LEDs As Photodiode Light Sensors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a
 By selection of different semiconductor materials, single-color LEDs can be made that emit light in a narrow band of wavelengths from near-infrared through the visible spectrum and into the ultraviolet range. The required operating voltages of LEDs increase as the emitted wavelengths become shorter (higher energy, red to blue), because of their increasing semiconductor band gap.
Blue LEDs have an active region consisting of one or more InGaN quantum wells sandwiched between thicker layers of GaN, called cladding layers. By varying the relative In/Ga fraction in the InGaN quantum wells, the light emission can in theory be varied from violet to amber.
By selection of different semiconductor materials, single-color LEDs can be made that emit light in a narrow band of wavelengths from near-infrared through the visible spectrum and into the ultraviolet range. The required operating voltages of LEDs increase as the emitted wavelengths become shorter (higher energy, red to blue), because of their increasing semiconductor band gap.
Blue LEDs have an active region consisting of one or more InGaN quantum wells sandwiched between thicker layers of GaN, called cladding layers. By varying the relative In/Ga fraction in the InGaN quantum wells, the light emission can in theory be varied from violet to amber.
 Mixing red, green, and blue sources to produce white light needs electronic circuits to control the blending of the colors. Since LEDs have slightly different emission patterns, the color balance may change depending on the angle of view, even if the RGB sources are in a single package, so RGB diodes are seldom used to produce white lighting. Nonetheless, this method has many applications because of the flexibility of mixing different colors, and in principle, this mechanism also has higher
Mixing red, green, and blue sources to produce white light needs electronic circuits to control the blending of the colors. Since LEDs have slightly different emission patterns, the color balance may change depending on the angle of view, even if the RGB sources are in a single package, so RGB diodes are seldom used to produce white lighting. Nonetheless, this method has many applications because of the flexibility of mixing different colors, and in principle, this mechanism also has higher
 This method involves
This method involves  Among the challenges being faced to improve the efficiency of LED-based white light sources is the development of more efficient phosphors. As of 2010, the most efficient yellow phosphor is still the YAG phosphor, with less than 10% Stokes shift loss. Losses attributable to internal optical losses due to re-absorption in the LED chip and in the LED packaging itself account typically for another 10% to 30% of efficiency loss. Currently, in the area of phosphor LED development, much effort is being spent on optimizing these devices to higher light output and higher operation temperatures. For instance, the efficiency can be raised by adapting better package design or by using a more suitable type of phosphor. Conformal coating process is frequently used to address the issue of varying phosphor thickness.
Some phosphor-based white LEDs encapsulate InGaN blue LEDs inside phosphor-coated epoxy. Alternatively, the LED might be paired with a remote phosphor, a preformed polycarbonate piece coated with the phosphor material. Remote phosphors provide more diffuse light, which is desirable for many applications. Remote phosphor designs are also more tolerant of variations in the LED emissions spectrum. A common yellow phosphor material is
Among the challenges being faced to improve the efficiency of LED-based white light sources is the development of more efficient phosphors. As of 2010, the most efficient yellow phosphor is still the YAG phosphor, with less than 10% Stokes shift loss. Losses attributable to internal optical losses due to re-absorption in the LED chip and in the LED packaging itself account typically for another 10% to 30% of efficiency loss. Currently, in the area of phosphor LED development, much effort is being spent on optimizing these devices to higher light output and higher operation temperatures. For instance, the efficiency can be raised by adapting better package design or by using a more suitable type of phosphor. Conformal coating process is frequently used to address the issue of varying phosphor thickness.
Some phosphor-based white LEDs encapsulate InGaN blue LEDs inside phosphor-coated epoxy. Alternatively, the LED might be paired with a remote phosphor, a preformed polycarbonate piece coated with the phosphor material. Remote phosphors provide more diffuse light, which is desirable for many applications. Remote phosphor designs are also more tolerant of variations in the LED emissions spectrum. A common yellow phosphor material is
Electronic Design, 19 November 2013 The sapphire apparatus must be coupled with a mirror-like collector to reflect light that would otherwise be wasted. It was predicted that since 2020, 40% of all GaN LEDs are made with GaN-on-Si. Manufacturing large sapphire material is difficult, while large silicon material is cheaper and more abundant. LED companies shifting from using sapphire to silicon should be a minimal investment.
 There are RGBW LEDs that combine RGB units with a phosphor white LED on the market. Doing so retains the extremely tunable color of RGB LED, but allows color rendering and efficiency to be optimized when a color close to white is selected.
