|
Double Data Rate
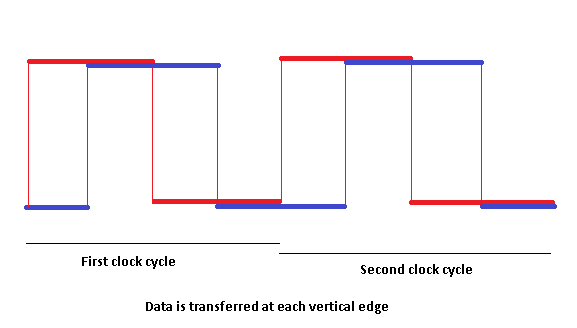
In computing, double data rate (DDR) describes a computer bus that transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal and hence doubles the memory bandwidth by transferring data twice per clock cycle. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory. Overview The simplest way to design a clocked electronic circuit is to make it perform one transfer per full cycle (rise and fall) of a clock signal. This, however, requires that the clock signal changes twice per transfer, while the data lines change at most once per transfer. When operating at a high bandwidth, signal integrity limitations constrain the clock frequency. By using both edges of the clock, the data signals operate with the same limiting frequency, thereby doubling the data transmission rate. This technique has been used for microprocessor front-side busses, Ultra-3 SCSI, expansion buses ( AGP, PCI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDR5
Double Data Rate 5 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR5 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory. Compared to its predecessor DDR4 SDRAM, DDR5 was planned to reduce power consumption, while doubling bandwidth. The standard, originally targeted for 2018, was released on July 14, 2020. A new feature called Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE) enables input/output (I/O) speed scalability for higher bandwidth and performance improvement. DDR5 has about the same latency as DDR4 and DDR3. DDR5 octuples the maximum DIMM capacity from 64 GB to 512 GB. DDR5 also has higher frequencies than DDR4, up to 9600 MT/s is currently possible, 8200 MT/s translates into around 66 GB/s of bandwidth. Using liquid nitrogen 13000 MT/s speeds were achieved. Rambus announced a working DDR5 dual in-line memory module (DIMM) in September 2017. On November 15, 2018, SK Hynix announced completion of its first DDR5 RAM chip; running at 5.2 GT/s at 1.1 V. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabytes Per Second
In telecommunications, data transfer rate is the average number of bits (bitrate), characters or symbols ( baudrate), or data blocks per unit time passing through a communication link in a data-transmission system. Common data rate units are multiples of bits per second (bit/s) and bytes per second (B/s). For example, the data rates of modern residential high-speed Internet connections are commonly expressed in megabits per second (Mbit/s). Standards for unit symbols and prefixes Unit symbol The ISQ symbols for the bit and byte are ''bit'' and ''B'', respectively. In the context of data-rate units, one byte consists of 8 bits, and is synonymous with the unit octet. The abbreviation bps is often used to mean bit/s, so that when a ''1 Mbps'' connection is advertised, it usually means that the maximum achievable bandwidth is 1 Mbit/s (one million bits per second), which is 0.125 MB/s ( megabyte per second), or about 0.1192 MiB/s ( mebibyte per second). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MT/s
In computer technology, transfers per second and its more common secondary terms gigatransfers per second (abbreviated as GT/s) and megatransfers per second (MT/s) are informal language that refer to the number of operations transferring data that occur in each second in some given data-transfer channel. It is also known as sample rate, i.e. the number of data samples captured per second, each sample normally occurring at the clock edge. The terms are neutral with respect to the method of physically accomplishing each such data-transfer operation; nevertheless, they are most commonly used in the context of transmission of digital data. is 106 or one million transfers per second; similarly, means 109, or equivalently in the US/ short scale, one billion transfers per second. Units These terms alone do not specify the bit rate at which binary data is being transferred because they do not specify the number of bits transferred in each transfer operation (known as the channel width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base units is 1/s or s−1, meaning that one hertz is one per second or the Inverse second, reciprocal of one second. It is used only in the case of periodic events. It is named after Heinrich Hertz, Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. For high frequencies, the unit is commonly expressed in metric prefix, multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beat (music)
In music and music theory, the beat is the basic unit of time, the pulse (regularly repeating event), of the ''mensural level'' (or ''beat level''). The beat is often defined as the rhythm listeners would tap their toes to when listening to a piece of music, or the numbers a musician counts while performing, though in practice this may be technically incorrect (often the first multiple level). In popular use, ''beat'' can refer to a variety of related concepts, including pulse, tempo, meter, specific rhythms, and groove. Rhythm in music is characterized by a repeating sequence of stressed and unstressed beats (often called "strong" and "weak") and divided into bars organized by time signature and tempo indications. Beats are related to and distinguished from pulse, rhythm (grouping), and meter: Metric levels faster than the beat level are division levels, and slower levels are multiple levels. Beat has always been an important part of music. Some music genres such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfiniBand
InfiniBand (IB) is a computer networking communications standard used in high-performance computing that features very high throughput and very low latency. It is used for data interconnect both among and within computers. InfiniBand is also used as either a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. It is designed to be scalable and uses a switched fabric network topology. Between 2014 and June 2016, it was the most commonly used interconnect in the TOP500 list of supercomputers. Mellanox (acquired by Nvidia) manufactures InfiniBand host bus adapters and network switches, which are used by large computer system and database vendors in their product lines. As a computer cluster interconnect, IB competes with Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and Intel Omni-Path. The technology is promoted by the InfiniBand Trade Association. History InfiniBand originated in 1999 from the merger of two competing designs: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-clocking
In telecommunications and electronics, a self-clocking signal is one that can be decoded without the need for a separate clock signal or other source of Synchronization (computer science), synchronization. This is usually done by including embedded synchronization information within the signal, and adding constraints on the coding of the data payload such that false synchronization can easily be detected. Most line codes are designed to be self-clocking. Isochronicity and anisochronicity If a clock signal is embedded in the data transmission, there are two possibilities: the clock signals are sent at the same time as the data (isochronous), or at a different time (anisochronous). Isochronous self-clocking signals If the embedded clock signal is isochronous, it gets sent simultaneously with the data. Below is an example signal, in this case using the Manchester code self-clocking signal. The data and clock cycles can be thought of as "adding up" to a combination, where both the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quad Data Rate
Quad data rate (QDR, or quad pumping) is a communication signaling technique wherein data are transmitted at four points in the clock cycle: on the rising and falling edges, and at two intermediate points between them. The intermediate points are defined by a second clock that is 90° out of phase from the first. The effect is to deliver four bits of data per signal line per clock cycle. In a quad data rate system, the data lines operate at twice the frequency of the clock signal. This is in contrast to double data rate systems, in which the clock and data lines operate at the same frequency. Quad data rate technology was introduced by Intel in its Willamette-core Pentium 4 processor, and was subsequently employed in its Atom, Pentium 4, Celeron, Pentium D and Core 2 processor ranges. This technology has allowed Intel to produce chipsets and processors that can communicate with each other at data rates expected of the traditional front-side bus (FSB) tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-channel Architecture
In the fields of digital electronics and computer hardware, multi-channel memory architecture is a technology that increases the data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically, this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual-channel memory employs two channels. The technique goes back as far as the 1960s having been used in IBM System/360 Model 91 and in CDC 6600. Modern high-end desktop and workstation processors such as the Advanced Micro Devices, AMD Ryzen Threadripper series and the Intel List of Intel Core i9 processors, Core i9 Extreme Edition lineup support quad-channel memory. Server processors from the AMD Epyc series and the Intel Xeon platforms give support to memory bandwidth starting from quad-channel module layout to up to 12-channel layout. In March 2010, AMD released Socket G34 and Magny-Cours Opteron 6100 series processors with support for quad- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |