Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a
proprietary
{{Short pages monitor
, a fictional unit of time from the 1978 ''Battlestar Galactica'' American television series
* ''Centon'', a range of photographic equipment sold in the United Kingdom by Jesso ...
(64 GB and 128 GB) and
Lexar
Lexar Media, Inc. is a Chinese brand of flash memory products manufactured by the Chinese company Longsys.
The Lexar "JumpDrive" trademark was often used synonymously with the term USB flash drives when the technology was first adopted.
Histo ...
(128 GB) began shipping SDXC cards rated at Speed Class 10. Pretec offered cards from 8 GB to 128 GB rated at Speed Class 16. In September 2011, SanDisk released a 64 GB microSDXC card. Kingmax released a comparable product in 2011.
2012
In April 2012, Panasonic introduced
MicroP2
MicroP2 is a memory card format introduced by Panasonic.
The cards were announced in April 2012 and shipped in March 2013.
Physically, MicroP2 is a SDXC/SDHC
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile fla ...
card format for professional video applications. The cards are essentially full-size SDHC or SDXC UHS-II cards, rated at UHS Speed Class U1.
An adapter allows MicroP2 cards to work in current
P2 card equipment.
2013
Panasonic MicroP2 cards shipped in March 2013 and were the first UHS-II compliant products on market; initial offer includes a 32GB SDHC card and a 64GB SDXC card.
Later that year, Lexar released the first 256 GB SDXC card, based on 20 nm
NAND flash
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both us ...
technology.
2014
In February 2014, SanDisk introduced the first 128 GB microSDXC card, which was followed by a 200 GB microSDXC card in March 2015. September 2014 saw SanDisk announce the first 512 GB SDXC card.
2016
Samsung announced the world's first EVO Plus 256 GB microSDXC card in May 2016, and in September 2016
Western Digital
Western Digital Corporation (WDC, commonly known as Western Digital or WD) is an American computer drive manufacturer and data storage company, headquartered in San Jose, California. It designs, manufactures and sells data technology products ...
(SanDisk) announced that a prototype of the first 1 TB SDXC card would be demonstrated at
Photokina
Photokina (rendered in the promoters' branding as "photokina") is a trade fair held in Europe for the photographic and imaging industries. It is the world's largest such trade fair. The first Photokina was held in Cologne, Germany, in 1950, a ...
.
2017
In August 2017, SanDisk launched a 400 GB microSDXC card.
2018
In January 2018, Integral Memory unveiled its 512 GB microSDXC card. In May 2018,
PNY launched a 512 GB microSDXC card. In June 2018
Kingston
Kingston may refer to:
Places
* List of places called Kingston, including the five most populated:
** Kingston, Jamaica
** Kingston upon Hull, England
** City of Kingston, Victoria, Australia
** Kingston, Ontario, Canada
** Kingston upon Thames, ...
announced its Canvas series of MicroSD cards which were capable of capacities up to 512 GB,
in three variations, Select, Go!, and React.
2019
In February 2019,
Micron
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer ( American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Un ...
and
SanDisk
SanDisk is a brand for flash memory products, including memory cards and readers, USB flash drives, solid-state drives, and digital audio players, manufactured and marketed by Western Digital. The original company, SanDisk Corporation was acquire ...
unveiled their microSDXC cards of 1 TB capacity.
2019–present: SDUC
The Secure Digital Ultra Capacity (SDUC) format supports cards up to 128
TB and offers speeds up to 985 MB/s.
Capacity
Secure Digital includes five card families available in three sizes. The five families are the original Standard-Capacity (SDSC), the High-Capacity (SDHC), the eXtended-Capacity (
SDXC
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
The standard was introduced in August 1999 by joint efforts between San ...
), the Ultra-Capacity (
SDUC
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
The standard was introduced in August 1999 by joint efforts between SanDis ...
) and the
SDIO SDIO may refer to:
* Secure Digital Input Output, a type of Secure Digital card interface. It can be used as an interface for input or output devices.
* Strategic Defense Initiative Organization
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisivel ...
, which combines
input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, possibly a human or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals ...
functions with data storage.
The
three form factors are the original size, the mini size, and the micro size. Electrically passive adapters allow a smaller card to fit and function in a device built for a larger card. The SD card's small footprint is an ideal storage medium for smaller, thinner, and more portable electronic devices.
SD (SDSC)

The second-generation Secure Digital (SDSC or Secure Digital Standard Capacity) card was developed to improve on the
MultiMediaCard
The MultiMediaCard, officially abbreviated as MMC, is a memory card standard used for solid-state storage. Unveiled in 1997 by SanDisk and Siemens, MMC is based on a surface-contact low pin-count serial interface using a single memory stack s ...
(MMC) standard, which continued to evolve, but in a different direction. Secure Digital changed the MMC design in several ways:
* Asymmetrical shape of the sides of the SD card prevent inserting it upside down (whereas an MMC goes in most of the way but makes no contact if inverted).
* Most SD cards are thick, compared to for MMCs. The SD specification defines a card called Thin SD with a thickness of 1.4 mm, but they occur only rarely, as the SDA went on to define even smaller form factors.
* The card's electrical contacts are recessed beneath the surface of the card, protecting them from contact with a user's fingers.
* The SD specification envisioned capacities and transfer rates exceeding those of MMC, and both of these functionalities have grown over time. For a comparison table, see
below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
* Soil
* Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
* Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
* Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fr ...
.
* While MMC uses a single pin for data transfers, the SD card added a four-wire bus mode for higher data rates.
* The SD card added
Content Protection for Recordable Media
Content Protection for Recordable Media and Pre-Recorded Media (CPRM / CPPM) is a mechanism for controlling the copying, moving, and deletion of digital media on a host device, such as a personal computer, or other player. It is a form of digit ...
(CPRM) security circuitry for
digital rights management
Digital rights management (DRM) is the management of legal access to digital content. Various tools or technological protection measures (TPM) such as access control technologies can restrict the use of proprietary hardware and copyrighted work ...
(DRM) content-protection.
* Addition of a write-protect notch
Full-size SD cards do not fit into the slimmer MMC slots, and other issues also affect the ability to use one format in a host device designed for the other.
SDHC

The Secure Digital High Capacity (SDHC) format, announced in January 2006 and defined in version 2.0 of the SD specification, supports cards with capacities up to 32 GB.
The SDHC trademark is licensed to ensure compatibility.
[What are SDHC, miniSDHC, and microSDHC?]
SanDisk.
SDHC cards are physically and electrically identical to standard-capacity SD cards (SDSC). The major compatibility issues between SDHC and SDSC cards are the redefinition of the Card-Specific Data (CSD) register in version 2.0 (see
below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
* Soil
* Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
* Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
* Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fr ...
), and the fact that SDHC cards are shipped preformatted with the
FAT32
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
file system.
Version 2.0 also introduces a High-speed bus mode for both SDSC and SDHC cards, which doubles the original Standard Speed clock to produce 25
MB/s
In telecommunications, data-transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are mult ...
.
[Bus Speed (Default Speed/ High Speed/ UHS)]
SDcard.
SDHC host devices are required to accept older SD cards.
[About Compatibility with Host Devices](_blank)
SD Association. However, older host devices do not recognize SDHC or SDXC memory cards, although some devices can do so through a firmware upgrade. Older Windows operating systems released before Windows 7 require patches or service packs to support access to SDHC cards.
SDXC

The Secure Digital eXtended Capacity (SDXC) format, announced in January 2009 and defined in version 3.01 of the SD specification, supports cards up to 2 TB,
compared to a limit of 32 GB
for SDHC cards in the SD 2.0 specification. SDXC adopts Microsoft's
exFAT
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards. exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specificat ...
file system as a mandatory feature.
Version 3.01 also introduced the Ultra High Speed (UHS) bus for both SDHC and SDXC cards, with interface speeds from 50 MB/s to 104 MB/s for four-bit UHS-I bus.
(this number has since been exceeded with SanDisk proprietary technology for 170 MB/s read, which is not proprietary anymore, as Lexar has the 1066x running at 160 MB/s read and 120 MB/s write via UHS 1, and Kingston also has their Canvas Go! Plus, also running at 170 MB/s).
Version 4.0, introduced in June 2011, allows speeds of 156 MB/s to 312 MB/s over the four-lane (two differential lanes) UHS-II bus, which requires an additional row of physical pins.
Version 5.0 was announced in February 2016 at CP+ 2016, and added "Video Speed Class" ratings for UHS cards to handle higher resolution video formats like
8K.
The new ratings define a minimal write speed of 90 MB/s.
SDUC

The Secure Digital Ultra Capacity (SDUC) format, described in the SD 7.0 specification, and announced in June 2018, supports cards up to 128 TB
and offers speeds up to 985 MB/s, regardless of form factor, either micro or full size, or interface type including UHS-I, UHS-II, UHS-III or SD Express. The SD Express interface can also be used with SDHC and SDXC cards.
exFAT filesystem
SDXC and SDUC cards are normally formatted using the
exFAT
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards. exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specificat ...
file system, thereby limiting their use to a limited set of operating systems. Therefore, exFAT-formatted SDXC cards are not a 100% universally readable exchange medium.
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years before, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of ...
(SP1) and later and
OS X
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and la ...
(10.6.5 and later) have native support for exFAT. (Windows XP and Server 2003 can support exFAT via an optional update from Microsoft.)
Most
BSD
The Berkeley Software Distribution or Berkeley Standard Distribution (BSD) is a discontinued operating system based on Research Unix, developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Be ...
and
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which i ...
distributions did not, for legal reasons; though in Linux kernel 5.4 Microsoft open-sourced the spec and allowed the inclusion of an exFAT driver. Users of older kernels or BSD can manually install third-party implementations of exFAT (as a
FUSE
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
module) in order to be able to mount exFAT-formatted volumes. However, SDXC cards can be reformatted to use any file system (such as
ext4
ext4 (fourth extended filesystem) is a journaling file system for Linux, developed as the successor to ext3.
ext4 was initially a series of backward-compatible extensions to ext3, many of them originally developed by Cluster File Systems fo ...
,
UFS UFS may refer to:
Computers
*Universal Flash Storage
*Unix File System
*Unsupervised Forward Selection, a data reduction algorithm
Other
* UFS (trade union), former trade union in the United Kingdom
* United Family Services
* United Feature Sy ...
, or
VFAT
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
), alleviating the restrictions associated with exFAT availability.
Except for the change of file system, SDXC cards are mostly backward compatible with SDHC readers, and many SDHC host devices can use SDXC cards if they are first reformatted to the FAT32 file system.
Nevertheless, in order to be fully compliant with the SDXC card specification, some SDXC-capable host devices are firmware-programmed to expect exFAT on cards larger than 32 GB. Consequently, they may not accept SDXC cards reformatted as FAT32, even if the device supports FAT32 on smaller cards (for SDHC compatibility). Therefore, even if a file system is supported in general, it is not always possible to use alternative file systems on SDXC cards at all depending on how strictly the SDXC card specification has been implemented in the host device. This bears a risk of accidental loss of data, as a host device may treat a card with an unrecognized file system as blank or damaged and
reformat the card.
The SD Association provides a formatting utility for Windows and Mac OS X that checks and formats SD, SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC cards.
Comparison
Speed
SD card speed is customarily rated by its sequential read or write speed. The sequential performance aspect is the most relevant for storing and retrieving large files (relative to block sizes internal to the
flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
), such as images and multimedia. Small data (such as file names, sizes and timestamps) falls under the much lower
speed limit of random access, which can be the limiting factor in some use cases.
With early SD cards, a few card manufacturers specified the speed as a "times" ("×") rating, which compared the average speed of reading data to that of the original
CD-ROM drive. This was superseded by the Speed Class Rating, which guarantees a minimum rate at which data can be written to the card.
The newer families of SD card improve card speed by increasing the bus rate (the frequency of the clock signal that strobes information into and out of the card). Whatever the bus rate, the card can signal to the host that it is "busy" until a read or a write operation is complete. Compliance with a higher speed rating is a guarantee that the card limits its use of the "busy" indication.
Bus
Default Speed
SD Cards will read and write at speeds of 12.5 MB/s.
High Speed
High Speed Mode (25 MB/s) was introduced to support digital cameras with 1.10 spec version.
Ultra High Speed (UHS)
The Ultra High Speed (UHS) bus is available on some SDHC and SDXC cards.
Cards that comply with UHS show Roman numerals 'I', 'II' or 'III' next to the SD card logo,
and report this capability to the host device. Use of UHS-I requires that the host device command the card to drop from 3.3-volt to 1.8-volt operation over the I/O interface pins and select the four-bit transfer mode, while UHS-II requires 0.4-volt operation.
The higher speed rates are achieved by using a two-lane low voltage (0.4 V pp) differential interface. Each lane is capable of transferring up to 156 MB/s. In full-duplex mode, one lane is used for Transmit while the other is used for Receive. In half-duplex mode both lanes are used for the same direction of data transfer allowing a double data rate at the same clock speed. In addition to enabling higher data rates, the UHS-II interface allows for lower interface power consumption, lower I/O voltage and lower electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The following ultra-high speeds are specified:
= UHS-I
=
Specified in SD version 3.01.
Supports a clock frequency of 100 MHz (a quadrupling of the original "Default Speed"), which in four-bit transfer mode could transfer 50 MB/s (SDR50). UHS-I cards declared as UHS104 (SDR104) also support a clock frequency of 208 MHz, which could transfer 104 MB/s.
Double data rate
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in ...
operation at 50 MHz (DDR50) is also specified in Version 3.01, and is mandatory for microSDHC and microSDXC cards labeled as UHS-I. In this mode, four bits are transferred when the clock signal rises and another four bits when it falls, transferring an entire byte on each full clock cycle, hence a 50 MB/s operation could be transferred using a 50 MHz clock.
There is a proprietary UHS-I extension primarily by SanDisk that increases transfer speed further to 170 MB/s, called DDR208 (or DDR200). Unlike UHS-II, it does not use additional pins. It achieves this by using the 208 MHz frequency of the standard SDR104 mode, but using DDR transfers. This extension has since then been used by Lexar for their 1066x series (160 MB/s), Kingston Canvas Go Plus (170 MB/s) and the MyMemory PRO SD card (180 MB/s).
= UHS-II
=

Specified in version 4.0, further raises the data transfer rate to a theoretical maximum of 156 MB/s (full-
duplex
Duplex (Latin, 'double') may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Duplex'' (film), or ''Our House'', a 2003 American black comedy film
* Duplex (band), a Dutch electronic music duo
* Duplex (Norwegian duo)
* Duplex!, a Canadian children's music ...
) or 312 MB/s (half-duplex) using an additional row of pins
(a total of 17 pins for full-size and 16 pins for micro-size cards).
While first implementations in compact system cameras were seen three years after specification (2014), it took many more years until UHS-II was implemented on a regular basis. At the beginning of 2021, there were more than 50 DSLR and compact system cameras using UHS-II.
= UHS-III
=
Version 6.0, released in February 2017, added two new data rates to the standard. FD312 provides 312 MB/s while FD624 doubles that. Both are full-duplex. The physical interface and pin-layout are the same as with UHS-II, retaining backward compatibility.
SD Express

The SD Express bus was released in June 2018 with SD specification 7.0. It uses a single
PCIe
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common m ...
lane to provide full-duplex 985 MB/s transfer speed. Supporting cards must also implement the
NVM Express
NVM Express (NVMe) or Non-Volatile Memory Host Controller Interface Specification (NVMHCIS) is an open, logical-device interface specification for accessing a computer's non-volatile storage media usually attached via PCI Express (PCIe) bus. The ...
storage access protocol. The Express bus can be implemented by SDHC, SDXC, and SDUC cards. For legacy application use, SD Express cards must also support High Speed bus and UHS-I bus. The Express bus re-uses the pin layout of UHS-II cards and reserves the space for additional two pins that may be introduced in the future.
Hosts which implement version 7.0 of the spec allow SD Cards to do
direct memory access
Direct memory access (DMA) is a feature of computer systems and allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system memory independently of the central processing unit (CPU).
Without DMA, when the CPU is using programmed input/output, it is ...
, which increases the attack surface of the host dramatically in the face of malicious SD cards.
Version 8.0 was announced on 19 May 2020, with support for two PCIe lanes with additional row of contacts and PCIe 4.0 transfer rates, for a maximum bandwidth of 3938 MB/s.
= microSD Express
=
In February 2019, the SD Association announced microSD Express. The microSD Express cards offer PCI Express and NVMe interfaces, as the June 2018 SD Express release did, alongside the legacy microSD interface for continued backwards compatibility. The SDA also released visual marks to denote microSD Express memory cards to make matching the card and device easier for optimal device performance.
Bus speed comparison
Compatibility
NOTE: If the card reader uses the DDR208 controller on the UHS 1 pins, the card reader will perform at 180MB/s on applicable UHS 1 cards
Class



The
SD Association
The SD Association (SDA) is an American nonprofit organization that sets standards for the SD memory card format. SanDisk, Panasonic (Matsushita) and Toshiba formed the SD Association in January 2000. In 2010, the SDA had approximately 1,000 mem ...
defines standard speed classes for SDHC/SDXC cards indicating minimum performance (minimum serial data writing speed). Both read and write speeds must exceed the specified value. The specification defines these classes in terms of performance curves that translate into the following minimum read-write performance levels on an empty card and suitability for different applications:
The SD Association defines three types of Speed Class ratings: the original Speed Class, UHS Speed Class, and Video Speed Class.
(Original) Speed Class
Speed Class ratings 2, 4, and 6 assert that the card supports the respective number of megabytes per second as a minimum sustained write speed for a card in a fragmented state.
Class 10 asserts that the card supports 10 MB/s as a minimum non-fragmented sequential write speed and uses a High Speed bus mode.
The host device can read a card's speed class and warn the user if the card reports a speed class that falls below an application's minimum need.
By comparison, the older "×" rating measured maximum speed under ideal conditions, and was vague as to whether this was read speed or write speed.
The graphical symbol for the speed class has a number encircled with 'C' (C2, C4, C6, and C10).
UHS Speed Class
UHS-I and UHS-II cards can use UHS Speed Class rating with two possible grades: class 1 for minimum write performance of at least 10 MB/s ('U1' symbol featuring number 1 inside 'U') and class 3 for minimum write performance of 30 MB/s ('U3' symbol featuring 3 inside 'U'), targeted at recording
4K video
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the domina ...
. Before November 2013, the rating was branded ''UHS Speed Grade'' and contained grades 0 (no symbol) and 1 ('U1' symbol). Manufacturers can also display standard speed class symbols (C2, C4, C6, and C10) alongside, or in place of UHS speed class.
UHS memory cards work best with UHS host devices. The combination lets the user record HD resolution videos with
tapeless camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right side, hot-swa ...
s while performing other functions. It is also suitable for real-time broadcasts and capturing large HD videos.
Video Speed Class
Video Speed Class defines a set of requirements for UHS cards to match the modern
MLC NAND flash memory
and supports progressive 4K and 8K video with minimum sequential writing speeds of 6 – 90 MB/s.
The graphical symbols use a stylized 'V' followed by a number designating write speed (''i.e.'' V6, V10, V30, V60, and V90).
Comparison
Application Performance Class
''Application Performance Class'' is a newly defined standard from the SD Specification 5.1 and 6.0 which not only define sequential Writing Speeds but also mandates a minimum
IOPS
Input/output operations per second (IOPS, pronounced ''eye-ops'') is an input/output performance measurement used to characterize computer storage devices like hard disk drives (HDD), solid state drives (SSD), and storage area networks (SAN). ...
for reading and writing. Class A1 requires a minimum of 1500 reading and 500 writing operations per second, while class A2 requires 4000 and 2000 IOPS. A2 class cards require host driver support as they use command queuing and write caching to achieve their higher speeds. If used in an unsupported host, they might even be slower than other A1 cards, and if power is lost before cached data is actually written from the card's internal RAM to the card's internal flash RAM, that data is likely to be lost.
"×" rating
The "×" rating, that was used by some card manufacturers and made obsolete by speed classes, is a multiple of the standard
CD-ROM drive speed of 150
KB/s
In telecommunications, data-transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are mult ...
(approximately 1.23
Mbit/s
In telecommunications, data-transfer rate is the average number of bits ( bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are mul ...
). Basic cards transfer data at up to six times (6×) the CD-ROM speed; that is, 900 kbit/s or 7.37 Mbit/s. The 2.0 specification defines speeds up to 200×, but is not as specific as Speed Classes are on how to measure speed. Manufacturers may report best-case speeds and may report the card's fastest read speed, which is typically faster than the write speed. Some vendors, including
Transcend and
Kingston
Kingston may refer to:
Places
* List of places called Kingston, including the five most populated:
** Kingston, Jamaica
** Kingston upon Hull, England
** City of Kingston, Victoria, Australia
** Kingston, Ontario, Canada
** Kingston upon Thames, ...
, report their cards' write speed. When a card lists both a speed class and an "×" rating, the latter may be assumed a read speed only.
Real-world performance
In applications that require sustained write throughput, such as video recording, the device might not perform satisfactorily if the SD card's class rating falls below a particular speed. For example, a high-definition
camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video camera, video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right s ...
may require a card of not less than Class 6, suffering dropouts or corrupted video if a slower card is used.
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devic ...
s with slow cards may take a noticeable time after taking a photograph before being ready for the next, while the camera writes the first picture.
The speed class rating does not totally characterize card performance. Different cards of the same class may vary considerably while meeting class specifications. A card's speed depends on many factors, including:
* The frequency of soft errors that the card's controller must re-try
*
Write amplification
Write amplification (WA) is an undesirable phenomenon associated with flash memory and solid-state drives (SSDs) where the actual amount of information physically written to the storage media is a multiple of the logical amount intended to be wr ...
: The flash controller may need to overwrite more data than requested. This has to do with performing read-modify-write operations on write blocks, freeing up (the much larger) erase blocks, while moving data around to achieve
wear leveling Wear leveling (also written as wear levelling) is a technique Wear leveling techniques for flash memory systems. for prolonging the service life of some kinds of erasable computer storage media, such as flash memory, which is used in solid-state d ...
.
*
File fragmentation
In computing, file system fragmentation, sometimes called file system aging, is the tendency of a file system to lay out the contents of files non-continuously to allow in-place modification of their contents. It is a special case of data fragment ...
: where there is not sufficient space for a file to be recorded in a contiguous region, it is split into non-contiguous fragments. This does not cause rotational or head-movement delays as with electromechanical
hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magne ...
s, but may decrease speed — for instance, by requiring additional reads and computation to determine where on the card the file's next fragment is stored.
In addition, speed may vary markedly between writing a large amount of data to a single file (
sequential access
Sequential access is a term describing a group of elements (such as data in a memory array or a disk file or on magnetic tape data storage) being accessed in a predetermined, ordered sequence. It is the opposite of random access, the ability to a ...
, as when a
digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devic ...
records large photographs or videos) and writing a large number of small files (a
random-access
Random access (more precisely and more generally called direct access) is the ability to access an arbitrary element of a sequence in equal time or any datum from a population of addressable elements roughly as easily and efficiently as any othe ...
use common in
smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
s). A study in 2012 found that, in this random-access use, some Class 2 cards achieved a write speed of 1.38
MB/s
In telecommunications, data-transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are mult ...
, while all cards tested of Class 6 or greater (and some of lower Classes; lower Class does not ''necessarily'' mean better small-file performance), including those from major manufacturers, were over 100 times slower.
[ In 2014, a blogger measured a 300-fold performance difference on small writes; this time, the best card in this category was a class 4 card.][
]
Features
Card security
Cards can protect their contents from erasure or modification, prevent access by non-authorized users, and protect copyrighted content using digital rights management.
Commands to disable writes
The host device can command the SD card to become read-only (to reject subsequent commands to write information to it). There are both reversible and irreversible host commands that achieve this.
Write-protect notch

 Most full-size SD cards have a "mechanical write protect switch" allowing the user to advise the host computer that the user wants the device to be treated as read-only. This does not protect the data on the card if the host is compromised: "It is the responsibility of the host to protect the card. The position .e., settingof the write protect switch is unknown to the internal circuitry of the card." Some host devices do not support write protection, which is an optional feature of the SD specification, and drivers and devices that do obey a read-only indication may give the user a way to override it.
The switch is a sliding tab that covers a notch in the card. The miniSD and microSD formats do not directly support a write protection notch, but they can be inserted into full-size adapters which do.
When looking at the SD card from the top, the right side (the side with the beveled corner) must be notched.
On the left side, there may be a write-protection notch. If the notch is omitted, the card can be read and written. If the card is notched, it is read-only. If the card has a notch and a sliding tab which covers the notch, the user can slide the tab upward (toward the contacts) to declare the card read/write, or downward to declare it read-only. The diagram to the right shows an orange sliding write-protect tab in both the unlocked and locked positions.
Cards sold with content that must not be altered are permanently marked read-only by having a notch and no sliding tab.
Most full-size SD cards have a "mechanical write protect switch" allowing the user to advise the host computer that the user wants the device to be treated as read-only. This does not protect the data on the card if the host is compromised: "It is the responsibility of the host to protect the card. The position .e., settingof the write protect switch is unknown to the internal circuitry of the card." Some host devices do not support write protection, which is an optional feature of the SD specification, and drivers and devices that do obey a read-only indication may give the user a way to override it.
The switch is a sliding tab that covers a notch in the card. The miniSD and microSD formats do not directly support a write protection notch, but they can be inserted into full-size adapters which do.
When looking at the SD card from the top, the right side (the side with the beveled corner) must be notched.
On the left side, there may be a write-protection notch. If the notch is omitted, the card can be read and written. If the card is notched, it is read-only. If the card has a notch and a sliding tab which covers the notch, the user can slide the tab upward (toward the contacts) to declare the card read/write, or downward to declare it read-only. The diagram to the right shows an orange sliding write-protect tab in both the unlocked and locked positions.
Cards sold with content that must not be altered are permanently marked read-only by having a notch and no sliding tab.
Card password
 A host device can lock an SD card using a password of up to 16 bytes, typically supplied by the user. A locked card interacts normally with the host device except that it rejects commands to read and write data. A locked card can be unlocked only by providing the same password. The host device can, after supplying the old password, specify a new password or disable locking. Without the password (typically, in the case that the user forgets the password), the host device can command the card to erase all the data on the card for future re-use (except card data under DRM), but there is no way to gain access to the existing data.
A host device can lock an SD card using a password of up to 16 bytes, typically supplied by the user. A locked card interacts normally with the host device except that it rejects commands to read and write data. A locked card can be unlocked only by providing the same password. The host device can, after supplying the old password, specify a new password or disable locking. Without the password (typically, in the case that the user forgets the password), the host device can command the card to erase all the data on the card for future re-use (except card data under DRM), but there is no way to gain access to the existing data.
Windows Phone 7
Windows Phone 7 is the first release of the Windows Phone mobile client operating system, released worldwide on October 21, 2010, and in the United States on November 8, 2010. It runs on the Windows CE 6.0 kernel.
It received multiple large upda ...
devices use SD cards designed for access only by the phone manufacturer or mobile provider. An SD card inserted into the phone underneath the battery compartment becomes locked "to the phone with an automatically generated key" so that "the SD card cannot be read by another phone, device, or PC". Symbian
Symbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. It was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for personal digital assistants in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian ...
devices, however, are some of the few that can perform the necessary low-level format operations on locked SD cards. It is therefore possible to use a device such as the Nokia N8
The Nokia N8 is a touchscreen-based smartphone developed by Nokia. Announced on 27 April 2010, the Nokia N8 was the first device to run on the Symbian^3 mobile operating system and it was the company's flagship device for the year. It was relea ...
to reformat the card for subsequent use in other devices.
smartSD cards
A smartSD memory card is a microSD card with an internal "secure element" that allows the transfer of ISO 7816 Application Protocol Data Unit commands to, for example, JavaCard
Java Card is a software technology that allows Java-based applications (applets) to be run securely on smart cards and more generally on similar secure small memory footprint deviceswhich are called “secure elements” (SE). Today, a Secure E ...
applets running on the internal secure element through the SD bus.
Some of the earliest versions of microSD memory cards with secure elements were developed in 2009 by DeviceFidelity, Inc., a pioneer in near field communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be ...
(NFC) and mobile payments
A mobile payment, also referred to as mobile money, mobile money transfer and mobile wallet, is any of various payment processing services operated under financial regulations and performed from or via a mobile device, as the cardinal class of ...
, with the introduction of In2Pay and CredenSE products, later commercialized and certified for mobile contactless transactions by Visa
Visa most commonly refers to:
*Visa Inc., a US multinational financial and payment cards company
** Visa Debit card issued by the above company
** Visa Electron, a debit card
** Visa Plus, an interbank network
*Travel visa, a document that allows ...
in 2010. DeviceFidelity also adapted the In2Pay microSD to work with the Apple iPhone using the iCaisse, and pioneered the first NFC transactions and mobile payments on an Apple device in 2010.
Various implementations of smartSD cards have been done for payment applications and secured authentication. In 2012 Good Technology
Good Technology, owned by BlackBerry Limited, is a mobile security provider headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, United States.
The company serves more than 5,000 organizations worldwide in industries such as financial services, healthcare, ...
partnered with DeviceFidelity to use microSD cards with secure elements for mobile identity
Mobile identity is a development of online authentication and digital signatures, where the SIM card of one’s mobile phone works as an identity tool. Mobile identity enables legally binding authentication and transaction signing for online b ...
and access control
In the fields of physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the selective restriction of access to a place or other resource, while access management describes the process. The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming ...
.
microSD cards with Secure Elements and NFC (near field communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be ...
) support are used for mobile payments, and have been used in direct-to-consumer mobile wallets and mobile banking solutions, some of which were launched by major banks around the world, including Bank of America
The Bank of America Corporation (often abbreviated BofA or BoA) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services holding company headquartered at the Bank of America Corporate Center in Charlotte, North Carolina. The bank ...
, US Bank
U.S. Bancorp (stylized as us bancorp) is an American bank holding company based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and incorporated in Delaware. It is the parent company of U.S. Bank National Association, and is the fifth largest banking institution ...
, and Wells Fargo
Wells Fargo & Company is an American multinational financial services company with corporate headquarters in San Francisco, California; operational headquarters in Manhattan; and managerial offices throughout the United States and inter ...
, while others were part of innovative new direct-to-consumer neobank
A neobank (also known as an online bank, internet-only bank, virtual bank or digital bank) is a type of direct bank that operates exclusively online without traditional physical branch networks. The term " challenger bank" is used in the UK to r ...
programs such as moneto, first launched in 2012.
microSD cards with Secure Elements have also been used for secure voice encryption
Secure voice (alternatively secure speech or ciphony) is a term in cryptography for the encryption of voice communication over a range of communication types such as radio, telephone or IP.
History
The implementation of voice encryption dat ...
on mobile devices, which allows for one of the highest levels of security in person-to-person voice communications. Such solutions are heavily used in intelligence and security.
In 2011, HID Global
HID Global is an American manufacturer of secure identity products. The company is an independent brand of Assa Abloy, a Swedish door and access control conglomerate. Björn Lidefelt was appointed CEO on 27 January 2020. He succeeded Stefan Wid ...
partnered with Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public research university in the Phoenix metropolitan area. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, ASU is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in t ...
to launch campus access solutions for students using microSD with Secure Element and MiFare
MIFARE is the NXP Semiconductors-owned trademark of a series of integrated circuit (IC) chips used in contactless smart cards and proximity cards.
The brand name covers proprietary solutions based upon various levels of the ISO/IEC 14443 Type A ...
technology provided by DeviceFidelity, Inc. This was the first time regular mobile phones could be used to open doors without need for electronic access keys.
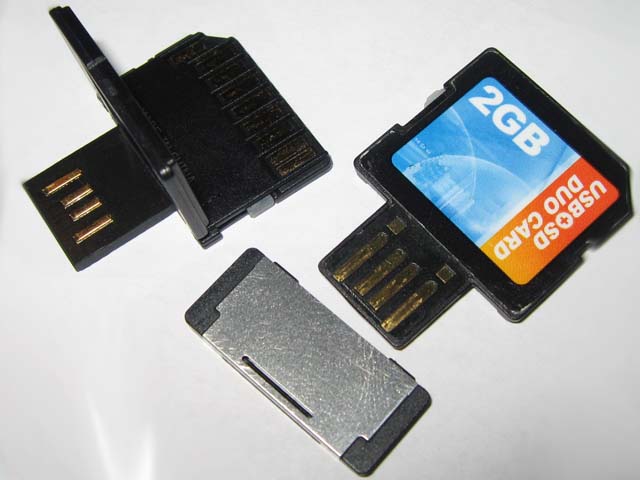
Vendor enhancements
 Vendors have sought to differentiate their products in the market through various vendor-specific features:
* Integrated
Vendors have sought to differentiate their products in the market through various vendor-specific features:
* Integrated Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio w ...
– Several companies produce SD cards with built-in Wi-Fi transceivers supporting static security (WEP 40; 104; and 128, WPA-PSK, and WPA2-PSK). The card lets any digital camera with an SD slot transmit captured images over a wireless network, or store the images on the card's memory until it is in range of a wireless network. Examples include: Eye-Fi
Eye-Fi was a company based in Mountain View, California, that produced SD memory cards with Wi-Fi capabilities. Using an Eye-Fi card inside a digital camera, one could wirelessly and automatically upload digital photos to a local computer or ...
/ SanDisk
SanDisk is a brand for flash memory products, including memory cards and readers, USB flash drives, solid-state drives, and digital audio players, manufactured and marketed by Western Digital. The original company, SanDisk Corporation was acquire ...
, Transcend Wi-Fi
Transcend may refer to:
* ''Transcend'' (album) (2004), an album by Canadian singer-songwriter Carole Pope
* Transcend Information, a Taiwanese electronics manufacturer
* Transcend Music, a British record label
* '' Transcend: Nine Steps to Livi ...
, Toshiba FlashAir
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems ...
, Trek Flucard
Flucard is a wireless SD card that is used primarily with digital cameras. The Flucard is manufactured by Trek 2000 International, which is the Singaporean company that is one of the purported inventors of the ThumbDrive technology.
Features
Th ...
, PQI Air Card PQI may refer to:
* Presque Isle International Airport, IATA airport code
* Print Quality Improvement, data exchange format of Advanced Photo System
* Predictive Quantities Indicator, used for College and university rankings
* Pittsburgh Quantum I ...
and LZeal ez Share. Some models geotag
Geotagging, or GeoTagging, is the process of adding geographical identification metadata to various media such as a geotagged photograph or video, websites, SMS messages, QR Codes or RSS feeds and is a form of geospatial metadata. This data u ...
their pictures.
* Pre-loaded content – In 2006, SanDisk announced Gruvi Gruvi was a short-lived memory card format compatible with microSD developed by Sandisk in 2006. It used the company's TrustedFlash card technology, which functioned like the conventional SD card but it could be extended to on-demand content. The ca ...
, a microSD card with extra digital rights management features, which they intended as a medium for publishing content. SanDisk again announced pre-loaded cards in 2008, under the slotMusic
slotMusic was a brand of microSD memory card developed by SanDisk preloaded with music in MP3 format. They were first available at Wal-Mart and Best Buy stores in October 2008. The current selection of songs comes from Universal Music Group, Sony B ...
name, this time not using any of the DRM capabilities of the SD card. In 2011, SanDisk offered various collections of 1000 songs on a single slotMusic card for about $40, now restricted to compatible devices and without the ability to copy the files.
* Integrated USB connector – The SanDisk
SanDisk is a brand for flash memory products, including memory cards and readers, USB flash drives, solid-state drives, and digital audio players, manufactured and marketed by Western Digital. The original company, SanDisk Corporation was acquire ...
SD Plus product can be plugged directly into a USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply ( interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers. A broa ...
port without needing a USB card reader. Other companies introduced comparable products, such as the Duo SD product of OCZ Technology and the 3 Way (microSDHC, SDHC, and USB) product of A-DATA, which was available in 2008 only.
* Different colors – SanDisk has used various colors of plastic or adhesive label, including a "gaming" line in translucent plastic colors that indicated the card's capacity.
* Integrated display – In 2006, A-DATA announced a Super Info SD card with a digital display that provided a two-character label and showed the amount of unused memory on the card.
SDIO cards
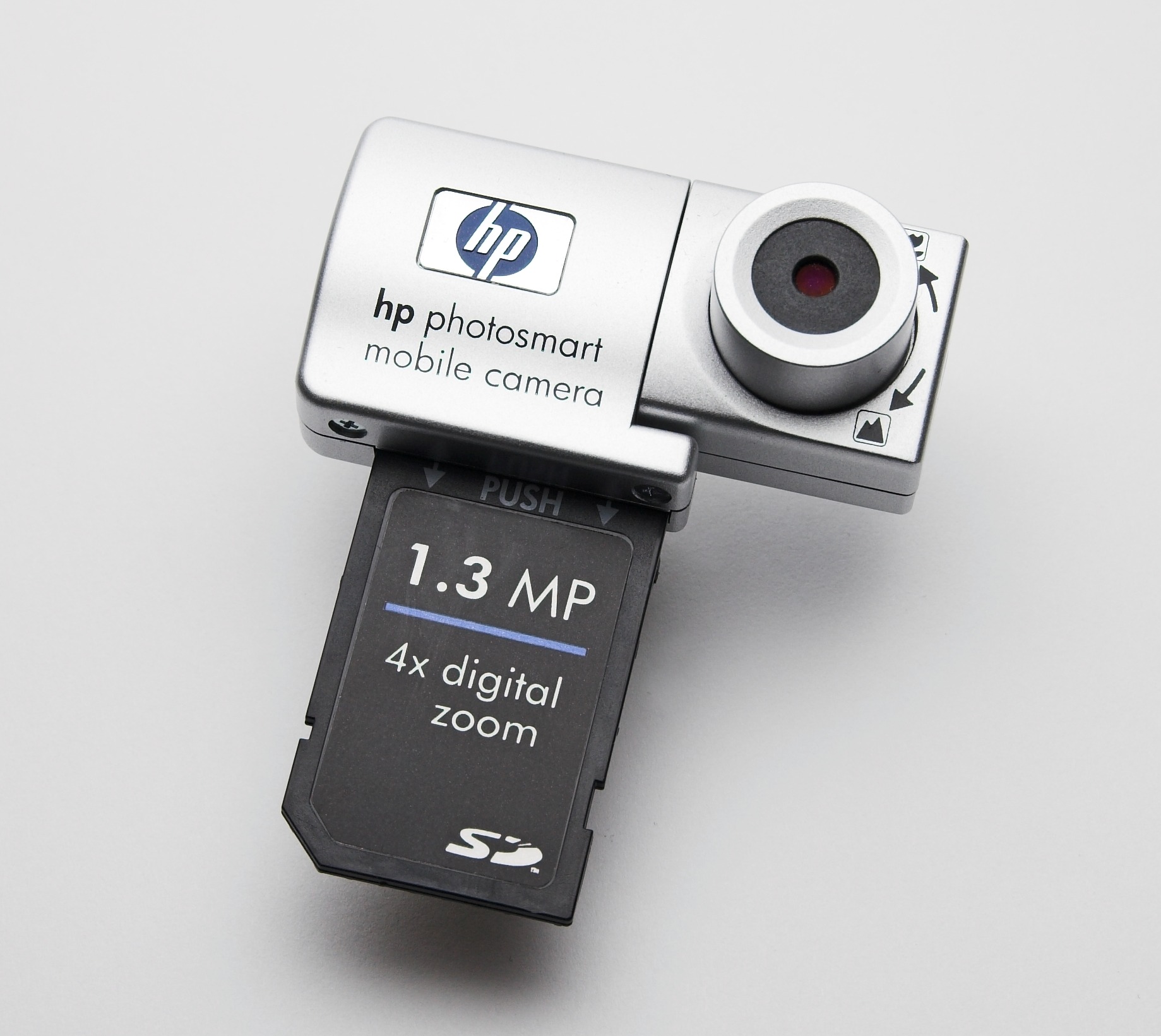 A SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output) card is an extension of the SD specification to cover I/O functions. SDIO cards are only fully functional in host devices designed to support their input-output functions (typically PDAs like the
A SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output) card is an extension of the SD specification to cover I/O functions. SDIO cards are only fully functional in host devices designed to support their input-output functions (typically PDAs like the Palm Treo
The Palm Treo (stylized as Trēo) is a discontinued line of smartphones originally developed by Handspring, which was bought by Palm, Inc. They were then manufactured and maintained by Palm, Inc. Treos had a number of integrated features such ...
, but occasionally laptops or mobile phones). These devices can use the SD slot to support GPS
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite sy ...
receivers, modem
A modulator-demodulator or modem is a computer hardware device that converts data from a digital format into a format suitable for an analog transmission medium such as telephone or radio. A modem transmits data by modulating one or more c ...
s, barcode reader
A barcode reader is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes, decode the data contained in the barcode to a computer. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens and a light sensor for translating optical impulses into ...
s, FM radio tuners, TV tuners, RFID
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electroma ...
readers, digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devic ...
s, and interfaces to Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio w ...
, Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limit ...
, Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in ...
, and IrDA
The Infrared Data Association (IrDA) is an industry-driven interest group that was founded in 1994 by around 50 companies. IrDA provides specifications for a complete set of protocols for wireless infrared communications, and the name "IrDA" also ...
. Many other SDIO devices have been proposed, but it is now more common for I/O devices to connect using the USB interface.
SDIO cards support most of the memory commands of SD cards. SDIO cards can be structured as eight logical cards, although currently, the typical way that an SDIO card uses this capability is to structure itself as one I/O card and one memory card.
The SDIO and SD interfaces are mechanically and electrically identical. Host devices built for SDIO cards generally accept SD memory cards without I/O functions. However, the reverse is not true, because host devices need suitable drivers and applications to support the card's I/O functions. For example, an HP SDIO camera usually does not work with PDAs that do not list it as an accessory. Inserting an SDIO card into any SD slot causes no physical damage nor disruption to the host device, but users may be frustrated that the SDIO card does not function fully when inserted into a seemingly compatible slot. (USB and Bluetooth devices exhibit comparable compatibility issues, although to a lesser extent thanks to standardized USB device classes and Bluetooth profiles
In order to use Bluetooth, a device must be compatible with the subset of Bluetooth ''profiles'' (often called services or functions) necessary to use the desired services. A Bluetooth profile is a specification regarding an aspect of Bluetooth-b ...
.)
The SDIO SDIO may refer to:
* Secure Digital Input Output, a type of Secure Digital card interface. It can be used as an interface for input or output devices.
* Strategic Defense Initiative Organization
The Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI), derisivel ...
family comprises Low-Speed and Full-Speed cards. Both types of SDIO cards support SPI and one-bit SD bus types. Low-Speed SDIO cards are allowed to also support the four-bit SD bus; Full-Speed SDIO cards are required to support the four-bit SD bus. To use an SDIO card as a "combo card" (for both memory and I/O), the host device must first select four-bit SD bus operation. Two other unique features of Low-Speed SDIO are a maximum clock rate of 400 kHz for all communications, and the use of Pin 8 as "interrupt" to try to initiate dialogue with the host device.
Ganging cards together
The one-bit SD protocol was derived from the MMC protocol, which envisioned the ability to put up to three cards on a bus of common signal lines. The cards use open collector
An open collector is a common type of output found on many integrated circuits (IC), which behaves like a switch that is either connected to ground or disconnected. Instead of outputting a signal of a specific voltage or current, the output sig ...
interfaces, where a card may pull a line to the low voltage level; the line is at the high voltage level (because of a pull-up resistor
In electronic logic circuits, a pull-up resistor (PU) or pull-down resistor (PD) is a resistor used to ensure a known state for a signal. It is typically used in combination with components such as switches and transistors, which physically in ...
) if no card pulls it low. Though the cards shared clock and signal lines, each card had its own chip select
Chip select (CS) or slave select (SS) is the name of a control line in digital electronics used to select one (or a set) of integrated circuits (commonly called "chips") out of several connected to the same computer bus, usually utilizing the th ...
line to sense that the host device had selected it.
The SD protocol envisioned the ability to gang 30 cards together without separate chip select lines. The host device would broadcast commands to all cards and identify the card to respond to the command using its unique serial number.
In practice, cards are rarely ganged together because open-collector operation has problems at high speeds and increases power consumption. Newer versions of the SD specification recommend separate lines to each card.
Compatibility
Host devices that comply with newer versions of the specification provide backward compatibility
Backward compatibility (sometimes known as backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with input designed for such a system, especially ...
and accept older SD cards.file system
In computing, file system or filesystem (often abbreviated to fs) is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one lar ...
the host device cannot navigate (FAT32
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
for SDHC, exFAT
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards. exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specificat ...
for SDXC)
* Use of an SDIO card requires the host device be designed for the input/output functions the card provides.
* The hardware interface of the card was changed starting with the version 2.0 (new high-speed bus clocks, redefinition of storage capacity bits) and SDHC
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile flash memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
The standard was introduced in August 1999 by joint efforts between Sa ...
family (Ultra-high speed (UHS) bus)
* UHS-II has physically more pins but is backwards compatible to UHS-I and non-UHS for both slot and card.
Markets
Due to their compact size, Secure Digital cards are used in many consumer electronic devices, and have become a widespread means of storing several gigabytes of data in a small size. Devices in which the user may remove and replace cards often, such as digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devic ...
s, camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video camera, video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right s ...
s, and video game console
A video game console is an electronic device that outputs a video signal or image to display a video game that can be played with a game controller. These may be home consoles, which are generally placed in a permanent location connected to ...
s, tend to use full-sized cards. Devices in which small size is paramount, such as mobile phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive telephone call, calls over a radio freq ...
s, action camera
An action camera or action cam is a digital camera designed for recording action while being immersed in it. Action cameras are therefore typically compact and rugged, and waterproof at surface-level. They typically use CMOS image sensors, and ...
s such as the GoPro Hero series, and camera drones, tend to use microSD cards.
Mobile phones
The microSD card has helped propel the smartphone market by giving both manufacturers and consumers greater flexibility and freedom.
While cloud storage
Cloud storage is a model of computer data storage in which the digital data is stored in logical pools, said to be on "the cloud". The physical storage spans multiple servers (sometimes in multiple locations), and the physical environment is ty ...
depends on stable internet connection and sufficiently voluminous data plan
Data plan refers to data quotas from a telecommunications or data hosting contract. Data plans are offered by internet service providers. These include mobile data plans, offered on cellular networks, from cellular telephony companies, and those ...
s, memory cards in mobile devices provide location-independent and private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* "In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorded ...
storage expansion with much higher transfer rates and no latency (engineering)
Latency, from a general point of view, is a time delay between the cause and the effect of some physical change in the system being observed. Lag, as it is known in gaming circles, refers to the latency between the input to a simulation and ...
(), enabling applications such as photography
Photography is the visual art, art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It i ...
and video recording
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) system ...
. While data stored internally on bricked devices is inaccessible, data stored on the memory card can be salvaged and accessed externally by the user as mass storage
In computing, mass storage refers to the storage of large amounts of data in a persisting and machine-readable fashion. In general, the term is used as large in relation to contemporaneous hard disk drives, but it has been used large in relati ...
device. A benefit over USB on the go
USB On-The-Go (USB OTG or just OTG) is a specification first used in late 2001 that allows USB devices, such as tablets or smartphones, to act as a host, allowing other USB devices, such as USB flash drives, digital cameras, mouse or keyboard ...
storage expansion is uncompromised ergonomy
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learnin ...
. The usage of a memory card also protects the mobile phone's non-replaceable internal storage from weardown from heavy applications such as excessive camera usage and portable FTP server hosting over WiFi Direct
Wi-Fi Direct (formerly Wi-Fi Peer-to-Peer) is a Wi-Fi standard for peer-to-peer wireless connections that allows two devices to establish a direct Wi-Fi connection without an intermediary wireless access point, router, or Internet connection. Wi- ...
. Due to the technical development
Technological change (TC) or technological development is the overall process of invention, innovation and diffusion of technology or processes.From ''The New Palgrave Dictionary otechnical change by S. Metcalfe. •biased and biased tec ...
of memory cards, users of existing mobile devices are able to expand their storage further and priceworthier with time.
Recent versions of major operating systems such as Windows Mobile
Windows Mobile is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.
Its origin dated back to Windows CE in 1996, though Windows Mobile itself first appeared in 2000 as Pock ...
and Android
Android may refer to:
Science and technology
* Android (robot), a humanoid robot or synthetic organism designed to imitate a human
* Android (operating system), Google's mobile operating system
** Bugdroid, a Google mascot sometimes referred to ...
allow applications to run from microSD cards, creating possibilities for new usage models for SD cards in mobile computing markets, as well as clearing available internal storage space.
SD cards are not the most economical solution in devices that need only a small amount of non-volatile memory, such as station presets in small radios. They may also not present the best choice for applications that require higher storage capacities or speeds as provided by other flash card standards such as CompactFlash
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.
CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the ...
. These limitations may be addressed by evolving memory technologies, such as the new SD 7.0 specifications which allow storage capabilities of up to 128 TB.PC card
In computing, PC Card is a configuration for computer parallel communication peripheral interface, designed for laptop computers. Originally introduced as PCMCIA, the PC Card standard as well as its successors like CardBus were defined and devel ...
, ExpressBus, USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors and protocols for connection, communication and power supply ( interfacing) between computers, peripherals and other computers. A broa ...
, FireWire
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony a ...
, and the parallel printer port. Active adapters also let SD cards be used in devices designed for other formats, such as CompactFlash
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.
CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the ...
. The FlashPath
FlashPath (FlashPath Floppy Disk Adapter) were a series of devices produced by SmartDisk that allowed a variety of memory cards to be used in a 3.5" Floppy disk drive. The initial version introduced in May 1998 allowed SmartMedia cards to be us ...
adapter lets SD cards be used in a floppy disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, or a diskette) is an obsolescent type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined ...
drive.
Some devices such as the Samsung Galaxy Fit (2011) and Samsung Galaxy Note 8.0
The Samsung Galaxy Note 8.0 is an 8-inch Android-based tablet computer produced and marketed by Samsung Electronics. It belongs to the second generation of the Samsung Galaxy Note series tablets, which also includes a 10.1-inch model, the Galax ...
(2013) have an SD card compartment located externally and accessible by hand, while it is located under the battery cover on other devices. More recent mobile phones use a pin-hole ejection system for the tray which houses both the memory card and SIM card
A typical SIM card (mini-SIM with micro-SIM cutout)
A file:Simkarte NFC SecureElement.jpg">thumb"> thumb">A TracFone Wireless SIM card has no distinctive carrier markings and is only marked as a "SIM card"
A SIM card (full form Subscriber Ide ...
.
Counterfeits
 Commonly found on the market are mislabeled or counterfeit Secure Digital cards that report a fake capacity or run slower than labeled.
Commonly found on the market are mislabeled or counterfeit Secure Digital cards that report a fake capacity or run slower than labeled.random data
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of pattern or predictability in events. A random sequence of events, symbols or steps often has no order and does not follow an intelligible pattern or combination. Individual ran ...
to the SD card until the card's capacity is reached, and copying them back. The files that were copied back can be tested either by comparing checksums (e.g. MD5), or trying to compress
compress is a Unix shell compression program based on the LZW compression algorithm. Compared to more modern compression utilities such as gzip and bzip2, compress performs faster and with less memory usage, at the cost of a significantly l ...
them. The latter approach leverages the fact that counterfeited cards let the user read back files, which then consist of easily compressible uniform data (for example, repeating 0xFF
255 (two hundred ndfifty-five) is the natural number following 254 and preceding 256.
In mathematics
Its factorization makes it a sphenic number. Since 255 = 28 – 1, it is a Mersenne number (though not a pernicious one), and the fourth such ...
s).
Digital cameras
 SD/MMC cards replaced
SD/MMC cards replaced Toshiba
, commonly known as Toshiba and stylized as TOSHIBA, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Its diversified products and services include power, industrial and social infrastructure systems ...
's SmartMedia
SmartMedia is an obsolete flash memory card standard owned by Toshiba, with capacities ranging from 2 MB to 128 MB. The format mostly saw application in the early 2000s in digital cameras and audio production. SmartMedia memory cards ar ...
as the dominant memory card format used in digital cameras. In 2001, SmartMedia had achieved nearly 50% use, but by 2005 SD/MMC had achieved over 40% of the digital camera market and SmartMedia's share had plummeted by 2007.
At this time, all the leading digital camera manufacturers used SD in their consumer product lines, including Canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the conceptual material accepted as official in a fictional universe by its fan base
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western can ...
, Casio
is a Japanese multinational electronics manufacturing corporation headquartered in Shibuya, Tokyo, Japan. Its products include calculators, mobile phones, digital cameras, electronic musical instruments, and analogue and digital watches. I ...
, Fujifilm
, trading as Fujifilm, or simply Fuji, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, operating in the realms of photography, optics, office and medical electronics, biotechnology, and chemicals.
The offerings from ...
, Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
, Leica
Leica Camera AG () is a German company that manufactures cameras, optical lenses, photographic lenses, binoculars, rifle scopes and microscopes. The company was founded by Ernst Leitz in 1869 (Ernst Leitz Wetzlar), in Wetzlar, Germany.
...
, Nikon
(, ; ), also known just as Nikon, is a Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, specializing in optics and imaging products. The companies held by Nikon form the Nikon Group.
Nikon's products include cameras, camera ...
, Olympus, Panasonic
formerly between 1935 and 2008 and the first incarnation of between 2008 and 2022, is a major Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka. It was founded by Kōnosuke Matsushita in 1918 as a lightbulb ...
, Pentax
is a brand name used primarily by the Japanese multinational imaging and electronics company Ricoh for DSLR cameras, lenses, sport optics (including binoculars and rifle scopes), and CCTV optics. The Pentax brand is also used by Hoya Corpora ...
, Ricoh
is a Japanese multinational imaging and electronics company. It was founded by the now-defunct commercial division of the Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (Riken) known as the ''Riken Concern'', on 6 February 1936 as . Ricoh's he ...
, Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
, and Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
. Formerly, Olympus and Fujifilm
, trading as Fujifilm, or simply Fuji, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, operating in the realms of photography, optics, office and medical electronics, biotechnology, and chemicals.
The offerings from ...
used XD-Picture Card
The xD-Picture Card is an obsolete form of flash memory card, used in digital cameras made by Olympus and Fujifilm during the 2000s. The xD in the xD-Picture Card stands for eXtreme Digital.
xD cards were manufactured with capacities of 16&n ...
s (xD cards) exclusively, while Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
only used Memory Stick
The Memory Stick is a removable flash memory card format, originally launched by Sony in late 1998. In addition to the original Memory Stick, this family includes the Memory Stick PRO, a revision that allows greater maximum storage capacity an ...
; by early 2010 all three supported SD.
Some prosumer
A prosumer is an individual who both consumes and produces. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''producer'' and ''consumer''. Research has identified six types of prosumers: DIY prosumers, self-service prosumers, customizing prosumers, colla ...
and professional digital cameras continued to offer CompactFlash
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.
CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the ...
(CF), either on a second card slot or as the only storage, as CF supports much higher maximum capacities and historically was cheaper for the same capacity.
Secure Digital memory cards can be used in Sony XDCAM
XDCAM is a series of products for digital recording using random access solid-state memory media, introduced by Sony in 2003. Four different product lines the XDCAM SD, XDCAM HD, XDCAM EX and XDCAM HD422 differ in types of en ...
EX camcorder
A camcorder is a self-contained portable electronic device with video camera, video and recording as its primary function. It is typically equipped with an articulating screen mounted on the left side, a belt to facilitate holding on the right s ...
s with an adapter and in Panasonic P2 card equipment with a MicroP2
MicroP2 is a memory card format introduced by Panasonic.
The cards were announced in April 2012 and shipped in March 2013.
Physically, MicroP2 is a SDXC/SDHC
Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile fla ...
adapter.
Personal computers
Although many personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tech ...
s accommodate SD cards as an auxiliary storage device using a built-in slot, or can accommodate SD cards by means of a USB adapter, SD cards cannot be used as the primary hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with mag ...
through the onboard ATA controller, because none of the SD card variants support ATA signalling. Primary hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with mag ...
use requires a separate SD host controller or an SD-to-CompactFlash converter. However, on computers that support bootstrapping
In general, bootstrapping usually refers to a self-starting process that is supposed to continue or grow without external input.
Etymology
Tall boots may have a tab, loop or handle at the top known as a bootstrap, allowing one to use fingers ...
from a USB interface, an SD card in a USB adapter can be the boot disk, provided it contains an operating system that supports USB access once the bootstrap is complete.
In laptop and tablet computer
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being comput ...
s, memory cards in an integrated memory card reader
A memory card reader is a device for accessing the data on a memory card such as a CompactFlash (CF), Secure Digital (SD) or MultiMediaCard (MMC). Most card readers also offer write capability, and together with the card, this can function as ...
offer an ergonomic
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learnin ...
al benefit over USB flash drive
A flash drive is a portable computer drive that uses flash memory. Flash drives are the larger memory modules consisting of a number of flash chips. A flash chip is used to read the contents of a single cell, but it can write entire block of cell ...
s, as the latter sticks out of the device, and the user would need to be cautious not to bump it while transporting the device, which could damage the USB port. Memory cards have a unified shape and do not reserve a USB port when inserted into a computer's dedicated card slot.
Since late 2009, newer Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ances ...
computers with installed SD card readers have been able to boot in macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
from SD storage devices, when properly formatted to Mac OS Extended file format and the default partition table set to GUID Partition Table
The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers, which are also known as globally unique ...
. (See Other file systems below).
SD cards are increasing in usage and popularity among owners of vintage computers like 8-bit Atari. For example SIO2SD (SIO
Sio may refer to:
Places
* Sió, an artificial channel in Hungary
* Siø, a small Danish island in the South Funen Archipelago
* Sio, Burkina Faso, a village in Burkina Faso
* Sio, Mali, a commune in Mali
* Sio, Papua New Guinea, a town in ...
is an Atari port for connecting external devices) is used nowadays. Software for an 8-bit Atari may be included on one SD card that may have less than 4-8 GB of disk size (2019).
Embedded systems
 In 2008, the SDA specified Embedded SD, "leverag ngwell-known SD standards" to enable non-removable SD-style devices on printed circuit boards. However this standard was not adopted by the market while the
In 2008, the SDA specified Embedded SD, "leverag ngwell-known SD standards" to enable non-removable SD-style devices on printed circuit boards. However this standard was not adopted by the market while the MMC MMC may stand for:
Business
*Mail.com Media Corp., a former name of the US digital media company PMC
* Marsh & McLennan Companies, an American-based global professional services firm
*Master Municipal Clerk, a certification in the US for a munic ...
standard became the de facto standard for embedded systems. SanDisk provides such embedded memory components under the iNAND brand.
Most modern microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs ( processor cores) along with memory and programma ...
s have built-in SPI
SPI may refer to:
Organizations
* Indian Protection Service (''Serviço de Proteção ao Índio''), Brazil
* Shotmed Paper Industries, an Egyptian paper manufacturers
* Simulations Publications, Inc., a former US board game publisher
* Sony P ...
logic that can interface to an SD card operating in its SPI mode, providing non-volatile storage. Even if a microcontroller lacks the SPI feature, the feature can be emulated by bit banging
In computer engineering and electrical engineering, bit banging is a "term of art" for any method of data transmission that employs software as a substitute for dedicated hardware to generate transmitted signals or process received signals. Sof ...
. For example, a home-brew hack
Hack may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Games
* ''Hack'' (Unix video game), a 1984 roguelike video game
* ''.hack'' (video game series), a series of video games by the multimedia franchise ''.hack''
Music
* ''Hack'' (album), a 199 ...
combines spare General Purpose Input/Output
A general-purpose input/output (GPIO) is an uncommitted digital signal pin on an integrated circuit or electronic circuit (e.g. MCUs/ MPUs ) board which may be used as an input or output, or both, and is controllable by software.
GPIOs have n ...
(GPIO) pins of the processor of the Linksys
Linksys is an American brand of data networking hardware products mainly sold to home users and small businesses. It was founded in 1988 by the couple Victor and Janie Tsao, both Taiwanese immigrants to the United States. Linksys products in ...
WRT54G
The Linksys WRT54G Wi-Fi series is a series of Wi-Fi–capable residential gateways marketed by Linksys, a subsidiary of Cisco from 2003 until acquired by Belkin in 2013. A ''residential gateway'' connects a local area network (such as a home netw ...
router with MMC support code from the Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU ...
. This technique can achieve throughput of up to .
Music distribution
Prerecorded microSDs have been used to commercialize music under the brands slotMusic
slotMusic was a brand of microSD memory card developed by SanDisk preloaded with music in MP3 format. They were first available at Wal-Mart and Best Buy stores in October 2008. The current selection of songs comes from Universal Music Group, Sony B ...
and slotRadio
slotRadio was a proprietary format developed by SanDisk that delivered music on a microSD memory card. Up to 1,000 songs were preloaded on microSD cards which were DRM protected. Users had no direct access to the music to copy songs, organize ...
by SanDisk
SanDisk is a brand for flash memory products, including memory cards and readers, USB flash drives, solid-state drives, and digital audio players, manufactured and marketed by Western Digital. The original company, SanDisk Corporation was acquire ...
and MQS by Astell & Kern
Astell & Kern is a South Korean consumer electronics company founded in October 2013, and is wholly owned by Dreamus. The company manufactures media players, CD players, headphones, and home cinema products. It was launched as a premium successo ...
.
Technical details
Physical size
The SD card specification defines three physical sizes. The SD and SDHC families are available in all three sizes, but the SDXC and SDUC families are not available in the mini size, and the SDIO family is not available in the micro size. Smaller cards are usable in larger slots through use of a passive adapter.
Standard
 * SD (SDSC), SDHC, SDXC, SDIO, SDUC
*
* (as thin as MMC) for Thin SD (rare)
* SD (SDSC), SDHC, SDXC, SDIO, SDUC
*
* (as thin as MMC) for Thin SD (rare)
MiniSD
* miniSD, miniSDHC, miniSDIO
*
microSD
The micro form factor is the smallest SD card format.
Transfer modes
Cards may support various combinations of the following bus types and transfer modes. The SPI bus mode and one-bit SD bus mode are mandatory for all SD families, as explained in the next section. Once the host device and the SD card negotiate a bus interface mode, the usage of the numbered pins is the same for all card sizes.
* SPI bus mode: Serial Peripheral Interface Bus
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) is a synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication, primarily in embedded systems. The interface was developed by Motorola in the mid-1980s and has become ...
is primarily used by embedded microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs ( processor cores) along with memory and programma ...
s. This bus type supports only a 3.3-volt interface. This is the only bus type that does not require a host license.
* One-bit SD bus mode: Separate command and data channels and a proprietary transfer format.
* Four-bit SD bus mode: Uses extra pins plus some reassigned pins. This is the same protocol as the one-bit SD bus mode which uses one command and four data lines for faster data transfer. All SD cards support this mode. UHS-I and UHS-II require this bus type.
* Two differential lines SD UHS-II mode: Uses two low-voltage differential interfaces to transfer commands and data. UHS-II cards include this interface in addition to the SD bus modes.
The physical interface comprises 9 pins, except that the miniSD card adds two unconnected pins in the center and the microSD card omits one of the two VSS (Ground) pins.
 Notes:
# Direction is relative to card. I = Input, O = Output.
# PP = Push-Pull logic, OD =
Notes:
# Direction is relative to card. I = Input, O = Output.
# PP = Push-Pull logic, OD = Open-Drain
An open collector is a common type of output found on many integrated circuits (IC), which behaves like a switch that is either connected to ground or disconnected. Instead of outputting a signal of a specific voltage or current, the output sig ...
logic.
# S = Power Supply
A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a ...
, NC = Not Connected (or logical high).
Interface


Command interface
SD cards and host devices initially communicate through a synchronous
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronou ...
one-bit interface, where the host device provides a clock signal that strobes single bits in and out of the SD card. The host device thereby sends 48-bit commands and receives responses. The card can signal that a response will be delayed, but the host device can abort the dialogue.MultiMediaCard
The MultiMediaCard, officially abbreviated as MMC, is a memory card standard used for solid-state storage. Unveiled in 1997 by SanDisk and Siemens, MMC is based on a surface-contact low pin-count serial interface using a single memory stack s ...
(MMC) interface. SD cards dropped support for some of the commands in the MMC protocol, but added commands related to copy protection. By using only commands supported by both standards until determining the type of card inserted, a host device can accommodate both SD and MMC cards.
Electrical interface
All SD card families initially use a 3.3 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference ( voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
D ...
electrical interface. On command, SDHC and SDXC cards can switch to 1.8 V operation.
Achieving higher card speeds
The SD specification defines four-bit-wide transfers. (The MMC specification supports this and also defines an eight-bit-wide mode; MMC cards with extended bits were not accepted by the market.) Transferring several bits on each clock pulse improves the card speed. Advanced SD families have also improved speed by offering faster clock frequencies and double data rate (explained here
Here is an adverb that means "in, on, or at this place". It may also refer to:
Software
* Here Technologies, a mapping company
* Here WeGo (formerly Here Maps), a mobile app and map website by Here
Television
* Here TV (formerly "here!"), a ...
) in a high-speed differential interface (UHS-II).
File system
Like other types of flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
card, an SD card of any SD family is a block-addressable storage device, in which the host device can read or write fixed-size blocks by specifying their block number.
MBR and FAT
Most SD cards ship preformatted with one or more MBR partitions, where the first or only partition contains a file system
In computing, file system or filesystem (often abbreviated to fs) is a method and data structure that the operating system uses to control how data is stored and retrieved. Without a file system, data placed in a storage medium would be one lar ...
. This lets them operate like the hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with mag ...
of a personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tech ...
. Per the SD card specification, an SD card is formatted with MBR and the following file system:
* For SDSC cards:
** Capacity of less than 32,680 logical sectors (smaller than 16 MB [here, MB = 10242 B]): FAT12
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
with partition type 01h and BPB 3.0
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
or EBPB 4.1
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
FAT16
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by c ...
with partition type 04h and BPB 3.0
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
or EBPB 4.1
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
FAT16B
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
with partition type 06h and EBPB 4.1
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
FAT32
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
with partition type 0Bh and EBPB 7.1
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
** Capacity of at least 16,450,560 logical sectors (larger than 7.8 GB): FAT32
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
with partition type 0Ch and EBPB 7.1
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
* For SDXC cards: exFAT
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards. exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specificat ...
with partition type 07h
Most consumer products that take an SD card expect that it is partitioned and formatted in this way. Universal support for FAT12, FAT16, FAT16B, and FAT32 allows the use of SDSC and SDHC cards on most host computers with a compatible SD reader, to present the user with the familiar method of named files in a hierarchical directory tree.
On such SD cards, standard utility programs such as Mac OS X's "" or Windows' SCANDISK can be used to repair a corrupted filing system and sometimes recover deleted files. Defragmentation
In the maintenance of file systems, defragmentation is a process that reduces the degree of fragmentation. It does this by physically organizing the contents of the mass storage device used to store files into the smallest number of contigu ...
tools for FAT file systems may be used on such cards. The resulting consolidation of files may provide a marginal improvement in the time required to read or write the file,flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
; newer technology to increase the storage capacity of a card provides worse write endurance.
When reformatting an SD card with a capacity of at least 32 MBFAT16B
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by ...
with partition type 06h and EBPB 4.1
In computing, the BIOS parameter block, often shortened to BPB, is a data structure in the volume boot record (VBR) describing the physical layout of a data storage volume. On partitioned devices, such as hard disks, the BPB describes the volum ...
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at th ...
's  Specified in version 4.0, further raises the data transfer rate to a theoretical maximum of 156 MB/s (full-
Specified in version 4.0, further raises the data transfer rate to a theoretical maximum of 156 MB/s (full- The SD Express bus was released in June 2018 with SD specification 7.0. It uses a single
The SD Express bus was released in June 2018 with SD specification 7.0. It uses a single 

 The
The  Most full-size SD cards have a "mechanical write protect switch" allowing the user to advise the host computer that the user wants the device to be treated as read-only. This does not protect the data on the card if the host is compromised: "It is the responsibility of the host to protect the card. The position .e., settingof the write protect switch is unknown to the internal circuitry of the card." Some host devices do not support write protection, which is an optional feature of the SD specification, and drivers and devices that do obey a read-only indication may give the user a way to override it.
The switch is a sliding tab that covers a notch in the card. The miniSD and microSD formats do not directly support a write protection notch, but they can be inserted into full-size adapters which do.
When looking at the SD card from the top, the right side (the side with the beveled corner) must be notched.
On the left side, there may be a write-protection notch. If the notch is omitted, the card can be read and written. If the card is notched, it is read-only. If the card has a notch and a sliding tab which covers the notch, the user can slide the tab upward (toward the contacts) to declare the card read/write, or downward to declare it read-only. The diagram to the right shows an orange sliding write-protect tab in both the unlocked and locked positions.
Cards sold with content that must not be altered are permanently marked read-only by having a notch and no sliding tab.
Most full-size SD cards have a "mechanical write protect switch" allowing the user to advise the host computer that the user wants the device to be treated as read-only. This does not protect the data on the card if the host is compromised: "It is the responsibility of the host to protect the card. The position .e., settingof the write protect switch is unknown to the internal circuitry of the card." Some host devices do not support write protection, which is an optional feature of the SD specification, and drivers and devices that do obey a read-only indication may give the user a way to override it.
The switch is a sliding tab that covers a notch in the card. The miniSD and microSD formats do not directly support a write protection notch, but they can be inserted into full-size adapters which do.
When looking at the SD card from the top, the right side (the side with the beveled corner) must be notched.
On the left side, there may be a write-protection notch. If the notch is omitted, the card can be read and written. If the card is notched, it is read-only. If the card has a notch and a sliding tab which covers the notch, the user can slide the tab upward (toward the contacts) to declare the card read/write, or downward to declare it read-only. The diagram to the right shows an orange sliding write-protect tab in both the unlocked and locked positions.
Cards sold with content that must not be altered are permanently marked read-only by having a notch and no sliding tab.
 A host device can lock an SD card using a password of up to 16 bytes, typically supplied by the user. A locked card interacts normally with the host device except that it rejects commands to read and write data. A locked card can be unlocked only by providing the same password. The host device can, after supplying the old password, specify a new password or disable locking. Without the password (typically, in the case that the user forgets the password), the host device can command the card to erase all the data on the card for future re-use (except card data under DRM), but there is no way to gain access to the existing data.
A host device can lock an SD card using a password of up to 16 bytes, typically supplied by the user. A locked card interacts normally with the host device except that it rejects commands to read and write data. A locked card can be unlocked only by providing the same password. The host device can, after supplying the old password, specify a new password or disable locking. Without the password (typically, in the case that the user forgets the password), the host device can command the card to erase all the data on the card for future re-use (except card data under DRM), but there is no way to gain access to the existing data.
 Vendors have sought to differentiate their products in the market through various vendor-specific features:
* Integrated
Vendors have sought to differentiate their products in the market through various vendor-specific features:
* Integrated  A SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output) card is an extension of the SD specification to cover I/O functions. SDIO cards are only fully functional in host devices designed to support their input-output functions (typically PDAs like the
A SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output) card is an extension of the SD specification to cover I/O functions. SDIO cards are only fully functional in host devices designed to support their input-output functions (typically PDAs like the  Commonly found on the market are mislabeled or counterfeit Secure Digital cards that report a fake capacity or run slower than labeled.
Software tools exist to check and detect counterfeit products. Detection of counterfeit cards usually involves copying files with
Commonly found on the market are mislabeled or counterfeit Secure Digital cards that report a fake capacity or run slower than labeled.
Software tools exist to check and detect counterfeit products. Detection of counterfeit cards usually involves copying files with  SD/MMC cards replaced
SD/MMC cards replaced  In 2008, the SDA specified Embedded SD, "leverag ngwell-known SD standards" to enable non-removable SD-style devices on printed circuit boards. However this standard was not adopted by the market while the
In 2008, the SDA specified Embedded SD, "leverag ngwell-known SD standards" to enable non-removable SD-style devices on printed circuit boards. However this standard was not adopted by the market while the  * SD (SDSC), SDHC, SDXC, SDIO, SDUC
*
* (as thin as MMC) for Thin SD (rare)
* SD (SDSC), SDHC, SDXC, SDIO, SDUC
*
* (as thin as MMC) for Thin SD (rare)
 Notes:
# Direction is relative to card. I = Input, O = Output.
# PP = Push-Pull logic, OD =
Notes:
# Direction is relative to card. I = Input, O = Output.
# PP = Push-Pull logic, OD = 

