|
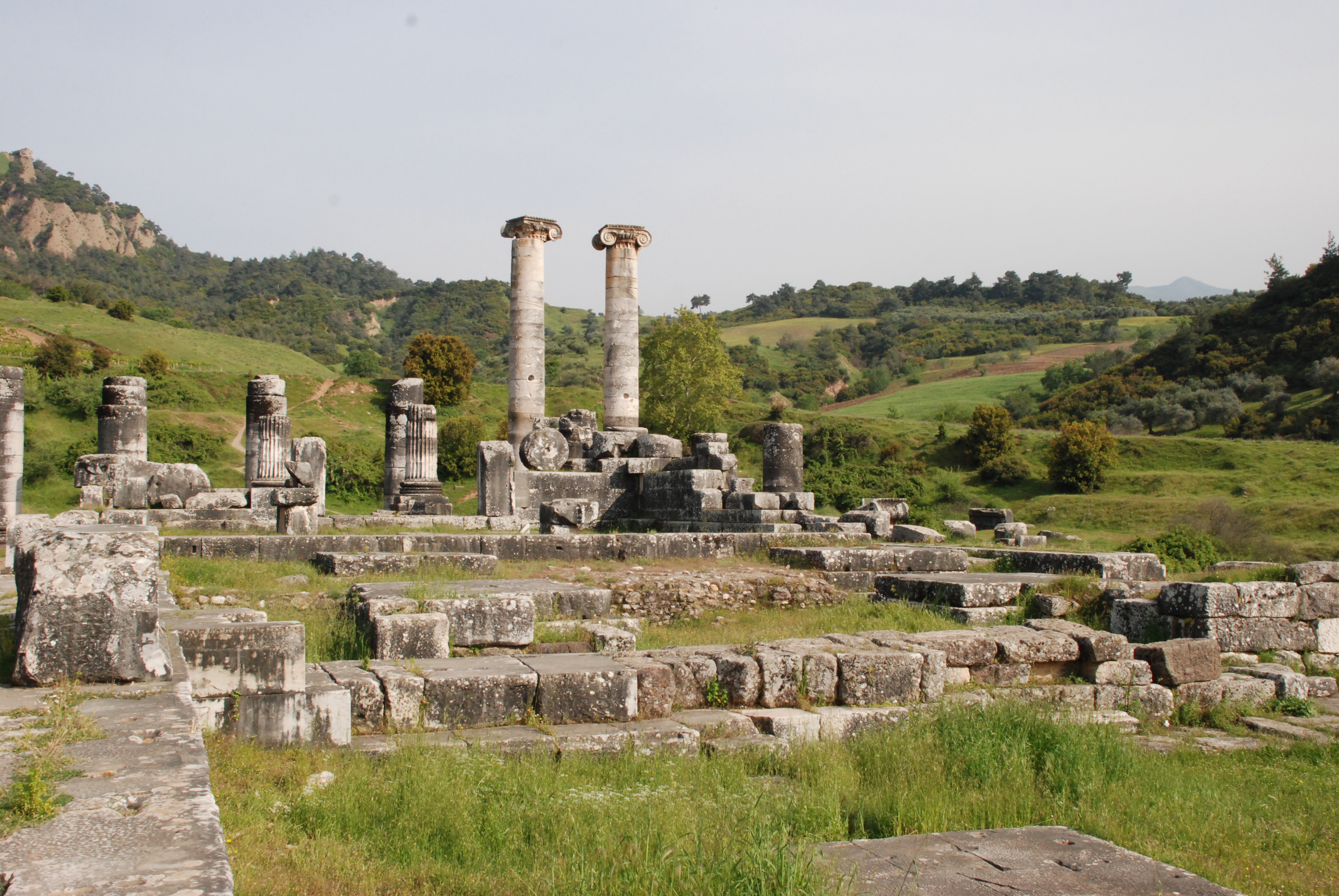
Sardis
Sardis ( ) or Sardes ( ; Lydian language, Lydian: , romanized: ; ; ) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of Lydia and later a major center of Hellenistic Greece, Hellenistic and Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine culture. Now an active archaeological site, it is located in modern day Turkey, in Manisa Province, near the town of ''Sart, Salihli, Sart''. History Sardis was occupied for at least 3500 years. In that time, it fluctuated between a wealthy city of international importance and a collection of modest hamlets. Early settlement Sardis was settled before 1500 BC. However, the size and nature of early settlement is not known since only small extramural portions of these layers have been excavated. Evidence of occupation consists largely of Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age pottery which shows affinities with Mycenaean Greece and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis. At some point before 800 BC, the Lydian people achieved some sort of political cohesion, and existed as an independent kingdom by the 600s BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a Lydia (satrapy), satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, known as ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman Republic, Roman Asia (Roman province), province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of electrum, are among the oldest in existence, dated to around the 7th century BC. Geography Lydia is generally located east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak Province, Uşak, Manisa Province, Manisa and inland İzmir Province, İzmir.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydian Empire
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis. At some point before 800 BC, the Lydian people achieved some sort of political cohesion, and existed as an independent kingdom by the 600s BC. At its greatest extent, during the 7th century BC, it covered all of western Anatolia. In 546 BC, it became a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, known as ''Sparda'' in Old Persian. In 133 BC, it became part of the Roman province of Asia. Lydian coins, made of electrum, are among the oldest in existence, dated to around the 7th century BC. Geography Lydia is generally located east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak, Manisa and inland İzmir.Rhodes, P.J. ''A History of the Classical Greek World 478–323 BC''. 2nd edition. Chichester: Wiley-Blackwell, 2010, p. 6. The boundaries of historical Lydia va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydian Language
Lydian is an extinct Indo-European language, Indo-European Anatolian languages, Anatolian language spoken in the region of Lydia, in western Anatolia (now in Turkey). The language is attested in graffiti and in coin legends from the late 8th century or the early 7th century to the 3rd century BCE, but well-preserved inscriptions of significant length are so far limited to the 5th century and the 4th century BCE, during the period of Achaemenid Empire, Persian domination. Thus, Lydian texts are effectively contemporaneous with those in Lycian language, Lycian. Strabo mentions that around his time (1st century BCE), the Lydian language was no longer spoken in Lydia proper but was still being spoken among the multicultural population of Kibyra (now Gölhisar) in southwestern Anatolia, by the descendants of the Lydians, Lydian colonists, who had founded the city. Text corpus and decipherment In 1916 the Sardis bilingual inscription, a bilingual inscription in Aramaic and Lydian all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croesus
Croesus ( ; ; Latin: ; reigned: ) was the Monarch, king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his Siege of Sardis (547 BC), defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. According to Herodotus, he reigned 14 years. Croesus was renowned for his wealth; Herodotus and Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias noted that his gifts were preserved at Delphi. The fall of Croesus had a profound effect on the Greeks, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least", James Allan Stewart Evans, J. A. S. Evans has remarked, "Croesus had become a figure of myth, who stood outside the conventional restraints of chronology." Name The name of Croesus was not attested in contemporary inscriptions in the Lydian language. In 2019, D. Sasseville and K. Euler published a research of Lydian coins apparently minted during his rule, where the name of the ruler was rendered as ''Qλdãns''. The name comes from the Latin language, Latin transliteration of the Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kroisos
Croesus ( ; ; Latin: ; reigned: ) was the king of Lydia, who reigned from 585 BC until his defeat by the Persian king Cyrus the Great in 547 or 546 BC. According to Herodotus, he reigned 14 years. Croesus was renowned for his wealth; Herodotus and Pausanias noted that his gifts were preserved at Delphi. The fall of Croesus had a profound effect on the Greeks, providing a fixed point in their calendar. "By the fifth century at least", J. A. S. Evans has remarked, "Croesus had become a figure of myth, who stood outside the conventional restraints of chronology." Name The name of Croesus was not attested in contemporary inscriptions in the Lydian language. In 2019, D. Sasseville and K. Euler published a research of Lydian coins apparently minted during his rule, where the name of the ruler was rendered as ''Qλdãns''. The name comes from the Latin transliteration of the Greek , which was thought by J.M. Kearns to be the ancient Hellenic adaptation of the reconstructed Lyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Crosby Butler
Howard Crosby Butler (March 7, 1872 Croton Falls, New York – August 13, 1922 Neuilly) was an American archaeologist. Butler graduated from Princeton University, and later pursued special studies at the Columbia School of Architecture and at the American School of Classical Studies in Rome and in Athens. In 1899, 1904, and 1909, he was at the head of archaeological expeditions in Syria. He became professor of the history of architecture at Princeton in 1905. Turkey's unsolicited request that he oversee the excavation of Sardis represented a rare distinction for an American and a Christian. He directed five seasons of archaeological work at Sardis from 1910 to 1914, interrupted by the World War I. Most of the resulting finds kept in the excavation house perished in the Greco-Turkish War of 1919–22, thwarting the publication of projected volumes on pottery, lamps, bronze and stone objects, ivories, bones and glass. Butler became unwell on August 11, 1922 after returning from Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
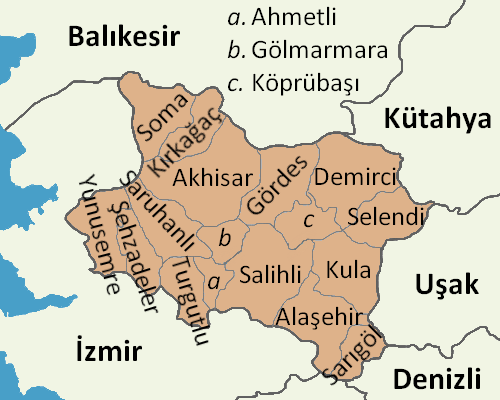
Manisa Province
Manisa Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality in western Turkey. Its area is 13,339 km2, and its population is 1,468,279 (2022). Its neighboring provinces are İzmir Province, İzmir to the west, Aydın Province, Aydın to the south, Denizli Province, Denizli to the southeast, Uşak Province, Uşak to the east, Kütahya Province, Kütahya to the northeast, and Balıkesir Province, Balıkesir to the north. The city of Manisa is the seat and capital of the province. The traffic code is 45. Districts Sites of interest Mount Sipylus List of national parks of Turkey, National Park (''Spil Dağı Milli Parkı'') near the city of Manisa embraces a richly forested area, hot springs, the famous "crying rock" of Niobe, and a Hittites, Hittite carving of the mother-goddess Cybele. The park boasts about 120 varieties of native plants within its boundaries, especially wild tulips. The park provides opportuni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian peoples, Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the List of largest empires#Timeline of largest empires to date, largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Basin, Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydia (satrapy)
