Oxygen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Oxygen is a
 Swedish pharmacist
Swedish pharmacist
 Lavoisier conducted the first adequate quantitative experiments on
Lavoisier conducted the first adequate quantitative experiments on
 By the late 19th century scientists realized that air could be liquefied and its components isolated by compressing and cooling it. Using a
By the late 19th century scientists realized that air could be liquefied and its components isolated by compressing and cooling it. Using a
 At
At
Google Books
accessed January 31, 2015. This combination of cancellations and σ and π overlaps results in dioxygen's double-bond character and reactivity, and a triplet electronic ground state. An electron configuration with two unpaired electrons, as is found in dioxygen orbitals (see the filled π* orbitals in the diagram) that are of equal energy—i.e., degenerate orbitals, degenerate—is a configuration termed a spin triplet state. Hence, the ground state of the molecule is referred to as triplet oxygen. The highest-energy, partially filled orbitals are antibonding, and so their filling weakens the bond order from three to two. Because of its unpaired electrons, triplet oxygen reacts only slowly with most organic molecules, which have paired electron spins; this prevents spontaneous combustion. In the triplet form, molecules are paramagnetism, paramagnetic. That is, they impart magnetic character to oxygen when it is in the presence of a magnetic field, because of the Spin (physics), spin magnetic moments of the unpaired electrons in the molecule, and the negative exchange energy between neighboring molecules. Liquid oxygen is so magnetic that, in laboratory demonstrations, a bridge of liquid oxygen may be supported against its own weight between the poles of a powerful magnet. Oxygen's paramagnetism can be used analytically in paramagnetic oxygen gas analysers that determine gaseous oxygen concentration, especially in industrial process control and medicine.
Singlet oxygen is a name given to several higher-energy species of molecular in which all the electron spins are paired. It is much more reactive with common organic compound, organic molecules than is normal (triplet) molecular oxygen. In nature, singlet oxygen is commonly formed from water during photosynthesis, using the energy of sunlight. It is also produced in the troposphere by the photolysis of ozone by light of short wavelength and by the immune system as a source of active oxygen. Carotenoids in photosynthetic organisms (and possibly animals) play a major role in absorbing energy from singlet oxygen and converting it to the unexcited ground state before it can cause harm to tissues.
In the triplet form, molecules are paramagnetism, paramagnetic. That is, they impart magnetic character to oxygen when it is in the presence of a magnetic field, because of the Spin (physics), spin magnetic moments of the unpaired electrons in the molecule, and the negative exchange energy between neighboring molecules. Liquid oxygen is so magnetic that, in laboratory demonstrations, a bridge of liquid oxygen may be supported against its own weight between the poles of a powerful magnet. Oxygen's paramagnetism can be used analytically in paramagnetic oxygen gas analysers that determine gaseous oxygen concentration, especially in industrial process control and medicine.
Singlet oxygen is a name given to several higher-energy species of molecular in which all the electron spins are paired. It is much more reactive with common organic compound, organic molecules than is normal (triplet) molecular oxygen. In nature, singlet oxygen is commonly formed from water during photosynthesis, using the energy of sunlight. It is also produced in the troposphere by the photolysis of ozone by light of short wavelength and by the immune system as a source of active oxygen. Carotenoids in photosynthetic organisms (and possibly animals) play a major role in absorbing energy from singlet oxygen and converting it to the unexcited ground state before it can cause harm to tissues.
 The common Allotropy, allotrope of elemental oxygen on Earth is called Allotropes of oxygen, dioxygen, , the major part of the Earth's atmospheric oxygen (see #Occurrence, Occurrence). O2 has a bond length of 121 Picometre, pm and a bond energy of 498 joule per mole, kJ/mol.
Trioxygen () is usually known as
The common Allotropy, allotrope of elemental oxygen on Earth is called Allotropes of oxygen, dioxygen, , the major part of the Earth's atmospheric oxygen (see #Occurrence, Occurrence). O2 has a bond length of 121 Picometre, pm and a bond energy of 498 joule per mole, kJ/mol.
Trioxygen () is usually known as
 Oxygen Solubility, dissolves more readily in water than nitrogen does. Water in equilibrium with air contains approximately 1 molecule of dissolved for every 2 molecules of (1:2), compared with an atmospheric ratio of approximately 1:4. The solubility of oxygen in water is temperature-dependent, and about twice as much () dissolves at than at ().
At and of air, freshwater can dissolve about 6.04 Litre, milliliters (mL) of oxygen per liter, and seawater contains about 4.95 mL per liter.
At the solubility increases to 9.0 mL (50% more than at ) per liter for freshwater and 7.2 mL (45% more) per liter for sea water.
Oxygen condenses at 90.20 kelvin, K (−182.95 °C, −297.31 °F) and freezes at 54.36 K (−218.79 °C, −361.82 °F). Both liquid oxygen, liquid and solid oxygen, solid are clear substances with a light diffuse sky radiation, sky-blue color caused by absorption in the red (in contrast with the blue color of the sky, which is due to Rayleigh scattering of blue light). High-purity liquid is usually obtained by the
Oxygen Solubility, dissolves more readily in water than nitrogen does. Water in equilibrium with air contains approximately 1 molecule of dissolved for every 2 molecules of (1:2), compared with an atmospheric ratio of approximately 1:4. The solubility of oxygen in water is temperature-dependent, and about twice as much () dissolves at than at ().
At and of air, freshwater can dissolve about 6.04 Litre, milliliters (mL) of oxygen per liter, and seawater contains about 4.95 mL per liter.
At the solubility increases to 9.0 mL (50% more than at ) per liter for freshwater and 7.2 mL (45% more) per liter for sea water.
Oxygen condenses at 90.20 kelvin, K (−182.95 °C, −297.31 °F) and freezes at 54.36 K (−218.79 °C, −361.82 °F). Both liquid oxygen, liquid and solid oxygen, solid are clear substances with a light diffuse sky radiation, sky-blue color caused by absorption in the red (in contrast with the blue color of the sky, which is due to Rayleigh scattering of blue light). High-purity liquid is usually obtained by the
 Naturally occurring oxygen is composed of three stable isotopes, oxygen-16, 16O, oxygen-17, 17O, and oxygen-18, 18O, with 16O being the most abundant (99.762% natural abundance).
16O is the one of the dominant fusion products in massive stars. It is nucleosynthesis, synthesized at the end of the helium fusion process with some synthesis in the neon burning process. Both 17O and 18O require seed nuclei. 17O is primarily made by the burning of hydrogen into
Naturally occurring oxygen is composed of three stable isotopes, oxygen-16, 16O, oxygen-17, 17O, and oxygen-18, 18O, with 16O being the most abundant (99.762% natural abundance).
16O is the one of the dominant fusion products in massive stars. It is nucleosynthesis, synthesized at the end of the helium fusion process with some synthesis in the neon burning process. Both 17O and 18O require seed nuclei. 17O is primarily made by the burning of hydrogen into
 Free oxygen also occurs in solution in the world's water bodies. The increased solubility of at lower temperatures (see #Physical properties, Physical properties) has important implications for ocean life, as polar oceans support a much higher density of life due to their higher oxygen content. Scientists assess this aspect of water quality by measuring the water's biochemical oxygen demand, or the amount of needed to restore it to a normal concentration. Emsley 2001, p. 301
Significant deoxygenation has been observed in tropical oceans. Warming oceans waters are expected to lose oxygen over the next century and into the future for a thousand years; the possible consequences include minimal oxygen zones which are unable to support macrofauna.
Free oxygen also occurs in solution in the world's water bodies. The increased solubility of at lower temperatures (see #Physical properties, Physical properties) has important implications for ocean life, as polar oceans support a much higher density of life due to their higher oxygen content. Scientists assess this aspect of water quality by measuring the water's biochemical oxygen demand, or the amount of needed to restore it to a normal concentration. Emsley 2001, p. 301
Significant deoxygenation has been observed in tropical oceans. Warming oceans waters are expected to lose oxygen over the next century and into the future for a thousand years; the possible consequences include minimal oxygen zones which are unable to support macrofauna.
 Paleoclimatology, Paleoclimatologists measure the ratio of oxygen-18 and oxygen-16 in the Exoskeleton, shells and skeletons of marine organisms to determine the climate millions of years ago (see oxygen isotope ratio cycle). Seawater molecules that contain the lighter isotope, oxygen-16, evaporate at a slightly faster rate than water molecules containing the 12% heavier oxygen-18, and this disparity increases at lower temperatures. Emsley 2001, p. 304 During periods of lower global temperatures, snow and rain from that evaporated water tends to be higher in oxygen-16, and the seawater left behind tends to be higher in oxygen-18. Marine organisms then incorporate more oxygen-18 into their skeletons and shells than they would in a warmer climate. Paleoclimatologists also directly measure this ratio in the water molecules of ice core samples as old as hundreds of thousands of years.
Geology of solar terrestrial planets, Planetary geologists have measured the relative quantities of oxygen isotopes in samples from the Earth, the Moon, Mars, and meteorites, but were long unable to obtain reference values for the isotope ratios in the Sun, believed to be the same as those of the Nebular hypothesis, primordial solar nebula. Analysis of a silicon wafer exposed to the solar wind in space and returned by the crashed Genesis (spacecraft), Genesis spacecraft has shown that the Sun has a higher proportion of oxygen-16 than does the Earth. The measurement implies that an unknown process depleted oxygen-16 from the Sun's Protoplanetary disk, disk of protoplanetary material prior to the coalescence of dust grains that formed the Earth.
Oxygen presents two spectrophotometric absorption bands peaking at the wavelengths 687 and 760 Nanometre, nm. Some remote sensing scientists have proposed using the measurement of the radiance coming from vegetation canopies in those bands to characterize plant health status from a Earth observation satellite, satellite platform. This approach exploits the fact that in those bands it is possible to discriminate the vegetation's reflectance from its fluorescence, which is much weaker. The measurement is technically difficult owing to the low signal-to-noise ratio and the physical structure of vegetation; but it has been proposed as a possible method of monitoring the carbon cycle from satellites on a global scale.
Paleoclimatology, Paleoclimatologists measure the ratio of oxygen-18 and oxygen-16 in the Exoskeleton, shells and skeletons of marine organisms to determine the climate millions of years ago (see oxygen isotope ratio cycle). Seawater molecules that contain the lighter isotope, oxygen-16, evaporate at a slightly faster rate than water molecules containing the 12% heavier oxygen-18, and this disparity increases at lower temperatures. Emsley 2001, p. 304 During periods of lower global temperatures, snow and rain from that evaporated water tends to be higher in oxygen-16, and the seawater left behind tends to be higher in oxygen-18. Marine organisms then incorporate more oxygen-18 into their skeletons and shells than they would in a warmer climate. Paleoclimatologists also directly measure this ratio in the water molecules of ice core samples as old as hundreds of thousands of years.
Geology of solar terrestrial planets, Planetary geologists have measured the relative quantities of oxygen isotopes in samples from the Earth, the Moon, Mars, and meteorites, but were long unable to obtain reference values for the isotope ratios in the Sun, believed to be the same as those of the Nebular hypothesis, primordial solar nebula. Analysis of a silicon wafer exposed to the solar wind in space and returned by the crashed Genesis (spacecraft), Genesis spacecraft has shown that the Sun has a higher proportion of oxygen-16 than does the Earth. The measurement implies that an unknown process depleted oxygen-16 from the Sun's Protoplanetary disk, disk of protoplanetary material prior to the coalescence of dust grains that formed the Earth.
Oxygen presents two spectrophotometric absorption bands peaking at the wavelengths 687 and 760 Nanometre, nm. Some remote sensing scientists have proposed using the measurement of the radiance coming from vegetation canopies in those bands to characterize plant health status from a Earth observation satellite, satellite platform. This approach exploits the fact that in those bands it is possible to discriminate the vegetation's reflectance from its fluorescence, which is much weaker. The measurement is technically difficult owing to the low signal-to-noise ratio and the physical structure of vegetation; but it has been proposed as a possible method of monitoring the carbon cycle from satellites on a global scale.
 In nature, free oxygen is produced as a
In nature, free oxygen is produced as a
 Free oxygen gas was almost nonexistent in Earth's atmosphere before photosynthetic archaea and bacteria evolved, probably about 3.5 billion years ago. Free oxygen first appeared in significant quantities during the Paleoproterozoic era (between 3.0 and 2.3 billion years ago). Even if there was much dissolved iron in the oceans when oxygenic photosynthesis was getting more common, it appears the banded iron formations were created by anoxyenic or micro-aerophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria which dominated the deeper areas of the photic zone, while oxygen-producing cyanobacteria covered the shallows. Free oxygen began to Outgassing, outgas from the oceans 3–2.7 billion years ago, reaching 10% of its present level around 1.7 billion years ago.
The presence of large amounts of dissolved and free oxygen in the oceans and atmosphere may have driven most of the extant anaerobic organisms to extinction during the Great Oxygenation Event (''oxygen catastrophe'') about 2.4 billion years ago. Cellular respiration using enables aerobic organisms to produce much more Adenosine triphosphate, ATP than anaerobic organisms. Cellular respiration of occurs in all eukaryotes, including all complex multicellular organisms such as plants and animals.
Since the beginning of the Cambrian period 540 million years ago, atmospheric levels have fluctuated between 15% and 30% by volume. Towards the end of the Carboniferous period (about 300 million years ago) atmospheric levels reached a maximum of 35% by volume, which may have contributed to the large size of insects and amphibians at this time.
Variations in atmospheric oxygen concentration have shaped past climates. When oxygen declined, atmospheric density dropped, which in turn increased surface evaporation, causing precipitation increases and warmer temperatures.
At the current rate of photosynthesis it would take about 2,000 years to regenerate the entire in the present atmosphere.
It is estimated that oxygen on Earth will last for about one billion years.
Free oxygen gas was almost nonexistent in Earth's atmosphere before photosynthetic archaea and bacteria evolved, probably about 3.5 billion years ago. Free oxygen first appeared in significant quantities during the Paleoproterozoic era (between 3.0 and 2.3 billion years ago). Even if there was much dissolved iron in the oceans when oxygenic photosynthesis was getting more common, it appears the banded iron formations were created by anoxyenic or micro-aerophilic iron-oxidizing bacteria which dominated the deeper areas of the photic zone, while oxygen-producing cyanobacteria covered the shallows. Free oxygen began to Outgassing, outgas from the oceans 3–2.7 billion years ago, reaching 10% of its present level around 1.7 billion years ago.
The presence of large amounts of dissolved and free oxygen in the oceans and atmosphere may have driven most of the extant anaerobic organisms to extinction during the Great Oxygenation Event (''oxygen catastrophe'') about 2.4 billion years ago. Cellular respiration using enables aerobic organisms to produce much more Adenosine triphosphate, ATP than anaerobic organisms. Cellular respiration of occurs in all eukaryotes, including all complex multicellular organisms such as plants and animals.
Since the beginning of the Cambrian period 540 million years ago, atmospheric levels have fluctuated between 15% and 30% by volume. Towards the end of the Carboniferous period (about 300 million years ago) atmospheric levels reached a maximum of 35% by volume, which may have contributed to the large size of insects and amphibians at this time.
Variations in atmospheric oxygen concentration have shaped past climates. When oxygen declined, atmospheric density dropped, which in turn increased surface evaporation, causing precipitation increases and warmer temperatures.
At the current rate of photosynthesis it would take about 2,000 years to regenerate the entire in the present atmosphere.
It is estimated that oxygen on Earth will last for about one billion years.
 One hundred million tonnes of are extracted from air for industrial uses annually by two primary methods. The most common method is
One hundred million tonnes of are extracted from air for industrial uses annually by two primary methods. The most common method is  In academic laboratories, oxygen can be prepared by heating together potassium chlorate mixed with a small proportion of manganese dioxide.
Oxygen gas can also be produced through electrolysis of water into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. DC electricity must be used: if AC is used, the gases in each limb consist of hydrogen and oxygen in the explosive ratio 2:1. A similar method is the electrocatalytic evolution from oxides and oxoacids. Chemical catalysts can be used as well, such as in chemical oxygen generators or oxygen candles that are used as part of the life-support equipment on submarines, and are still part of standard equipment on commercial airliners in case of depressurization emergencies. Another air separation method is forcing air to dissolve through ceramic membranes based on zirconium dioxide by either high pressure or an electric current, to produce nearly pure gas.
In academic laboratories, oxygen can be prepared by heating together potassium chlorate mixed with a small proportion of manganese dioxide.
Oxygen gas can also be produced through electrolysis of water into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. DC electricity must be used: if AC is used, the gases in each limb consist of hydrogen and oxygen in the explosive ratio 2:1. A similar method is the electrocatalytic evolution from oxides and oxoacids. Chemical catalysts can be used as well, such as in chemical oxygen generators or oxygen candles that are used as part of the life-support equipment on submarines, and are still part of standard equipment on commercial airliners in case of depressurization emergencies. Another air separation method is forcing air to dissolve through ceramic membranes based on zirconium dioxide by either high pressure or an electric current, to produce nearly pure gas.
 Oxygen storage methods include high-pressure oxygen tanks, cryogenics and chemical compounds. For reasons of economy, oxygen is often transported in bulk as a liquid in specially insulated tankers, since one litre, liter of liquefied oxygen is equivalent to 840 liters of gaseous oxygen at atmospheric pressure and . Such tankers are used to refill bulk liquid-oxygen storage containers, which stand outside hospitals and other institutions that need large volumes of pure oxygen gas. Liquid oxygen is passed through heat exchangers, which convert the cryogenic liquid into gas before it enters the building. Oxygen is also stored and shipped in smaller cylinders containing the compressed gas; a form that is useful in certain portable medical applications and oxy-fuel welding and cutting.
Oxygen storage methods include high-pressure oxygen tanks, cryogenics and chemical compounds. For reasons of economy, oxygen is often transported in bulk as a liquid in specially insulated tankers, since one litre, liter of liquefied oxygen is equivalent to 840 liters of gaseous oxygen at atmospheric pressure and . Such tankers are used to refill bulk liquid-oxygen storage containers, which stand outside hospitals and other institutions that need large volumes of pure oxygen gas. Liquid oxygen is passed through heat exchangers, which convert the cryogenic liquid into gas before it enters the building. Oxygen is also stored and shipped in smaller cylinders containing the compressed gas; a form that is useful in certain portable medical applications and oxy-fuel welding and cutting.
 Uptake of from the air is the essential purpose of Respiration (physiology), respiration, so oxygen supplementation is used in medicine. Treatment not only increases oxygen levels in the patient's blood, but has the secondary effect of decreasing resistance to blood flow in many types of diseased lungs, easing work load on the heart. Oxygen therapy is used to treat emphysema, pneumonia, some heart disorders (congestive heart failure), some disorders that cause increased pulmonary artery pressure, and any disease that impairs the body's ability to take up and use gaseous oxygen. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 510
Treatments are flexible enough to be used in hospitals, the patient's home, or increasingly by portable devices. Oxygen tents were once commonly used in oxygen supplementation, but have since been replaced mostly by the use of oxygen masks or nasal cannulas.
Hyperbaric medicine, Hyperbaric (high-pressure) medicine uses special hyperbaric oxygen chamber, oxygen chambers to increase the partial pressure of around the patient and, when needed, the medical staff. Carbon monoxide poisoning, gas gangrene, and decompression sickness (the 'bends') are sometimes addressed with this therapy. Increased concentration in the lungs helps to displace carbon monoxide from the heme group of hemoglobin. Oxygen gas is poisonous to the anaerobic bacteria that cause gas gangrene, so increasing its partial pressure helps kill them. Decompression sickness occurs in divers who decompress too quickly after a dive, resulting in bubbles of inert gas, mostly nitrogen and helium, forming in the blood. Increasing the pressure of as soon as possible helps to redissolve the bubbles back into the blood so that these excess gasses can be exhaled naturally through the lungs. Normobaric oxygen administration at the highest available concentration is frequently used as first aid for any diving injury that may involve inert gas bubble formation in the tissues. There is epidemiological support for its use from a statistical study of cases recorded in a long term database.
Uptake of from the air is the essential purpose of Respiration (physiology), respiration, so oxygen supplementation is used in medicine. Treatment not only increases oxygen levels in the patient's blood, but has the secondary effect of decreasing resistance to blood flow in many types of diseased lungs, easing work load on the heart. Oxygen therapy is used to treat emphysema, pneumonia, some heart disorders (congestive heart failure), some disorders that cause increased pulmonary artery pressure, and any disease that impairs the body's ability to take up and use gaseous oxygen. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 510
Treatments are flexible enough to be used in hospitals, the patient's home, or increasingly by portable devices. Oxygen tents were once commonly used in oxygen supplementation, but have since been replaced mostly by the use of oxygen masks or nasal cannulas.
Hyperbaric medicine, Hyperbaric (high-pressure) medicine uses special hyperbaric oxygen chamber, oxygen chambers to increase the partial pressure of around the patient and, when needed, the medical staff. Carbon monoxide poisoning, gas gangrene, and decompression sickness (the 'bends') are sometimes addressed with this therapy. Increased concentration in the lungs helps to displace carbon monoxide from the heme group of hemoglobin. Oxygen gas is poisonous to the anaerobic bacteria that cause gas gangrene, so increasing its partial pressure helps kill them. Decompression sickness occurs in divers who decompress too quickly after a dive, resulting in bubbles of inert gas, mostly nitrogen and helium, forming in the blood. Increasing the pressure of as soon as possible helps to redissolve the bubbles back into the blood so that these excess gasses can be exhaled naturally through the lungs. Normobaric oxygen administration at the highest available concentration is frequently used as first aid for any diving injury that may involve inert gas bubble formation in the tissues. There is epidemiological support for its use from a statistical study of cases recorded in a long term database.
 Smelting of iron ore into steel consumes 55% of commercially produced oxygen. In this process, is injected through a high-pressure lance into molten iron, which removes sulfur impurities and excess carbon as the respective oxides, and . The reactions are exothermic reaction, exothermic, so the temperature increases to 1,700 °Celsius, C.
Another 25% of commercially produced oxygen is used by the chemical industry. Ethylene is reacted with to create ethylene oxide, which, in turn, is converted into ethylene glycol; the primary feeder material used to manufacture a host of products, including antifreeze and polyester polymers (the precursors of many plastics and fabrics).
Most of the remaining 20% of commercially produced oxygen is used in medical applications, gas welding, metal cutting and welding, as an oxidizer in rocket fuel, and in water treatment. Oxygen is used in oxyacetylene welding, burning acetylene with to produce a very hot flame. In this process, metal up to thick is first heated with a small oxy-acetylene flame and then quickly cut by a large stream of . Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 508
Smelting of iron ore into steel consumes 55% of commercially produced oxygen. In this process, is injected through a high-pressure lance into molten iron, which removes sulfur impurities and excess carbon as the respective oxides, and . The reactions are exothermic reaction, exothermic, so the temperature increases to 1,700 °Celsius, C.
Another 25% of commercially produced oxygen is used by the chemical industry. Ethylene is reacted with to create ethylene oxide, which, in turn, is converted into ethylene glycol; the primary feeder material used to manufacture a host of products, including antifreeze and polyester polymers (the precursors of many plastics and fabrics).
Most of the remaining 20% of commercially produced oxygen is used in medical applications, gas welding, metal cutting and welding, as an oxidizer in rocket fuel, and in water treatment. Oxygen is used in oxyacetylene welding, burning acetylene with to produce a very hot flame. In this process, metal up to thick is first heated with a small oxy-acetylene flame and then quickly cut by a large stream of . Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 508
 The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1/2 (superoxides), −1/3 (ozonides), 0 (Allotropes of oxygen, elemental, hypofluorous acid), +1/2 (dioxygenyl), +1 (dioxygen difluoride), and +2 (oxygen difluoride).
The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1/2 (superoxides), −1/3 (ozonides), 0 (Allotropes of oxygen, elemental, hypofluorous acid), +1/2 (dioxygenyl), +1 (dioxygen difluoride), and +2 (oxygen difluoride).
 Due to its electronegativity, oxygen forms chemical bonds with almost all other elements to give corresponding
Due to its electronegativity, oxygen forms chemical bonds with almost all other elements to give corresponding
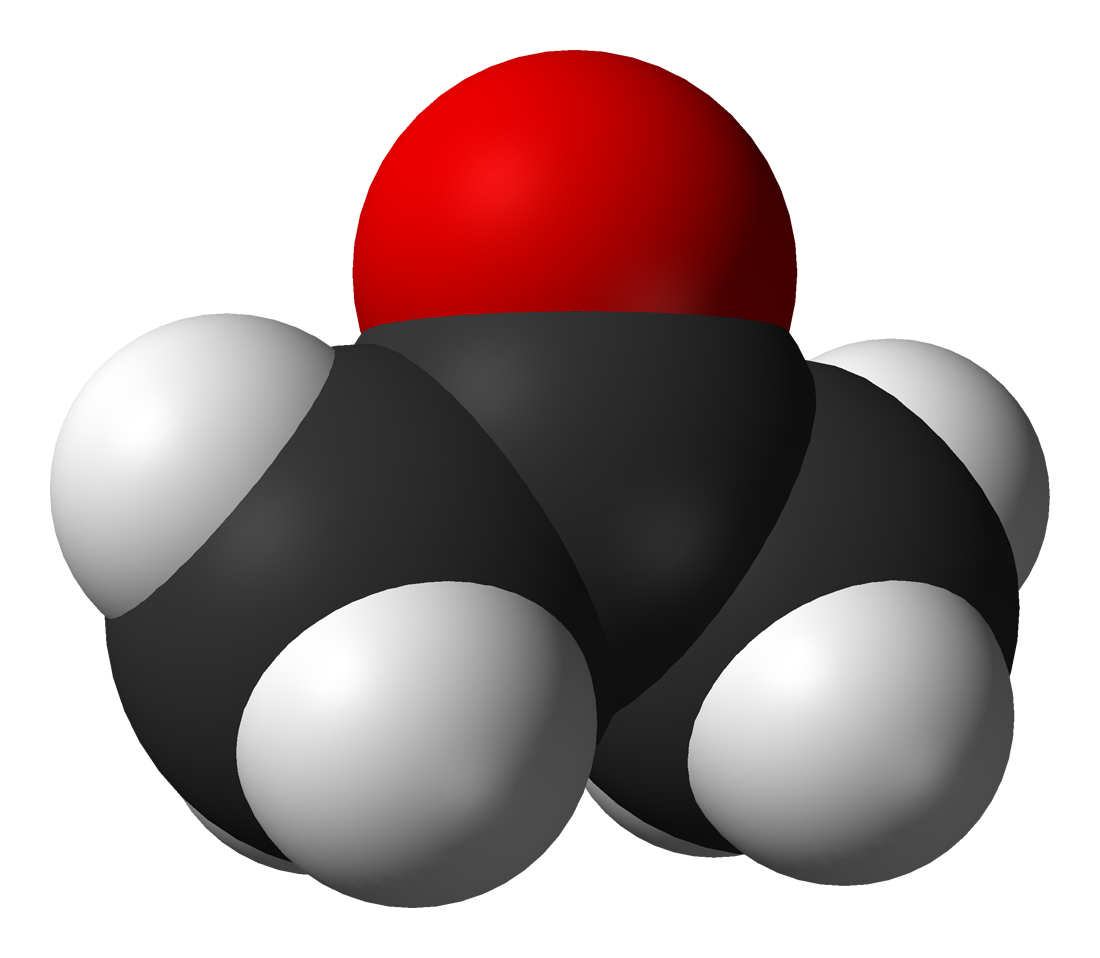 Among the most important classes of organic compounds that contain oxygen are (where "R" is an organic group): Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols (); ethers (); ketones (); aldehydes (); carboxylic acids (); esters (); Organic acid anhydride, acid anhydrides (); and amides (). There are many important organic solvents that contain oxygen, including: acetone, methanol, ethanol, Isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol, furan, tetrahydrofuran, THF, diethyl ether, 1,4-Dioxane, dioxane, ethyl acetate, dimethylformamide, DMF, dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO, acetic acid, and formic acid. Acetone () and phenol () are used as feeder materials in the synthesis of many different substances. Other important organic compounds that contain oxygen are: glycerol, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, citric acid, acetic anhydride, and acetamide. Epoxides are ethers in which the oxygen atom is part of a ring of three atoms. The element is similarly found in almost all biomolecules that are important to (or generated by) life.
Oxygen reacts spontaneously with many organic chemistry, organic compounds at or below room temperature in a process called autoxidation. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 506 Most of the organic compounds that contain oxygen are not made by direct action of . Organic compounds important in industry and commerce that are made by direct oxidation of a precursor include ethylene oxide and peracetic acid.
Among the most important classes of organic compounds that contain oxygen are (where "R" is an organic group): Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols (); ethers (); ketones (); aldehydes (); carboxylic acids (); esters (); Organic acid anhydride, acid anhydrides (); and amides (). There are many important organic solvents that contain oxygen, including: acetone, methanol, ethanol, Isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol, furan, tetrahydrofuran, THF, diethyl ether, 1,4-Dioxane, dioxane, ethyl acetate, dimethylformamide, DMF, dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO, acetic acid, and formic acid. Acetone () and phenol () are used as feeder materials in the synthesis of many different substances. Other important organic compounds that contain oxygen are: glycerol, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, citric acid, acetic anhydride, and acetamide. Epoxides are ethers in which the oxygen atom is part of a ring of three atoms. The element is similarly found in almost all biomolecules that are important to (or generated by) life.
Oxygen reacts spontaneously with many organic chemistry, organic compounds at or below room temperature in a process called autoxidation. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 506 Most of the organic compounds that contain oxygen are not made by direct action of . Organic compounds important in industry and commerce that are made by direct oxidation of a precursor include ethylene oxide and peracetic acid.
 Oxygen gas () can be Oxygen toxicity, toxic at elevated partial pressures, leading to convulsions and other health problems.Since 's partial pressure is the fraction of times the total pressure, elevated partial pressures can occur either from high fraction in breathing gas or from high breathing gas pressure, or a combination of both. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 511 Oxygen toxicity usually begins to occur at partial pressures more than 50 kiloPascal (unit), pascals (kPa), equal to about 50% oxygen composition at standard pressure or 2.5 times the normal sea-level partial pressure of about 21 kPa. This is not a problem except for patients on mechanical ventilators, since gas supplied through oxygen masks in medical applications is typically composed of only 30–50% by volume (about 30 kPa at standard pressure).
At one time, Premature birth, premature babies were placed in incubators containing -rich air, but this practice was discontinued after some babies were blinded by the oxygen content being too high.
Breathing pure in space applications, such as in some modern space suits, or in early spacecraft such as Apollo spacecraft, Apollo, causes no damage due to the low total pressures used. In the case of spacesuits, the partial pressure in the breathing gas is, in general, about 30 kPa (1.4 times normal), and the resulting partial pressure in the astronaut's arterial blood is only marginally more than normal sea-level partial pressure.
Oxygen toxicity to the lungs and central nervous system can also occur in deep scuba diving and surface-supplied diving. Prolonged breathing of an air mixture with an partial pressure more than 60 kPa can eventually lead to permanent pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure to an partial pressure greater than 160 kPa (about 1.6 atm) may lead to convulsions (normally fatal for divers). Acute oxygen toxicity (causing seizures, its most feared effect for divers) can occur by breathing an air mixture with 21% at or more of depth; the same thing can occur by breathing 100% at only .
Oxygen gas () can be Oxygen toxicity, toxic at elevated partial pressures, leading to convulsions and other health problems.Since 's partial pressure is the fraction of times the total pressure, elevated partial pressures can occur either from high fraction in breathing gas or from high breathing gas pressure, or a combination of both. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 511 Oxygen toxicity usually begins to occur at partial pressures more than 50 kiloPascal (unit), pascals (kPa), equal to about 50% oxygen composition at standard pressure or 2.5 times the normal sea-level partial pressure of about 21 kPa. This is not a problem except for patients on mechanical ventilators, since gas supplied through oxygen masks in medical applications is typically composed of only 30–50% by volume (about 30 kPa at standard pressure).
At one time, Premature birth, premature babies were placed in incubators containing -rich air, but this practice was discontinued after some babies were blinded by the oxygen content being too high.
Breathing pure in space applications, such as in some modern space suits, or in early spacecraft such as Apollo spacecraft, Apollo, causes no damage due to the low total pressures used. In the case of spacesuits, the partial pressure in the breathing gas is, in general, about 30 kPa (1.4 times normal), and the resulting partial pressure in the astronaut's arterial blood is only marginally more than normal sea-level partial pressure.
Oxygen toxicity to the lungs and central nervous system can also occur in deep scuba diving and surface-supplied diving. Prolonged breathing of an air mixture with an partial pressure more than 60 kPa can eventually lead to permanent pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure to an partial pressure greater than 160 kPa (about 1.6 atm) may lead to convulsions (normally fatal for divers). Acute oxygen toxicity (causing seizures, its most feared effect for divers) can occur by breathing an air mixture with 21% at or more of depth; the same thing can occur by breathing 100% at only .
 Highly concentrated sources of oxygen promote rapid combustion. Fire and explosion hazards exist when concentrated oxidants and fuels are brought into close proximity; an ignition event, such as heat or a spark, is needed to trigger combustion. Oxygen is the oxidant, not the fuel.
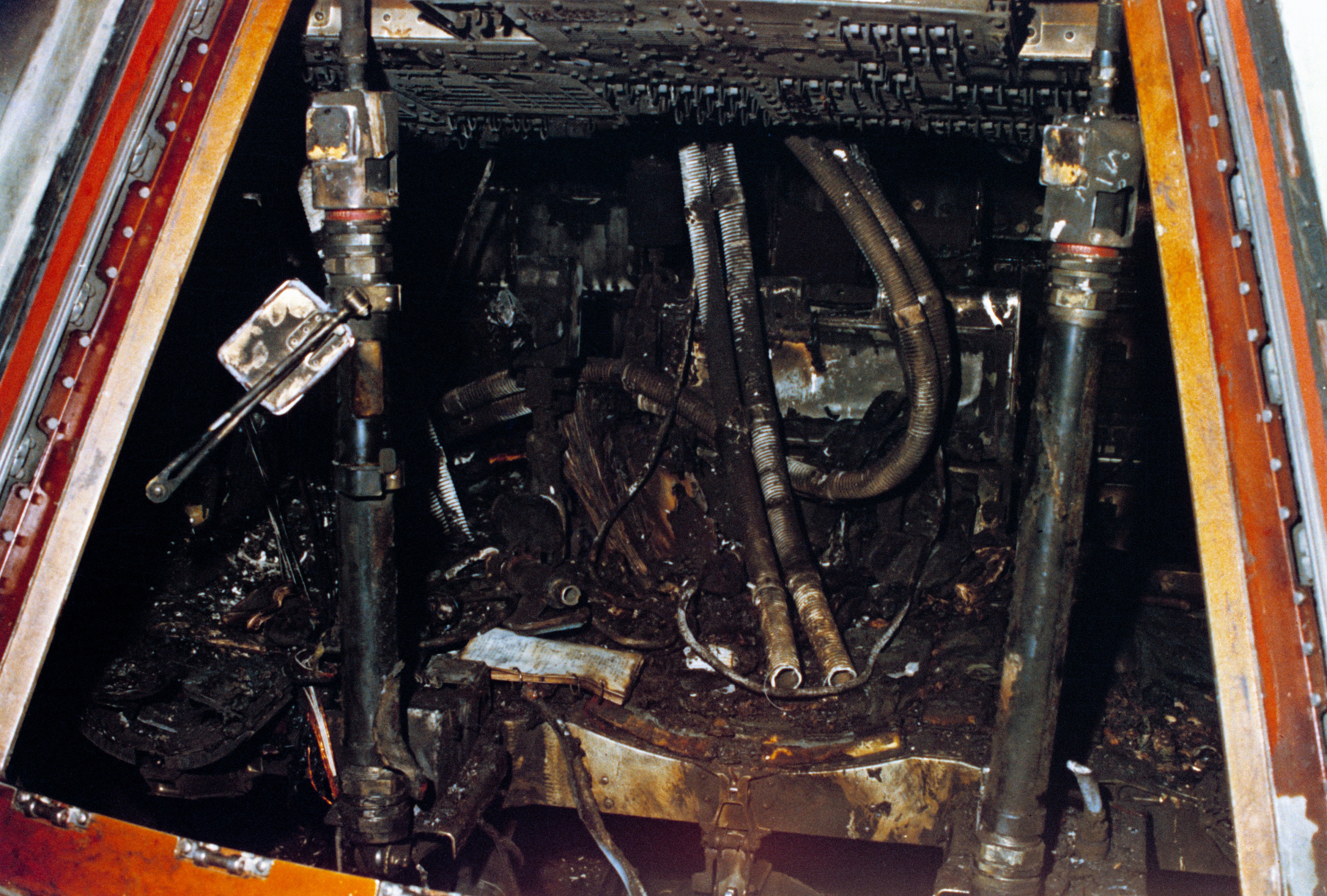
Concentrated will allow combustion to proceed rapidly and energetically. Steel pipes and storage vessels used to store and transmit both gaseous and liquid oxygen will act as a fuel; and therefore the design and manufacture of systems requires special training to ensure that ignition sources are minimized. The fire that killed the Apollo 1 crew in a launch pad test spread so rapidly because the capsule was pressurized with pure but at slightly more than atmospheric pressure, instead of the normal pressure that would be used in a mission.
Liquid oxygen spills, if allowed to soak into organic matter, such as wood, petrochemicals, and Bitumen, asphalt can cause these materials to Detonation, detonate unpredictably on subsequent mechanical impact.
Highly concentrated sources of oxygen promote rapid combustion. Fire and explosion hazards exist when concentrated oxidants and fuels are brought into close proximity; an ignition event, such as heat or a spark, is needed to trigger combustion. Oxygen is the oxidant, not the fuel.
Concentrated will allow combustion to proceed rapidly and energetically. Steel pipes and storage vessels used to store and transmit both gaseous and liquid oxygen will act as a fuel; and therefore the design and manufacture of systems requires special training to ensure that ignition sources are minimized. The fire that killed the Apollo 1 crew in a launch pad test spread so rapidly because the capsule was pressurized with pure but at slightly more than atmospheric pressure, instead of the normal pressure that would be used in a mission.
Liquid oxygen spills, if allowed to soak into organic matter, such as wood, petrochemicals, and Bitumen, asphalt can cause these materials to Detonation, detonate unpredictably on subsequent mechanical impact.
Oxygen
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Oxidizing Agents > Oxygen
Roald Hoffmann article on "The Story of O"
*
Scripps Institute: Atmospheric Oxygen has been dropping for 20 years
{{featured article Oxygen, Chemical elements Diatomic nonmetals Reactive nonmetals Chalcogens Chemical substances for emergency medicine Breathing gases E-number additives Oxidizing agents
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
O and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
8. It is a member of the chalcogen
The chalcogens (ore forming) ( ) are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family. Group 16 consists of the elements oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and the rad ...
group in the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
, a highly reactive nonmetal
In the context of the periodic table, a nonmetal is a chemical element that mostly lacks distinctive metallic properties. They range from colorless gases like hydrogen to shiny crystals like iodine. Physically, they are usually lighter (less ...
, and a potent oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ''electron donor''). In ot ...
that readily forms oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
in the form of various oxides such as water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
s and silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
s.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
.
At standard temperature and pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used ...
, two oxygen atoms will bind
BIND () is a suite of software for interacting with the Domain Name System (DNS). Its most prominent component, named (pronounced ''name-dee'': , short for ''name Daemon (computing), daemon''), performs both of the main DNS server roles, acting ...
covalently to form dioxygen
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (). Others are:
* Ato ...
, a colorless and odorless diatomic
Diatomic molecules () are molecules composed of only two atoms, of the same or different chemical elements. If a diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element, such as hydrogen () or oxygen (), then it is said to be homonuclear mol ...
gas with the chemical formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as pare ...
. Dioxygen gas currently constitutes approximately 20.95% molar fraction
In chemistry, the Mole (unit), mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity (science), quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of substance, amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (ex ...
of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time in Earth's history
The natural history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by consta ...
. A much rarer triatomic allotrope of oxygen, ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
(), strongly absorbs the UVB and UVC wavelengths and forms a protective ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the a ...
at the lower stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second-lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is composed of stratified temperature zones, with the warmer layers of air located higher ...
, which shields the biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
from ionizing ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
. However, ozone present at the surface is a corrosive
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
byproduct of smog
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words ''smoke'' and ''fog'' to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odour. The word was then inte ...
and thus an air pollutant
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be gases like ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles like soot and dust. It affects both outdoor ...
.
All eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s, including plants, animals, fungi, algae and most protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s, need oxygen for cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cell ...
, a process that extracts chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when the substances undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (20 ...
by the reaction of oxygen with organic molecules derived from food and releases carbon dioxide as a waste product.
Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s, carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s and fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
s, as do the major constituent inorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''.
Inorgan ...
s of animal shells, teeth, and bone. Most of the mass of living organisms is oxygen as a component of water, the major constituent of lifeforms. Oxygen in Earth's atmosphere is produced by biotic photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, in which photon energy
Photon energy is the energy carried by a single photon. The amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon's electromagnetic frequency and thus, equivalently, is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The higher the photon's frequenc ...
in sunlight is captured by chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
to split water molecules and then react with carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s and oxygen is released as a byproduct
A by-product or byproduct is a secondary product derived from a production process, manufacturing process or chemical reaction; it is not the primary product or service being produced.
A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be cons ...
. Oxygen is too chemically reactive to remain a free element in air without being continuously replenished by the photosynthetic activities of autotroph
An autotroph is an organism that can convert Abiotic component, abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by Heterotroph, other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohy ...
s such as cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
, chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
-bearing algae and plants.
Oxygen was isolated by Michael Sendivogius before 1604, but it is commonly believed that the element was discovered independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish Pomerania, German-Swedish pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified the elements molybd ...
, in Uppsala
Uppsala ( ; ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the capital of Uppsala County and the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Loc ...
, in 1773 or earlier, and Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, Unitarian, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher, English Separatist, separatist theologian, Linguist, grammarian, multi-subject educator and Classical libera ...
in Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated to Wilts) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It borders Gloucestershire to the north, Oxfordshire to the north-east, Berkshire to the east, Hampshire to the south-east, Dorset to the south, and Somerset to ...
, in 1774. Priority is often given for Priestley because his work was published first. Priestley, however, called oxygen "dephlogisticated air", and did not recognize it as a chemical element. The name ''oxygen'' was coined in 1777 by Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that i ...
, who first recognized oxygen as a chemical element and correctly characterized the role it plays in combustion.
Common industrial uses of oxygen include production of steel, plastics and textiles, brazing, welding and cutting of steels and other metals, rocket propellant
Rocket propellant is used as reaction mass ejected from a rocket engine to produce thrust. The energy required can either come from the propellants themselves, as with a chemical rocket, or from an external source, as with ion engines.
Overvi ...
, oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy, also referred to as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Supplemental oxygen can also refer to the use of oxygen enriched air at altitude. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood o ...
, and life support systems in aircraft, submarines, spaceflight and diving.
History of study
The modern concept of the element oxygen developed over five centuries and included many related discoveries and unsuccessful theories. Multiple people made different contributions to the concept: no one person discovered oxygen.Early experiments
One of the first known experiments on the relationship betweencombustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
and air was conducted by the 2nd-century BCE Greek writer on mechanics, Philo of Byzantium
Philo of Byzantium (, ''Phílōn ho Byzántios'', ), also known as Philo Mechanicus (Latin for "Philo the Engineer"), was a Greek engineer, physicist and writer on mechanics, who lived during the latter half of the 3rd century BC. Although he wa ...
. In his work ', Philo observed that inverting a vessel over a burning candle and surrounding the vessel's neck with water resulted in some water rising into the neck. Philo incorrectly surmised that parts of the air in the vessel were converted into the classical element fire and thus were able to escape through pores in the glass.
Many centuries later Ibn al-Nafis
ʿAlāʾ al-Dīn Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn Abī Ḥazm al-Qarashī (Arabic: علاء الدين أبو الحسن عليّ بن أبي حزم القرشي ), known as Ibn al-Nafīs (Arabic: ابن النفيس), was an Arab polymath whose area ...
, writing in 1250CE, correctly described oxygenation of blood in the circulatory system; Michael Servetus rediscovered this concept in 1553 but his books were systematically destroyed. A scientifically based and influential description was published by William Harvey
William Harvey (1 April 1578 – 3 June 1657) was an English physician who made influential contributions to anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, pulmonary and systemic circulation ...
in 1628.
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
observed that a portion of air is consumed during combustion and respiration. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 499.
Polish alchemist, philosopher, and physician Michael Sendivogius (Michał Sędziwój), writing in 1604, described a substance contained in air, referring to it as ('food of life'); this substance is identical with oxygen. During his experiments, performed between 1598 and 1604, Sendivogius properly recognized that the substance is equivalent to the gaseous byproduct released by the thermal decomposition of potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nit ...
. However, this important connection was not understood by contemporary scientists like Robert Boyle.
Unaware of Sendivogius's work, John Mayow wrote about a portion of air that provided heat in a fire and the human body. This work was ignored because it failed to align with the prevailing phlogiston theory of air and fire.
Mayow observed that antimony
Antimony is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Sb () and atomic number 51. A lustrous grey metal or metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient t ...
increased in weight when heated, and inferred that the must have combined with it. He also thought that the lungs separate from air and pass it into the blood and that animal heat and muscle movement result from the reaction of with certain substances in the body. Accounts of these and other experiments and ideas were published in 1668 in his work ' in the tract "".
After Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, Alchemy, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the foun ...
proved that air is necessary for combustion in the late 17th century, English chemist John Mayow (1641–1679) refined this work by showing that fire requires only a part of air that he called . In one experiment, he found that placing either a mouse or a lit candle in a closed container over water caused the water to rise and replace one-fourteenth of the air's volume before extinguishing the subjects. From this, he surmised that is consumed in both respiration and combustion.
Phlogiston theory
Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath who was active as a physicist ("natural philosopher"), astronomer, geologist, meteorologist, and architect. He is credited as one of the first scientists to investigate living ...
, Ole Borch, Mikhail Lomonosov
Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov (; , ; – ) was a Russian polymath, scientist and writer, who made important contributions to literature, education, and science. Among his discoveries were the atmosphere of Venus and the law of conservation of ...
, and Pierre Bayen all produced oxygen in experiments in the 17th and the 18th century but none of them recognized it as a chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
. Emsley 2001, p. 299 This may have been in part due to the prevalence of the philosophy of combustion and corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
called the ''phlogiston theory'', which was then the favored explanation of those processes.
Established in 1667 by the German alchemist J. J. Becher
Johann Joachim Becher (; 6 May 1635 – October 1682) was a German people, German physician, Alchemy, alchemist, precursor of chemistry, scholar, polymath and adventurer, best known for his ''terra pinguis'' theory which became the phlogiston theo ...
, and modified by the chemist Georg Ernst Stahl by 1731, phlogiston theory stated that all combustible materials were made of two parts. One part, called phlogiston, was given off when the substance containing it was burned, while the dephlogisticated part was thought to be its true form, or calx
Calx is a substance formed from an ore or mineral that has been heated. Calx, especially of a metal, is now understood to be an oxide. The term is also sometimes used in older texts on artists' techniques to mean calcium oxide.
According to the ...
.
Highly combustible materials that leave little residue, such as wood or coal, were thought to be made mostly of phlogiston; non-combustible substances that corrode, such as iron, contained very little. Air did not play a role in phlogiston theory, nor were any initial quantitative experiments conducted to test the idea; instead, it was based on observations of what happens when something burns, that most common objects appear to become lighter and seem to lose something in the process.
Scientific era
 Swedish pharmacist
Swedish pharmacist Carl Wilhelm Scheele
Carl Wilhelm Scheele (, ; 9 December 1742 – 21 May 1786) was a Swedish Pomerania, German-Swedish pharmaceutical chemist.
Scheele discovered oxygen (although Joseph Priestley published his findings first), and identified the elements molybd ...
produced and described some properties of oxygen sometime around 1770-1775, but did not publish his work until a few years later because he was unable to interpret his work in the framework of the phlogiston theory. Scheele had produced oxygen gas by heating mercuric oxide (HgO) and various nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
s in 1771–1772. After reading about Priestley's work in 1775, Scheele published in 1777, calling the gas "fire air" because it was then the only known agent to support combustion. Emsley 2001, p. 300
In the meantime, on August 1, 1774, an experiment conducted by the British clergyman Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, Unitarian, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher, English Separatist, separatist theologian, Linguist, grammarian, multi-subject educator and Classical libera ...
focused sunlight on mercuric oxide contained in a glass tube, which liberated a gas he named "dephlogisticated air". Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 500 He noted that candles burned brighter in the gas and that a mouse was more active and lived longer while breathing
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxy ...
it. After breathing the gas himself, Priestley wrote: "The feeling of it to my lungs was not sensibly different from that of common air, but I fancied that my breast felt peculiarly light and easy for some time afterwards." Priestley published his findings in 1775 in a paper titled "An Account of Further Discoveries in Air", which was included in the second volume of his book titled '' Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air''.
The French chemist Antoine Lavoisier
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier ( ; ; 26 August 17438 May 1794), When reduced without charcoal, it gave off an air which supported respiration and combustion in an enhanced way. He concluded that this was just a pure form of common air and that i ...
later claimed to have discovered the new substance independently. Priestley visited Lavoisier in October 1774 and told him about his experiment and how he liberated the new gas. Scheele had also dispatched a letter to Lavoisier on September 30, 1774, which described his discovery of the previously unknown substance, but Lavoisier never acknowledged receiving it (a copy of the letter was found in Scheele's belongings after his death).
Discrediting Philogiston theory
 Lavoisier conducted the first adequate quantitative experiments on
Lavoisier conducted the first adequate quantitative experiments on oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
and gave the first correct explanation of how combustion works. He used these and similar experiments, all started in 1774, to discredit the phlogiston theory and to prove that the substance discovered by Priestley and Scheele was a chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
.
In one experiment, Lavoisier observed that there was no overall increase in weight when tin and air were heated in a closed container. He noted that air rushed in when he opened the container, which indicated that part of the trapped air had been consumed. He also noted that the tin had increased in weight and that increase was the same as the weight of the air that rushed back in. This and other experiments on combustion were documented in his book ', which was published in 1777. In that work, he proved that air is a mixture of two gases; 'vital air', which is essential to combustion and respiration, and (from Greek 'lifeless'), which did not support either. later became ''nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
'' in English, although it has kept the earlier name in French and several other European languages.
Etymology
Lavoisier renamed "vital air" to in 1777 from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
roots (; "acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
", literally 'sharp', from the taste of acids) and (; "producer", literally 'begetter'), because he mistakenly believed that oxygen was a constituent of all acids. Chemists (such as Sir Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, e ...
in 1812) eventually determined that Lavoisier was wrong in this regard (e.g. Hydrogen chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hyd ...
(HCl) is a strong acid that does not contain oxygen), but by then the name was too well established.
''Oxygen'' entered the English language despite opposition by English scientists and the fact that the Englishman Priestley had first isolated the gas and written about it. This is partly due to a poem praising the gas titled "Oxygen" in the popular book '' The Botanic Garden'' (1791) by Erasmus Darwin, grandfather of Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
.
Later history
John Dalton
John Dalton (; 5 or 6 September 1766 – 27 July 1844) was an English chemist, physicist and meteorologist. He introduced the atomic theory into chemistry. He also researched Color blindness, colour blindness; as a result, the umbrella term ...
's original atomic hypothesis presumed that all elements were monatomic and that the atoms in compounds would normally have the simplest atomic ratios with respect to one another. For example, Dalton assumed that water's formula was HO, leading to the conclusion that the atomic mass
Atomic mass ( or ) is the mass of a single atom. The atomic mass mostly comes from the combined mass of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with minor contributions from the electrons and nuclear binding energy. The atomic mass of atoms, ...
of oxygen was 8 times that of hydrogen, instead of the modern value of about 16. In 1805, Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac ( , ; ; 6 December 1778 – 9 May 1850) was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume (with Alexander von Humboldt), f ...
and Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
showed that water is formed of two volumes of hydrogen and one volume of oxygen; and by 1811 Amedeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto (, also , ; 9 August 17769 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro's law, which states that equal volu ...
had arrived at the correct interpretation of water's composition, based on what is now called Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law (sometimes referred to as Avogadro's hypothesis or Avogadro's principle) or Avogadro-Ampère's hypothesis is an experimental gas law relating the volume of a gas to the amount of substance of gas present. The law is a specific cas ...
and the diatomic elemental molecules in those gases.
In 1879 the French brothers Quentin and Arthur
Brin discovered a commercially viable reaction to create oxygen. They realized that the known reversible reaction
(s) + (g) ↔ (s) was deactivated by the formation of barium carbonate from carbon dioxide in the air; treating air to remove the carbon dioxide allowed the reaction be reversed indefinitely. Their company used the process between 1886 and 1906 when more economical fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation ...
began to be used.
 By the late 19th century scientists realized that air could be liquefied and its components isolated by compressing and cooling it. Using a
By the late 19th century scientists realized that air could be liquefied and its components isolated by compressing and cooling it. Using a cascade
Cascade, or Cascading may refer to:
Science and technology Science
* Air shower (physics), a cascade (particle shower) of subatomic particles and ionized nuclei
** Particle shower, a cascade of secondary particles produced as the result of a high ...
method, Swiss chemist and physicist Raoul Pierre Pictet evaporated liquid sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
in order to liquefy carbon dioxide, which in turn was evaporated to cool oxygen gas enough to liquefy it. He sent a telegram on December 22, 1877, to the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefron ...
in Paris announcing his discovery of liquid oxygen. Just two days later, French physicist Louis Paul Cailletet announced his own method of liquefying molecular oxygen. Only a few drops of the liquid were produced in each case and no meaningful analysis could be conducted. Oxygen was liquefied in a stable state for the first time on March 29, 1883, by Polish scientists from Jagiellonian University, Zygmunt Wróblewski and Karol Olszewski.
In 1891 Scottish chemist James Dewar was able to produce enough liquid oxygen for study. Emsley 2001, p. 303 The first commercially viable process for producing liquid oxygen was independently developed in 1895 by German engineer Carl von Linde and British engineer William Hampson. Both men lowered the temperature of air until it liquefied and then distillation, distilled the component gases by boiling them off one at a time and capturing them separately. Later, in 1901, oxyacetylene welding was demonstrated for the first time by burning a mixture of acetylene and compressed . This method of welding and cutting metal later became common.
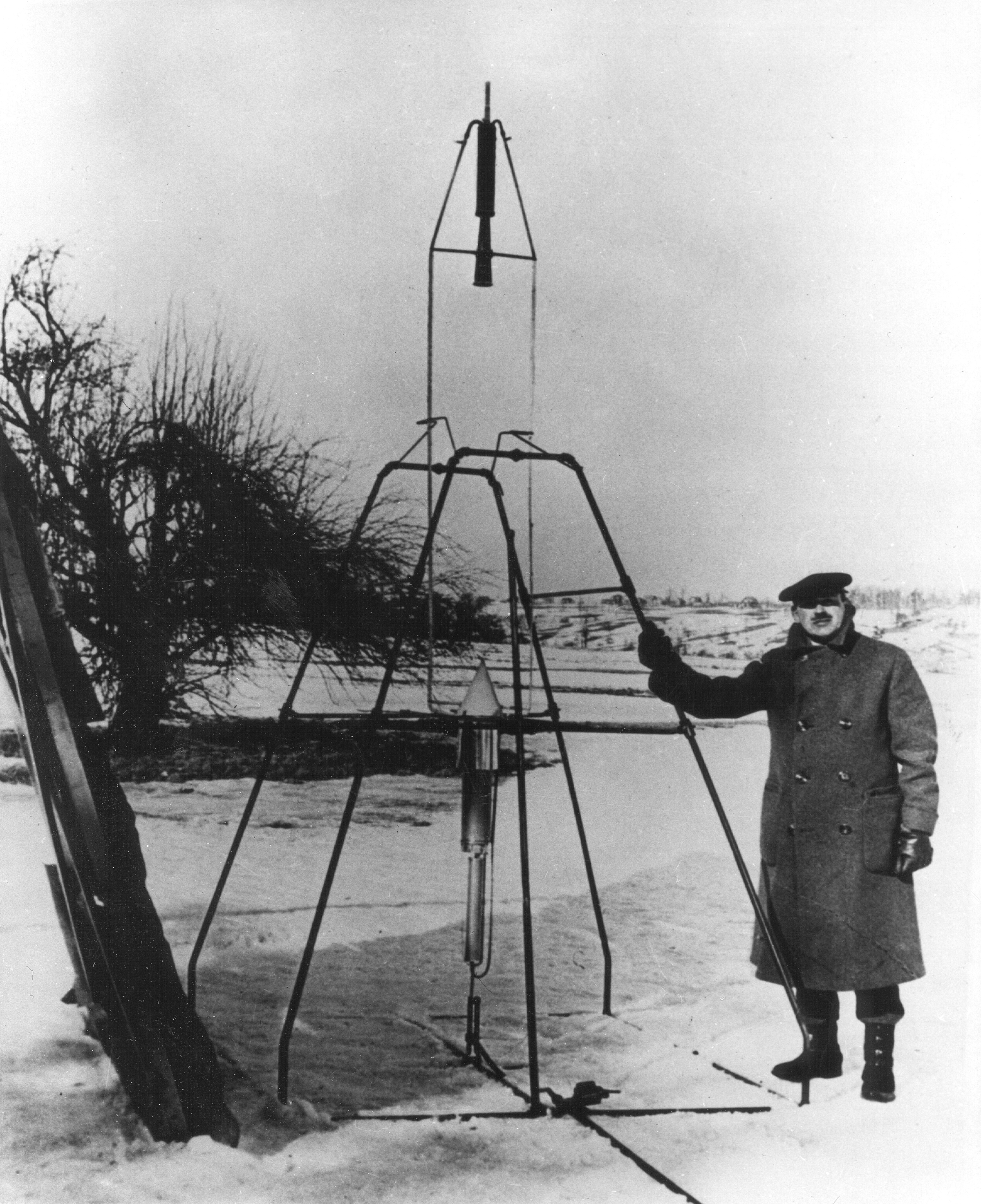
In 1923, the American scientist Robert H. Goddard became the first person to develop a rocket engine that burned liquid fuel; the engine used gasoline for fuel and liquid oxygen as the oxidizer. Goddard successfully flew a small liquid-fueled rocket 56 m at 97 km/h on March 16, 1926, in Auburn, Massachusetts, US.
Characteristics
Properties and molecular structure
standard temperature and pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used ...
, oxygen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas with the molecular formula , referred to as dioxygen.
As ''dioxygen'', two oxygen atoms are chemical bond, chemically bound to each other. The bond can be variously described based on level of theory, but is reasonably and simply described as a covalent double bond that results from the filling of molecular orbitals formed from the atomic orbitals of the individual oxygen atoms, the filling of which results in a bond order of two. More specifically, the double bond is the result of sequential, low-to-high energy, or Aufbau principle, Aufbau, filling of orbitals, and the resulting cancellation of contributions from the 2s electrons, after sequential filling of the low σ and σ* orbitals; σ overlap of the two atomic 2p orbitals that lie along the O–O molecular axis and π overlap of two pairs of atomic 2p orbitals perpendicular to the O–O molecular axis, and then cancellation of contributions from the remaining two 2p electrons after their partial filling of the π* orbitals.Jack Barrett, 2002, "Atomic Structure and Periodicity", (Basic concepts in chemistry, Vol. 9 of Tutorial chemistry texts), Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry, p. 153, . SeGoogle Books
accessed January 31, 2015. This combination of cancellations and σ and π overlaps results in dioxygen's double-bond character and reactivity, and a triplet electronic ground state. An electron configuration with two unpaired electrons, as is found in dioxygen orbitals (see the filled π* orbitals in the diagram) that are of equal energy—i.e., degenerate orbitals, degenerate—is a configuration termed a spin triplet state. Hence, the ground state of the molecule is referred to as triplet oxygen. The highest-energy, partially filled orbitals are antibonding, and so their filling weakens the bond order from three to two. Because of its unpaired electrons, triplet oxygen reacts only slowly with most organic molecules, which have paired electron spins; this prevents spontaneous combustion.
 In the triplet form, molecules are paramagnetism, paramagnetic. That is, they impart magnetic character to oxygen when it is in the presence of a magnetic field, because of the Spin (physics), spin magnetic moments of the unpaired electrons in the molecule, and the negative exchange energy between neighboring molecules. Liquid oxygen is so magnetic that, in laboratory demonstrations, a bridge of liquid oxygen may be supported against its own weight between the poles of a powerful magnet. Oxygen's paramagnetism can be used analytically in paramagnetic oxygen gas analysers that determine gaseous oxygen concentration, especially in industrial process control and medicine.
Singlet oxygen is a name given to several higher-energy species of molecular in which all the electron spins are paired. It is much more reactive with common organic compound, organic molecules than is normal (triplet) molecular oxygen. In nature, singlet oxygen is commonly formed from water during photosynthesis, using the energy of sunlight. It is also produced in the troposphere by the photolysis of ozone by light of short wavelength and by the immune system as a source of active oxygen. Carotenoids in photosynthetic organisms (and possibly animals) play a major role in absorbing energy from singlet oxygen and converting it to the unexcited ground state before it can cause harm to tissues.
In the triplet form, molecules are paramagnetism, paramagnetic. That is, they impart magnetic character to oxygen when it is in the presence of a magnetic field, because of the Spin (physics), spin magnetic moments of the unpaired electrons in the molecule, and the negative exchange energy between neighboring molecules. Liquid oxygen is so magnetic that, in laboratory demonstrations, a bridge of liquid oxygen may be supported against its own weight between the poles of a powerful magnet. Oxygen's paramagnetism can be used analytically in paramagnetic oxygen gas analysers that determine gaseous oxygen concentration, especially in industrial process control and medicine.
Singlet oxygen is a name given to several higher-energy species of molecular in which all the electron spins are paired. It is much more reactive with common organic compound, organic molecules than is normal (triplet) molecular oxygen. In nature, singlet oxygen is commonly formed from water during photosynthesis, using the energy of sunlight. It is also produced in the troposphere by the photolysis of ozone by light of short wavelength and by the immune system as a source of active oxygen. Carotenoids in photosynthetic organisms (and possibly animals) play a major role in absorbing energy from singlet oxygen and converting it to the unexcited ground state before it can cause harm to tissues.
Allotropes
 The common Allotropy, allotrope of elemental oxygen on Earth is called Allotropes of oxygen, dioxygen, , the major part of the Earth's atmospheric oxygen (see #Occurrence, Occurrence). O2 has a bond length of 121 Picometre, pm and a bond energy of 498 joule per mole, kJ/mol.
Trioxygen () is usually known as
The common Allotropy, allotrope of elemental oxygen on Earth is called Allotropes of oxygen, dioxygen, , the major part of the Earth's atmospheric oxygen (see #Occurrence, Occurrence). O2 has a bond length of 121 Picometre, pm and a bond energy of 498 joule per mole, kJ/mol.
Trioxygen () is usually known as ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
and is a very reactive allotrope of oxygen that is damaging to lung tissue. Ozone is produced in the upper atmosphere when combines with atomic oxygen made by the splitting of by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Since ozone absorbs strongly in the UV region of the Electromagnetic spectrum, spectrum, the ozone layer
The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation. It contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) in relation to other parts of the a ...
of the upper atmosphere functions as a protective radiation shield for the planet. Near the Earth's surface, it is a air pollution, pollutant formed as a by-product of exhaust system, automobile exhaust. At low earth orbit altitudes, sufficient atomic oxygen is present to cause corrosion in space, corrosion of spacecraft.
The Metastability in molecules, metastable molecule tetraoxygen () was discovered in 2001, and was assumed to exist in one of the six phases of solid oxygen. In 2006 this phase, created by pressurizing to 20 Pascal (unit), GPa, was shown to form a rhombohedral Cluster chemistry, cluster. This cluster has the potential to be a much more powerful oxidizing agent, oxidizer than either or and may therefore be used in Rocket propellant, rocket fuel. A metallic phase was discovered in 1990 when solid oxygen is subjected to a pressure of above 96 GPa and it was shown in 1998 that at very low temperatures, this phase becomes superconductivity, superconducting.
Physical properties
 Oxygen Solubility, dissolves more readily in water than nitrogen does. Water in equilibrium with air contains approximately 1 molecule of dissolved for every 2 molecules of (1:2), compared with an atmospheric ratio of approximately 1:4. The solubility of oxygen in water is temperature-dependent, and about twice as much () dissolves at than at ().
At and of air, freshwater can dissolve about 6.04 Litre, milliliters (mL) of oxygen per liter, and seawater contains about 4.95 mL per liter.
At the solubility increases to 9.0 mL (50% more than at ) per liter for freshwater and 7.2 mL (45% more) per liter for sea water.
Oxygen condenses at 90.20 kelvin, K (−182.95 °C, −297.31 °F) and freezes at 54.36 K (−218.79 °C, −361.82 °F). Both liquid oxygen, liquid and solid oxygen, solid are clear substances with a light diffuse sky radiation, sky-blue color caused by absorption in the red (in contrast with the blue color of the sky, which is due to Rayleigh scattering of blue light). High-purity liquid is usually obtained by the
Oxygen Solubility, dissolves more readily in water than nitrogen does. Water in equilibrium with air contains approximately 1 molecule of dissolved for every 2 molecules of (1:2), compared with an atmospheric ratio of approximately 1:4. The solubility of oxygen in water is temperature-dependent, and about twice as much () dissolves at than at ().
At and of air, freshwater can dissolve about 6.04 Litre, milliliters (mL) of oxygen per liter, and seawater contains about 4.95 mL per liter.
At the solubility increases to 9.0 mL (50% more than at ) per liter for freshwater and 7.2 mL (45% more) per liter for sea water.
Oxygen condenses at 90.20 kelvin, K (−182.95 °C, −297.31 °F) and freezes at 54.36 K (−218.79 °C, −361.82 °F). Both liquid oxygen, liquid and solid oxygen, solid are clear substances with a light diffuse sky radiation, sky-blue color caused by absorption in the red (in contrast with the blue color of the sky, which is due to Rayleigh scattering of blue light). High-purity liquid is usually obtained by the fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation ...
of liquefied air. Liquid oxygen may also be condensed from air using liquid nitrogen as a coolant. Liquid oxygen is a highly reactive substance and must be segregated from combustible materials.
The spectroscopy of molecular oxygen is associated with the atmospheric processes of aurora and airglow. The absorption in the Herzberg continuum and Schumann–Runge bands in the ultraviolet produces atomic oxygen that is important in the chemistry of the middle atmosphere. Excited-state singlet molecular oxygen is responsible for red chemiluminescence in solution.
Table of thermal and physical properties of oxygen (O2) at atmospheric pressure:
Isotopes and stellar origin
helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
during the CNO cycle, making it a common isotope in the hydrogen burning zones of stars. Most 18O is produced when Nitrogen-14, 14N (made abundant from CNO burning) captures a Helium-4, 4He nucleus, making 18O common in the helium-rich zones of Stellar evolution#Massive stars, evolved, massive stars.
Fifteen radioisotopes have been characterized, ranging from 11O to 28O. The most stable are 15O with a half-life of 122.24 seconds and 14O with a half-life of 70.606 seconds. All of the remaining Radioactive decay, radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 27 seconds and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 83 milliseconds. The most common decay mode of the isotopes lighter than 16O is positron emission, β+ decay to yield nitrogen, and the most common mode for the isotopes heavier than 18O is beta decay to yield fluorine.
Occurrence
Oxygen is the third most abundant chemical element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium. Emsley 2001, p. 297 About 0.9% of the Sun's mass is oxygen. Oxygen constitutes 49.2% of theEarth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
by mass as part of oxide compounds such as silicon dioxide and is the most abundant element by mass in the crust (geology)#Earth's crust and mantle, Earth's crust. It is also the major component of the world's oceans (88.8% by mass). Oxygen gas is the second most common component of the Earth's atmosphere, taking up 20.8% of its volume and 23.1% of its mass (some 1015 tonnes). Emsley 2001, p. 298Figures given are for values up to above the surface
Earth is unusual among the planets of the Solar System in having such a high concentration of oxygen gas in its atmosphere: Mars (with 0.1% by volume) and Venus have much less. The surrounding those planets is produced solely by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen-containing molecules such as carbon dioxide.
The unusually high concentration of oxygen gas on Earth is the result of the oxygen cycle. This biogeochemical cycle describes the movement of oxygen within and between its three main reservoirs on Earth: the atmosphere, the biosphere, and the lithosphere. The main driving factor of the oxygen cycle is photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
, which is responsible for modern Earth's atmosphere. Photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, while Cellular respiration, respiration, Decomposition, decay, and combustion remove it from the atmosphere. In the present equilibrium, production and consumption occur at the same rate.
Oxygen levels in the atmosphere are trending slightly downward globally, possibly because of fossil-fuel burning.
 Free oxygen also occurs in solution in the world's water bodies. The increased solubility of at lower temperatures (see #Physical properties, Physical properties) has important implications for ocean life, as polar oceans support a much higher density of life due to their higher oxygen content. Scientists assess this aspect of water quality by measuring the water's biochemical oxygen demand, or the amount of needed to restore it to a normal concentration. Emsley 2001, p. 301
Significant deoxygenation has been observed in tropical oceans. Warming oceans waters are expected to lose oxygen over the next century and into the future for a thousand years; the possible consequences include minimal oxygen zones which are unable to support macrofauna.
Free oxygen also occurs in solution in the world's water bodies. The increased solubility of at lower temperatures (see #Physical properties, Physical properties) has important implications for ocean life, as polar oceans support a much higher density of life due to their higher oxygen content. Scientists assess this aspect of water quality by measuring the water's biochemical oxygen demand, or the amount of needed to restore it to a normal concentration. Emsley 2001, p. 301
Significant deoxygenation has been observed in tropical oceans. Warming oceans waters are expected to lose oxygen over the next century and into the future for a thousand years; the possible consequences include minimal oxygen zones which are unable to support macrofauna.
Analysis
 Paleoclimatology, Paleoclimatologists measure the ratio of oxygen-18 and oxygen-16 in the Exoskeleton, shells and skeletons of marine organisms to determine the climate millions of years ago (see oxygen isotope ratio cycle). Seawater molecules that contain the lighter isotope, oxygen-16, evaporate at a slightly faster rate than water molecules containing the 12% heavier oxygen-18, and this disparity increases at lower temperatures. Emsley 2001, p. 304 During periods of lower global temperatures, snow and rain from that evaporated water tends to be higher in oxygen-16, and the seawater left behind tends to be higher in oxygen-18. Marine organisms then incorporate more oxygen-18 into their skeletons and shells than they would in a warmer climate. Paleoclimatologists also directly measure this ratio in the water molecules of ice core samples as old as hundreds of thousands of years.
Geology of solar terrestrial planets, Planetary geologists have measured the relative quantities of oxygen isotopes in samples from the Earth, the Moon, Mars, and meteorites, but were long unable to obtain reference values for the isotope ratios in the Sun, believed to be the same as those of the Nebular hypothesis, primordial solar nebula. Analysis of a silicon wafer exposed to the solar wind in space and returned by the crashed Genesis (spacecraft), Genesis spacecraft has shown that the Sun has a higher proportion of oxygen-16 than does the Earth. The measurement implies that an unknown process depleted oxygen-16 from the Sun's Protoplanetary disk, disk of protoplanetary material prior to the coalescence of dust grains that formed the Earth.
Oxygen presents two spectrophotometric absorption bands peaking at the wavelengths 687 and 760 Nanometre, nm. Some remote sensing scientists have proposed using the measurement of the radiance coming from vegetation canopies in those bands to characterize plant health status from a Earth observation satellite, satellite platform. This approach exploits the fact that in those bands it is possible to discriminate the vegetation's reflectance from its fluorescence, which is much weaker. The measurement is technically difficult owing to the low signal-to-noise ratio and the physical structure of vegetation; but it has been proposed as a possible method of monitoring the carbon cycle from satellites on a global scale.
Paleoclimatology, Paleoclimatologists measure the ratio of oxygen-18 and oxygen-16 in the Exoskeleton, shells and skeletons of marine organisms to determine the climate millions of years ago (see oxygen isotope ratio cycle). Seawater molecules that contain the lighter isotope, oxygen-16, evaporate at a slightly faster rate than water molecules containing the 12% heavier oxygen-18, and this disparity increases at lower temperatures. Emsley 2001, p. 304 During periods of lower global temperatures, snow and rain from that evaporated water tends to be higher in oxygen-16, and the seawater left behind tends to be higher in oxygen-18. Marine organisms then incorporate more oxygen-18 into their skeletons and shells than they would in a warmer climate. Paleoclimatologists also directly measure this ratio in the water molecules of ice core samples as old as hundreds of thousands of years.
Geology of solar terrestrial planets, Planetary geologists have measured the relative quantities of oxygen isotopes in samples from the Earth, the Moon, Mars, and meteorites, but were long unable to obtain reference values for the isotope ratios in the Sun, believed to be the same as those of the Nebular hypothesis, primordial solar nebula. Analysis of a silicon wafer exposed to the solar wind in space and returned by the crashed Genesis (spacecraft), Genesis spacecraft has shown that the Sun has a higher proportion of oxygen-16 than does the Earth. The measurement implies that an unknown process depleted oxygen-16 from the Sun's Protoplanetary disk, disk of protoplanetary material prior to the coalescence of dust grains that formed the Earth.
Oxygen presents two spectrophotometric absorption bands peaking at the wavelengths 687 and 760 Nanometre, nm. Some remote sensing scientists have proposed using the measurement of the radiance coming from vegetation canopies in those bands to characterize plant health status from a Earth observation satellite, satellite platform. This approach exploits the fact that in those bands it is possible to discriminate the vegetation's reflectance from its fluorescence, which is much weaker. The measurement is technically difficult owing to the low signal-to-noise ratio and the physical structure of vegetation; but it has been proposed as a possible method of monitoring the carbon cycle from satellites on a global scale.
Biological production and role of O2
Photosynthesis and respiration
byproduct
A by-product or byproduct is a secondary product derived from a production process, manufacturing process or chemical reaction; it is not the primary product or service being produced.
A by-product can be useful and marketable or it can be cons ...
of photolysis, light-driven splitting of water during chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
ic photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
. According to some estimates, marine photoautotrophs such as red algae, red/green algae and cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
provide about 70% of the free oxygen produced on Earth, and the rest is produced in terrestrial environments by plants. Other estimates of the oceanic contribution to atmospheric oxygen are higher, while some estimates are lower, suggesting oceans produce ~45% of Earth's atmospheric oxygen each year.
A simplified overall formula for photosynthesis is
: 6 + 6 + photons → + 6
or simply
: carbon dioxide + water + sunlight → glucose + dioxygen
Photolytic oxygen evolution occurs in the thylakoid membranes of photosynthetic organisms and requires the energy of four photons.Thylakoid membranes are part of chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
s in algae and plants while they simply are one of many membrane structures in cyanobacteria. In fact, chloroplasts are thought to have evolved from cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
that were once symbiotic partners with the progenitors of plants and algae. Many steps are involved, but the result is the formation of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, which is used to synthesize adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via photophosphorylation.#Reference-idRaven2005, Raven 2005, 115–27 The remaining (after production of the water molecule) is released into the atmosphere.Water oxidation is catalyzed by a manganese-containing enzyme complex known as the oxygen evolving complex (OEC) or water-splitting complex found associated with the lumenal side of thylakoid membranes. Manganese is an important Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor, and calcium and chloride are also required for the reaction to occur. (Raven 2005)
Oxygen is used in mitochondria of eukaryotes to generate ATP during oxidative phosphorylation. The reaction for aerobic respiration is essentially the reverse of photosynthesis and is simplified as
: + 6 → 6 + 6 + 2880 kJ/mol
In aquatic animals, dissolved oxygen in water is absorbed by gills, cutaneous respiration, through the skin or enteral respiration, via the gut; in terrestrial animals such as tetrapods, oxygen in air is breathing, actively taken into the body via lungs, where gas exchange takes place to diffusion, diffuse oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide out, and the body's circulatory system then transports the oxygen to other tissues where cellular respiration takes place. However in insects, the most successful and biodiverse terrestrial clade, oxygen is directly conducted to the internal tissues via respiratory system of insects, a deep network of airways. Hemoglobin in red blood cells binds , changing color from bluish red to bright red ( is released from another part of hemoglobin through the Bohr effect). Other terrestrial invertebrates use hemocyanin (molluscs and some arthropods) or hemerythrin (spiders and lobsters) instead. A liter of blood can dissolve up to 200 cm3 of .
Until the discovery of anaerobic organism, anaerobic animal, metazoa, oxygen was thought to be a requirement for all complex life.
Reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide ion () and hydrogen peroxide (), are reactive by-products of oxygen use in organisms. Parts of the immune system of higher organisms create peroxide, superoxide, and singlet oxygen to destroy invading microbes. Reactive oxygen species also play an important role in the hypersensitive response of plants against pathogen attack. Oxygen is damaging to Obligate anaerobe, obligately anaerobic organisms, which were the dominant form of Evolutionary history of life, early life on Earth until began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago during the Great Oxygenation Event, about a billion years after the first appearance of these organisms.
An adult human at rest inhales 1.8 to 2.4 grams of oxygen per minute. This amounts to more than 6 billion tonnes of oxygen inhaled by humanity per year.(1.8 grams/min/person)×(60 min/h)×(24 h/day)×(365 days/year)×(6.6 billion people)/1,000,000 g/t=6.24 billion tonnes
Living organisms
The free oxygen partial pressure in the body of a living vertebrate organism is highest in the respiratory system, and decreases along any arterial system, peripheral tissues, and venous system, respectively. Partial pressure is the pressure that oxygen would have if it alone occupied the volume.Build-up in the atmosphere
Extraterrestrial free oxygen
In the field of astrobiology and in the search for extraterrestrial life oxygen is a strong biosignature. That said it might not be a definite biosignature, being Extraterrestrial atmosphere#Abiotic oxygen, possibly produced abiotically on celestial bodies with processes and conditions (such as a peculiar hydrosphere) which allow free oxygen, like with Europa (moon), Europa's and Ganymede (moon), Ganymede's thin oxygen atmospheres.Industrial production
fractional distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation ...
of liquefied air, with distillation, distilling as a vapor while is left as a liquid.
The other primary method of producing is passing a stream of clean, dry air through one bed of a pair of identical zeolite molecular sieves, which absorbs the nitrogen and delivers a gas stream that is 90% to 93% . Simultaneously, nitrogen gas is released from the other nitrogen-saturated zeolite bed, by reducing the chamber operating pressure and diverting part of the oxygen gas from the producer bed through it, in the reverse direction of flow. After a set cycle time the operation of the two beds is interchanged, thereby allowing for a continuous supply of gaseous oxygen to be pumped through a pipeline. This is known as pressure swing adsorption. Oxygen gas is increasingly obtained by these non-cryogenics, cryogenic technologies (see also the related vacuum swing adsorption).
 In academic laboratories, oxygen can be prepared by heating together potassium chlorate mixed with a small proportion of manganese dioxide.
Oxygen gas can also be produced through electrolysis of water into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. DC electricity must be used: if AC is used, the gases in each limb consist of hydrogen and oxygen in the explosive ratio 2:1. A similar method is the electrocatalytic evolution from oxides and oxoacids. Chemical catalysts can be used as well, such as in chemical oxygen generators or oxygen candles that are used as part of the life-support equipment on submarines, and are still part of standard equipment on commercial airliners in case of depressurization emergencies. Another air separation method is forcing air to dissolve through ceramic membranes based on zirconium dioxide by either high pressure or an electric current, to produce nearly pure gas.
In academic laboratories, oxygen can be prepared by heating together potassium chlorate mixed with a small proportion of manganese dioxide.
Oxygen gas can also be produced through electrolysis of water into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. DC electricity must be used: if AC is used, the gases in each limb consist of hydrogen and oxygen in the explosive ratio 2:1. A similar method is the electrocatalytic evolution from oxides and oxoacids. Chemical catalysts can be used as well, such as in chemical oxygen generators or oxygen candles that are used as part of the life-support equipment on submarines, and are still part of standard equipment on commercial airliners in case of depressurization emergencies. Another air separation method is forcing air to dissolve through ceramic membranes based on zirconium dioxide by either high pressure or an electric current, to produce nearly pure gas.
Storage
 Oxygen storage methods include high-pressure oxygen tanks, cryogenics and chemical compounds. For reasons of economy, oxygen is often transported in bulk as a liquid in specially insulated tankers, since one litre, liter of liquefied oxygen is equivalent to 840 liters of gaseous oxygen at atmospheric pressure and . Such tankers are used to refill bulk liquid-oxygen storage containers, which stand outside hospitals and other institutions that need large volumes of pure oxygen gas. Liquid oxygen is passed through heat exchangers, which convert the cryogenic liquid into gas before it enters the building. Oxygen is also stored and shipped in smaller cylinders containing the compressed gas; a form that is useful in certain portable medical applications and oxy-fuel welding and cutting.
Oxygen storage methods include high-pressure oxygen tanks, cryogenics and chemical compounds. For reasons of economy, oxygen is often transported in bulk as a liquid in specially insulated tankers, since one litre, liter of liquefied oxygen is equivalent to 840 liters of gaseous oxygen at atmospheric pressure and . Such tankers are used to refill bulk liquid-oxygen storage containers, which stand outside hospitals and other institutions that need large volumes of pure oxygen gas. Liquid oxygen is passed through heat exchangers, which convert the cryogenic liquid into gas before it enters the building. Oxygen is also stored and shipped in smaller cylinders containing the compressed gas; a form that is useful in certain portable medical applications and oxy-fuel welding and cutting.
Applications
Medical
 Uptake of from the air is the essential purpose of Respiration (physiology), respiration, so oxygen supplementation is used in medicine. Treatment not only increases oxygen levels in the patient's blood, but has the secondary effect of decreasing resistance to blood flow in many types of diseased lungs, easing work load on the heart. Oxygen therapy is used to treat emphysema, pneumonia, some heart disorders (congestive heart failure), some disorders that cause increased pulmonary artery pressure, and any disease that impairs the body's ability to take up and use gaseous oxygen. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 510
Treatments are flexible enough to be used in hospitals, the patient's home, or increasingly by portable devices. Oxygen tents were once commonly used in oxygen supplementation, but have since been replaced mostly by the use of oxygen masks or nasal cannulas.
Hyperbaric medicine, Hyperbaric (high-pressure) medicine uses special hyperbaric oxygen chamber, oxygen chambers to increase the partial pressure of around the patient and, when needed, the medical staff. Carbon monoxide poisoning, gas gangrene, and decompression sickness (the 'bends') are sometimes addressed with this therapy. Increased concentration in the lungs helps to displace carbon monoxide from the heme group of hemoglobin. Oxygen gas is poisonous to the anaerobic bacteria that cause gas gangrene, so increasing its partial pressure helps kill them. Decompression sickness occurs in divers who decompress too quickly after a dive, resulting in bubbles of inert gas, mostly nitrogen and helium, forming in the blood. Increasing the pressure of as soon as possible helps to redissolve the bubbles back into the blood so that these excess gasses can be exhaled naturally through the lungs. Normobaric oxygen administration at the highest available concentration is frequently used as first aid for any diving injury that may involve inert gas bubble formation in the tissues. There is epidemiological support for its use from a statistical study of cases recorded in a long term database.
Uptake of from the air is the essential purpose of Respiration (physiology), respiration, so oxygen supplementation is used in medicine. Treatment not only increases oxygen levels in the patient's blood, but has the secondary effect of decreasing resistance to blood flow in many types of diseased lungs, easing work load on the heart. Oxygen therapy is used to treat emphysema, pneumonia, some heart disorders (congestive heart failure), some disorders that cause increased pulmonary artery pressure, and any disease that impairs the body's ability to take up and use gaseous oxygen. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 510
Treatments are flexible enough to be used in hospitals, the patient's home, or increasingly by portable devices. Oxygen tents were once commonly used in oxygen supplementation, but have since been replaced mostly by the use of oxygen masks or nasal cannulas.
Hyperbaric medicine, Hyperbaric (high-pressure) medicine uses special hyperbaric oxygen chamber, oxygen chambers to increase the partial pressure of around the patient and, when needed, the medical staff. Carbon monoxide poisoning, gas gangrene, and decompression sickness (the 'bends') are sometimes addressed with this therapy. Increased concentration in the lungs helps to displace carbon monoxide from the heme group of hemoglobin. Oxygen gas is poisonous to the anaerobic bacteria that cause gas gangrene, so increasing its partial pressure helps kill them. Decompression sickness occurs in divers who decompress too quickly after a dive, resulting in bubbles of inert gas, mostly nitrogen and helium, forming in the blood. Increasing the pressure of as soon as possible helps to redissolve the bubbles back into the blood so that these excess gasses can be exhaled naturally through the lungs. Normobaric oxygen administration at the highest available concentration is frequently used as first aid for any diving injury that may involve inert gas bubble formation in the tissues. There is epidemiological support for its use from a statistical study of cases recorded in a long term database.
Life support and recreational use
An application of as a low-pressure breathing gas is in modern space suits, which surround their occupant's body with the breathing gas. These devices use nearly pure oxygen at about one-third normal pressure, resulting in a normal blood partial pressure of . This trade-off of higher oxygen concentration for lower pressure is needed to maintain suit flexibility. Scuba diving, Scuba and Surface-supplied diving, surface-supplied underwater diving, underwater divers and submarines also rely on artificially delivered . Submarines, submersibles and atmospheric diving suits usually operate at normal atmospheric pressure. Breathing air is scrubbed of carbon dioxide by chemical extraction and oxygen is replaced to maintain a constant partial pressure. Ambient pressure divers breathe air or gas mixtures with an oxygen fraction suited to the operating depth. Pure or nearly pure use in diving at pressures higher than atmospheric is usually limited to rebreathers, or Decompression (diving), decompression at relatively shallow depths (~6 meters depth, or less), or Hyperbaric treatment schedules, medical treatment in recompression chambers at pressures up to 2.8 bar, where acute oxygen toxicity can be managed without the risk of drowning. Deeper diving requires significant dilution of with other gases, such as nitrogen or helium, to prevent oxygen toxicity. People who climb mountains or fly in non-pressurized fixed-wing aircraft sometimes have supplemental supplies.The reason is that increasing the proportion of oxygen in the breathing gas at low pressure acts to augment the inspired partial pressure nearer to that found at sea-level. Pressurized commercial airplanes have an emergency supply of automatically supplied to the passengers in case of cabin depressurization. Sudden cabin pressure loss activates chemical oxygen generators above each seat, causing oxygen masks to drop. Pulling on the masks "to start the flow of oxygen" as cabin safety instructions dictate, forces iron filings into the sodium chlorate inside the canister. A steady stream of oxygen gas is then produced by the exothermic reaction. Oxygen, as a mild euphoria, euphoric, has a history of recreational use in oxygen bars and in sports. Oxygen bars are establishments found in the United States since the late 1990s that offer higher than normal exposure for a minimal fee. Professional athletes, especially in American football, sometimes go off-field between plays to don oxygen masks to boost performance. The pharmacological effect is doubted; a placebo effect is a more likely explanation. Available studies support a performance boost from oxygen enriched mixtures only if it is inhaled ''during'' aerobic exercise. Other recreational uses that do not involve breathing include pyrotechnic applications, such as George Goble's five-second ignition of barbecue grills.Industrial
 Smelting of iron ore into steel consumes 55% of commercially produced oxygen. In this process, is injected through a high-pressure lance into molten iron, which removes sulfur impurities and excess carbon as the respective oxides, and . The reactions are exothermic reaction, exothermic, so the temperature increases to 1,700 °Celsius, C.
Another 25% of commercially produced oxygen is used by the chemical industry. Ethylene is reacted with to create ethylene oxide, which, in turn, is converted into ethylene glycol; the primary feeder material used to manufacture a host of products, including antifreeze and polyester polymers (the precursors of many plastics and fabrics).
Most of the remaining 20% of commercially produced oxygen is used in medical applications, gas welding, metal cutting and welding, as an oxidizer in rocket fuel, and in water treatment. Oxygen is used in oxyacetylene welding, burning acetylene with to produce a very hot flame. In this process, metal up to thick is first heated with a small oxy-acetylene flame and then quickly cut by a large stream of . Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 508
Smelting of iron ore into steel consumes 55% of commercially produced oxygen. In this process, is injected through a high-pressure lance into molten iron, which removes sulfur impurities and excess carbon as the respective oxides, and . The reactions are exothermic reaction, exothermic, so the temperature increases to 1,700 °Celsius, C.
Another 25% of commercially produced oxygen is used by the chemical industry. Ethylene is reacted with to create ethylene oxide, which, in turn, is converted into ethylene glycol; the primary feeder material used to manufacture a host of products, including antifreeze and polyester polymers (the precursors of many plastics and fabrics).
Most of the remaining 20% of commercially produced oxygen is used in medical applications, gas welding, metal cutting and welding, as an oxidizer in rocket fuel, and in water treatment. Oxygen is used in oxyacetylene welding, burning acetylene with to produce a very hot flame. In this process, metal up to thick is first heated with a small oxy-acetylene flame and then quickly cut by a large stream of . Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 508
Compounds
 The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1/2 (superoxides), −1/3 (ozonides), 0 (Allotropes of oxygen, elemental, hypofluorous acid), +1/2 (dioxygenyl), +1 (dioxygen difluoride), and +2 (oxygen difluoride).
The oxidation state of oxygen is −2 in almost all known compounds of oxygen. The oxidation state −1 is found in a few compounds such as peroxides. Compounds containing oxygen in other oxidation states are very uncommon: −1/2 (superoxides), −1/3 (ozonides), 0 (Allotropes of oxygen, elemental, hypofluorous acid), +1/2 (dioxygenyl), +1 (dioxygen difluoride), and +2 (oxygen difluoride).
Oxides and other inorganic compounds
Water () is an oxide ofhydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and the most familiar oxygen compound. Hydrogen atoms are covalent bonding, covalently bonded to oxygen in a water molecule but also have an additional attraction (about 23.3 kJ/mol per hydrogen atom) to an adjacent oxygen atom in a separate molecule. These hydrogen bonds between water molecules hold them approximately 15% closer than what would be expected in a simple liquid with just van der Waals forces.Also, since oxygen has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen, the charge difference makes it a polar molecule. The interactions between the different dipoles of each molecule cause a net attraction force.
 Due to its electronegativity, oxygen forms chemical bonds with almost all other elements to give corresponding
Due to its electronegativity, oxygen forms chemical bonds with almost all other elements to give corresponding oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s. The surface of most metals, such as aluminium and titanium, are oxidized in the presence of air and become coated with a thin film of oxide that Passivation (chemistry), passivates the metal and slows further corrosion
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
. Many oxides of the transition metals are non-stoichiometric compounds, with slightly less metal than the chemical formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as pare ...
would show. For example, the mineral Iron(II) oxide, FeO (wüstite) is written as , where ''x'' is usually around 0.05.
Oxygen is present in the atmosphere in trace quantities in the form of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(). The Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
al Rock (geology), rock is composed in large part of oxides of silicon (Silicon dioxide, silica , as found in granite and quartz), aluminium (aluminium oxide , in bauxite and corundum), iron (iron(III) oxide , in hematite and rust), and calcium carbonate (in limestone). The rest of the Earth's crust is also made of oxygen compounds, in particular various complex silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
s (in silicate minerals). The Earth's mantle, of much larger mass than the crust, is largely composed of silicates of magnesium and iron.
Water-solubility, soluble silicates in the form of , , and are used as detergents and adhesives. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 507
Oxygen also acts as a ligand for transition metals, forming transition metal dioxygen complexes, which feature metal–. This class of compounds includes the heme proteins hemoglobin and myoglobin. An exotic and unusual reaction occurs with platinum hexafluoride, , which oxidizes oxygen to give , dioxygenyl hexafluoroplatinate. Cook & Lauer 1968, p.505
Organic compounds
 Among the most important classes of organic compounds that contain oxygen are (where "R" is an organic group): Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols (); ethers (); ketones (); aldehydes (); carboxylic acids (); esters (); Organic acid anhydride, acid anhydrides (); and amides (). There are many important organic solvents that contain oxygen, including: acetone, methanol, ethanol, Isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol, furan, tetrahydrofuran, THF, diethyl ether, 1,4-Dioxane, dioxane, ethyl acetate, dimethylformamide, DMF, dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO, acetic acid, and formic acid. Acetone () and phenol () are used as feeder materials in the synthesis of many different substances. Other important organic compounds that contain oxygen are: glycerol, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, citric acid, acetic anhydride, and acetamide. Epoxides are ethers in which the oxygen atom is part of a ring of three atoms. The element is similarly found in almost all biomolecules that are important to (or generated by) life.
Oxygen reacts spontaneously with many organic chemistry, organic compounds at or below room temperature in a process called autoxidation. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 506 Most of the organic compounds that contain oxygen are not made by direct action of . Organic compounds important in industry and commerce that are made by direct oxidation of a precursor include ethylene oxide and peracetic acid.
Among the most important classes of organic compounds that contain oxygen are (where "R" is an organic group): Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols (); ethers (); ketones (); aldehydes (); carboxylic acids (); esters (); Organic acid anhydride, acid anhydrides (); and amides (). There are many important organic solvents that contain oxygen, including: acetone, methanol, ethanol, Isopropyl alcohol, isopropanol, furan, tetrahydrofuran, THF, diethyl ether, 1,4-Dioxane, dioxane, ethyl acetate, dimethylformamide, DMF, dimethyl sulfoxide, DMSO, acetic acid, and formic acid. Acetone () and phenol () are used as feeder materials in the synthesis of many different substances. Other important organic compounds that contain oxygen are: glycerol, formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde, citric acid, acetic anhydride, and acetamide. Epoxides are ethers in which the oxygen atom is part of a ring of three atoms. The element is similarly found in almost all biomolecules that are important to (or generated by) life.
Oxygen reacts spontaneously with many organic chemistry, organic compounds at or below room temperature in a process called autoxidation. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 506 Most of the organic compounds that contain oxygen are not made by direct action of . Organic compounds important in industry and commerce that are made by direct oxidation of a precursor include ethylene oxide and peracetic acid.
Safety and precautions
The NFPA 704 standard rates compressed oxygen gas as nonhazardous to health, nonflammable and nonreactive, but an oxidizer. Refrigerated liquid oxygen (LOX) is given a health hazard rating of 3 (for increased risk of hyperoxia from condensed vapors, and for hazards common to cryogenic liquids such as frostbite), and all other ratings are the same as the compressed gas form.Toxicity
 Oxygen gas () can be Oxygen toxicity, toxic at elevated partial pressures, leading to convulsions and other health problems.Since 's partial pressure is the fraction of times the total pressure, elevated partial pressures can occur either from high fraction in breathing gas or from high breathing gas pressure, or a combination of both. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 511 Oxygen toxicity usually begins to occur at partial pressures more than 50 kiloPascal (unit), pascals (kPa), equal to about 50% oxygen composition at standard pressure or 2.5 times the normal sea-level partial pressure of about 21 kPa. This is not a problem except for patients on mechanical ventilators, since gas supplied through oxygen masks in medical applications is typically composed of only 30–50% by volume (about 30 kPa at standard pressure).
At one time, Premature birth, premature babies were placed in incubators containing -rich air, but this practice was discontinued after some babies were blinded by the oxygen content being too high.
Breathing pure in space applications, such as in some modern space suits, or in early spacecraft such as Apollo spacecraft, Apollo, causes no damage due to the low total pressures used. In the case of spacesuits, the partial pressure in the breathing gas is, in general, about 30 kPa (1.4 times normal), and the resulting partial pressure in the astronaut's arterial blood is only marginally more than normal sea-level partial pressure.
Oxygen toxicity to the lungs and central nervous system can also occur in deep scuba diving and surface-supplied diving. Prolonged breathing of an air mixture with an partial pressure more than 60 kPa can eventually lead to permanent pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure to an partial pressure greater than 160 kPa (about 1.6 atm) may lead to convulsions (normally fatal for divers). Acute oxygen toxicity (causing seizures, its most feared effect for divers) can occur by breathing an air mixture with 21% at or more of depth; the same thing can occur by breathing 100% at only .
Oxygen gas () can be Oxygen toxicity, toxic at elevated partial pressures, leading to convulsions and other health problems.Since 's partial pressure is the fraction of times the total pressure, elevated partial pressures can occur either from high fraction in breathing gas or from high breathing gas pressure, or a combination of both. Cook & Lauer 1968, p. 511 Oxygen toxicity usually begins to occur at partial pressures more than 50 kiloPascal (unit), pascals (kPa), equal to about 50% oxygen composition at standard pressure or 2.5 times the normal sea-level partial pressure of about 21 kPa. This is not a problem except for patients on mechanical ventilators, since gas supplied through oxygen masks in medical applications is typically composed of only 30–50% by volume (about 30 kPa at standard pressure).
At one time, Premature birth, premature babies were placed in incubators containing -rich air, but this practice was discontinued after some babies were blinded by the oxygen content being too high.
Breathing pure in space applications, such as in some modern space suits, or in early spacecraft such as Apollo spacecraft, Apollo, causes no damage due to the low total pressures used. In the case of spacesuits, the partial pressure in the breathing gas is, in general, about 30 kPa (1.4 times normal), and the resulting partial pressure in the astronaut's arterial blood is only marginally more than normal sea-level partial pressure.
Oxygen toxicity to the lungs and central nervous system can also occur in deep scuba diving and surface-supplied diving. Prolonged breathing of an air mixture with an partial pressure more than 60 kPa can eventually lead to permanent pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure to an partial pressure greater than 160 kPa (about 1.6 atm) may lead to convulsions (normally fatal for divers). Acute oxygen toxicity (causing seizures, its most feared effect for divers) can occur by breathing an air mixture with 21% at or more of depth; the same thing can occur by breathing 100% at only .
Combustion and other hazards
 Highly concentrated sources of oxygen promote rapid combustion. Fire and explosion hazards exist when concentrated oxidants and fuels are brought into close proximity; an ignition event, such as heat or a spark, is needed to trigger combustion. Oxygen is the oxidant, not the fuel.
Concentrated will allow combustion to proceed rapidly and energetically. Steel pipes and storage vessels used to store and transmit both gaseous and liquid oxygen will act as a fuel; and therefore the design and manufacture of systems requires special training to ensure that ignition sources are minimized. The fire that killed the Apollo 1 crew in a launch pad test spread so rapidly because the capsule was pressurized with pure but at slightly more than atmospheric pressure, instead of the normal pressure that would be used in a mission.
Liquid oxygen spills, if allowed to soak into organic matter, such as wood, petrochemicals, and Bitumen, asphalt can cause these materials to Detonation, detonate unpredictably on subsequent mechanical impact.
Highly concentrated sources of oxygen promote rapid combustion. Fire and explosion hazards exist when concentrated oxidants and fuels are brought into close proximity; an ignition event, such as heat or a spark, is needed to trigger combustion. Oxygen is the oxidant, not the fuel.
Concentrated will allow combustion to proceed rapidly and energetically. Steel pipes and storage vessels used to store and transmit both gaseous and liquid oxygen will act as a fuel; and therefore the design and manufacture of systems requires special training to ensure that ignition sources are minimized. The fire that killed the Apollo 1 crew in a launch pad test spread so rapidly because the capsule was pressurized with pure but at slightly more than atmospheric pressure, instead of the normal pressure that would be used in a mission.
Liquid oxygen spills, if allowed to soak into organic matter, such as wood, petrochemicals, and Bitumen, asphalt can cause these materials to Detonation, detonate unpredictably on subsequent mechanical impact.
See also
* Geological history of oxygen * Hypoxia (environmental) for depletion in aquatic ecology * Ocean deoxygenation * Hypoxia (medical), a lack of oxygen * Limiting oxygen concentration * :Oxygen compounds, Oxygen compounds * Oxygen plant * Oxygen sensor * Dark oxygenNotes
References
General references
* * *External links
Oxygen
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
Oxidizing Agents > Oxygen
Roald Hoffmann article on "The Story of O"
*
Scripps Institute: Atmospheric Oxygen has been dropping for 20 years
{{featured article Oxygen, Chemical elements Diatomic nonmetals Reactive nonmetals Chalcogens Chemical substances for emergency medicine Breathing gases E-number additives Oxidizing agents