Spermatocyte on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
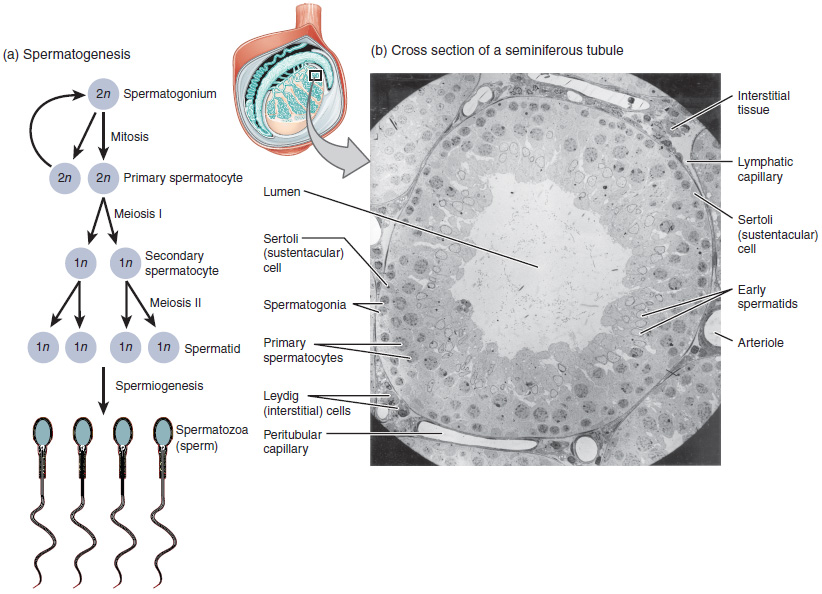 Spermatocytes are a type of
Spermatocytes are a type of
 The gene Stimulated By Retinoic Acid 8 (''STRA8'') is required for the retinoic-acid signaling pathway in humans, which leads to
The gene Stimulated By Retinoic Acid 8 (''STRA8'') is required for the retinoic-acid signaling pathway in humans, which leads to
 Primary
Primary
Spermatogenesis
{{Male reproductive system Germ cells Mammal male reproductive system
 Spermatocytes are a type of
Spermatocytes are a type of male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual repro ...
gametocyte
A gametocyte is a eukaryotic germ cell that divides by mitosis into other gametocytes or by meiosis into gametids during gametogenesis. Male gametocytes are called ''spermatocytes'', and female gametocytes are called ''oocytes''.
Development
T ...
in animals. They derive from immature germ cells
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo ...
called spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in human ...
. They are found in the testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
Structure
The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells ...
. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and secondary spermatocytes. Primary and secondary spermatocytes are formed through the process of spermatocytogenesis.
Primary spermatocytes are diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
(2N) cells. After meiosis I
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one co ...
, two secondary spermatocytes are formed. Secondary spermatocytes are haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
(N) cells that contain half the number of chromosomes.
In all animals, males
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
produce spermatocytes, even hermaphrodites
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
such as ''C. elegans'', which exist as a male or hermaphrodite. In hermaphrodite ''C. elegans'', sperm production occurs first and is then stored in the spermatheca
The spermatheca (pronounced : spermathecae ), also called ''receptaculum seminis'' (: ''receptacula seminis''), is an organ of the female reproductive tract in insects, e.g. ants, bees, some molluscs, Oligochaeta worms and certain other in ...
. Once the eggs are formed, they are able to self-fertilize and produce up to 350 progeny.
Development
Atpuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in human ...
located along the walls of the seminiferous tubules
Seminiferous tubules are located within the testicles, and are the specific location of meiosis, and the subsequent creation of male gametes, namely spermatozoa.
Structure
The epithelium of the tubule consists of a type of sustentacular cells ...
within the testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
will be initiated and start to divide mitotically, forming two types of A cells that contain an oval shaped nucleus with a nucleolus attached to the nuclear envelope; one is dark (Ad) and the other is pale (Ap). The Ad cells are spermatogonia that will stay in the basal compartment (outer region of the tubule); these cells are reserve spermatogonial stem cells that do not usually undergo mitosis. Type Ap are actively-dividing spermatogonial stem cells which begin differentiation to type B spermatogonia, which have round nuclei and heterochromatin attached to the nuclear envelope and the center of nucleolus. Type B cells will move on to the adluminal compartment (towards the inner region of tubule) and become primary spermatocytes; this process takes about 16 days to complete.
The primary spermatocytes within the adluminal compartment will continue on to meiosis I
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one co ...
and divide into two daughters cells, known as secondary spermatocytes, a process which takes 24 days to complete. Each secondary spermatocyte will form two spermatids
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are con ...
after meiosis II.
Although spermatocytes that divide mitotically and meiotically are sensitive to radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, spermatogonial stem cells are not. Therefore, after termination of radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
or chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, the spermatognia stems cells may re-initiate the formation of spermatogenesis.

Role of hormones
The formation of primary spermatocytes (a process known as spermatocytogenesis) begins in humans when a male is sexually matured atpuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
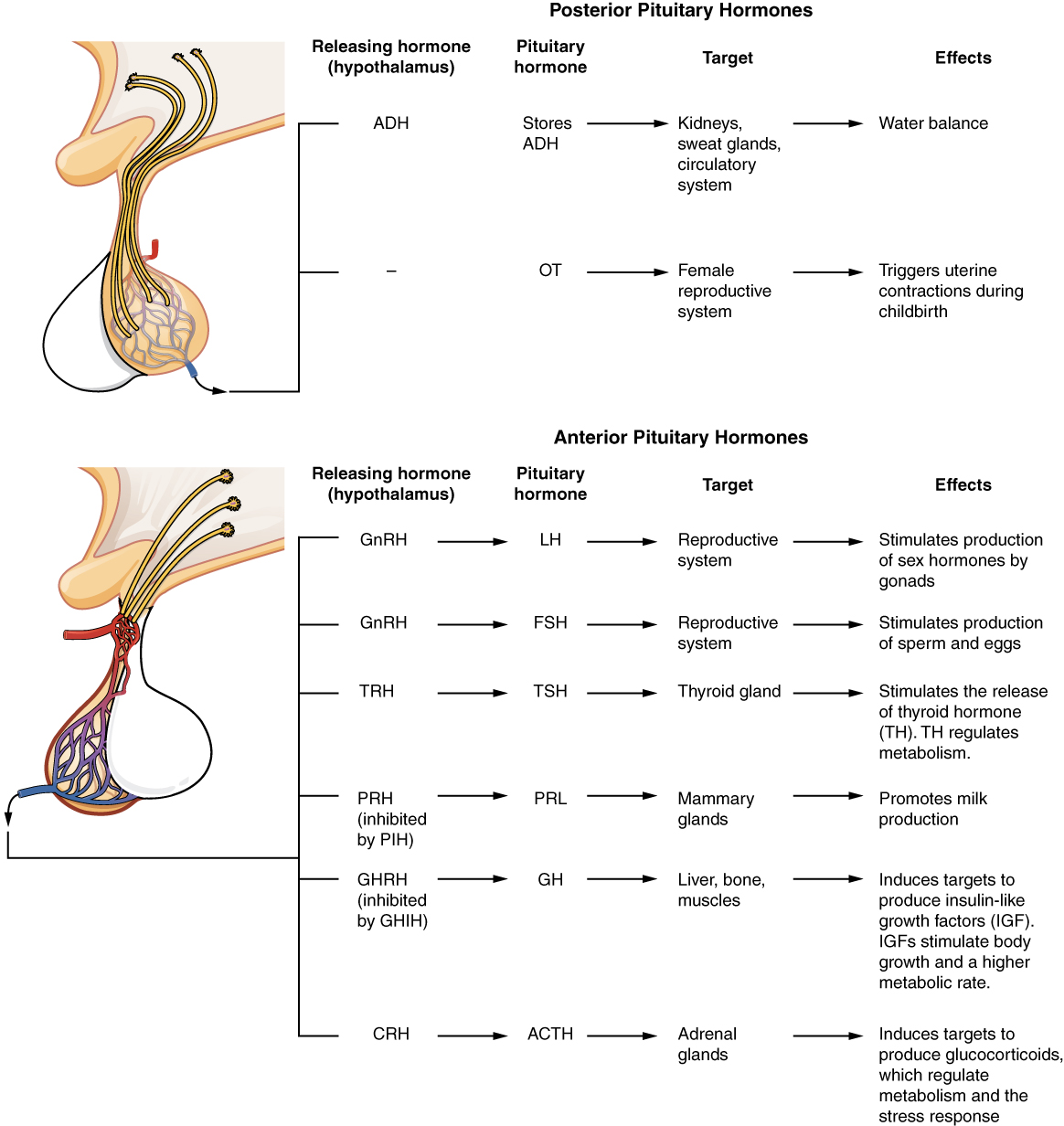
, around the age of 10 through 14. Formation is initiated upon the pulsated surges of gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and rele ...
(GnRH) from the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
, which leads to the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, puberty, pubertal maturat ...
(FSH) and luteinizing hormone
Luteinizing hormone (LH, also known as luteinising hormone, lutropin and sometimes lutrophin) is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (G ...
(LH) produced by the anterior pituitary gland
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, anterior lobe that together with the posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) makes up ...
. The release of FSH into the testes will enhance spermatogenesis and lead to the development of Sertoli cells
Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm) as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-sti ...
, which act as nursing cells where spermatids
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are con ...
will go to mature after meiosis II. LH promotes Leydig cell
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of the testes and interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle and produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH). They are polyhedral ...
secretion of testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
into the testes and blood, which induce spermatogenesis and aid the formation of secondary sex characteristics. From this point on, the secretion of FSH and LH (inducing production of testosterone) will stimulate spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
until the male dies. Increasing the hormones
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones a ...
FSH and LH in males will not increase the rate of spermatogenesis. However, with age, the rate of production will decrease, even when the amount of hormone that is secreted is constant; this is due to higher rates of degeneration of germ cells
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo ...
during meiotic
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy ...
prophase
Prophase () is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin retic ...
.
Cell type summary
In the following table, ploidy, copy number and chromosome/chromatid counts listed are for a single cell, generally prior to DNA synthesis and division (in G1 if applicable). Primary spermatocytes are arrested after DNA synthesis and prior to division.Physiology
Damage, repair, and failure
Spermatocytes regularly overcome double-strand breaks and other DNA damages in the prophase stage ofmeiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
. These damages can arise by the programmed activity of Spo11
Spo11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SPO11'' gene. Spo11, in a complex with mTopVIB, creates double strand breaks to initiate meiotic recombination. Its active site contains a tyrosine which ligates and dissociates with DNA to p ...
, an enzyme employed in meiotic recombination, as well as by un-programmed breakages in DNA, such as those caused by oxidative free radicals produced as products of normal metabolism. These damages are repaired by homologous recombination pathways and utilize RAD1 and γ H2AX, which recognize double strand breaks and modify chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
, respectively. As a result, double strand breaks in meiotic cells, unlike mitotic cells, do not typically lead to apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
, or cell death. Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which genetic information is exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of double-stranded or single-stranded nucleic acids (usually DNA as in Cell (biology), cellular organi ...
al repair (HRR) of double-strand breaks occurs in mice during sequential stages of spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
but is most prominent in spermatocytes. In spermatocytes, HRR events occur mainly in the pachytene stage of meiosis and the gene conversion
Gene conversion is the process by which one DNA sequence replaces a homologous sequence such that the sequences become identical after the conversion. Gene conversion can be either allelic, meaning that one allele of the same gene replaces another ...
type of HRR is predominant, whereas in other stages of spermatogenesis the reciprocal exchange type of HRR is more frequent. During mouse spermatogenesis, the mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
frequencies of cells at the different stages, including pachytene spermatocytes, are 5 to 10-fold lower than the mutation frequencies in somatic cell
In cellular biology, a somatic cell (), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Somatic cells compose the body of an organism ...
s. Because of their elevated DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
capability, spermatocytes likely play a central role in the maintenance of these lower mutation rates, and thus in the preservation of the genetic integrity of the male germ line.
It is known that heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
chromosomal rearrangements lead to spermatogenic disturbance or failure; however the molecular mechanisms that cause this are not as well known. It is suggested that a passive mechanism involving asynaptic region clustering in spermatocytes is a possible cause. Asynaptic regions are associated with BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a ...
, kinase ATR and γ H2AX presence in pachytene spermatocytes.
Specific mutations
 The gene Stimulated By Retinoic Acid 8 (''STRA8'') is required for the retinoic-acid signaling pathway in humans, which leads to
The gene Stimulated By Retinoic Acid 8 (''STRA8'') is required for the retinoic-acid signaling pathway in humans, which leads to meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
initiation. ''STRA8'' expression is higher in preleptotene spermatocytes (at the earliest stage of prophase I in meiosis) than in spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in human ...
. ''STRA8''-mutant spermatocytes have been shown to be capable of meiosis initiation; however, they cannot complete the process. Mutations in leptotene spermatocytes can result in premature chromosome condensation.
Mutations in ''Mtap2'', a microtubule-associated protein
In cell biology, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are proteins that interact with the microtubules of the cellular cytoskeleton. MAPs are integral to the stability of the cell and its internal structures and the transport of components withi ...
, as observed in ''repro4'' mutant spermatocytes, have been shown to arrest spermatogenesis progress during the prophase of meiosis I
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one co ...
. This is observed by a reduction in spermatid
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are co ...
presence in ''repro4'' mutants.
Recombinant-defective mutations can occur in ''Spo11
Spo11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SPO11'' gene. Spo11, in a complex with mTopVIB, creates double strand breaks to initiate meiotic recombination. Its active site contains a tyrosine which ligates and dissociates with DNA to p ...
'', ''DMC1'', ''ATM'' and ''MSH5
MutS protein homolog 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MSH5'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a member of the mutS family of proteins that are involved in DNA mismatch repair or meiotic recombination processes. This protein is ...
'' genes of spermatocytes. These mutations involve double strand break repair impairment, which can result in arrest of spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
at stage IV of the seminiferous epithelium cycle.
History
Thespermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
process has been elucidated throughout the years by researchers who divided the process into multiple stages or phases, depending on intrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass i ...
(germ and Sertoli cells) and extrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass i ...
(FSH and LH) factors. The spermatogenesis process in mammals as a whole, involving cellular transformation, mitosis, and meiosis, has been well studied and documented from the 1950s to 1980s. However, during the 1990s and 2000s researchers have focused around increasing understanding of the regulation of spermatogenesis via genes, proteins, and signaling pathways, and the biochemical and molecular mechanisms involved in these processes. Most recently, the environmental effects on spermatogenesis have become a focus as male infertility
Male infertility refers to a sexually mature male's inability to impregnate a fertile female. Male infertility can wholly or partially account for 40% of infertility among couples who are trying to have children. "A problem with the male is the s ...
in men has become more prevalent.
An important discovery in the spermatogenesis process was the identification of the seminiferous epithelial cycle in mammals—work by C.P. Leblound and Y. Clermont in 1952 that studied the spermatogonia, spermatocyte layers and spermatids in rat seminiferous tubules. Another critical discovery was that of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular hormone chain, which plays a role in spermatogenesis regulation; this was studied by R. M. Sharpe in 1994.
Other animals
 Primary
Primary cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
are common organelles
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence ''organelle,'' th ...
found in eukaryotic cells; they play an important role in development of animals. ''Drosophila'' have unique properties in their spermatocyte primary cilia—they are assembled by four centrioles
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers ( Pinophyta), flowering plants ( angiosperms) and most fungi, an ...
independently in the G2 phase
G2 phase, Gap 2 phase, or Growth 2 phase, is the third subphase of interphase in the cell cycle directly preceding mitosis. It follows the successful completion of S phase, during which the cell’s DNA is replicated. G2 phase ends with the o ...
and are sensitive to microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter bet ...
-targeting drugs. Normally, primary cilia will develop from one centriole in the G0/G1 phase and are not affected by microtubule targeting drugs.
'' Mesostoma ehrenbergii'' is a rhabdocoel flatworm
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), ...
with a distinctive male meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
stage within the formation of spermatocytes. During the pre-anaphase stage, cleavage furrows are formed in the spermatocyte cells containing four univalent chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
. By the end of the anaphase
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maxim ...
stage, there is one at each pole moving between the spindle poles without actually having physical interactions with one another (also known as distance segregation). These unique traits allow researchers to study the force created by the spindle poles to allow the chromosomes to move, cleavage furrow management and distance segregation.
See also
*Germ cells
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo ...
*Gametes
A gamete ( ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the Ge ...
* Gametocytogenesis
* Leydig
*Mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
*Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
*Sertoli cells
Sertoli cells are a type of sustentacular "nurse" cell found in human testes which contribute to the process of spermatogenesis (the production of sperm) as a structural component of the seminiferous tubules. They are activated by follicle-sti ...
*Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testicle. This process starts with the Mitosis, mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of ...
*Spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles.
There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in human ...
*Spermatid
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
Spermatids are co ...
* Spermatocytogenesis
* Spermatidogenesis
*Sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
References
External links
Spermatogenesis
{{Male reproductive system Germ cells Mammal male reproductive system