Some phosphor white LED units are "tunable white", blending two extremes of color temperatures (commonly 2700K and 6500K) to produce intermediate values. This feature allows users to change the lighting to suit the current use of a multifunction room. As illustrated by a straight line on the chromaticity diagram, simple two-white blends will have a pink bias, becoming most severe in the middle. A small amount of green light, provided by another LED, could correct the problem. Some products are RGBWW, i.e. RGBW with tunable white.
A final class of white LED with mixed light is dim-to-warm. These are ordinary 2700K white LED bulbs with a small red LED that turns on when the bulb is dimmed. Doing so makes the color warmer, emulating an incandescent light bulb.
There are RGBW LEDs that combine RGB units with a phosphor white LED on the market. Doing so retains the extremely tunable color of RGB LED, but allows color rendering and efficiency to be optimized when a color close to white is selected.
Some phosphor white LED units are "tunable white", blending two extremes of color temperatures (commonly 2700K and 6500K) to produce intermediate values. This feature allows users to change the lighting to suit the current use of a multifunction room. As illustrated by a straight line on the chromaticity diagram, simple two-white blends will have a pink bias, becoming most severe in the middle. A small amount of green light, provided by another LED, could correct the problem. Some products are RGBWW, i.e. RGBW with tunable white.
A final class of white LED with mixed light is dim-to-warm. These are ordinary 2700K white LED bulbs with a small red LED that turns on when the bulb is dimmed. Doing so makes the color warmer, emulating an incandescent light bulb.
 LEDs are made in different packages for different applications. A single or a few LED junctions may be packed in one miniature device for use as an indicator or pilot lamp. An LED array may include controlling circuits within the same package, which may range from a simple
LEDs are made in different packages for different applications. A single or a few LED junctions may be packed in one miniature device for use as an indicator or pilot lamp. An LED array may include controlling circuits within the same package, which may range from a simple

 These are mostly single-die LEDs used as indicators, and they come in various sizes from 1.8 mm to 10 mm, through-hole and surface mount packages. Typical current ratings range from around 1 mA to above 20 mA. LED's can be soldered to a flexible PCB strip to form LED tape popularly used for decoration.
Common package shapes include round, with a domed or flat top, rectangular with a flat top (as used in bar-graph displays), and triangular or square with a flat top. The encapsulation may also be clear or tinted to improve contrast and viewing angle. Infrared devices may have a black tint to block visible light while passing infrared radiation, such as the Osram SFH 4546.
5 V and 12 V LEDs are ordinary miniature LEDs that have a series resistor for direct connection to a 5V or 12V supply.
These are mostly single-die LEDs used as indicators, and they come in various sizes from 1.8 mm to 10 mm, through-hole and surface mount packages. Typical current ratings range from around 1 mA to above 20 mA. LED's can be soldered to a flexible PCB strip to form LED tape popularly used for decoration.
Common package shapes include round, with a domed or flat top, rectangular with a flat top (as used in bar-graph displays), and triangular or square with a flat top. The encapsulation may also be clear or tinted to improve contrast and viewing angle. Infrared devices may have a black tint to block visible light while passing infrared radiation, such as the Osram SFH 4546.
5 V and 12 V LEDs are ordinary miniature LEDs that have a series resistor for direct connection to a 5V or 12V supply.

 ; Flashing: Flashing LEDs are used as attention seeking indicators without requiring external electronics. Flashing LEDs resemble standard LEDs but they contain an integrated
; Flashing: Flashing LEDs are used as attention seeking indicators without requiring external electronics. Flashing LEDs resemble standard LEDs but they contain an integrated  Simple electronic circuits integrated into the LED package have been around since at least 2011 which produce a random LED intensity pattern reminiscent of a flickering
Simple electronic circuits integrated into the LED package have been around since at least 2011 which produce a random LED intensity pattern reminiscent of a flickering
WS2812
being common) or a brand name such as NeoPixel. ; Filament: An LED filament consists of multiple LED chips connected in series on a common longitudinal substrate that forms a thin rod reminiscent of a traditional incandescent filament. These are being used as a low-cost decorative alternative for traditional light bulbs that are being phased out in many countries. The filaments use a rather high voltage, allowing them to work efficiently with mains voltages. Often a simple rectifier and capacitive current limiting are employed to create a low-cost replacement for a traditional light bulb without the complexity of the low voltage, high current converter that single die LEDs need. Usually, they are packaged in bulb similar to the lamps they were designed to replace, and filled with inert gas at slightly lower than ambient pressure to remove heat efficiently and prevent corrosion. ; Chip-on-board arrays: Surface-mounted LEDs are frequently produced in chip on board (COB) arrays, allowing better heat dissipation than with a single LED of comparable luminous output. The LEDs can be arranged around a cylinder, and are called "corn cob lights" because of the rows of yellow LEDs.
 The current in an LED or other diodes rises exponentially with the applied voltage (see Shockley diode equation), so a small change in voltage can cause a large change in current. Current through the LED must be regulated by an external circuit such as a constant current source to prevent damage. Since most common power supplies are (nearly) constant-voltage sources, LED fixtures must include a power converter, or at least a current-limiting resistor. In some applications, the internal resistance of small batteries is sufficient to keep current within the LED rating.
LEDs are sensitive to voltage. They must be supplied with a voltage above their
The current in an LED or other diodes rises exponentially with the applied voltage (see Shockley diode equation), so a small change in voltage can cause a large change in current. Current through the LED must be regulated by an external circuit such as a constant current source to prevent damage. Since most common power supplies are (nearly) constant-voltage sources, LED fixtures must include a power converter, or at least a current-limiting resistor. In some applications, the internal resistance of small batteries is sufficient to keep current within the LED rating.
LEDs are sensitive to voltage. They must be supplied with a voltage above their

 LEDs are used in
LEDs are used in
Color cycling LED in a single two pin package
* {{Use mdy dates, date=March 2013 LED lamps Optical diodes Display technology Signage 20th-century inventions
semiconductor device
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material (primarily silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors) for its function. Its conductivit ...
that emits light when current flows through it. Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
s in the semiconductor recombine with electron hole
In physics, chemistry, and electronic engineering, an electron hole (often simply called a hole) is a quasiparticle denoting the lack of an electron at a position where one could exist in an atom or crystal structure, atomic lattice. Since in ...
s, releasing energy in the form of photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap
In solid-state physics and solid-state chemistry, a band gap, also called a bandgap or energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap refers to t ...
of the semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
on the semiconductor device.
Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
(IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red.
Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment display
A seven-segment display is a display device for Arabic numerals, less complex than a device that can show more characters such as dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, ...
s. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
(UV), and infrared wavelengths with high, low, or intermediate light output, for instance, white LEDs suitable for room and outdoor lighting. LEDs have also given rise to new types of displays and sensors, while their high switching rates are useful in advanced communications technology. LEDs have been used in diverse applications such as aviation lighting, fairy lights, strip lights, automotive headlamps, advertising, stage lighting
Stage lighting is the craft of lighting as it applies to the production of theater, dance, opera, and other performance arts.
, general lighting, traffic signals
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – also known as robots in South Africa, Zambia, and Namibia – are signaling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order t ...
, camera flashes, lighted wallpaper, horticultural grow lights, and medical devices.
LEDs have many advantages over incandescent light sources, including lower power consumption, a longer lifetime, improved physical robustness, smaller sizes, and faster switching. In exchange for these generally favorable attributes, disadvantages of LEDs include electrical limitations to low voltage and generally to DC (not AC) power, the inability to provide steady illumination from a pulsing DC or an AC electrical supply source, and a lesser maximum operating temperature and storage temperature.
LEDs are transducer
A transducer is a device that Energy transformation, converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.
Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, M ...
s of electricity into light. They operate in reverse of photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
s, which convert light into electricity.
History
Electroluminescence
Electroluminescence (EL) is an optical phenomenon, optical and electrical phenomenon, in which a material emits light in response to the passage of an electric current or to a strong electric field. This is distinct from black body light emission ...
, from a solid state diode, was discovered, in 1906, by Henry Joseph Round, of Marconi Labs, and published, in February 1907, in Electrical World; Round observing various carborundum (silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder a ...
) crystals would emit yellow, light green, orange or blue light, when a voltage was passed between the poles.
A silicon carbide
Silicon carbide (SiC), also known as carborundum (), is a hard chemical compound containing silicon and carbon. A wide bandgap semiconductor, it occurs in nature as the extremely rare mineral moissanite, but has been mass-produced as a powder a ...
LED was created by Soviet inventor Oleg Losev in 1927.
Commercially viable LEDs only became available after Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
engineers patented efficient near-infrared emission from a diode based on GaAs
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circui ...
in 1962.
From 1968, commercial LEDs were extremely costly and saw no practical use. Monsanto
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed ...
and Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California ...
led the development of LEDs to the point where, in the 1970s, a unit cost less than five cents.
In the early 1990s, Shuji Nakamura, Hiroshi Amano and Isamu Akasaki invented blue light-emitting diodes that were dramatically more efficient than their predecessors, bringing a new generation of bright, energy-efficient white lighting and full-color LED displays into practical use and winning the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the ...
.
Physics of light production and emission
In a light-emitting diode, the recombination of electrons and electron holes in a semiconductor produces light (be it infrared, visible or UV), a process called "electroluminescence
Electroluminescence (EL) is an optical phenomenon, optical and electrical phenomenon, in which a material emits light in response to the passage of an electric current or to a strong electric field. This is distinct from black body light emission ...
". The wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of the light depends on the energy band gap
In solid-state physics and solid-state chemistry, a band gap, also called a bandgap or energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap refers to t ...
of the semiconductors used. Since these materials have a high index of refraction, design features of the devices such as special optical coatings and die shape are required to efficiently emit light.
Unlike a laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
, the light emitted from an LED is neither spectrally coherent
Coherence is, in general, a state or situation in which all the parts or ideas fit together well so that they form a united whole.
More specifically, coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics ...
nor even highly monochromatic
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, mon ...
. Its spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
is sufficiently narrow that it appears to the human eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to light, visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and Balance (ability), keeping balance.
The eye can be considered as a living ...
as a pure ( saturated) color. Also unlike most lasers, its radiation is not spatially coherent, so it cannot approach the very high intensity
Intensity may refer to:
In colloquial use
* Strength (disambiguation)
*Amplitude
* Level (disambiguation)
* Magnitude (disambiguation)
In physical sciences
Physics
*Intensity (physics), power per unit area (W/m2)
*Field strength of electric, m ...
characteristic of laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radi ...
s.
Single-color LEDs
 By selection of different semiconductor materials, single-color LEDs can be made that emit light in a narrow band of wavelengths from near-infrared through the visible spectrum and into the ultraviolet range. The required operating voltages of LEDs increase as the emitted wavelengths become shorter (higher energy, red to blue), because of their increasing semiconductor band gap.
Blue LEDs have an active region consisting of one or more InGaN quantum wells sandwiched between thicker layers of GaN, called cladding layers. By varying the relative In/Ga fraction in the InGaN quantum wells, the light emission can in theory be varied from violet to amber.
By selection of different semiconductor materials, single-color LEDs can be made that emit light in a narrow band of wavelengths from near-infrared through the visible spectrum and into the ultraviolet range. The required operating voltages of LEDs increase as the emitted wavelengths become shorter (higher energy, red to blue), because of their increasing semiconductor band gap.
Blue LEDs have an active region consisting of one or more InGaN quantum wells sandwiched between thicker layers of GaN, called cladding layers. By varying the relative In/Ga fraction in the InGaN quantum wells, the light emission can in theory be varied from violet to amber.
Aluminium gallium nitride Aluminium gallium nitride (AlGaN) is a semiconductor material. It is any alloy of aluminium nitride and gallium nitride.
The bandgap of AlxGa1−xN can be tailored from 4.3eV (xAl=0) to 6.2eV (xAl=1).
AlGaN is used to manufacture light-emitting di ...
(AlGaN) of varying Al/Ga fraction can be used to manufacture the cladding and quantum well layers for ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
LEDs, but these devices have not yet reached the level of efficiency and technological maturity of InGaN/GaN blue/green devices. If unalloyed GaN is used in this case to form the active quantum well layers, the device emits near-ultraviolet light with a peak wavelength centred around 365 nm. Green LEDs manufactured from the InGaN/GaN system are far more efficient and brighter than green LEDs produced with non-nitride material systems, but practical devices still exhibit efficiency too low for high-brightness applications.
With AlGaN and AlGaInN, even shorter wavelengths are achievable. Near-UV emitters at wavelengths around 360–395 nm are already cheap and often encountered, for example, as black light
A blacklight, also called a UV-A light, Wood's lamp, or ultraviolet light, is a lamp (fixture), lamp that emits long-wave (UV-A) ultraviolet light and very little visible light. One type of lamp has a violet light filter, filter material, eith ...
lamp replacements for inspection of anti-counterfeiting
A counterfeit is a fake or unauthorized replica of a genuine product, such as money, documents, designer items, or other valuable goods. Counterfeiting generally involves creating an imitation of a genuine item that closely resembles the original ...
UV watermarks in documents and bank notes, and for UV curing
UV curing (ultraviolet curing) is the process by which ultraviolet light initiates a photochemical reaction that generates a crosslinked network of polymers through radical polymerization or cationic polymerization. UV curing is adaptable to inkj ...
