|
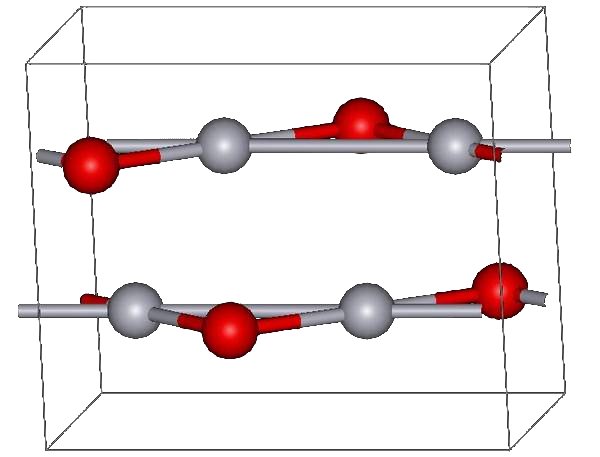
Mercuric Oxide
Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Hg O. It has a red or orange color. Mercury(II) oxide is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The mineral form montroydite is very rarely found. History An experiment for the preparation of mercuric oxide was first described by 11th century Arab-Spanish alchemist, Maslama al-Majriti, in ''Rutbat al-hakim.'' It was historically called red precipitate (as opposed to white precepitate being the mercuric amidochloride). In 1774, Joseph Priestley discovered that oxygen was released by heating mercuric oxide, although he did not identify the gas as oxygen (rather, Priestley called it " dephlogisticated air," as that was the paradigm that he was working under at the time). Synthesis and reactions The red form of HgO can be made by heating Hg in oxygen at roughly 350 °C, or by pyrolysis of Hg(NO3)2. The yellow form can be obtained by precipitation of aque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montroydite
Montroydite is the mineral form of mercury(II) oxide with formula HgO. It is a rare mercury mineral. It was first described for an occurrence in the mercury deposit at Terlingua, Texas, Terlingua, Texas and named for Montroyd Sharp who was an owner of the deposit. Montroydite occurs in mercury deposits of hydrothermal origin. Associated minerals include: native mercury, cinnabar, metacinnabar, calomel, eglestonite, terlinguaite, mosesite, kleinite, edgarbaileyite, gypsum, calcite and Dolomite (mineral), dolomite. References Mercury(II) minerals Oxide minerals Orthorhombic minerals {{oxide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury(II) Iodide
Mercury(II) iodide is a chemical compound with the molecular formula Hg I2. It is typically produced synthetically but can also be found in nature as the extremely rare mineral coccinite. Unlike the related mercury(II) chloride it is hardly soluble in water (<100 ppm). Production Mercury(II) iodide is produced by adding an aqueous solution of to an aqueous solution of with stirring; the precipitate is filtered off, washed and dried at 70 °C. : HgCl2 + 2 KI → HgI2 + 2 KClProperties Mercury(II) iodide displays thermochr ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury(II) Nitrate
Mercury(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is the Mercury (element), mercury(II) Salt (chemistry), salt of nitric acid . It contains mercury(II) cations and nitrate anions , and water of crystallization in the case of a hydrous salt. Mercury(II) nitrate forms hydrates . Anhydrous and hydrous Salt (chemistry), salts are colorless or white Solubility, soluble crystalline solids that are occasionally used as a reagents. Mercury(II) nitrate is made by treating mercury with hot concentrated nitric acid. Neither anhydrous nor monohydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The anhydrous material is more widely used. Uses Mercury(II) nitrate is used as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis, as a nitrification agent, as an analytical reagent in laboratories, in the manufacture of felt, and in the manufacture of mercury fulminate. An alternative qualitative Zeisel test can be done with the use of mercury(II) nitrate instead of silver nitrate, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Greek language, Greek-derived morpheme, elements ''pyro-'' (from Ancient Greek : - "fire, heat, fever") and ''lysis'' ( : - "separation, loosening"). Applications Pyrolysis is most commonly used in the treatment of organic compound, organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in the charring of wood or pyrolysis of biomass. In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves Char (chemistry), char, a carbon-rich solid residue. Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly carbon as the residue, is called carbonization. Pyrolysis is considered one of the steps in the processes of gasification or combustion. Laypeople often confuse pyrolysis gas with syngas. Pyrolysis gas has a high percentage of heavy tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnabar Structure
Cinnabar (; ), or cinnabarite (), also known as ''mercurblende'' is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of Mercury sulfide, mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining mercury (element), elemental mercury and is the historic source for the brilliant red or scarlet pigment termed vermilion and associated red mercury pigments. Cinnabar generally occurs as a vein-filling mineral associated with volcanic activity and Alkaline earth metal, alkaline hot springs. The mineral resembles quartz in symmetry and it exhibits birefringence. Cinnabar has a mean refractive index near 3.2, a mohs scale of mineral hardness, hardness between 2.0 and 2.5, and a specific gravity of approximately 8.1. The color and properties derive from a structure that is a hexagonal crystalline bravais lattice, lattice belonging to the trigonal crystal system, crystals that sometimes exhibit Crystal twinning, twinning. Cinnabar has been used for its color since antiquity in the Near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradigm
In science and philosophy, a paradigm ( ) is a distinct set of concepts or thought patterns, including theories, research methods, postulates, and standards for what constitute legitimate contributions to a field. The word ''paradigm'' is Ancient Greek, Greek in origin, meaning "pattern". Etymology ''Paradigm'' comes from Greek παράδειγμα (''paradeigma''); "pattern, example, sample"; from the verb παραδείκνυμι (''paradeiknumi''); "exhibit, represent, expose"; and that from παρά (''para''); "beside, beyond"; and δείκνυμι (''deiknumi''); "to show, to point out". In classical (Greek-based) rhetoric, a paradeigma aims to provide an audience with an illustration of a similar occurrence. This illustration is not meant to take the audience to a conclusion; however, it is used to help guide them to get there. One way of how a ''paradeigma'' is meant to guide an audience would be exemplified by the role of a personal accountant. It is not the job of a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlogiston
The phlogiston theory, a superseded scientific theory, postulated the existence of a fire-like element dubbed phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burning up''), from (''flame''). The idea of a substance was first proposed in 1667 by Johann Joachim Becher and later put together more formally in 1697 by Georg Ernst Stahl. Phlogiston theory attempted to explain chemical processes such as combustion and rusting, now collectively known as oxidation. The theory was challenged by the concomitant mass increase and was abandoned before the end of the 18th century following experiments by Antoine Lavoisier in the 1770s and by other scientists. Phlogiston theory led to experiments that ultimately resulted in the identification (), and naming (1777), of oxygen by Joseph Priestley and Antoine Lavoisier, respectively. Theory Phlogiston theory states that ''phlogisticated'' substances contain phlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, Unitarian, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher, English Separatist, separatist theologian, Linguist, grammarian, multi-subject educator and Classical liberalism, classical liberal Political philosophy, political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted experiments in several areas of science. Priestley is credited with his independent discovery of oxygen by the thermal decomposition of mercuric oxide, having isolated it in 1774. During his lifetime, Priestley's considerable scientific reputation rested on his invention of carbonated water, his writings on electricity, and his discovery of several "airs" (gases), the most famous being what Priestley dubbed "dephlogisticated air" (oxygen). Priestley's determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution eventually left him isolated within the scientific community. Priestley's science was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercuric Amidochloride
Mercuric amidochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula . Preparation and properties It arises from the reaction of mercury(II) chloride and ammonia (Calomel reaction), where the resulting mercuric amidochloride is highly insoluble. It forms white crystals in the shape of small prisms. It tastes earthy and metallic, but is a deadly poison and should not be ingested. At the molecular level, it organizes as a zig-zag 1-dimensional polymer with chloride counterions. It is stable in air, but darkens on exposure to light. It does not melt, even at dull red heat, instead subliming and decomposing to gaseous mercury, hydrogen chloride, and nitrogen oxides. Consequently sealed containers with this chemical may explode when heated. The substance is a deadly poison, although not a carcinogen. It is toxic unto lethality by inhalation, ingestion or dermal absorption. In lesser cases, it may instead cause dermatitis and skin lesions or corrode the mucous membranes. If i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Precepitate
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on television and computer screens is created by a mixture of red, blue, and green light. The color white can be given with white pigments, especially titanium dioxide. In ancient Egypt and ancient Rome, priestesses wore white as a symbol of purity, and Romans wore white togas as symbols of citizenship. In the Middle Ages and Renaissance a white unicorn symbolized chastity, and a white lamb sacrifice and purity. It was the royal color of the kings of France as well as the flag of monarchist France from 1815 to 1830, and of the monarchist movement that opposed the Bolsheviks during the Russian Civil War (1917–1922). Greek temples and Roman temples were faced with white marble, and beginning in the 18th century, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Precipitate
Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Hg O. It has a red or orange color. Mercury(II) oxide is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The mineral form montroydite is very rarely found. History An experiment for the preparation of mercuric oxide was first described by 11th century Arab-Spanish alchemist, Maslama al-Majriti, in ''Rutbat al-hakim.'' It was historically called red precipitate (as opposed to white precepitate being the mercuric amidochloride). In 1774, Joseph Priestley discovered that oxygen was released by heating mercuric oxide, although he did not identify the gas as oxygen (rather, Priestley called it " dephlogisticated air," as that was the paradigm that he was working under at the time). Synthesis and reactions The red form of HgO can be made by heating Hg in oxygen at roughly 350 °C, or by pyrolysis of Hg(NO3)2. The yellow form can be obtained by precipitation of aqueous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |