|
Metabolic Waste
Metabolic wastes or excrements are substances left over from metabolic processes (such as cellular respiration) which cannot be used by the organism (they are surplus or toxic), and must therefore be excreted. This includes nitrogen compounds, water, CO2, phosphates, sulphates, etc. Animals treat these compounds as excretes. Plants have metabolic pathways which transforms some of them (primarily the oxygen compounds) into useful substances. All the metabolic wastes are excreted in a form of water solutes through the excretory organs ( nephridia, Malpighian tubules, kidneys), with the exception of CO2, which is excreted together with the water vapor throughout the lungs. The elimination of these compounds enables the chemical homeostasis of the organism. Nitrogen wastes The nitrogen compounds through which excess nitrogen is eliminated from organisms are called nitrogenous wastes () or nitrogen wastes. They are ammonia, urea, uric acid, and creatinine. All of these subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephridia
The nephridium (: nephridia) is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Nephridia come in two basic categories: metanephridia and protonephridia. All nephridia- and kidney- having animals belong to the clade Nephrozoa. Metanephridia A metanephridium (''meta'' = "after") is a type of excretory gland found in many types of invertebrates such as annelids, arthropods and mollusca. (In mollusca, it is known as the Bojanus organ.) A metanephridium typically consists of the nephrostome (a ciliated funnel) opening into the body cavity, connected to a duct which may be variously glandularized, folded or expanded (vesiculate) and which typically opens to the organism's exterior. These ciliated tubules pump water carrying surplus ions, metabolic waste, toxins from food, and useless hormones out of the organism by directing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially-altered bilirubin and dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. Feces are discharged through the anus or cloaca during defecation. Feces can be used as fertilizer or soil conditioner in agriculture. They can also be burned as dry animal dung fuel, fuel or dried and used for wattle and daub, construction. Some medicinal uses have been found. In the case of human feces, fecal transplants or fecal bacteriotherapy are in use. Urine and feces together are called excretion, excreta. Characteristics The distinctive odor of feces is due to skatole, and thiols (sulfur-containing compounds), as well as amines and carboxylic acids. Sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
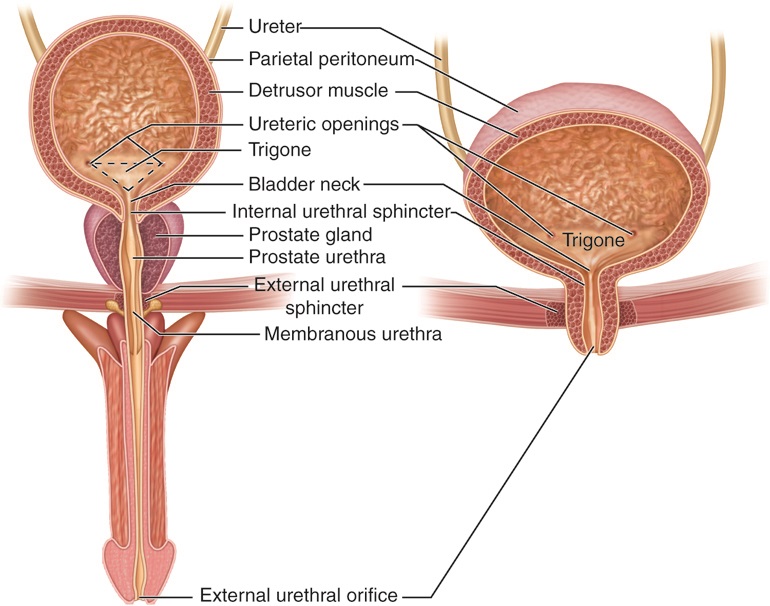
Urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (males) or urethral meatus of the vulva (females) during urination. In other vertebrates, urine is excreted through the cloaca. Urine contains water-soluble by-products of Cell (biology), cellular metabolism that are rich in nitrogen and must be clearance (medicine), cleared from the Circulatory system, bloodstream, such as urea, uric acid and creatinine. A urinalysis can detect nitrogenous wastes of the mammalian body. Urine plays an important role in the earth's nitrogen cycle. In balanced ecosystems, urine fertilizes the soil and thus helps plants to grow. Therefore, Reuse of excreta, urine can be used as a fertilizer. Some animals use it to territory (animal)#Scent marking, mark their territories. Historically, aged or fermented urine (kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Metabolism
Protein metabolism denotes the various biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism. The steps of protein synthesis include transcription, translation, and post translational modifications. During transcription, RNA polymerase transcribes a coding region of the DNA in a cell producing a sequence of RNA, specifically messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA sequence contains codons: 3 nucleotide long segments that code for a specific amino acid. Ribosomes translate the codons to their respective amino acids. In humans, non-essential amino acids are synthesized from intermediates in major metabolic pathways such as the Citric Acid Cycle. Essential amino acids must be consumed and are made in other organisms. The amino acids are joined by peptide bonds making a polypeptide chain. This polypeptide chain then goes through post translational modifications and is sometimes joined with other polypeptide cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass). Biological relevance Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an important indicator of kidney function, because it is an easily measured byproduct of muscle metabolism that is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Creatinine itself is produced via a biological system involving creatine, phosphocreatine (also known as creatine phosphate), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP, the body's immediate energy supply). Creatine is synthesized primarily in the liver by methylation of glycocyamine (guanidino acetate, synthesized in the kidney from the amino acids arginine and glycine) by S-adenosyl methionine. It is then transported in the blood to other organs, muscles, and the brain, where it is phosphorylated to phosphocreatine, a high-energy compound. Creatine conversion to phosphocreatine is catalysed by creatine ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uric Acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotides, and it is a normal component of urine. Hyperuricemia, High blood concentrations of uric acid can lead to gout and are associated with other medical conditions, including diabetes and the formation of ammonium acid urate kidney stones. Chemistry Uric acid was first isolated from kidney stones in 1776 by Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele. In 1882, the Ukrainian chemist Ivan Horbaczewski first synthesized uric acid by melting urea with glycine. Uric acid displays lactam–lactim tautomerism. Uric acid crystallizes in the lactam form, with computational chemistry also indicating that tautomer to be the most stable. Uric acid is a diprotic acid with pKa, p''K''a1 = 5.4 and p''K''a2 =&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
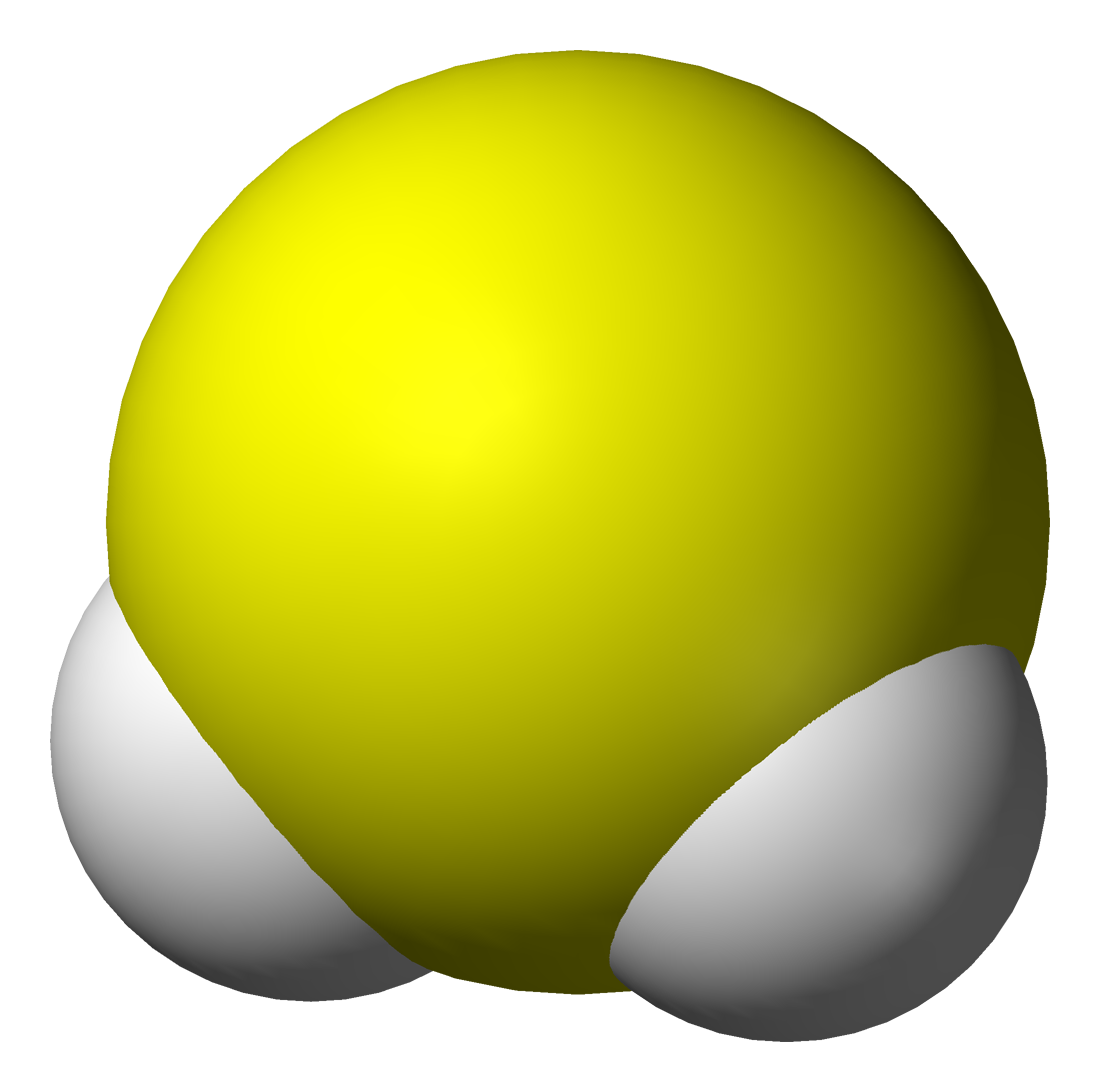
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions, as well as the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms; it is thought to be the central motivation for all organic action. All home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |