Suffrage Special on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Suffrage Special was an event created by the Congressional Union for Woman Suffrage in 1916. The Suffrage Special toured the "free states" which had already allowed
The Suffrage Special was an event created by the Congressional Union for Woman Suffrage in 1916. The Suffrage Special toured the "free states" which had already allowed
 Before the Suffrage Special left Washington, D.C., there was a farewell luncheon with speakers and music held at the headquarters for the Congressional Union. Florence Finch Kelley served as the event's
Before the Suffrage Special left Washington, D.C., there was a farewell luncheon with speakers and music held at the headquarters for the Congressional Union. Florence Finch Kelley served as the event's  The Suffrage Special arrived in
The Suffrage Special arrived in  The Suffrage Special arrived in
The Suffrage Special arrived in  The train spent several hours in
The train spent several hours in
 Delegates represented several states in the Eastern United States and the
Delegates represented several states in the Eastern United States and the
 The Suffrage Special was an event created by the Congressional Union for Woman Suffrage in 1916. The Suffrage Special toured the "free states" which had already allowed
The Suffrage Special was an event created by the Congressional Union for Woman Suffrage in 1916. The Suffrage Special toured the "free states" which had already allowed women's suffrage in the United States
In the 1700's to early 1800's New Jersey did allow Women the right to vote before the passing of the 19th Amendment, but in 1807 the state restricted the right to vote to "...tax-paying, white male citizens..."
Women's legal right to vote w ...
. The delegates were raising awareness of the national women's suffrage amendment. They were also looking to start a new political party, the National Women's Party
The National Woman's Party (NWP) was an American women's political organization formed in 1916 to fight for women's suffrage. After achieving this goal with the 1920 adoption of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, the NW ...
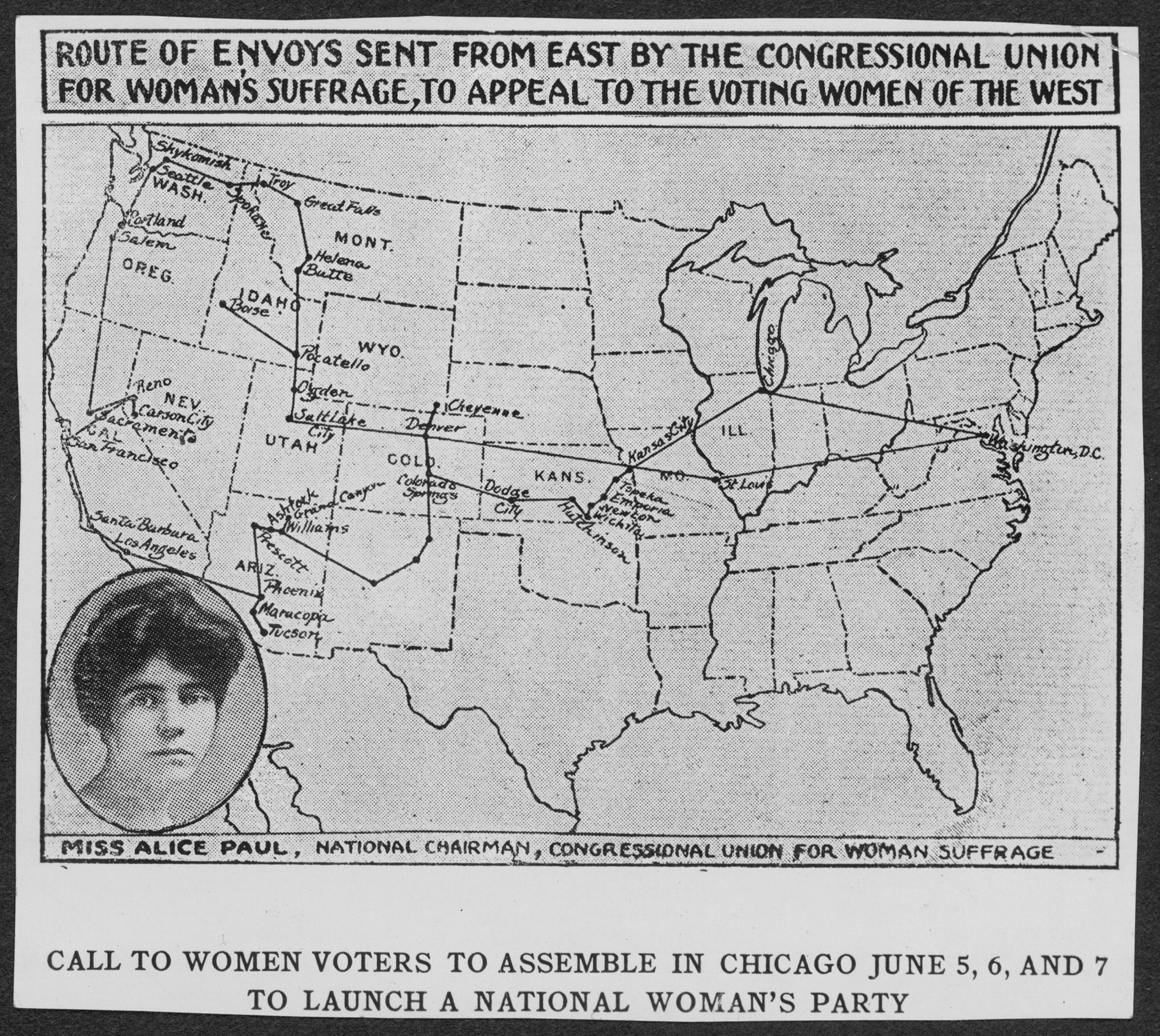
(NWP). The Suffrage Special, also known as the "flying squadron" left Washington, D.C. and toured the Western states by train for 38 days starting on April 9, 1916. Famous and well-known suffragists made up the envoy of the Suffrage Special. They toured several states during their journey and were largely well-received. When the tour was over, the delegates of the Suffrage Special visited Congress where they presented petitions for women's suffrage they had collected on their journey.
About
The Congressional Union for Woman Suffrage started planning a tour of woman's clubs in the Western United States in Spring of 1916. Since most of the states that had passed the women's vote were in the West, the idea was to recruit and use the voices of women voters from these states to speak for national women's suffrage. The suffragists wanted the women who were allowed to vote in their home states to support the national amendment. The group intended to announce plans to form aNational Woman's Party
The National Woman's Party (NWP) was an American women's political organization formed in 1916 to fight for women's suffrage. After achieving this goal with the 1920 adoption of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, the NW ...
. In addition, they obtained petition
A petition is a request to do something, most commonly addressed to a government official or public entity. Petitions to a deity are a form of prayer called supplication.
In the colloquial sense, a petition is a document addressed to some offic ...
s from across the country to present to President Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of P ...
. The tour lasted 38 days and covered the states that had already allowed women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the women's rights, right of women to Suffrage, vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to gran ...
.
The Special was planned to leave Washington, D.C. on April 9, 1916. Louisine Havemeyer, who was unable to take part, donated $300 to the Suffrage Special. Much of the financing for the trip was carried out by Alva Belmont
Alva Erskine Belmont (née Smith; January 17, 1853 – January 26, 1933), known as Alva Vanderbilt from 1875 to 1896, was an American multi-millionaire socialite and women's suffrage activist. She was noted for her energy, intelligence, strong ...
.
Ella Reigel and Lucy Burns
Lucy Burns (July 28, 1879 – December 22, 1966) was an American suffragist and women's rights advocate.Bland, 1981 (p. 8) She was a passionate activist in the United States and the United Kingdom, who joined the militant suffragettes. Burns w ...
led the delegation which was planned to consist of 36 women. Twenty-three envoys actually made the trip when the Special left on April 9. They were also known as the "flying squadron" of the Congressional Union.
Many of the women involved were considered "famous" and it was a draw to see them speaking live. Abby Scott Baker, Alva Belmont
Alva Erskine Belmont (née Smith; January 17, 1853 – January 26, 1933), known as Alva Vanderbilt from 1875 to 1896, was an American multi-millionaire socialite and women's suffrage activist. She was noted for her energy, intelligence, strong ...
, Harriet Stanton Blatch, Lucy Burns
Lucy Burns (July 28, 1879 – December 22, 1966) was an American suffragist and women's rights advocate.Bland, 1981 (p. 8) She was a passionate activist in the United States and the United Kingdom, who joined the militant suffragettes. Burns w ...
