|
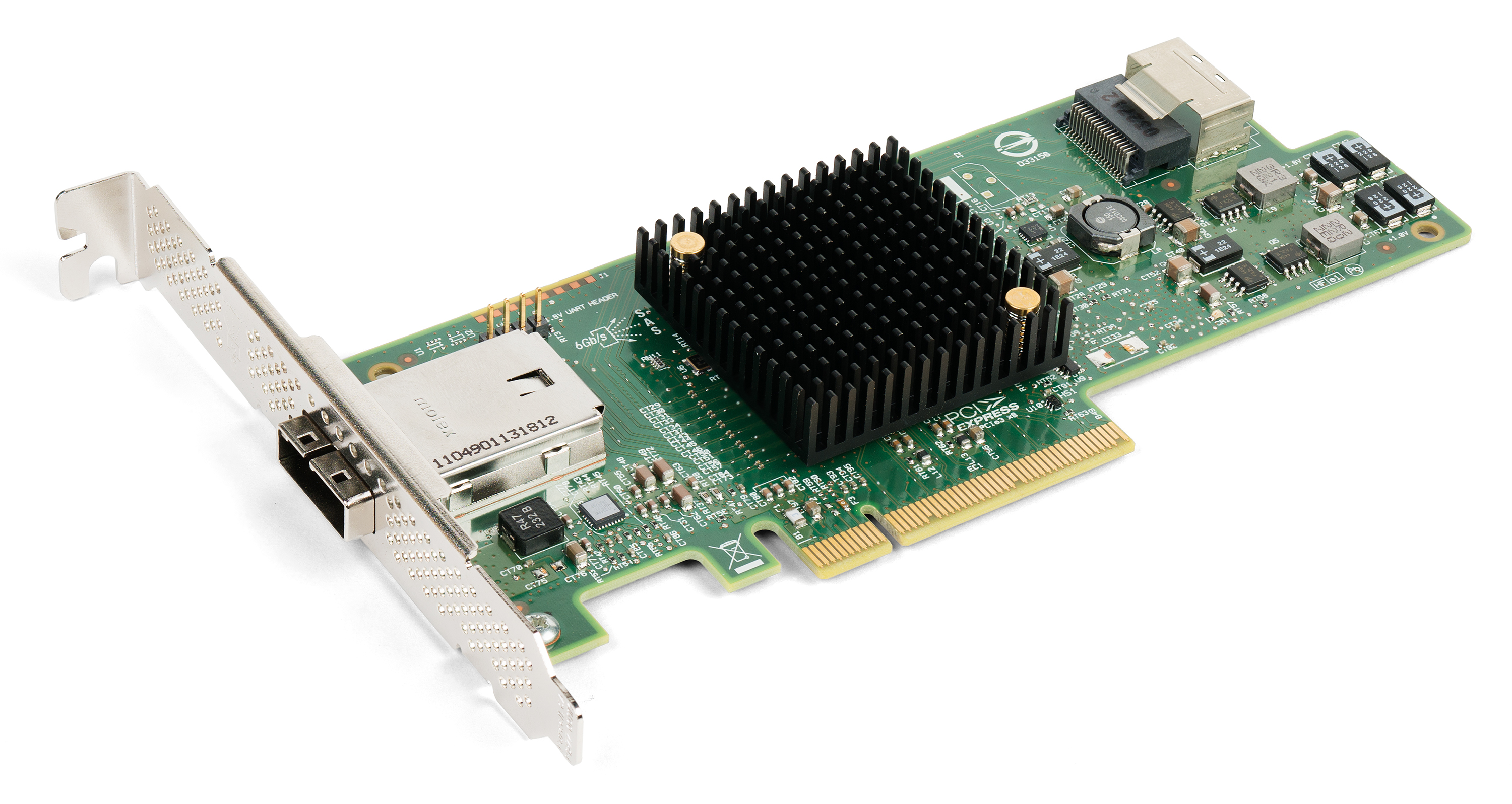
PCIE
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a high-speed standard used to connect hardware components inside computers. It is designed to replace older expansion bus standards such as Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI, PCI-X and Accelerated Graphics Port, AGP. Developed and maintained by the PCI-SIG (PCI Special Interest Group), PCIe is commonly used to connect graphics cards, sound cards, Wi-Fi and Ethernet adapters, and storage devices such as solid-state drives and hard disk drives. Compared to earlier standards, PCIe supports faster data transfer, uses fewer pins, takes up less space, and allows devices to be added or removed while the computer is running (hot swapping). It also includes better error detection and supports newer features like I/O virtualization for advanced computing needs. PCIe connections are made through "lanes," which are pairs of wires that send and receive data. Devices can use one or more lanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Card
A graphics card (also called a video card, display card, graphics accelerator, graphics adapter, VGA card/VGA, video adapter, display adapter, or colloquially GPU) is a computer expansion card that generates a feed of graphics output to a display device such as a computer monitor, monitor. Graphics cards are sometimes called ''discrete'' or ''dedicated'' graphics cards to emphasize their distinction to an graphics processing unit#Integrated graphics processing unit, integrated graphics processor on the motherboard or the central processing unit (CPU). A graphics processing unit (GPU) that performs the necessary computations is the main component in a graphics card, but the acronym "GPU" is sometimes also used to refer to the graphics card as a whole erroneously. Most graphics cards are not limited to simple display output. The graphics processing unit can be used for additional processing, which reduces the load from the CPU. Additionally, computing platforms such as OpenCL and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) is a local computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer and is part of the PCI Local Bus standard. The PCI bus supports the functions found on a processor bus but in a standardized format that is independent of any given processor's native bus. Devices connected to the PCI bus appear to a bus master to be connected directly to its own bus and are assigned addresses in the processor's address space. It is a parallel bus, synchronous to a single bus clock. Attached devices can take either the form of an integrated circuit fitted onto the motherboard (called a ''planar device'' in the PCI specification) or an expansion card that fits into a slot. The PCI Local Bus was first implemented in IBM PC compatibles, where it displaced the combination of several slow Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) slots and one fast VESA Local Bus (VLB) slot as the bus configuration. It has subsequently been adopted for other computer types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bus (computing)
In computer architecture, a bus (historically also called a data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers Data (computing), data between components inside a computer or between computers. It encompasses both Computer hardware, hardware (e.g., wires, optical fiber) and software, including communication protocols. At its core, a bus is a shared physical pathway, typically composed of wires, traces on a circuit board, or busbars, that allows multiple devices to communicate. To prevent conflicts and ensure orderly data exchange, buses rely on a communication protocol to manage which device can transmit data at a given time. Buses are categorized based on their role, such as system buses (also known as internal buses, internal data buses, or memory buses) connecting the Central processing unit, CPU and Computer memory, memory. Expansion buses, also called peripheral buses, extend the system to connect additional devices, including peripherals. Examples of widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer components such as central processing units (CPUs) and related products for business and consumer markets. It is one of the world's List of largest semiconductor chip manufacturers, largest semiconductor chip manufacturers by revenue, and ranked in the Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 list of the List of largest companies in the United States by revenue, largest United States corporations by revenue for nearly a decade, from 2007 to 2016 Fiscal year, fiscal years, until it was removed from the ranking in 2018. In 2020, it was reinstated and ranked 45th, being the List of Fortune 500 computer software and information companies, 7th-largest technology company in the ranking. It was one of the first companies listed on Nasdaq. Intel supplies List of I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Swapping
Hot swapping is the replacement or addition of components to a computer system without stopping, shutting down, or rebooting the system. Hot plugging describes only the addition of components to a running computer system. Components which have such functionality are said to be ''hot-swappable'' or ''hot-pluggable''; likewise, components which do not are ''cold-swappable'' or ''cold-pluggable''. Although the broader concept of hot swapping can apply to electrical or mechanical systems, it is usually mentioned in the context of computer systems. An example of hot swapping is the express ability to pull a Universal Serial Bus (USB) peripheral device, such as a thumb drive, mouse, keyboard, or printer out of a computer's USB slot without powering down the computer first. Most desktop computer hardware, such as CPUs and memory, are only cold-pluggable. However, it is common for mid to high-end servers and mainframes to feature hot-swappable capability for hardware componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I/O Virtualization
In virtualization, input/output virtualization (I/O virtualization) is a methodology to simplify management, lower costs and improve performance of servers in enterprise environments. I/O virtualization environments are created by abstracting the upper layer protocols from the physical connections. The technology enables one physical adapter card to appear as multiple virtual network interface cards (vNICs) and virtual host bus adapters (vHBAs). Virtual NICs and HBAs function as conventional NICs and HBAs, and are designed to be compatible with existing operating systems, hypervisors, and applications. To networking resources (LANs and SANs), they appear as normal cards. In the physical view, virtual I/O replaces a server’s multiple I/O cables with a single cable that provides a shared transport for all network and storage connections. That cable (or commonly two cables for redundancy) connects to an external device, which then provides connections to the data center netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SATA Express
SATA Express (sometimes unofficially shortened to SATAe) is a computer bus interface that supports both Serial ATA (SATA) and PCI Express (PCIe) storage devices, initially standardized in the SATA 3.2 specification. The SATA Express connector used on the host side is backward compatible with the standard SATA data connector, while it also provides two PCI Express lanes as a pure PCI Express connection to the storage device. Instead of continuing with the SATA interface's usual approach of doubling its native speed with each major version, SATA 3.2 specification included the PCI Express bus for achieving data transfer speeds greater than the SATA 3.0 speed limit of 6 Gbit/s. Designers of the SATA interface concluded that doubling the native SATA speed would take too much time to catch up with the advancements in solid-state drive (SSD) technology, would require too many changes to the SATA standard, and would result in a much greater power consumption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Example PCI Express Topology
Example may refer to: * ''exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, and example.edu: second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (, ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |