|
Alyattes
Alyattes ( Lydian language: ; ; reigned c. 635 – c. 585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyattes, grandson of Ardys, and great-grandson of Gyges. He died after a reign of 57 years and was succeeded by his son Croesus. Alyattes was the first monarch who issued coins, made from electrum (and his successor Croesus was the first to issue gold coins). Alyattes is therefore sometimes mentioned as the originator of coinage, or of currency. Name The most likely etymology for the name derives it, via a form with initial digamma (), itself originally from a Lydian ( Lydian alphabet: ). The name meant "lion-ness" (i.e. the state of being a lion), and was composed of the Lydian term (), meaning "lion", to which was added an abstract suffix (). Chronology Dates for the Mermnad kings are uncertain and are based on a computation by J. B. Bury and Russell Meiggs (1975) who estimated c.687–c.652 BC fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyde Of Lydia
Alyattes (Lydian language: ; ; reigned c. 635 – c. 585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyattes, grandson of Ardys, and great-grandson of Gyges. He died after a reign of 57 years and was succeeded by his son Croesus. Alyattes was the first monarch who issued coins, made from electrum (and his successor Croesus was the first to issue gold coins). Alyattes is therefore sometimes mentioned as the originator of coinage, or of currency. Name The most likely etymology for the name derives it, via a form with initial digamma (), itself originally from a Lydian ( Lydian alphabet: ). The name meant "lion-ness" (i.e. the state of being a lion), and was composed of the Lydian term (), meaning "lion", to which was added an abstract suffix (). Chronology Dates for the Mermnad kings are uncertain and are based on a computation by J. B. Bury and Russell Meiggs (1975) who estimated c.687–c.652 BC for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
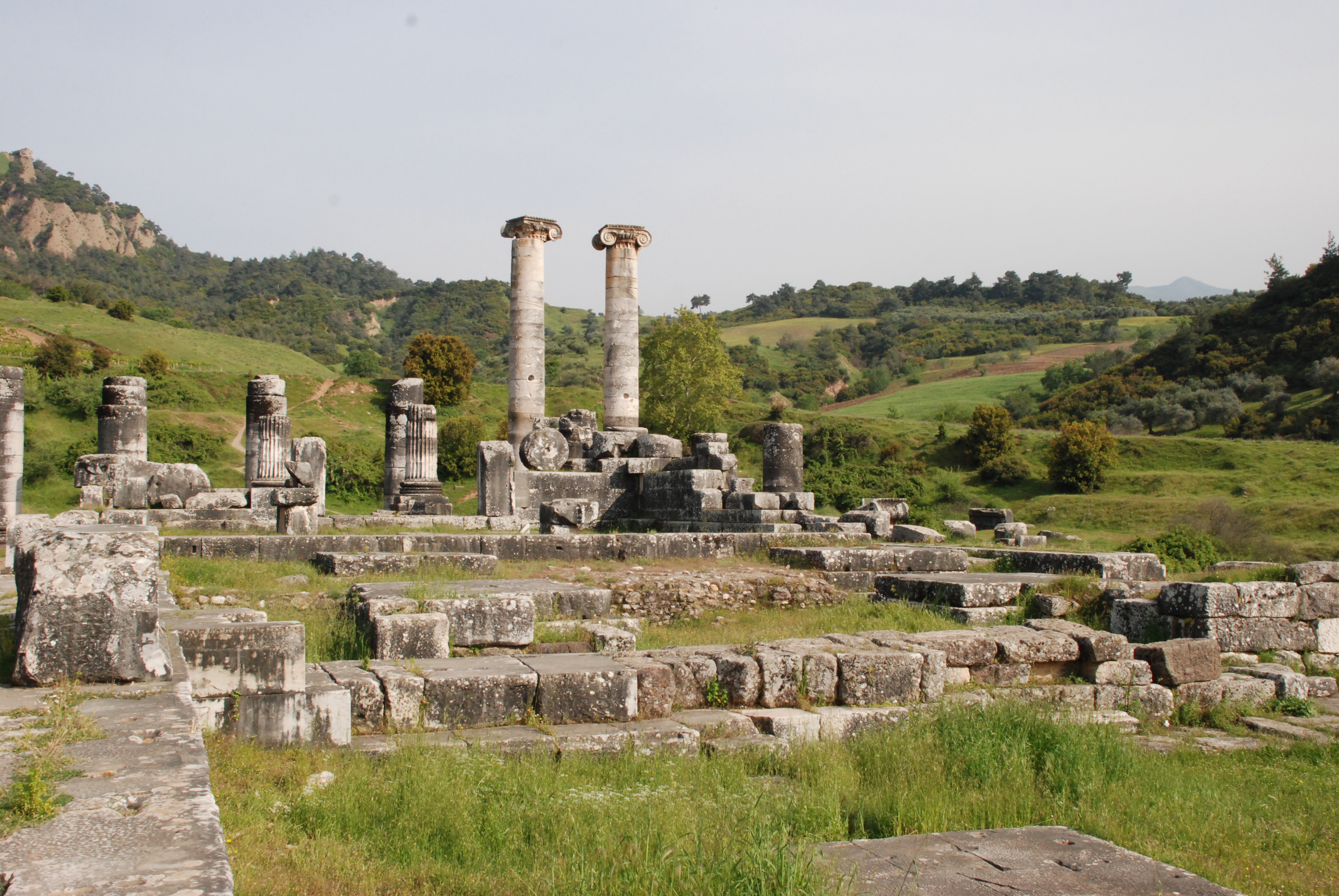
Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis. At some point before 800 BC, the Lydian people achieved some sort of political cohesion, and existed as an independent kingdom by the 600s BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, known as ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman Republic, Roman Asia (Roman province), province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of electrum, are among the oldest in existence, dated to around the 7th century BC. Geography Lydia is generally located east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak Province, Uşak, Manisa Province, Manisa and inland İzmir Province, İzmir.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croesus
Croesus ( ; ; Latin: ; reigned: ) was the Monarch, king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his Siege of Sardis (547 BC), defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. According to Herodotus, he reigned 14 years. Croesus was renowned for his wealth; Herodotus and Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias noted that his gifts were preserved at Delphi. The fall of Croesus had a profound effect on the Greeks, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least", James Allan Stewart Evans, J. A. S. Evans has remarked, "Croesus had become a figure of myth, who stood outside the conventional restraints of chronology." Name The name of Croesus was not attested in contemporary inscriptions in the Lydian language. In 2019, D. Sasseville and K. Euler published a research of Lydian coins apparently minted during his rule, where the name of the ruler was rendered as ''Qλdãns''. The name comes from the Latin language, Latin transliteration of the Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyges Of Lydia
Gyges (reigned c. 680–644 BC) was the founder of the Mermnad dynasty of Lydian kings and the first known king of the Lydian kingdom to have attempted to transform it into a powerful empire. Gyges reigned 38 years according to Herodotus. Attestations and etymology The name is derived from the Ancient Greek form () recorded by Graeco-Roman authors. In addition, the annals of the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal refer several times to , king of , to be identified with Gyges, king of the Lydians. and are respectively the Akkadian and Greek forms of the Lydian name (), which means "grandfather". is derived from a common Proto-Indo-European root from which evolved Hittite (), Luwian () and (), and Lycian () in the Anatolian languages family, as well as Latin , all meaning "grandfather". Another derivation for suggests that it might be a loanword from Carian (), which was represented in Greek as (), and was a cognate of the various Anatolian words for "grandfather": ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bin Tepe
Bin Tepe is an archaeological site on the southern shore of Marmara Lake in Manisa Province, Turkey. Consisting of over 100 tumuli, it served as a cemetery for the elites of nearby Sardis. Site Bin Tepe is an ancient cemetery consisting of over 100 tumuli. Located near the Lydian capital city of Sardis, it served local elites during the Lydian and Achaemenid periods. Bin Tepe sits on a low limestone ridge to the north of Sardis. Its elevation and proximity to a major travel route made the tumuli conspicuous to ancient travellers, as they continue to be for modern visitors. The site's proximity to earlier Bronze Age settlement mounds suggests that it may have been chosen to provide a symbolic link to the past. The burials were organized in groups, likely corresponding to families or estates. While there were once at least 149 tumuli at the site, there are now only around 115, the others having been destroyed for farmland. The tumuli consist of stone burial chambers covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryenis
Aryenis (; ) was, according to Herodotus, the daughter of King Alyattes of Lydia and the sister of King Croesus of Lydia.Alyattes Livius.org. Retrieved 08 May 2015 Name The name comes from the of the (), which was itself the Hellenised form of a Lydian name cognate with the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadyattes
Sadyattes (; ; reigned 637–) was the third king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Ardys and the grandson of Gyges of Lydia. Sadyattes reigned 12 years according to Herodotus. Reign Background Sadyattes came to power during period of severe crisis that Lydia was facing because of several waves of invasions by the Cimmerians, a nomadic people from the Eurasian Steppe who had invaded the Western Asia. The Cimmerians attacked Lydia several times but had been repelled by Sadyattes's grandfather, Gyges, but in 644 BC, the Cimmerians attacked Lydia for the third time, led by their king Lygdamis. The Lydians were defeated, Sardis was sacked, and Gyges was killed, following which he was succeeded by his son, Ardys, who was the father of Sadyattes. In 637 BC, that is in Ardys's seventh regnal year, the Thracian Treres tribe who had migrated across the Thracian Bosporus and invaded Anatolia, under their king Kobos, and in alliance with the Cimmerians and the Lycians, attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
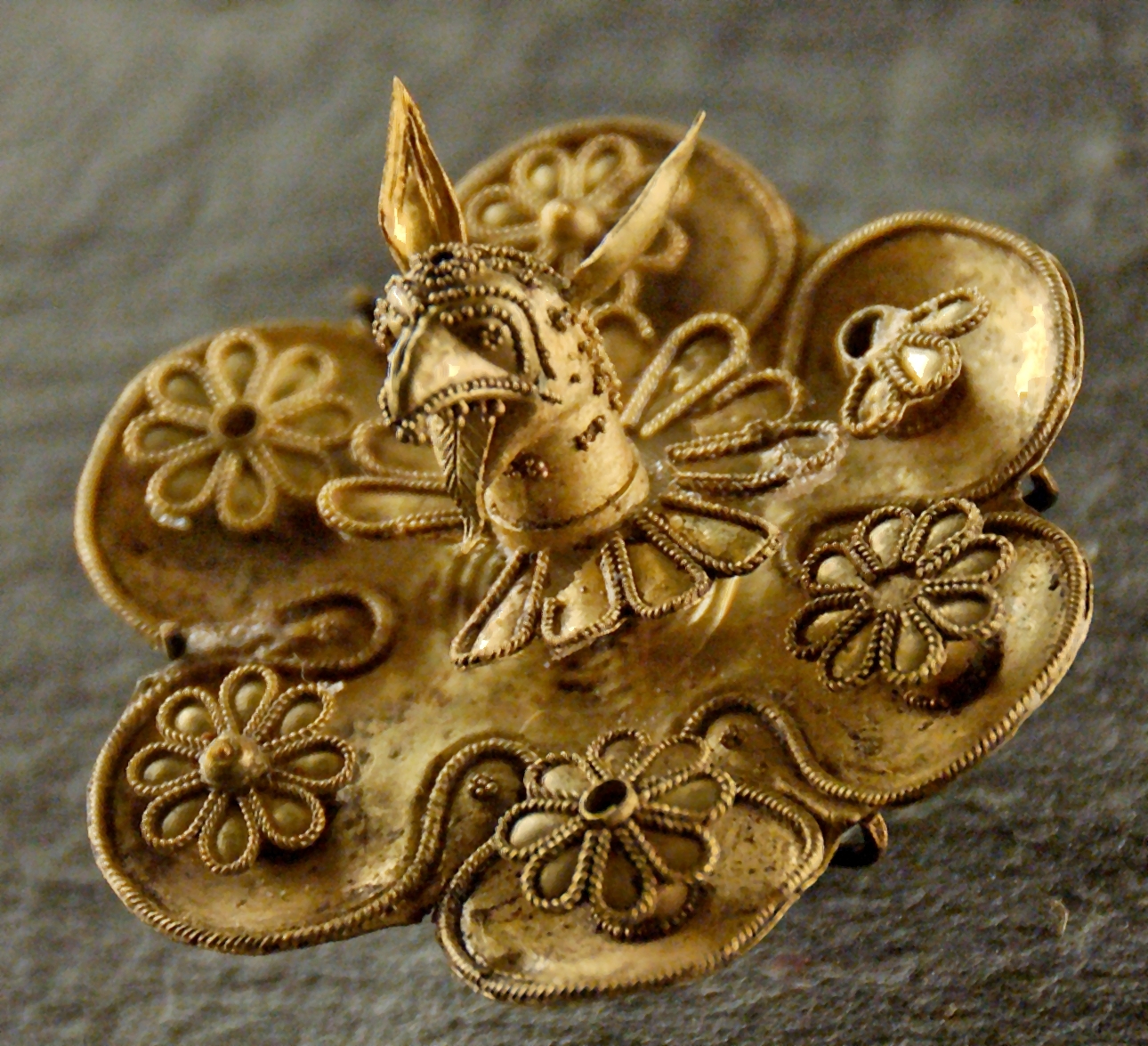
Coin
A coin is a small object, usually round and flat, used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. The faces of coins or medals are sometimes called the ''obverse'' and the ''reverse'', referring to the front and back sides, respectively. The obverse of a coin is commonly called ''heads'', because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse is known as ''tails''. The first metal coins – invented in the ancient Greek world and disseminated during the Hellenistic period – were precious metal–based, and were invented in order to simplify and regularize the task of measuring and weighing bullion (bulk metal) carried around for the purpose of transactions. They carried their value within the coins themselves, but the stampings also induced manip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrum
Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of gold and silver, with trace amounts of copper and other metals. Its color ranges from pale to bright yellow, depending on the proportions of gold and silver. It has been produced artificially and is also known as "Colored gold#Green gold, green gold".Emsley, John (2003Nature's building blocks: an A–Z guide to the elements Oxford University Press. p. 168. . Electrum was used as early as the third millennium BC in the Old Kingdom of Egypt, sometimes as an exterior coating to the pyramidion, pyramidia atop ancient Egyptian pyramids and obelisks. It was also used in the making of ancient Beaker (archaeology) , drinking vessels. The first known metal coins made were of electrum, dating back to the end of the 7th century or the beginning of the 6th century BC. Etymology The name ''electrum'' is the Latinized form of the Greek language, Greek word ἤλεκτρον (''ḗlektron''), mentioned in the ''Odyssey'', referring to a metallic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West Asia. Although the Cimmerians were Scythian cultures, culturally Scythian, they formed an ethnic unit separate from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related and who displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.: "As the Cimmerians cannot be differentiated archeologically from the Scythians, it is possible to speculate about their Iranian origins. In the Neo-Babylonian texts (according to D’yakonov, including at least some of the Assyrian texts in Babylonian dialect) and similar forms designate the Scythians and Central Asian Saka, reflecting the perception among inhabitants of Mesopotamia that Cimmerians and Scythians represented a single cultural and economic group" The Cimmerians themselves left no written records, and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific environment over time, especially for people in a nation state. Under this definition, the British Pound sterling (£), euros (€), Japanese yen (¥), and U.S. dollars (US$) are examples of (government-issued) fiat currencies. Currencies may act as stores of value and be traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are either chosen by users or decreed by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance; i.e., legal tender laws may require a particular unit of account for payments to government agencies. Other definitions of the term ''currency'' appear in the respective synonymous articles: banknote, coin, and money. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |