bimetal standard on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Bimetallism, also known as the bimetallic standard, is a 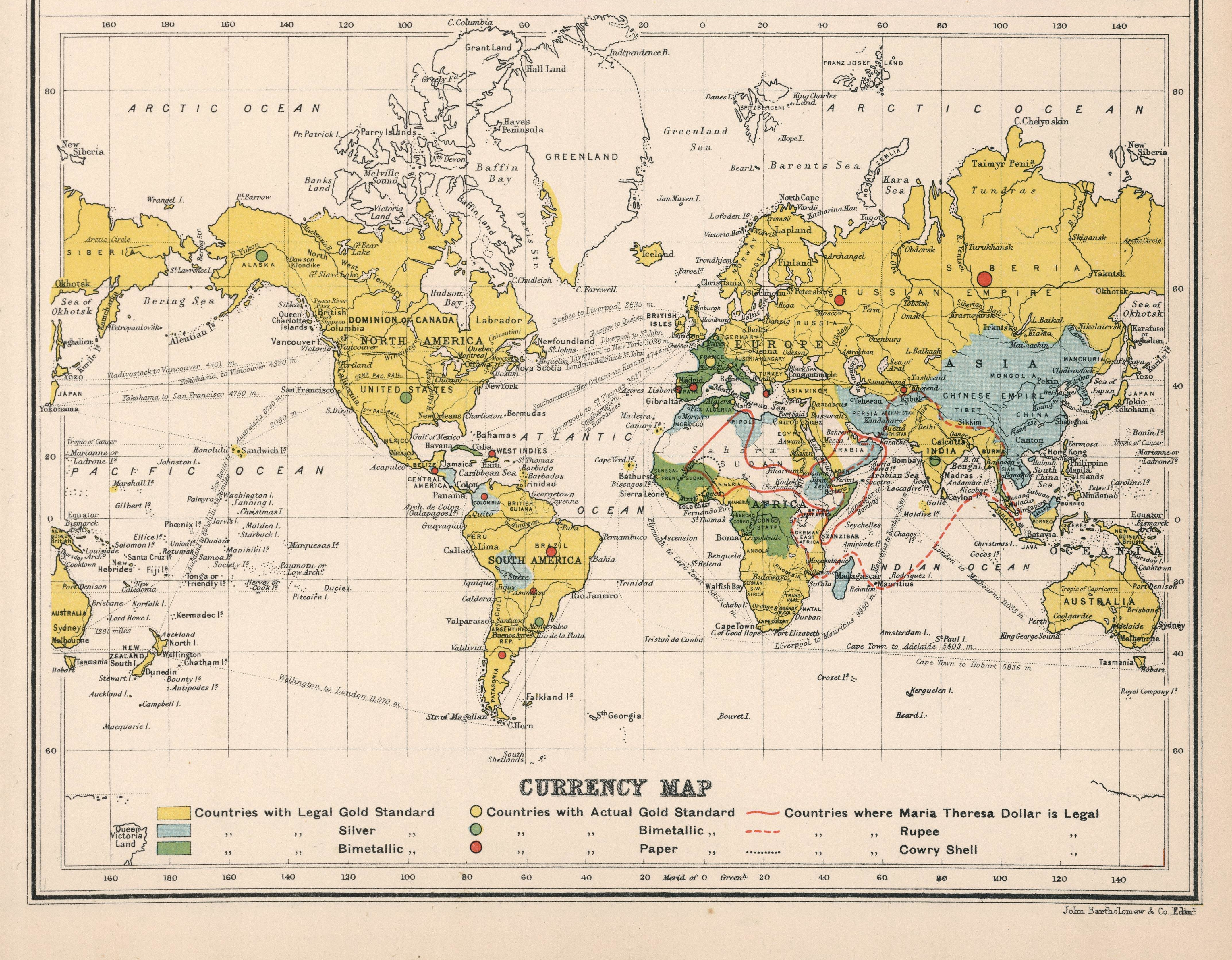 During the 19th century there was a great deal of scholarly debate and political controversy regarding the use of bimetallism in place of a
During the 19th century there was a great deal of scholarly debate and political controversy regarding the use of bimetallism in place of a
 Croesus (reigned – BCE), king of Lydia, who became associated with great wealth. Croesus is credited with issuing the
Croesus (reigned – BCE), king of Lydia, who became associated with great wealth. Croesus is credited with issuing the
 Many ancient bimetallic systems would follow, starting with
Many ancient bimetallic systems would follow, starting with
"Gold Democrats and the Decline of Classical Liberalism, 1896–1900"
Independent Review 4 (Spring 2000), 555–75. * Bordo, Michael D. "Bimetallism". in ''The New Palgrave Encyclopedia of Money and Finance'' edited by Peter K. Newman, Murray Milgate and John Eatwell. 1992. * Dighe, Ranjit S. ed. ''The Historian's Wizard of Oz: Reading L. Frank Baum's Classic as a Political and Monetary Allegory'' (2002) * Flandreau, Marc, 2004, The Glitter of Gold. France, Bimetallism and the Emergence of the International Gold Standard, 1848–1873, Oxford, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 343 p. * Friedman, Milton, 1990a, "The crime of 1873", ''Journal of Political Economy,'' Vol. 98, No. 6, December, pp. 1159–119
in JSTOR
* Friedman, Milton, 1990b, "Bimetallism revisited", Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 4, No. 4, Fall, pp. 85–104.
in JSTOR
* Friedman, Milton, and Anna J. Schwartz, 1963, ''A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'' Princeton University Press. . * Jeansonne, Glen. "Goldbugs, Silverites, and Satirists: Caricature and Humor in the Presidential Election of 1896". ''Journal of American Culture'' 1988 11(2): 1–8. * * * Littlefield, Henry M., 1964, "The Wizard of Oz: Parable on Populism", American quarterly, Vol. 16, No. 1, Spring, pp. 47–58.
Angela Redish, "Bimetallism"
* Rockoff, Hugh, 1990, "The Wizard of Oz as a monetary allegory", ''Journal of Political Economy'', Vol. 98, No. 4, August, pp. 739–760
in JSTOR
Velde, Francois R. "Following the Yellow Brick Road: How the United States Adopted the Gold Standard" Economic Perspectives. Volume: 26. Issue: 2. 2002.
*
a series of pages on bimetalism from Micheloud & cie.
Speeches before the 51st Congress (1889–1891)
regarding "free silver", digitized and available on FRASER (Federal Reserve Archival System for Economic Research).
Speeches before the 52nd Congress (1891–1893)
regarding "free silver", digitized and available on FRASER (Federal Reserve Archival System for Economic Research).
Speeches before the 53rd Congress (1893–1895)
regarding "free silver", digitized and available on FRASER (Federal Reserve Archival System for Economic Research).
The French Crime of 1873: An Essay on the Emergence of the International Gold Standard, 1870–1880 (PDF)
{{Authority control Metallism Numismatic terminology People's Party (United States) Monetary economics Gold Silver Currency Economic history of the United States
monetary standard
A monetary system is a system where a government manages money in a country's economy. Modern monetary systems usually consist of the national treasury, the mint, the central banks and commercial banks.
Commodity money system
A commodity mone ...
in which the value of the monetary unit
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environm ...
is defined as equivalent to certain quantities of two metals, typically gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, creating a fixed rate of exchange
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
between them.
For scholarly purposes, "proper" bimetallism is sometimes distinguished as permitting that both gold and silver money are legal tender
Legal tender is a form of money that Standard of deferred payment, courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment in court for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything ...
in unlimited amounts and that gold and silver may be taken to be coined by the government mints in unlimited quantities. This distinguishes it from "limping standard" bimetallism, where both gold and silver are legal tender but only one is freely coined (e.g. the monies of France, Germany, and the United States after 1873), and from "trade" bimetallism, where both metals are freely coined but only one is legal tender and the other is used as "trade money" (e.g. most monies in western Europe from the 13th to 18th centuries). Economists also distinguish ''legal'' bimetallism, where the law guarantees these conditions, and '' de facto'' bimetallism, where gold and silver coins circulate at a fixed rate.
 During the 19th century there was a great deal of scholarly debate and political controversy regarding the use of bimetallism in place of a
During the 19th century there was a great deal of scholarly debate and political controversy regarding the use of bimetallism in place of a gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
or silver standard
The silver standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is a fixed weight of silver. Silver was far more widespread than gold as the monetary standard worldwide, from the Sumerians 3000 BC until 1873. Following t ...
(monometallism
Metallism is the economic principle that the Value (economics) , value of money derives from the purchasing power of the commodity upon which it is based. The currency in a metallist monetary system may be made from the commodity itself (commodit ...
). Bimetallism was intended to increase the supply of money, stabilize prices, and facilitate setting exchange rates. Some scholars argued that bimetallism was inherently unstable owing to Gresham's law
In economics, Gresham's law is a monetary principle stating that "bad money drives out good". For example, if there are two forms of commodity money in circulation, which are accepted by law as having similar face value, the more valuable commo ...
, and that its replacement by a monometallic standard was inevitable. Other scholars claimed that in practice bimetallism had a stabilizing effect on economies. The controversy became largely moot after technological progress and the South African and Klondike Gold Rushes increased the supply of gold in circulation at the end of the century, ending most of the political pressure for greater use of silver. It became completely academic after the 1971 Nixon shock; since then, all of the world's currencies have operated as more or less freely floating fiat money
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tende ...
, unconnected to the value of silver or gold. Nonetheless, academics continue to debate, inconclusively, the relative use of the metallic standards.
Historical creation
From the 7th century BCE,Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, especially in the areas of Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis.
At some point before 800 BC, ...
and Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
, is known to have created a coinage based on electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially and is ...
, a natural occurring material that is a variable mix of gold and silver (with about 54% gold and 44% silver). Before Croesus
Croesus ( ; ; Latin: ; reigned:
)
was the Monarch, king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his Siege of Sardis (547 BC), defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. According to Herodotus, he reigned 14 years. Croesus was ...
, his father Alyattes
Alyattes ( Lydian language: ; ; reigned c. 635 – c. 585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyattes, grandson of Ardys, and great-grandson of Gyges. He died after a r ...
had already started to mint various types of non-standardized electrum coins. They were in use in Lydia and surrounding areas for about 80 years. The unpredictability of its composition implied that it had a variable value which was very hard to determine, which greatly hampered its development.
Croeseids
 Croesus (reigned – BCE), king of Lydia, who became associated with great wealth. Croesus is credited with issuing the
Croesus (reigned – BCE), king of Lydia, who became associated with great wealth. Croesus is credited with issuing the Croeseid
The Croeseid, anciently ''Kroiseioi stateres'', was a type of coin, either in gold or silver, which was minted in Sardis by the king of Lydia Croesus (561–546 Before Christ, BC) from around 550 BC. Croesus is credited with issuing the first true ...
, the first true gold coin
A gold coin is a coin that is made mostly or entirely of gold. Most gold coins minted since 1800 are 90–92% gold (22fineness#Karat, karat), while most of today's gold bullion coins are pure gold, such as the Britannia (coin), Britannia, Canad ...
s with a standardised purity for general circulation,
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
mentioned the innovation made by the Lydians:
Achaemenid coinage
 Many ancient bimetallic systems would follow, starting with
Many ancient bimetallic systems would follow, starting with Achaemenid coinage
The Achaemenid Empire issued coins from 520 BC–450 BC to 330 BC. The Persian daric was the first gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos (from , , '' shékel'') represented the first bimetallic monetary standard.Michael A ...
. From around 515 BCE under Darius I
Darius I ( ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his death in 486 BCE. He ruled the empire at its territorial peak, when it included much of West A ...
, the minting of Croesids in Sardis
Sardis ( ) or Sardes ( ; Lydian language, Lydian: , romanized: ; ; ) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Lydia (satrapy) ...
was replaced by the minting of Daric
The daric was a gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos, represented the bimetallic monetary standard of the Achaemenid Empire.Michael Alram"DARIC" ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'', December 15, 1994, last updated November 17, 2011 ...
s and Sigloi
The Achaemenid Empire issued coins from 520 BC–450 BC to 330 BC. The Persian daric was the first gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos (from , , '' shékel'') represented the first bimetallic monetary standard.Michael A ...
. The earliest gold coin of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, i ...
, the Daric
The daric was a gold coin which, along with a similar silver coin, the siglos, represented the bimetallic monetary standard of the Achaemenid Empire.Michael Alram"DARIC" ''Encyclopaedia Iranica'', December 15, 1994, last updated November 17, 2011 ...
, followed the weight standard of the Croeseid, and is therefore considered to be later and derived from the Croeseid. The weight of the Daric would then be modified through a metrological reform, probably under Darius I.