The Satrapy of Lydia, known as Sparda in Old Persian (Old Persian cuneiform Wikt:𐎿𐎱𐎼𐎭, 𐎿𐎱𐎼𐎭, ''Sparda''), was an administrative province (satrapy) of the Achaemenid Empire, located in the ancient kingdom of Lydia, with Sardis as its capital. Achaemenid satrapy Tabalus, appointed by Cyrus the Great, was the first satrap; however, his rule did not last long as the Lydians revolted. The insurrection was suppressed by general Mazares and his successor Harpagus. After Cyrus' death, Oroetus was appointed as satrap. Oroetus ruled during the reign of Cambyses II, Cambyses, and after the chaotic period that followed the Persian king's death, he conquered the Greece, Greek isle of Samos Island, Samos, killing its ruler Polycrates. Due to his growing power, Darius the Great had Bagaeus kill Oroetus. Bagaeus himself may have become satrap for a short period, but the next rulers were Otanes (son of Sisamnes), Otanes and Darius' younger brother, Artaphernes. Ionian rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian People
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They are indigenous to the Iranian plateau and comprise the majority of the population of Iran.Iran Census Results 2016 United Nations Alongside having a Culture of Iran, common cultural system, they are native speakers of the Persian language and of the Western Iranian languages that are closely related to it. In the Western world, "Persian" was largely understood as a demonym for all Iranians rather than as an ethnonym for the Persian people, but this understanding Name of Iran, shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaymakçı (archaeological Site)
Kaymakçı is a Bronze Age archaeological site overlooking Marmara Lake in Manisa Province, Turkey. Given its size and location, the settlement is considered a leading candidate for the capital city of the Seha River Land. Archaeology Occupation at Kaymakçı began in the Middle Bronze Age, and it became a major settlement during the Late Bronze Age. The site was settled continuously from 1700 BC to 1200 BC, contemporary with Troy VI and VIIa. Some occupation continued into the Iron Age, though it was no longer a major urban center. Like other citadels in the area, Kaymakçı shows evidence of having been burned, but it is unknown whether this destruction caused the abandonment of the site or dates from an earlier sacking. The site covers an area of at least 25 hectares, spanning across 1 kilometer of a bedrock ridge. Its elevation 140 meters over the lake provides a commanding view of the surrounding area. It consists of a 8.6 hectare citadel, a sprawling lower town, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turkish people, Turks, while ethnic Kurds in Turkey, Kurds are the Minorities in Turkey, largest ethnic minority. Officially Secularism in Turkey, a secular state, Turkey has Islam in Turkey, a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city and economic center. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya. First inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic, present-day Turkey was home to List of ancient peoples of Anatolia, various ancient peoples. The Hattians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |