Metabolism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of
 Most of the structures that make up animals, plants and microbes are made from four basic classes of
Most of the structures that make up animals, plants and microbes are made from four basic classes of
 Carbohydrates are aldehydes or
Carbohydrates are aldehydes or
 Metabolism involves a vast array of chemical reactions, but most fall under a few basic types of reactions that involve the transfer of
Metabolism involves a vast array of chemical reactions, but most fall under a few basic types of reactions that involve the transfer of 

 Fats are catabolized by
Fats are catabolized by
 Pumping protons out of the mitochondria creates a proton concentration difference across the membrane and generates an
Pumping protons out of the mitochondria creates a proton concentration difference across the membrane and generates an
 Photosynthesis is the synthesis of carbohydrates from sunlight and
Photosynthesis is the synthesis of carbohydrates from sunlight and
 Fatty acids are made by
Fatty acids are made by
 There are multiple levels of metabolic regulation. In intrinsic regulation, the metabolic pathway self-regulates to respond to changes in the levels of substrates or products; for example, a decrease in the amount of product can increase the flux through the pathway to compensate. This type of regulation often involves allosteric regulation of the activities of multiple enzymes in the pathway. Extrinsic control involves a cell in a multicellular organism changing its metabolism in response to signals from other cells. These signals are usually in the form of water-soluble messengers such as
There are multiple levels of metabolic regulation. In intrinsic regulation, the metabolic pathway self-regulates to respond to changes in the levels of substrates or products; for example, a decrease in the amount of product can increase the flux through the pathway to compensate. This type of regulation often involves allosteric regulation of the activities of multiple enzymes in the pathway. Extrinsic control involves a cell in a multicellular organism changing its metabolism in response to signals from other cells. These signals are usually in the form of water-soluble messengers such as
 The central pathways of metabolism described above, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, are present in all three domains of living things and were present in the
The central pathways of metabolism described above, such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, are present in all three domains of living things and were present in the
 Classically, metabolism is studied by a reductionist approach that focuses on a single metabolic pathway. Particularly valuable is the use of
Classically, metabolism is studied by a reductionist approach that focuses on a single metabolic pathway. Particularly valuable is the use of
 In these early studies, the mechanisms of these metabolic processes had not been identified and a vital force was thought to animate living tissue. In the 19th century, when studying the
In these early studies, the mechanisms of these metabolic processes had not been identified and a vital force was thought to animate living tissue. In the 19th century, when studying the
The Biochemistry of Metabolism
(archived 8 March 2005)
Sparknotes SAT biochemistry
Overview of biochemistry. School level.
Undergraduate-level guide to molecular biology. Human metabolism
Guide to human metabolic pathways. School level.
THE Medical Biochemistry Page
Comprehensive resource on human metabolism. Databases
Flow Chart of Metabolic Pathways
at ExPASy
IUBMB-Nicholson Metabolic Pathways Chart
SuperCYP: Database for Drug-Cytochrome-Metabolism
Metabolic pathways
* {{Authority control, state=collapsed Underwater diving physiology
life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms
An organism is any living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been pr ...
. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s, nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s, and some carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism.
Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic
Catabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that breaks down molecules into smaller units that are either oxidized to release energy or used in other anabolic reactions. Catabolism breaks down large molecules (such as polysaccharides, lipi ...
''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing biological fuels using an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which stores chemical energy in a biologically accessible form. Cell ...
); or ''anabolic
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catab ...
''—the ''building up'' ( synthesis) of compounds (such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids). Usually, catabolism releases energy, and anabolism consumes energy.
The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell (biology), cell. The reactants, products, and Metabolic intermediate, intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are ...
s, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, each step being facilitated by a specific enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
and will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst ...
—they allow a reaction to proceed more rapidly—and they also allow the regulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
of the rate of a metabolic reaction, for example in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.
The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
ous. For example, some prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s use hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The basal metabolic rate
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest.. In other words it is the energy required by body organs to perform normal It is reported in energy units per unit time ranging from watt ( ...
of an organism is the measure of the amount of energy consumed by all of these chemical reactions.
A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways among vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
s that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' and huge multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s like elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus ...
s. These similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and extinct organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to the present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for '' gigaannum'') and ...
, and their retention is likely due to their efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
. In various diseases, such as type II diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
, metabolic syndrome, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, normal metabolism is disrupted. The metabolism of cancer cells is also different from the metabolism of normal cells, and these differences can be used to find targets for therapeutic intervention in cancer.
Key biochemicals
 Most of the structures that make up animals, plants and microbes are made from four basic classes of
Most of the structures that make up animals, plants and microbes are made from four basic classes of molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s: amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s, nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
and lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s (often called fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
s). As these molecules are vital for life, metabolic reactions either focus on making these molecules during the construction of cells and tissues, or on breaking them down and using them to obtain energy, by their digestion. These biochemicals can be joined to make polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s such as DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, essential macromolecules of life.
Amino acids and proteins
Proteins are made ofamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s arranged in a linear chain joined by peptide bonds. Many proteins are enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s that catalyze the chemical reactions in metabolism. Other proteins have structural or mechanical functions, such as those that form the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is compos ...
, a system of scaffolding that maintains the cell shape. Proteins are also important in cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the Biological process, process by which a Cell (biology), cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all Cell (biol ...
, immune responses, cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as Cell_junction, cell junc ...
, active transport
In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellula ...
across membranes, and the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
. Amino acids also contribute to cellular energy metabolism by providing a carbon source for entry into the citric acid cycle ( tricarboxylic acid cycle), especially when a primary source of energy, such as glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
, is scarce, or when cells undergo metabolic stress.
Lipids
Lipids are the most diverse group of biochemicals. Their main structural uses are as part of internal and external biological membranes, such as thecell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
. Their chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when the substances undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (20 ...
can also be used. Lipids contain a long, non-polar hydrocarbon chain with a small polar region containing oxygen. Lipids are usually defined as hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
or amphipathic biological molecules but will dissolve in organic solvents such as ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
, benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
or chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and po ...
. The fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
s are a large group of compounds that contain fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s and glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
; a glycerol molecule attached to three fatty acids by ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
linkages is called a triacylglyceride. Several variations of the basic structure exist, including backbones such as sphingosine in sphingomyelin, and hydrophilic groups such as phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
in phospholipid
Phospholipids are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typ ...
s. Steroid
A steroid is an organic compound with four fused compound, fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration.
Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes t ...
s such as sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on ...
are another major class of lipids.
Carbohydrates
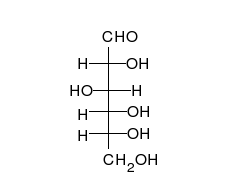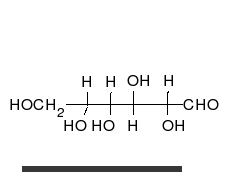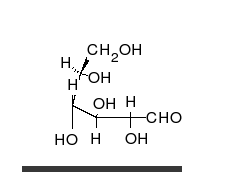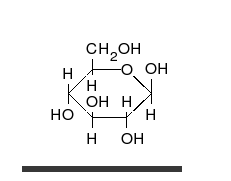
 Carbohydrates are aldehydes or
Carbohydrates are aldehydes or ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s, with many hydroxyl groups attached, that can exist as straight chains or rings. Carbohydrates are the most abundant biological molecules, and fill numerous roles, such as the storage and transport of energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
(starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
) and structural components (cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
in plants, chitin
Chitin (carbon, C8hydrogen, H13oxygen, O5nitrogen, N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of N-Acetylglucosamine, ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cell ...
in animals). The basic carbohydrate units are called monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
Chemically, monosaccharides are polyhy ...
s and include galactose, fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
, and most importantly glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
. Monosaccharides can be linked together to form polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
s in almost limitless ways.
Nucleotides
The two nucleic acids, DNA andRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
, are polymers of nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s. Each nucleotide is composed of a phosphate attached to a ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
or deoxyribose sugar group which is attached to a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids are critical for the storage and use of genetic information, and its interpretation through the processes of transcription and protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside Cell (biology), cells, homeostasis, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via Proteolysis, degradation or Protein targeting, export) through the produc ...
. This information is protected by DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is cons ...
mechanisms and propagated through DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all life, living organisms, acting as the most essential part of heredity, biolog ...
. Many virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es have an RNA genome, such as HIV, which uses reverse transcription to create a DNA template from its viral RNA genome. RNA in ribozymes such as spliceosomes and ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
s is similar to enzymes as it can catalyze chemical reactions. Individual nucleosides are made by attaching a nucleobase
Nucleotide bases (also nucleobases, nitrogenous bases) are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nuc ...
to a ribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
sugar. These bases are heterocyclic rings containing nitrogen, classified as purines or pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The oth ...
s. Nucleotides also act as coenzymes in metabolic-group-transfer reactions.
Coenzymes
functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is any substituent or moiety (chemistry), moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions r ...
s of atoms and their bonds within molecules. This common chemistry allows cells to use a small set of metabolic intermediates to carry chemical groups between different reactions. These group-transfer intermediates are called coenzyme
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or Metal ions in aqueous solution, metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalysis, catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can ...
s. Each class of group-transfer reactions is carried out by a particular coenzyme, which is the substrate for a set of enzymes that produce it, and a set of enzymes that consume it. These coenzymes are therefore continuously made, consumed and then recycled.
One central coenzyme is adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known ...
(ATP), the energy currency of cells. This nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
is used to transfer chemical energy between different chemical reactions. There is only a small amount of ATP in cells, but as it is continuously regenerated, the human body can use about its own weight in ATP per day. ATP acts as a bridge between catabolism and anabolism
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an Endergonic reaction, endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabo ...
. Catabolism breaks down molecules, and anabolism puts them together. Catabolic reactions generate ATP, and anabolic reactions consume it. It also serves as a carrier of phosphate groups in phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
reactions.
A vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
is an organic compound needed in small quantities that cannot be made in cells. In human nutrition
Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutrition ...
, most vitamins function as coenzymes after modification; for example, all water-soluble vitamins are phosphorylated or are coupled to nucleotides when they are used in cells. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a Cofactor (biochemistry), coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cell (biology), cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphat ...
(NAD+), a derivative of vitamin B3 ( niacin), is an important coenzyme that acts as a hydrogen acceptor. Hundreds of separate types of dehydrogenases remove electrons from their substrates and reduce NAD+ into NADH. This reduced form of the coenzyme is then a substrate for any of the reductases in the cell that need to transfer hydrogen atoms to their substrates. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide exists in two related forms in the cell, NADH and NADPH. The NAD+/NADH form is more important in catabolic reactions, while NADP+/NADPH is used in anabolic reactions.

Mineral and cofactors
Inorganic elements play critical roles in metabolism; some are abundant (e.g.sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
and potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
) while others function at minute concentrations. About 99% of a human's body weight is made up of the elements carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
, potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
, phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
and sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
. Organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s (proteins, lipids and carbohydrates) contain the majority of the carbon and nitrogen; most of the oxygen and hydrogen is present as water.
The abundant inorganic elements act as electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
s. The most important ions are sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
, potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
, calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
, phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
and the organic ion bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ...
. The maintenance of precise ion gradients across cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
s maintains osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a Solution (chemistry), solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane.
It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a soluti ...
and pH. Ions are also critical for nerve
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv ...
and muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
function, as action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
s in these tissues are produced by the exchange of electrolytes between the extracellular fluid and the cell's fluid, the cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondri ...
. Electrolytes enter and leave cells through proteins in the cell membrane called ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiol ...
s. For example, muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of Tension (physics), tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in musc ...
depends upon the movement of calcium, sodium and potassium through ion channels in the cell membrane and T-tubule
T-tubules (transverse tubules) are extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. With membranes that contain large concentrations of ion channels, transporters, and pumps, T-tubules permi ...
s.
Transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
s are usually present as trace elements in organisms, with zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
and iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
being most abundant of those. Metal cofactors are bound tightly to specific sites in proteins; although enzyme cofactors can be modified during catalysis, they always return to their original state by the end of the reaction catalyzed. Metal micronutrients are taken up into organisms by specific transporters and bind to storage proteins such as ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular and extracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. ...
or metallothionein when not in use.
Catabolism
Catabolism is the set of metabolic processes that break down large molecules. These include breaking down and oxidizing food molecules. The purpose of the catabolic reactions is to provide the energy and components needed by anabolic reactions which build molecules. The exact nature of these catabolic reactions differ from organism to organism, and organisms can be classified based on their sources of energy, hydrogen, and carbon (their primary nutritional groups), as shown in the table below. Organic molecules are used as a source of hydrogen atoms or electrons by organotrophs, while lithotrophs use inorganic substrates. Whereas phototrophs convert sunlight tochemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when the substances undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (20 ...
, chemotroph
A chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic ( chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phot ...
s depend on redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ...
reactions that involve the transfer of electrons from reduced donor molecules such as organic molecules, hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
, hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
or ferrous ions to oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
, nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
or sulfate. In animals, these reactions involve complex organic molecules that are broken down to simpler molecules, such as carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and water. Photosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
organisms, such as plants and cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
, use similar electron-transfer reactions to store energy absorbed from sunlight.
The most common set of catabolic reactions in animals can be separated into three main stages. In the first stage, large organic molecules, such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
s or lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s, are digested into their smaller components outside cells. Next, these smaller molecules are taken up by cells and converted to smaller molecules, usually acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA), which releases some energy. Finally, the acetyl group on acetyl-CoA is oxidized to water and carbon dioxide in the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
and electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
, releasing more energy while reducing the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a Cofactor (biochemistry), coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cell (biology), cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphat ...
(NAD+) into NADH.
Digestion
Macromolecules cannot be directly processed by cells. Macromolecules must be broken into smaller units before they can be used in cell metabolism. Different classes of enzymes are used to digest these polymers. These digestive enzymes includeprotease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s that digest proteins into amino acids, as well as glycoside hydrolases that digest polysaccharides into simple sugars known as monosaccharides.
Microbes simply secrete digestive enzymes into their surroundings, while animals only secrete these enzymes from specialized cells in their guts, including the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
and pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a ...
, and in salivary gland
The salivary glands in many vertebrates including mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of min ...
s. The amino acids or sugars released by these extracellular enzymes are then pumped into cells by active transport
In cellular biology, active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellula ...
proteins.
Energy from organic compounds
Carbohydrate catabolism is the breakdown of carbohydrates into smaller units. Carbohydrates are usually taken into cells after they have been digested intomonosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
Chemically, monosaccharides are polyhy ...
s such as glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
. Once inside, the major route of breakdown is glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
, in which glucose is converted into pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
. This process generates the energy-conveying molecule NADH from NAD+, and generates ATP from ADP for use in powering many processes within the cell. Pyruvate is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways, but the majority is converted to acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidation, o ...
and fed into the citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent–Györgyi–Krebs cycle, or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reaction, biochemical reactions that release the energy stored in nutrients through acetyl-Co ...
, which enables more ATP production by means of oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order ...
. This oxidation consumes molecular oxygen and releases water and the waste product carbon dioxide. When oxygen is lacking, or when pyruvate is temporarily produced faster than it can be consumed by the citric acid cycle (as in intense muscular exertion), pyruvate is converted to lactate by the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, a process that also oxidizes NADH back to NAD+ for re-use in further glycolysis, allowing energy production to continue. The lactate is later converted back to pyruvate for ATP production where energy is needed, or back to glucose in the Cori cycle. An alternative route for glucose breakdown is the pentose phosphate pathway, which produces less energy but supports anabolism
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an Endergonic reaction, endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabo ...
(biomolecule synthesis). This pathway reduces the coenzyme NADP+ to NADPH and produces pentose compounds such as ribose 5-phosphate for synthesis of many biomolecules such as nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s and aromatic amino acids.
 Fats are catabolized by
Fats are catabolized by hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
to free fatty acids and glycerol. The glycerol enters glycolysis and the fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta oxidation (also β-oxidation) is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA enter ...
to release acetyl-CoA, which then is fed into the citric acid cycle. Fatty acids release more energy upon oxidation than carbohydrates. Steroids are also broken down by some bacteria in a process similar to beta oxidation, and this breakdown process involves the release of significant amounts of acetyl-CoA, propionyl-CoA, and pyruvate, which can all be used by the cell for energy. ''M. tuberculosis'' can also grow on the lipid cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
as a sole source of carbon, and genes involved in the cholesterol-use pathway(s) have been validated as important during various stages of the infection lifecycle of ''M. tuberculosis''.
Amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s are either used to synthesize proteins and other biomolecules, or oxidized to urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
and carbon dioxide to produce energy. The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase. The amino group is fed into the urea cycle, leaving a deaminated carbon skeleton in the form of a keto acid. Several of these keto acids are intermediates in the citric acid cycle, for example α- ketoglutarate formed by deamination of glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
. The glucogenic amino acids can also be converted into glucose, through gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
.
Energy transformations
Oxidative phosphorylation
In oxidative phosphorylation, the electrons removed from organic molecules in areas such as the citric acid cycle are transferred to oxygen and the energy released is used to make ATP. This is done ineukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s by a series of proteins in the membranes of mitochondria called the electron transport chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples th ...
. In prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s, these proteins are found in the cell's inner membrane. These proteins use the energy from reduced molecules like NADH to pump proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s across a membrane.
 Pumping protons out of the mitochondria creates a proton concentration difference across the membrane and generates an
Pumping protons out of the mitochondria creates a proton concentration difference across the membrane and generates an electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts:
* The chemical gradient, or difference in Concentration, solute concentration across ...
. This force drives protons back into the mitochondrion through the base of an enzyme called ATP synthase. The flow of protons makes the stalk subunit rotate, causing the active site of the synthase domain to change shape and phosphorylate adenosine diphosphate
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP), also known as adenosine pyrophosphate (APP), is an important organic compound in metabolism and is essential to the flow of energy in living cells. ADP consists of three important structural components: a sugar backbon ...
—turning it into ATP.
Energy from inorganic compounds
Chemolithotrophy is a type of metabolism found inprokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s where energy is obtained from the oxidation of inorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''.
Inorgan ...
s. These organisms can use hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
, reduced sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
compounds (such as sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
, hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
and thiosulfate
Thiosulfate ( IUPAC-recommended spelling; sometimes thiosulphate in British English) is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula . Thiosulfate also refers to the compounds containing this anion, which are the salts of thiosulfuric acid, ...
), ferrous iron (Fe(II)) or ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
as sources of reducing power and they gain energy from the oxidation of these compounds. These microbial processes are important in global biogeochemical cycle
A biogeochemical cycle, or more generally a cycle of matter, is the movement and transformation of chemical elements and compounds between living organisms, the atmosphere, and the Earth's crust. Major biogeochemical cycles include the carbon cyc ...
s such as acetogenesis, nitrification and denitrification and are critical for soil fertility.
Energy from light
The energy in sunlight is captured byplant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s, cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
, purple bacteria, green sulfur bacteria and some protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s. This process is often coupled to the conversion of carbon dioxide into organic compounds, as part of photosynthesis, which is discussed below. The energy capture and carbon fixation systems can, however, operate separately in prokaryotes, as purple bacteria and green sulfur bacteria can use sunlight as a source of energy, while switching between carbon fixation and the fermentation of organic compounds.
In many organisms, the capture of solar energy is similar in principle to oxidative phosphorylation, as it involves the storage of energy as a proton concentration gradient. This proton motive force then drives ATP synthesis. The electrons needed to drive this electron transport chain come from light-gathering proteins called photosynthetic reaction centres. Reaction centers are classified into two types depending on the nature of photosynthetic pigment present, with most photosynthetic bacteria only having one type, while plants and cyanobacteria have two.
In plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, photosystem II uses light energy to remove electrons from water, releasing oxygen as a waste product. The electrons then flow to the cytochrome b6f complex, which uses their energy to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle, organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant cell, plant and algae, algal cells. Chloroplasts have a high concentration of chlorophyll pigments which captur ...
. These protons move back through the membrane as they drive the ATP synthase, as before. The electrons then flow through photosystem I and can then be used to reduce the coenzyme NADP+. This coenzyme can enter the Calvin cycle or be recycled for further ATP generation.
Anabolism
Anabolism is the set of constructive metabolic processes where the energy released by catabolism is used to synthesize complex molecules. In general, the complex molecules that make up cellular structures are constructed step-by-step from smaller and simpler precursors. Anabolism involves three basic stages. First, the production of precursors such asamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, monosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
Chemically, monosaccharides are polyhy ...
s, isoprenoids and nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s, secondly, their activation into reactive forms using energy from ATP, and thirdly, the assembly of these precursors into complex molecules such as protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s, polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
s, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s and nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nuclei ...
s.
Anabolism in organisms can be different according to the source of constructed molecules in their cells. Autotroph
An autotroph is an organism that can convert Abiotic component, abiotic sources of energy into energy stored in organic compounds, which can be used by Heterotroph, other organisms. Autotrophs produce complex organic compounds (such as carbohy ...
s such as plants can construct the complex organic molecules in their cells such as polysaccharides and proteins from simple molecules like carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and water. Heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but ...
s, on the other hand, require a source of more complex substances, such as monosaccharides and amino acids, to produce these complex molecules. Organisms can be further classified by ultimate source of their energy: photoautotrophs and photoheterotrophs obtain energy from light, whereas chemoautotrophs and chemoheterotrophs obtain energy from oxidation reactions.
Carbon fixation
 Photosynthesis is the synthesis of carbohydrates from sunlight and
Photosynthesis is the synthesis of carbohydrates from sunlight and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(CO2). In plants, cyanobacteria and algae, oxygenic photosynthesis splits water, with oxygen produced as a waste product. This process uses the ATP and NADPH produced by the photosynthetic reaction centres, as described above, to convert CO2 into glycerate 3-phosphate
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. T ...
, which can then be converted into glucose. This carbon-fixation reaction is carried out by the enzyme RuBisCO as part of the Calvin–Benson cycle. Three types of photosynthesis occur in plants, C3 carbon fixation, C4 carbon fixation and CAM photosynthesis. These differ by the route that carbon dioxide takes to the Calvin cycle, with C3 plants fixing CO2 directly, while C4 and CAM photosynthesis incorporate the CO2 into other compounds first, as adaptations to deal with intense sunlight and dry conditions.
In photosynthetic prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s the mechanisms of carbon fixation are more diverse. Here, carbon dioxide can be fixed by the Calvin–Benson cycle, a reversed citric acid cycle, or the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA. Prokaryotic chemoautotrophs also fix CO2 through the Calvin–Benson cycle, but use energy from inorganic compounds to drive the reaction.
Carbohydrates and glycans
In carbohydrate anabolism, simple organic acids can be converted intomonosaccharide
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
Chemically, monosaccharides are polyhy ...
s such as glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and then used to assemble polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
s such as starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
. The generation of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
from compounds like pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
, lactate, glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
, glycerate 3-phosphate
3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3PG, 3-PGA, or PGA) is the conjugate acid of 3-phosphoglycerate or glycerate 3-phosphate (GP or G3P). This glycerate is a biochemically significant metabolic intermediate in both glycolysis and the Calvin-Benson cycle. T ...
and amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s is called gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
. Gluconeogenesis converts pyruvate to glucose-6-phosphate through a series of intermediates, many of which are shared with glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
. However, this pathway is not simply glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvic acid, pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). The Thermodynamic free energy, free energy released in this process is used to form ...
run in reverse, as several steps are catalyzed by non-glycolytic enzymes. This is important as it allows the formation and breakdown of glucose to be regulated separately, and prevents both pathways from running simultaneously in a futile cycle.
Although fat is a common way of storing energy, in vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s such as humans the fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an ...
s in these stores cannot be converted to glucose through gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the biosynthesis of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verte ...
as these organisms cannot convert acetyl-CoA into pyruvate
Pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids, with a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group. Pyruvate, the conjugate base, CH3COCOO−, is an intermediate in several metabolic pathways throughout the cell.
Pyruvic ...
; plants do, but animals do not, have the necessary enzymatic machinery. As a result, after long-term starvation, vertebrates need to produce ketone bodies from fatty acids to replace glucose in tissues such as the brain that cannot metabolize fatty acids. In other organisms such as plants and bacteria, this metabolic problem is solved using the glyoxylate cycle, which bypasses the decarboxylation step in the citric acid cycle and allows the transformation of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate, where it can be used for the production of glucose. Other than fat, glucose is stored in most tissues, as an energy resource available within the tissue through glycogenesis which was usually being used to maintained glucose level in blood.
Polysaccharides and glycan
The terms glycans and polysaccharides are defined by IUPAC as synonyms meaning "compounds consisting of a large number of monosaccharides linked glycosidically". However, in practice the term glycan may also be used to refer to the carbohydrate ...
s are made by the sequential addition of monosaccharides by glycosyltransferase from a reactive sugar-phosphate donor such as uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glc) to an acceptor hydroxyl group on the growing polysaccharide. As any of the hydroxyl groups on the ring of the substrate can be acceptors, the polysaccharides produced can have straight or branched structures. The polysaccharides produced can have structural or metabolic functions themselves, or be transferred to lipids and proteins by the enzymes oligosaccharyltransferases.
Fatty acids, isoprenoids and sterol
fatty acid synthase
Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''FASN'' gene.
Fatty acid synthase is a multi-enzyme protein that catalyzes fatty acid synthesis. It is not a single enzyme but a whole enzymatic system composed of two ide ...
s that polymerize and then reduce acetyl-CoA units. The acyl chains in the fatty acids are extended by a cycle of reactions that add the acyl group, reduce it to an alcohol, dehydrate it to an alkene group and then reduce it again to an alkane group. The enzymes of fatty acid biosynthesis are divided into two groups: in animals and fungi, all these fatty acid synthase reactions are carried out by a single multifunctional type I protein, while in plant plastids and bacteria separate type II enzymes perform each step in the pathway.
Terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predomi ...
s and isoprenoids are a large class of lipids that include the carotenoids and form the largest class of plant natural products. These compounds are made by the assembly and modification of isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers ar ...
units donated from the reactive precursors isopentenyl pyrophosphate and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. These precursors can be made in different ways. In animals and archaea, the mevalonate pathway produces these compounds from acetyl-CoA, while in plants and bacteria the non-mevalonate pathway uses pyruvate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate as substrates. One important reaction that uses these activated isoprene donors is sterol biosynthesis. Here, the isoprene units are joined to make squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpene with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as '' Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). ...
and then folded up and formed into a set of rings to make lanosterol
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast, plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. In the eyes of vertebrates, lanosterol is a natural constituent, havin ...
. Lanosterol can then be converted into other sterols such as cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
and ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a mycosterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergostero ...
.
Proteins
Organisms vary in their ability to synthesize the 20 common amino acids. Most bacteria and plants can synthesize all twenty, but mammals can only synthesize eleven nonessential amino acids, so nineessential amino acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms ...
s must be obtained from food. Some simple parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s, such as the bacteria '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'', lack all amino acid synthesis and take their amino acids directly from their hosts. All amino acids are synthesized from intermediates in glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, or the pentose phosphate pathway. Nitrogen is provided by glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a Essential amino acid, non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that ...
and glutamine. Nonessensial amino acid synthesis depends on the formation of the appropriate alpha-keto acid, which is then transaminated to form an amino acid.
Amino acids are made into proteins by being joined in a chain of peptide bonds. Each different protein has a unique sequence of amino acid residues: this is its primary structure. Just as the letters of the alphabet can be combined to form an almost endless variety of words, amino acids can be linked in varying sequences to form a huge variety of proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids that have been activated by attachment to a transfer RNA molecule through an ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
bond. This aminoacyl-tRNA precursor is produced in an ATP-dependent reaction carried out by an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. This aminoacyl-tRNA is then a substrate for the ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
, which joins the amino acid onto the elongating protein chain, using the sequence information in a messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
.
Nucleotide synthesis and salvage
Nucleotides are made from amino acids, carbon dioxide and formic acid in pathways that require large amounts of metabolic energy. Consequently, most organisms have efficient systems to salvage preformed nucleotides. Purines are synthesized as nucleosides (bases attached toribose
Ribose is a simple sugar and carbohydrate with molecular formula C5H10O5 and the linear-form composition H−(C=O)−(CHOH)4−H. The naturally occurring form, , is a component of the ribonucleotides from which RNA is built, and so this comp ...
). Both adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
and guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
are made from the precursor nucleoside inosine monophosphate, which is synthesized using atoms from the amino acids glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (G ...
, glutamine, and aspartic acid, as well as formate transferred from the coenzyme
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or Metal ions in aqueous solution, metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalysis, catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can ...
tetrahydrofolate. Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The oth ...
s, on the other hand, are synthesized from the base orotate, which is formed from glutamine and aspartate.
Xenobiotics and redox metabolism
All organisms are constantly exposed to compounds that they cannot use as foods and that would be harmful if they accumulated in cells, as they have no metabolic function. These potentially damaging compounds are called xenobiotics. Xenobiotics such as synthetic drugs, natural poisons andantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s are detoxified by a set of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes. In humans, these include cytochrome P450 oxidases, UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, and glutathione ''S''-transferases. This system of enzymes acts in three stages to firstly oxidize the xenobiotic (phase I) and then conjugate water-soluble groups onto the molecule (phase II). The modified water-soluble xenobiotic can then be pumped out of cells and in multicellular organisms may be further metabolized before being excreted (phase III). In ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
, these reactions are particularly important in microbial biodegradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegrada ...
of pollutants and the bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
of contaminated land and oil spills. Many of these microbial reactions are shared with multicellular organisms, but due to the incredible diversity of types of microbes these organisms are able to deal with a far wider range of xenobiotics than multicellular organisms, and can degrade even persistent organic pollutants such as organochloride compounds.
A related problem for aerobic organism
An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment. The ability to exhibit aerobic respiration may yield benefits to the aerobic organism, as aerobic respiration yields more energy than anaerobic ...
s is oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
. Here, processes including oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order ...
and the formation of disulfide bonds during protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after Protein biosynthesis, synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of Amino acid, amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered protein tertiary structure, t ...
produce reactive oxygen species such as hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
. These damaging oxidants are removed by antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants ...
metabolites such as glutathione and enzymes such as catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting ...
s and peroxidases.
Thermodynamics of living organisms
Living organisms must obey the laws of thermodynamics, which describe the transfer of heat and work. Thesecond law of thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spont ...
states that in any isolated system, the amount of entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
(disorder) cannot decrease. Although living organisms' amazing complexity appears to contradict this law, life is possible as all organisms are open systems that exchange matter and energy with their surroundings. Living systems are not in equilibrium, but instead are dissipative systems that maintain their state of high complexity by causing a larger increase in the entropy of their environments. The metabolism of a cell achieves this by coupling the spontaneous processes of catabolism to the non-spontaneous processes of anabolism. In thermodynamic terms, metabolism maintains order by creating disorder.
Regulation and control
As the environments of most organisms are constantly changing, the reactions of metabolism must be finely regulated to maintain a constant set of conditions within cells, a condition calledhomeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
. Metabolic regulation also allows organisms to respond to signals and interact actively with their environments. Two closely linked concepts are important for understanding how metabolic pathways are controlled. Firstly, the ''regulation'' of an enzyme in a pathway is how its activity is increased and decreased in response to signals. Secondly, the ''control'' exerted by this enzyme is the effect that these changes in its activity have on the overall rate of the pathway (the flux through the pathway). For example, an enzyme may show large changes in activity (i.e. it is highly regulated) but if these changes have little effect on the flux of a metabolic pathway, then this enzyme is not involved in the control of the pathway.
hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s and growth factors and are detected by specific receptors on the cell surface. These signals are then transmitted inside the cell by second messenger system
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form of cell signaling, encompassing both first me ...
s that often involved the phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols:
:
This equation can be writ ...
of proteins.
A very well understood example of extrinsic control is the regulation of glucose metabolism by the hormone insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
. Insulin is produced in response to rises in blood glucose levels. Binding of the hormone to insulin receptors on cells then activates a cascade of protein kinase
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphates to them ( phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a f ...
s that cause the cells to take up glucose and convert it into storage molecules such as fatty acids and glycogen
Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body.
Glycogen functions as one of three regularly used forms ...
. The metabolism of glycogen is controlled by activity of phosphorylase, the enzyme that breaks down glycogen, and glycogen synthase, the enzyme that makes it. These enzymes are regulated in a reciprocal fashion, with phosphorylation inhibiting glycogen synthase, but activating phosphorylase. Insulin causes glycogen synthesis by activating protein phosphatases and producing a decrease in the phosphorylation of these enzymes.
Evolution
last universal common ancestor
The last universal common ancestor (LUCA) is the hypothesized common ancestral cell from which the three domains of life, the Bacteria, the Archaea, and the Eukarya originated. The cell had a lipid bilayer; it possessed the genetic code a ...
. This universal ancestral cell was prokaryotic and probably a methanogen
Methanogens are anaerobic archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of their energy metabolism, i.e., catabolism. Methane production, or methanogenesis, is the only biochemical pathway for Adenosine triphosphate, ATP generation in methanogens. A ...
that had extensive amino acid, nucleotide, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The retention of these ancient pathways during later evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
may be the result of these reactions having been an optimal solution to their particular metabolic problems, with pathways such as glycolysis and the citric acid cycle producing their end products highly efficiently and in a minimal number of steps. The first pathways of enzyme-based metabolism may have been parts of purine nucleotide metabolism, while previous metabolic pathways were a part of the ancient RNA world.
Many models have been proposed to describe the mechanisms by which novel metabolic pathways evolve. These include the sequential addition of novel enzymes to a short ancestral pathway, the duplication and then divergence of entire pathways as well as the recruitment of pre-existing enzymes and their assembly into a novel reaction pathway. The relative importance of these mechanisms is unclear, but genomic studies have shown that enzymes in a pathway are likely to have a shared ancestry, suggesting that many pathways have evolved in a step-by-step fashion with novel functions created from pre-existing steps in the pathway. An alternative model comes from studies that trace the evolution of proteins' structures in metabolic networks, this has suggested that enzymes are pervasively recruited, borrowing enzymes to perform similar functions in different metabolic pathways (evident in the MANET database) These recruitment processes result in an evolutionary enzymatic mosaic. A third possibility is that some parts of metabolism might exist as "modules" that can be reused in different pathways and perform similar functions on different molecules.
As well as the evolution of new metabolic pathways, evolution can also cause the loss of metabolic functions. For example, in some parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s metabolic processes that are not essential for survival are lost and preformed amino acids, nucleotides and carbohydrates may instead be scavenged from the host. Similar reduced metabolic capabilities are seen in endosymbiotic organisms.
Investigation and manipulation
 Classically, metabolism is studied by a reductionist approach that focuses on a single metabolic pathway. Particularly valuable is the use of
Classically, metabolism is studied by a reductionist approach that focuses on a single metabolic pathway. Particularly valuable is the use of radioactive tracer
A radioactive tracer, radiotracer, or radioactive label is a synthetic derivative of a natural compound in which one or more atoms have been replaced by a radionuclide (a radioactive atom). By virtue of its radioactive decay, it can be used to ...
s at the whole-organism, tissue and cellular levels, which define the paths from precursors to final products by identifying radioactively labelled intermediates and products. The enzymes that catalyze these chemical reactions can then be purified and their kinetics and responses to inhibitors investigated. A parallel approach is to identify the small molecules in a cell or tissue; the complete set of these molecules is called the metabolome. Overall, these studies give a good view of the structure and function of simple metabolic pathways, but are inadequate when applied to more complex systems such as the metabolism of a complete cell.
An idea of the complexity of the metabolic network
A metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell. As such, these networks comprise the chemical reactions of metabolism, the metabolic pathways, as ...
s in cells that contain thousands of different enzymes is given by the figure showing the interactions between just 43 proteins and 40 metabolites to the right: the sequences of genomes provide lists containing anything up to 26.500 genes. However, it is now possible to use this genomic data to reconstruct complete networks of biochemical reactions and produce more holistic mathematical models that may explain and predict their behavior. These models are especially powerful when used to integrate the pathway and metabolite data obtained through classical methods with data on gene expression
Gene expression is the process (including its Regulation of gene expression, regulation) by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, proteins or non-coding RNA, ...
from proteomic and DNA microarray studies. Using these techniques, a model of human metabolism has now been produced, which will guide future drug discovery and biochemical research. These models are now used in network analysis, to classify human diseases into groups that share common proteins or metabolites.
Bacterial metabolic networks are a striking example of bow-tie organization, an architecture able to input a wide range of nutrients and produce a large variety of products and complex macromolecules using a relatively few intermediate common currencies.
A major technological application of this information is metabolic engineering. Here, organisms such as yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
, plants or bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
are genetically modified to make them more useful in biotechnology
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and Engineering Science, engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services. Specialists ...
and aid the production of drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
s such as antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s or industrial chemicals such as 1,3-propanediol and shikimic acid. These genetic modifications usually aim to reduce the amount of energy used to produce the product, increase yields and reduce the production of wastes.
History
The term ''metabolism'' is derived from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
word μεταβολή—"metabole" for "a change" which is derived from μεταβάλλειν—"metaballein", meaning "to change"
Greek philosophy
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
's ''The Parts of Animals
''Parts of Animals'' (or ''On the Parts of Animals''; Ancient Greek, Greek Περὶ ζῴων μορίων; Latin ''De Partibus Animalium'') is one of Aristotle's major Aristotle's biology, texts on biology. It was written around 350 BC. The whole ...
'' sets out enough details of his views on metabolism for an open flow model to be made. He believed that at each stage of the process, materials from food were transformed, with heat being released as the classical element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to ...
of fire, and residual materials being excreted as urine, bile, or faeces.
Ibn al-Nafis described metabolism in his 1260 AD work titled Al-Risalah al-Kamiliyyah fil Siera al-Nabawiyyah (The Treatise of Kamil on the Prophet's Biography) which included the following phrase "Both the body and its parts are in a continuous state of dissolution and nourishment, so they are inevitably undergoing permanent change."
Application of the scientific method
The history of the scientific study of metabolism spans several centuries and has moved from examining whole animals in early studies, to examining individual metabolic reactions in modern biochemistry. The first controlledexperiment
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs whe ...
s in human metabolism were published by Santorio Santorio in 1614 in his book ''Ars de statica medicina''. He described how he weighed himself before and after eating, sleep
Sleep is a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain Sensory nervous system, sensory activity is inhibited. During sleep, there is a marked decrease in muscle activity and interactions with th ...
, working, sex, fasting, drinking, and excreting. He found that most of the food he took in was lost through what he called " insensible perspiration".
 In these early studies, the mechanisms of these metabolic processes had not been identified and a vital force was thought to animate living tissue. In the 19th century, when studying the
In these early studies, the mechanisms of these metabolic processes had not been identified and a vital force was thought to animate living tissue. In the 19th century, when studying the fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
of sugar to alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
by yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
, Louis Pasteur
Louis Pasteur (, ; 27 December 1822 – 28 September 1895) was a French chemist, pharmacist, and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, Fermentation, microbial fermentation, and pasteurization, the la ...
concluded that fermentation was catalyzed by substances within the yeast cells he called "ferments". He wrote that "alcoholic fermentation is an act correlated with the life and organization of the yeast cells, not with the death or putrefaction of the cells." This discovery, along with the publication by Friedrich Wöhler in 1828 of a paper on the chemical synthesis of urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
, and is notable for being the first organic compound prepared from wholly inorganic precursors. Wöhler's urea synthesis showed that organic compounds could be created from inorganic precursors, disputing the vital force theory that dominated early 19th-century science. Modern analyses consider this achievement as foundational for unifying organic and inorganic chemistry.
It was the discovery of enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s at the beginning of the 20th century by Eduard Buchner that separated the study of the chemical reactions of metabolism from the biological study of cells, and marked the beginnings of biochemistry
Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ...
. The mass of biochemical knowledge grew rapidly throughout the early 20th century. One of the most prolific of these modern biochemists was Hans Krebs who made huge contributions to the study of metabolism. He discovered the urea cycle and later, working with Hans Kornberg, the citric acid cycle and the glyoxylate cycle. Modern biochemical research has been greatly aided by the development of new techniques such as chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it ...
, NMR spectroscopy, electron microscopy and molecular dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics ( ...
simulations. These techniques have allowed the discovery and detailed analysis of the many molecules and metabolic pathways in cells.
See also
* * * * * * , a "metabolism first" theory of theorigin of life
Abiogenesis is the natural process by which life arises from abiotic component, non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to organism, living entities on ...
*
* Microphysiometry
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Oncometabolism
*
*
References
Further reading
Introductory * * * Advanced * * * * * * *External links
General informationThe Biochemistry of Metabolism
(archived 8 March 2005)
Sparknotes SAT biochemistry
Overview of biochemistry. School level.
Undergraduate-level guide to molecular biology. Human metabolism
Guide to human metabolic pathways. School level.
THE Medical Biochemistry Page
Comprehensive resource on human metabolism. Databases
Flow Chart of Metabolic Pathways
at ExPASy
IUBMB-Nicholson Metabolic Pathways Chart
SuperCYP: Database for Drug-Cytochrome-Metabolism
Metabolic pathways
* {{Authority control, state=collapsed Underwater diving physiology