, Florence Bayard Hilles
Florence Bayard Hilles (1865–1954) was an American suffragist, one of the founders of the National Woman's Party.
Biography
Hilles was born in 1865, the daughter of Thomas Francis Bayard. She was a munitions worker in World War I, and assi ...
and Inez Milholland
Inez Milholland Boissevain (August 6, 1886 – November 25, 1916) was a leading American suffragist, lawyer, and peace activist.
From her college days at Vassar, she campaigned aggressively for women’s rights as the principal issue of a wi ...
were famous at the time. "Working Woman," Melinda Scott, was also profiled. Overall, the women were generally well received in the West. Often, when they arrived, their stops were already decorated in purple, white and gold, the suffrage colors.
Stops
 Before the Suffrage Special left Washington, D.C., there was a farewell luncheon with speakers and music held at the headquarters for the Congressional Union. Florence Finch Kelley served as the event's
Before the Suffrage Special left Washington, D.C., there was a farewell luncheon with speakers and music held at the headquarters for the Congressional Union. Florence Finch Kelley served as the event's toastmaster
Toastmaster is a general term, prevalent in the United States in the mid-20th century, referring to a person in charge of the proceedings of a public speaking event. The toastmaster is typically charged with organization of the event, arrangin ...
. The suffragists' private train car was "christened" with grape juice
Grape juice is obtained from crushing and blending grapes into a liquid. In the wine industry, grape juice that contains 7–23 percent of pulp, skins, stems and seeds is often referred to as ''must''. The sugars in grape juice allow it to be us ...
before the train pulled out. Around five thousand supporters saw the train off and a brass band played " Onward Christian Soldiers" as they began their journey. The car itself was decorated with colors associated with the suffrage movement: yellow, white and purple.
The group arrived in Chicago on April 10. The suffragists had planned a parade from Union Station
A union station (also known as a union terminal, a joint station in Europe, and a joint-use station in Japan) is a railway station at which the tracks and facilities are shared by two or more separate railway companies, allowing passengers to ...
, proceeding to a reception at the Congressional Union headquarters in the Stevens building. Mounted police
Mounted police are police who patrol on horseback or camelback. Their day-to-day function is typically picturesque or ceremonial, but they are also employed in crowd control because of their mobile mass and height advantage and increasingly in ...
acted as escorts to the headquarters. There was a public reception at the Chicago Art Institute that evening and the next day, Governor Edward Fitzsimmons Dunne
Edward Fitzsimmons Dunne (October 12, 1853 – May 24, 1937) was an American politician who was the 24th Governor of Illinois from 1913 to 1917 and previously served as the 38th mayor of Chicago from April 5, 1905 to 1907. Dunne is the onl ...
met with the suffragists in the name of the state of Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Roc ...
. These events were well-attended. The Suffrage Special headed for Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to ...
in the evening of April 11.
The Suffrage Special stopped in Kansas City, Missouri for an hour and a half on April 12. They then went to Topeka, Kansas
Topeka ( ; Kansa: ; iow, Dópikˀe, script=Latn or ) is the capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat ...
where representatives were entertained at a luncheon on April 12. Mabel Vernon
Mabel is an English female given name derived from the Latin ''amabilis'', "lovable, dear".Reclams Namensbuch, 1987,
History
Amabilis of Riom (died 475) was a French male saint who logically would have assumed the name Amabilis upon enterin ...
met the Suffrage Special at the station. There were around 150 attending the luncheon in Topeka. After the luncheon, women marched into the business district and spoke on the topic of federal women's suffrage. They also went to Washburn College
Washburn University (WU) is a public university in Topeka, Kansas, United States. It offers undergraduate and graduate programs, as well as professional programs in law and business. Washburn has 550 faculty members, who teach more than 6,100 ...
, where their event in the Pelletier tea room was "packed to capacity." Vernon arranged for the women to meet in Wichita, Kansas
Wichita ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Kansas and the county seat of Sedgwick County. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 397,532. The Wichita metro area had a population of 647,610 in 2020. It is located in ...
the next day. There was a night meeting in Wichita and on April 14, the Suffrage Special stopped at Newton, Hutchinson, Emporia and Dodge City, Kansas
Dodge City is the county seat of Ford County, Kansas, United States, named after nearby Fort Dodge. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 27,788. The city is famous in American culture for its history as a wild frontier to ...
.
On April 15, the Suffrage Special arrived in Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the United ...
. The women continued to speak on the topic of national women's suffrage, held luncheons and a mass meeting. The group arrived in Colorado Springs
Colorado Springs is a home rule municipality in, and the county seat of, El Paso County, Colorado, United States. It is the largest city in El Paso County, with a population of 478,961 at the 2020 United States Census, a 15.02% increase since ...
on April 17. They were treated to a sightseeing
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring (disambiguation), touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tour (disambiguation), tours. Th ...
trip in the mountains and in the evening, spoke at a mass meeting. They also made a stop in Cheyenne, Wyoming
Cheyenne ( or ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Wyoming, as well as the county seat of Laramie County, with 65,132 residents, per the 2020 US Census. It is the principal city of the Cheyenne metropolitan statistica ...
.
 The Suffrage Special arrived in
The Suffrage Special arrived in Tucson, Arizona
, "(at the) base of the black ill
, nicknames = "The Old Pueblo", "Optics Valley", "America's biggest small town"
, image_map =
, mapsize = 260px
, map_caption = Interactive ...
on April 20. In Tucson, the suffragists were given a tour of the city and spoke at a luncheon and then at a banquet in the city. The train arrived in Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ; nv, Hoozdo; es, Fénix or , yuf-x-wal, Banyà:nyuwá) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona, with 1,608,139 residents as of 2020. It is the fifth-most populous city in the United States, and the o ...
on April 21, where Dr. Marian Walker Williams welcomed them at a luncheon at the Adams Hotel
The Adams Hotel is a site on the National Register of Historic Places located in Lavina, Montana
Lavina is a town in Golden Valley County, Montana, United States. The population was 136 at the 2020 census. The town is situated on the north ban ...
. The train had also stopped briefly in Maricopa.
On April 22, the Suffrage Special envoys had a smaller welcome in Los Angeles. Clara Shortridge Foltz met them at the station with a dozen women and took the group to the Alexandria Hotel for a reception. Women in Los Angeles were not excited about the mission of the delegates and were not overly supportive of the formation of another party. The train left Los Angeles on April 24 making a short stop in Santa Barbara. In San Francisco, the Suffrage Special arrived on April 26 and were welcomed by the mayor's secretary, Edward Rainey and later met with Mayor James Rolph
James "Sunny Jim" Rolph Jr. (August 23, 1869 – June 2, 1934) was an American politician. A member of the Republican Party, he was elected to a single term as the 27th governor of California from January 6, 1931, until his death on June 2 ...
. The group held a large meeting, which was run by Gail Laughlin
Abbie "Gail" Hill Laughlin (May 7, 1868 – March 13, 1952) was an American lawyer, suffragist, an expert for the United States Industrial commission, and a member of the Maine State Senate. She was the first woman from Maine to practice law. She ...
. The train arrived in Reno, Nevada
Reno ( ) is a city in the northwest section of the U.S. state of Nevada, along the Nevada-California border, about north from Lake Tahoe, known as "The Biggest Little City in the World". Known for its casino and tourism industry, Reno is the c ...
on April 26 in the evening. On April 27, the Suffrage Special arrived in Carson City, Nevada
Carson City is an independent city and the capital of the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 census, the population was 58,639, making it the sixth largest city in Nevada. The majority of the city's population lives in Eagle Valley, on th ...
where they were met by Governor Emmet D. Boyle. Like women in Los Angeles, women in Nevada were not very supportive of the idea of forming a new women's party. The train stopped in Sacramento
)
, image_map = Sacramento County California Incorporated and Unincorporated areas Sacramento Highlighted.svg
, mapsize = 250x200px
, map_caption = Location within Sacramento ...
in the morning on April 28, during which time the delegates attended a luncheon which included 1,500 invitees.
The Suffrage Special arrived in Salem, Oregon on April 29. In Oregon, a resolution had been passed by both men and women which criticized Congress for not passing an amendment for national women's suffrage. The delegates left with several cases of loganberry
The loganberry (''Rubus'' × ''loganobaccus'') is a hybrid of the North American blackberry ('' Rubus ursinus'') and the European raspberry ('' Rubus idaeus'').
The plant and the fruit resemble the blackberry more than the raspberry, but the fr ...
juice and continued in the morning of April 30 to Portland, Oregon
Portland (, ) is a port city in the Pacific Northwest and the largest city in the U.S. state of Oregon. Situated at the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers, Portland is the county seat of Multnomah County, the most populou ...
.
 The Suffrage Special arrived in
The Suffrage Special arrived in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a port, seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the county seat, seat of King County, Washington, King County, Washington (state), Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in bo ...
on May 1, spending two days with various events in the city. The delegates were met at the train depot, taken on a trip in the city and gave speeches, ending the first day with a mass meeting. The meeting took place at the Moore Theatre and had a crowd of 1,500 people. The next day, the envoys were guests of the Women's Civic Club, and there were additional meetings. In Seattle, Lucy Burns
Lucy Burns (July 28, 1879 – December 22, 1966) was an American suffragist and women's rights advocate.Bland, 1981 (p. 8) She was a passionate activist in the United States and the United Kingdom, who joined the militant suffragettes. Burns w ...
was treated to an airplane ride where she scattered leaflets over the city from the air. On May 4, the train stopped in Spokane in the evening and there was a reception in the Davenport Hotel. In Spokane, the group adopted a black, stray dog
A free-ranging dog is a dog that is not confined to a yard or house. Free-ranging dogs include street dogs, village dogs, stray dogs, feral dogs, etc., and may be owned or unowned. The global dog population is estimated to be 900 million, of w ...
and named him "Spokie." and Another event that took place with the group in Spokane was the planting of a tree in memory of the suffragist May Arkwright Hutton.
 The train spent several hours in
The train spent several hours in Great Falls, Montana
Great Falls is the third most populous city in the U.S. state of Montana and the county seat of Cascade County. The population was 60,442 according to the 2020 census. The city covers an area of and is the principal city of the Great Falls, M ...
on May 7. There was a mass meeting in Helena, Montana
Helena (; ) is the capital city of Montana, United States, and the county seat of Lewis and Clark County.
Helena was founded as a gold camp during the Montana gold rush, and established on October 30, 1864. Due to the gold rush, Helena would b ...
, and while Elizabeth Selden Rogers was speaking, the lights went out but Rogers continued with her speech. They arrived that afternoon in Butte
__NOTOC__
In geomorphology, a butte () is an isolated hill with steep, often vertical sides and a small, relatively flat top; buttes are smaller landforms than mesas, plateaus, and table (landform), tablelands. The word ''butte'' comes from a F ...
. In Butte, they visited the city's mines and then had dinner at the Thornton Hotel. Afterwards, they drove through the business district and went on to the city's auditorium for speeches, rallying the women to support a national suffrage amendment. In Butte, Spokie, the dog was kidnapped
Kidnapped may refer to:
* subject to the crime of kidnapping
In criminal law, kidnapping is the unlawful confinement of a person against their will, often including transportation/asportation. The asportation and abduction element is typically ...
and taken into a saloon, where the men thought the women would not dare to go. Abby Scott Baker retrieved the dog and got the bartender
A bartender (also known as a barkeep, barman, barmaid, or a mixologist) is a person who formulates and serves alcoholic or soft drink beverages behind the bar, usually in a licensed establishment as well as in restaurants and nightclubs, but ...
to drink to the "health of suffrage" during the event. The next day, the delegates visited another mine and held another luncheon with speakers at the Thornton Hotel.
They traveled from Pocatello
Pocatello () is the county seat of and largest city in Bannock County, with a small portion on the Fort Hall Indian Reservation in neighboring Power County, in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Idaho. It is the principal city of the P ...
to Boise
Boise (, , ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Idaho and is the county seat of Ada County. On the Boise River in southwestern Idaho, it is east of the Oregon border and north of the Nevada border. The downtown ...
, arriving there on May 9. The envoys arrived in Boise in the evening, where they were escorted to Pinney Theater for a mass meeting. On May 10, the envoys met with state officials at a morning reception. Governor Moses Alexander
Moses Alexander (November 13, 1853 – January 4, 1932) was an American businessman and politician who served as the 11th governor of Idaho, the second elected Jewish governor of a U.S. state, and the first who actually practiced that religion. ...
promised that Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and W ...
would ratify a national suffrage amendment. The train left at noon for a mass meeting to be held in Pocatello.
Ida Smoot was involved in welcoming the Suffrage Special to Salt Lake City
Salt Lake City (often shortened to Salt Lake and abbreviated as SLC) is the capital and most populous city of Utah, United States. It is the seat of Salt Lake County, the most populous county in Utah. With a population of 200,133 in 2020, th ...
on May 11. The group arrived in the morning and were escorted to Hotel Utah. After breakfast at the hotel, they were guests of the First Presidency
Among many churches in the Latter Day Saint movement, the First Presidency (also known as the Quorum of the Presidency of the Church) is the highest presiding or governing body. Present-day denominations of the movement led by a First Presidency ...
and entertained by an organ recital at the Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
. and They were then escorted by mounted police in a street parade. Meetings were carried on through the day. The next day, a business session was held at Hotel Utah and farewell demonstrations at Pioneer Park followed in the afternoon.
On May 14, the train stopped for three hours in St. Joseph, Missouri for dinner and a meeting at the Scottish Rite Cathedral.
The Suffrage Special returned to Washington, D.C. on May 16, where a "White Luncheon" took place in Union Station
A union station (also known as a union terminal, a joint station in Europe, and a joint-use station in Japan) is a railway station at which the tracks and facilities are shared by two or more separate railway companies, allowing passengers to ...
. Around 300 women attended the luncheon. A parade was held as the delegates took their petitions to the United States Congress. Three hundred schoolgirls dressed in white "formed aisles up the broad, impressive steps of the Capitol as the delegates marched in with their petitions." The delegates also had five girls precede them, "strewing flowers in their path." At the top of the steps, Belva Ann Lockwood
Belva Ann Bennett Lockwood (October 24, 1830 – May 19, 1917) was an American lawyer, politician, educator, and author who was active in the women's rights and women's suffrage movements. She was one of the first women lawyers in the United S ...
held a Congressional Union banner. As they marched, " The Women's Marseillaise" was played. The Senate officially recessed to receive the delegates. Legislators were surrounded by a rope held by a hundred women and around them, a ring of yellow ribbon was held by the girls. The women then addressed Congress and implored them to support women's suffrage. The envoys had brought a 150-pound iced cake as a gift for President Wilson.
Aftermath
In June 1916, the women involved with the Suffrage Special held a Woman's Party Convention in Chicago and created theNational Woman's Party
The National Woman's Party (NWP) was an American women's political organization formed in 1916 to fight for women's suffrage. After achieving this goal with the 1920 adoption of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, the NW ...
(NWP).
Delegates
 Delegates represented several states in the Eastern United States and the
Delegates represented several states in the Eastern United States and the Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. ...
. Anne Henrietta Martin
Anne Henrietta Martin (September 30, 1875 – April 15, 1951) (pseudonym, Anne O'Hara; nickname, Little Governor Anne) was a suffragist, Pacifism, pacifist, and author from the state of Nevada. Her main achievement was taking charge of the state l ...
from Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
accompanied the delegates for part of the journey. Women who had been chosen at the Woman Voter Conference in Salt Lake City accompanied the original envoys. Spokie, or Spokane, the adopted stray dog
A free-ranging dog is a dog that is not confined to a yard or house. Free-ranging dogs include street dogs, village dogs, stray dogs, feral dogs, etc., and may be owned or unowned. The global dog population is estimated to be 900 million, of w ...
who accompanied the delegates went with Helen Todd to New York after the trip.
Original delegates
*Lillian Ascough
Lillian Ascough (May 14, 1880 – December 1974) was an American suffragist. Originally from Detroit, Michigan, she served as the Connecticut chair of the National Woman's Party (NWP) and as the vice president of the Michigan branch of the NW ...
, Connecticut
* Abby Scott Baker, Washington, D.C.
*Alva Belmont
Alva Erskine Belmont (née Smith; January 17, 1853 – January 26, 1933), known as Alva Vanderbilt from 1875 to 1896, was an American multi-millionaire socialite and women's suffrage activist. She was noted for her energy, intelligence, strong ...
, New York
* Harriet Stanton Blatch, New York
*Lucy Burns
Lucy Burns (July 28, 1879 – December 22, 1966) was an American suffragist and women's rights advocate.Bland, 1981 (p. 8) She was a passionate activist in the United States and the United Kingdom, who joined the militant suffragettes. Burns w ...
, New York
*Mrs. A. R. Colvin, Minnesota
*Agnes Campbell
Lady Agnes Campbell (1526–1601) was the daughter of The 3rd Earl of Argyll and his wife, Lady Jean Gordon, daughter of The 3rd Earl of Huntly. She was likely born at Inveraray Castle. Her sister, Elizabeth, married The 1st Earl of Moray, an ...
, New Jersey
*Anna Constable
Anna may refer to:
People Surname and given name
* Anna (name)
Mononym
* Anna the Prophetess, in the Gospel of Luke
* Anna (wife of Artabasdos) (fl. 715–773)
* Anna (daughter of Boris I) (9th–10th century)
* Anna (Anisia) (fl. 1218 to 1221) ...
, New York
* Edith J. Goode, Ohio
*Jane Goode, Ohio
*Florence Bayard Hilles
Florence Bayard Hilles (1865–1954) was an American suffragist, one of the founders of the National Woman's Party.
Biography
Hilles was born in 1865, the daughter of Thomas Francis Bayard. She was a munitions worker in World War I, and assi ...
, Delaware
*Julia Hurlbut
Julia Hurlbut (1882–1962) was an American suffragist known for her participation in the picketing of the White House by the National Woman's Party in 1917.
Life
Born in 1882 in Morristown, New Jersey, Hurlbut served as the vice chairman of th ...
, New Jersey
* Caroline Katzenstein, Pennsylvania
* Winifred Mallon, Washington, D.C.
*Dorothy Mead
Dorothy Mead (1928–1975) was a British painter.
Biography
Mead was born in London, England, and adopted at three months old by a family in Walthamstow. Her mother had a florists shop.
She first met David Bomberg when he was teaching at the So ...
, Ohio
*Inez Milholland
Inez Milholland Boissevain (August 6, 1886 – November 25, 1916) was a leading American suffragist, lawyer, and peace activist.
From her college days at Vassar, she campaigned aggressively for women’s rights as the principal issue of a wi ...
, New York
*Agnes Morey, Massachusetts
* Katherine Morey, Massachusetts
* Gertrude B. Newell, Massachusetts
* Marion T. Read, Virginia
* Ella Riegel, Pennsylvania
* Elizabeth Selden Rogers, New York
*Melinda Scott
Melinda is a feminine given name.
Etymology
The modern name ''Melinda'' is a combination of "Mel" with the suffix "-inda". "Mel" can be derived from names such as Melanie meaning "dark, black" in Greek, or from Melissa (μέλισσα) meanin ...
, New York
*Mrs. Townsend Scott, Maryland
* Helen Todd, New York
Delegates from convention
* Mrs. John B. Allen, Washington * Mrs. Frederick C. Alsdorf, Arizona * Frances Axtell, Washington * Mrs. Dan Casement, Kansas * Elizabeth Gerberding, California * Mrs. Oscar Groshell, Utah * Frances Haire, Montana *Phoebe Hearst
Phoebe Elizabeth Apperson Hearst (December 3, 1842 – April 13, 1919) was an American philanthropist, feminist and suffragist. Hearst was the founder of the University of California Museum of Anthropology, now called the Phoebe A. Hearst M ...
, California
* Alice Reynolds, Utah
* Mrs. Wallace Williams, Washington
See also
*Prison Special
The "Prison Special" was a train tour organized by suffragists who, as members of the Silent Sentinels and other demonstrations, had been jailed for picketing the White House in support of passage of the federal women's suffrage amendment. In Fe ...
* National Women's Party
The National Woman's Party (NWP) was an American women's political organization formed in 1916 to fight for women's suffrage. After achieving this goal with the 1920 adoption of the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, the NW ...
References
Sources
* {{Authority Control Political activism Women's suffrage in the United States 1916 protests Feminist protests History of voting rights in the United States 1916 in women's history Women's suffrage advocacy groups in the United States