Sardis remained the central mint for the Persian Darics and Sigloi of Achaemenid coinage, and there is no evidence of other mints for the new Achaemenid coins during the whole time of the Achaemenid Empire. Although the gold Daric became an international currency which was found throughout the Ancient world, the circulation of the Sigloi remained very much limited to Asia Minor: important hoards of Sigloi are only found in these areas, and finds of Sigloi beyond are always very limited and marginal compared to Greek coins, even in Achaemenid territories.
Argentina
In 1881, a currency reform inArgentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
introduced a bimetallic standard, which went into effect in July 1883. Units of gold and silver peso
The peso is the monetary unit of several Hispanophone, Spanish-speaking countries in Latin America, as well as the Philippines. Originating in the Spanish Empire, the word translates to "weight". In most countries of the Americas, the symbol com ...
s would be exchanged with paper peso notes at given par values, and fixed exchange rates against key international currencies would thus be established. Unlike many metallic standards, the system was very decentralized: no national monetary authority existed, and all control over convertibility rested with the five banks of issue. This convertibility lasted only 17 months: from December 1884 the banks of issue refused to exchange gold at par for notes. The suspension of convertibility was soon accommodated by the Argentine government, since, having no institutional power over the monetary system, there was little they could do to prevent it.
France
A French law of 1803 granted anyone who brought gold or silver to its mint the right to have it coined at a nominal charge in addition to the official rates of 200 francs per kilogram of 90% silver, or 3100 francs per kilogram of 90% fine gold.Dickson Leavens, Silver Money, Chapter IV Bimetallism in France and the Latin Monetary Union, page 25 This effectively established a bimetallic standard at the rate which had been used for French coinage since 1785, i.e. a relative valuation of gold to silver of 15.5 to 1. In 1803 this ratio was close to the market rate, but for most of the next half century the market rate was above 15.5 to 1. As a consequence, silver powered the French economy and gold was exported. But when theCalifornia Gold Rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the U ...
increased the supply of gold, its value was reduced relative to silver. The market rate fell below 15.5 to 1, and remained below until 1866. Frenchmen responded by exporting silver to India and importing nearly two-fifths of the world's production of gold in the period from 1848 to 1870.Dickson Leavens, op. cit. page 26 Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
introduced five franc gold coins which provided a substitute for the silver five franc coins which were hoarded, but still maintained the formal bimetallism implicit in the 1803 law.
Latin Monetary Union
The national coinages introduced in Belgium (1832), Switzerland (1850), and Italy (1861) were based on France's bimetallic currency. These countries joined France in a treaty signed on 23 December 1865 which established theLatin Monetary Union
The Monetary Convention of 23 December 1865 was a unified system of coinage that provided a degree of monetary integration among several European countries, initially Belgium, France, Italy and Switzerland, at a time when the circulation of bank ...
(LMU). Greece joined the LMU in 1868 and about twenty other countries adhered to its standards. The LMU effectively adopted bimetallism by allowing unlimited free coinage of gold and silver at the 15.5 to 1 rate used in France, but also began to back away from bimetallism by allowing limited issues of low denomination silver coins struck to a lower standard for government accounts.John Porteous, op. cit. page 241 A surplus of silver led the LMU to limit free coinage of silver in 1874 and to end it in 1878, effectively abandoning bimetallism for the gold standard.
United Kingdom
Medieval and early modern England used both gold and silver, at fixed rates, to provide the necessary range of coin denominations; but silver coinage began to be restricted in the 18th century, first informally, and then by an Act of Parliament in 1774. After the suspension of metal convertibility from 1797 to 1819,Peel's Bill
Peel's Bill, or the Resumption of Cash Payments Act 1819 ( 59 Geo. 3. c. 49) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that marked the return of the British currency to the gold standard, after the Bank Restriction Act 1797 ( 37 Geo. 3 ...
set the country on the gold standard for the remainder of the century; however advocates of a return to bimetallism did not cease to appear. After the crash of 1825, William Huskisson
William Huskisson (11 March 177015 September 1830) was a British statesman, financier, and Member of Parliament for several constituencies, including Liverpool.
He is commonly known as the world's first widely reported railway passenger ca ...
argued strongly within the Government for bimetallism, as a way to increase credit (as well as to ease trade with South America). Similarly, after the banking crisis of 1847, Alexander Baring headed an external bimetallist movement hoping to prevent the undue restriction of the currency. It was, however, only in the last quarter of the century that the movement for bimetallism gathered real strength, drawing on Manchester cotton merchants and City financiers with Far East interests to offer a serious (if ultimately unsuccessful) challenge to the gold standard.
United States
In 1792, Secretary of the TreasuryAlexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first U.S. secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795 dur ...
proposed fixing the silver to gold exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
at 15:1, as well as establishing the mint
Mint or The Mint may refer to:
Plants
* Lamiaceae, the mint family
** ''Mentha'', the genus of plants commonly known as "mint"
Coins and collectibles
* Mint (facility), a facility for manufacturing coins
* Mint condition, a state of like-new ...
for the public services of free coinage and currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
regulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
"in order not to abridge the quantity of circulating medium". With its acceptance, Sec.11 of the Coinage Act of 1792 established: "That the proportional value of gold to silver in all coins which shall by law be current as money within the United States, shall be as fifteen to one, according to quantity in weight, of pure gold or pure silver;" the proportion had slipped by 1834
Events
January–March
* January 1 – Zollverein (Germany): Customs charges are abolished at borders within its member states.
* January 3 – The government of Mexico imprisons Stephen F. Austin in Mexico City.
* January – The W ...
to sixteen to one. Silver took a further hit with the Coinage Act of 1853
The Coinage Act of 185310 Stat. 160 was a piece of legislation passed by the United States Congress which lowered the silver content of the silver half dime, dime, quarter dollar, and half dollar, and authorized a three dollar gold piece. Altho ...
, when nearly all silver coin denominations were debased, effectively turning silver coinage into a fiduciary currency based on its face value rather than its weighted value. Bimetallism was effectively abandoned by the Coinage Act of 1873
The Coinage Act of 1873 or Mint Act of 1873 was a general revision of laws relating to the Mint of the United States. By ending the right of holders of silver bullion to have it coined into standard silver dollars, while allowing holders of g ...
, but not formally outlawed as legal currency until the early 20th century. The merits of the system were the subject of debate in the late 19th century. If the market forces of supply and demand for either metal caused its bullion value to exceed its nominal currency value, it tends to disappear from circulation by hoarding or melting down.
Political debate
In the United States, bimetallism became a center of political conflict toward the end of the 19th century. During theCivil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
, to finance the war the U.S. switched from bimetallism to a fiat money
Fiat money is a type of government-issued currency that is not backed by a precious metal, such as gold or silver, nor by any other tangible asset or commodity. Fiat currency is typically designated by the issuing government to be legal tende ...
currency. After the war, in 1873, the government passed the Fourth Coinage Act and soon resumption of specie payments began (without the free and unlimited coinage of silver, thus putting the U.S. on a mono-metallic gold standard.) Farmers, debtors, Westerners and others who felt they had benefited from wartime paper money formed the short-lived Greenback Party
The Greenback Party (known successively as the Independent Party, the National Independent Party and the Greenback Labor Party) was an Political parties in the United States, American political party with an Competition law, anti-monopoly ideolog ...
to press for cheap paper money backed by silver. The latter element—" free silver"—came increasingly to the fore as the answer to the same interest groups' concerns, and was taken up as a central plank by the Populist movement. Proponents of monetary silver, known as the silverites, referred back to the Fourth Coinage Act as "The Crime of '73", as it was judged to have inhibited inflation, and favored creditors over debtors. Some reformers, however, like Henry Demarest Lloyd
Henry Demarest Lloyd (May 1, 1847 – September 28, 1903) was an American journalist and political activist who was a prominent muckraker during the Progressive Era. He is best known for his exposés of Standard Oil which were written before Ida ...
, saw bimetallism as a red herring and feared that free silver was "the cowbird
Cowbirds are birds belonging to the genus ''Molothrus'' in the family Icteridae. They are of New World origin, but some species not native to North America are invasive there, and are obligate brood parasites, laying their eggs in the nests of o ...
of the reform movement", likely to push the other eggs out of the nest. Nevertheless, the Panic of 1893
The Panic of 1893 was an economic depression in the United States. It began in February 1893 and officially ended eight months later. The Panic of 1896 followed. It was the most serious economic depression in history until the Great Depression of ...
, a severe nationwide depression, brought the money issue strongly to the fore again. The "silverites" argued that using silver would inflate the money supply and mean more cash for everyone, which they equated with prosperity. The gold advocates claimed that silver would permanently depress the economy, but that sound money
In macroeconomics, hard currency, safe-haven currency, or strong currency is any globally traded currency that serves as a reliable and stable store of value. Factors contributing to a currency's ''hard'' status might include the stability and r ...
produced by a gold standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the ...
would restore prosperity.
Bimetallism and " Free Silver" were demanded by William Jennings Bryan
William Jennings Bryan (March 19, 1860 – July 26, 1925) was an American lawyer, orator, and politician. He was a dominant force in the History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, running three times as the party' ...
who took over leadership of the Democratic Party in 1896, as well as by the Populists. They were joined by a faction of Republicans from silver mining regions in the West, known as the Silver Republicans, who also endorsed Bryan. The Republican Party itself nominated William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Repub ...
on a platform supporting the gold standard, which was favored by financial interests on the East Coast.
In support of the cause, Bryan gave the famous "Cross of Gold" speech at the National Democratic Convention on July 9, 1896, asserting that "The gold standard has slain tens of thousands." He referred to "a struggle between 'the idle holders of idle capital' and 'the struggling masses, who produce the wealth and pay the taxes of the country;' and, my friends, the question we are to decide is: Upon which side will the Democratic party fight?" At the peroration
is the system used for the organization of arguments in the context of Western classical rhetoric. The word is Latin, and can be translated as "organization" or "arrangement".
It is the second of five canons of classical rhetoric (the first be ...
, he said: "You shall not press down upon the brow of labor this crown of thorns, you shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold." However, his presidential campaign was ultimately unsuccessful; this can be partially attributed to the discovery of the cyanide process
Gold cyanidation (also known as the cyanide process or the MacArthur–Forrest process) is a hydrometallurgical technique for extracting gold from low-grade ore through conversion to a water-soluble coordination complex. It is the most commonly u ...
by which gold could be extracted from low-grade ore. This process and the discoveries of large gold deposits in South Africa (Witwatersrand Gold Rush
The Witwatersrand Gold Rush was a gold rush that began in 1886 and led to the establishment of Johannesburg, South Africa. It was a part of the Mineral Revolution.
Origins
In the modern-day province of Mpumalanga, gold miners in the alluvial ...
of 1887 – with large-scale production starting in 1898) and the Klondike Gold Rush (1896) increased the world gold supply and the subsequent increase in money supply that free coinage of silver was supposed to bring. The McKinley campaign was effective at persuading voters in the business East that poor economic progress and unemployment would be exacerbated by the adoption of the Bryan platform. 1896 saw the election of McKinley. The direct link to gold was abandoned in 1934 in Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), also known as FDR, was the 32nd president of the United States, serving from 1933 until his death in 1945. He is the longest-serving U.S. president, and the only one to have served ...
's New Deal
The New Deal was a series of wide-reaching economic, social, and political reforms enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1938, in response to the Great Depression in the United States, Great Depressi ...
program and later the link was broken by Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 until Resignation of Richard Nixon, his resignation in 1974. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican ...
when he closed the gold window.
Economic analysis
In 1992, economistMilton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and ...
concluded that abandonment of the bimetallic standard in 1873 led to greater price instability than would have occurred otherwise, and thus resulted in long-term harm to the US economy. His retrospective analysis led him to write that the act of 1873 was "a mistake that had highly adverse consequences".Milton Friedman, ''Money Mischief'' (New York: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, 1992) 78.
See also
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
Primary sources
* ''Campaign Text-book of the National Democratic Party'' (1896) by Democratic Party (U.S.) National Committee: this is the Gold Democrats handbook; it strongly opposed Bryan. * Walker, ''International Bimetallism'' (New York, 1896) *Robert Giffen
Sir Robert Giffen (22 July 1837 – 12 April 1910) was a Scottish statistician and economist.
Life
Giffen was born at Strathaven, Lanarkshire. He entered a solicitor's office in Glasgow, and while in that city attended courses at the uni ...
, ''Case against Bimetallism'' (London, 1896)
* Joseph Shield Nicholson
Joseph Shield Nicholson, Fellow of the British Academy, FBA Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, FRSE (9 November 1850 – 12 May 1927) was an English people, English economist.
Life
Nicholson was born in Wrawby in Lincolnshire on 9 Nove ...
, ''Money and Monetary Problems'' (London, 1897)
* Samuel Dana Horton, ''The Silver Pound'' (London, 1887)
* Walker, ''Money'' (New York, 1878)
* Francis Amasa Walker
Francis Amasa Walker (July 2, 1840 – January 5, 1897) was an American economist, statistician, journalist, educator, academic administrator, and an officer in the Union Army. As a prolific author and the third president of the Massachusetts I ...
, ''Money, Trade and Industry'' (New York, 1879)
* Elisha Benjamin Andrews, ''An honest Dollar'' (Hartford, 1894)
* Helm, ''The Joint Standard'' (London, 1894)
* Frank William Taussig
Frank William Taussig (December 28, 1859 – November 11, 1940) was an American economist who is credited with creating the foundations of modern international trade, trade theory.
Early life
He was born on December 28, 1859, in St. Louis, Misso ...
, ''The Silver Situation in the United States'' (New York, 1893)
* Horace White (writer), ''Money and Banking'' (Boston, 1896)
* James Laurence Laughlin
James Laurence Laughlin (April 2, 1850 – November 28, 1933) was an American economist and professor at Cornell University, Harvard University, and the University of Chicago, who helped to found the Federal Reserve System and was "one of the m ...
, ''History of Bimetallism in the United States'' (New York, 1897)
* Langford Lovell Price, ''Money and its Relations to Prices'' (London and New York, 1896)
* Utley, ''Bimetallism'' (Los Angeles, 1899)
* Roger Q. Mills, '' What shall we do with silver?'' ('' The North American Review,'' Volume 150, Issue 402, May 1890.)
Secondary sources
* Epstein, David A. (2012). Left, Right, Out: The History of Third Parties in America. Arts and Letters Imperium Publications. . * James A. Barnes, "Myths of the Bryan Campaign", ''Mississippi Valley Historical Review'', 34 (December 1947) online in JSTOR * David T. Beito and Linda Royster Beito"Gold Democrats and the Decline of Classical Liberalism, 1896–1900"
Independent Review 4 (Spring 2000), 555–75. * Bordo, Michael D. "Bimetallism". in ''The New Palgrave Encyclopedia of Money and Finance'' edited by Peter K. Newman, Murray Milgate and John Eatwell. 1992. * Dighe, Ranjit S. ed. ''The Historian's Wizard of Oz: Reading L. Frank Baum's Classic as a Political and Monetary Allegory'' (2002) * Flandreau, Marc, 2004, The Glitter of Gold. France, Bimetallism and the Emergence of the International Gold Standard, 1848–1873, Oxford, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 343 p. * Friedman, Milton, 1990a, "The crime of 1873", ''Journal of Political Economy,'' Vol. 98, No. 6, December, pp. 1159–119
in JSTOR
* Friedman, Milton, 1990b, "Bimetallism revisited", Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 4, No. 4, Fall, pp. 85–104.
in JSTOR
* Friedman, Milton, and Anna J. Schwartz, 1963, ''A Monetary History of the United States, 1867–1960'' Princeton University Press. . * Jeansonne, Glen. "Goldbugs, Silverites, and Satirists: Caricature and Humor in the Presidential Election of 1896". ''Journal of American Culture'' 1988 11(2): 1–8. * * * Littlefield, Henry M., 1964, "The Wizard of Oz: Parable on Populism", American quarterly, Vol. 16, No. 1, Spring, pp. 47–58.
Angela Redish, "Bimetallism"
* Rockoff, Hugh, 1990, "The Wizard of Oz as a monetary allegory", ''Journal of Political Economy'', Vol. 98, No. 4, August, pp. 739–760
in JSTOR
Velde, Francois R. "Following the Yellow Brick Road: How the United States Adopted the Gold Standard" Economic Perspectives. Volume: 26. Issue: 2. 2002.
*
External links
a series of pages on bimetalism from Micheloud & cie.
Speeches before the 51st Congress (1889–1891)
regarding "free silver", digitized and available on FRASER (Federal Reserve Archival System for Economic Research).
Speeches before the 52nd Congress (1891–1893)
regarding "free silver", digitized and available on FRASER (Federal Reserve Archival System for Economic Research).
Speeches before the 53rd Congress (1893–1895)
regarding "free silver", digitized and available on FRASER (Federal Reserve Archival System for Economic Research).
The French Crime of 1873: An Essay on the Emergence of the International Gold Standard, 1870–1880 (PDF)
{{Authority control Metallism Numismatic terminology People's Party (United States) Monetary economics Gold Silver Currency Economic history of the United States