wave – (4 – 7 Hz) *Alpha wave
Alpha waves, or the alpha rhythm, are neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8–12 Hz likely originating from the synchronous and coherent ( in phase or constructive) neocortical neuronal electrical activity possibly involving thala ...
– (8 – 12 Hz)
* Mu wave – (7.5 – 12.5 Hz)
* SMR wave – (12.5 – 15.5 Hz)
* Beta wave – (16 – 31 Hz)
* Gamma wave – (32 – 100 Hz)
References
{{EEG Electroencephalography