. Substantially more expensive, shorter-wavelength diodes are commercially available for wavelengths down to 240 nm. As the photosensitivity of microorganisms approximately matches the absorption spectrum of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, with a peak at about 260 nm, UV LED emitting at 250–270 nm are expected in prospective disinfection and sterilization devices. Recent research has shown that commercially available UVA LEDs (365 nm) are already effective disinfection and sterilization devices.
UV-C wavelengths were obtained in laboratories using aluminium nitride
Aluminium nitride ( Al N) is a solid nitride of aluminium. It has a high thermal conductivity of up to 321 W/(m·K) and is an electrical insulator. Its wurtzite phase (w-AlN) has a band gap of ~6 eV at room temperature and has a potent ...
(210 nm), boron nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula B N. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexago ...
(215 nm) and diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
(235 nm).
White LEDs
There are two primary ways of producingwhite
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
light-emitting diodes. One is to use individual LEDs that emit three primary color
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color prin ...
s—red, green and blue—and then mix all the colors to form white light. The other, more often used method is to use a phosphor material to convert monochromatic light from a blue or UV LED to broad-spectrum white light, similar to a fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
. The yellow phosphor is cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ...
-doped YAG crystals suspended in the package or coated on the LED. This YAG phosphor causes white LEDs to appear yellow when off, and the space between the crystals allow some blue light to pass through in LEDs with partial phosphor conversion. Alternatively, white LEDs may use other phosphors like manganese(IV)-doped potassium fluorosilicate (PFS) or other engineered phosphors. PFS assists in red light generation, and is used in conjunction with conventional Ce:YAG phosphor.
In LEDs with PFS phosphor, some blue light passes through the phosphors, the Ce:YAG phosphor converts blue light to green and red (yellow) light, and the PFS phosphor converts blue light to red light. The color, emission spectrum or color temperature of white phosphor converted and other phosphor converted LEDs can be controlled by changing the concentration of several phosphors that form a phosphor blend used in an LED package.
The 'whiteness' of the light produced is engineered to suit the human eye. Because of metamerism, it is possible to have quite different spectra that appear white. The appearance of objects illuminated by that light may vary as the spectrum varies. This is the issue of color rendition, quite separate from color temperature. An orange or cyan object could appear with the wrong color and much darker as the LED or phosphor does not emit the wavelength it reflects. The best color rendition LEDs use a mix of phosphors, resulting in less efficiency and better color rendering.
The first white light-emitting diodes (LEDs) were offered for sale in the autumn of 1996. Nichia made some of the first white LEDs which were based on blue LEDs with Ce:YAG phosphor. Ce:YAG is often grown using the Czochralski method.
RGB systems
quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
in producing white light.
There are several types of multicolor white LEDs: di-, tri-
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
*triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, octagon ...
, and tetrachromatic white LEDs. Several key factors that play among these different methods include color stability, color rendering
The color rendering of a light source refers to its ability to reveal the colors of various objects faithfully (i.e. to produce Metamerism (color), illuminant metamerism) in comparison with an ideal or natural light source. Light sources with good ...
capability, and luminous efficacy. Often, higher efficiency means lower color rendering, presenting a trade-off between the luminous efficacy and color rendering. For example, the dichromatic white LEDs have the best luminous efficacy (120 lm/W), but the lowest color rendering capability. Although tetrachromatic white LEDs have excellent color rendering capability, they often have poor luminous efficacy. Trichromatic white LEDs are in between, having both good luminous efficacy (>70 lm/W) and fair color rendering capability.
One of the challenges is the development of more efficient green LEDs. The theoretical maximum for green LEDs is 683 lumens per watt but as of 2010 few green LEDs exceed even 100 lumens per watt. The blue and red LEDs approach their theoretical limits.
Multicolor LEDs offer a means to form light of different colors. Most perceivable colors can be formed by mixing different amounts of three primary colors. This allows precise dynamic color control. Their emission power decays exponentially with rising temperature,
resulting in a substantial change in color stability. Such problems inhibit industrial use. Multicolor LEDs without phosphors cannot provide good color rendering because each LED is a narrowband source. LEDs without phosphor, while a poorer solution for general lighting, are the best solution for displays, either backlight of LCD, or direct LED based pixels.
Dimming a multicolor LED source to match the characteristics of incandescent lamps is difficult because manufacturing variations, age, and temperature change the actual color value output. To emulate the appearance of dimming incandescent lamps may require a feedback system with color sensor to actively monitor and control the color.
Phosphor-based LEDs
 This method involves
This method involves coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, or substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. powder coatings.
Paints ...
LEDs of one color (mostly blue LEDs made of InGaN) with phosphor
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or ...
s of different colors to form white light; the resultant LEDs are called phosphor-based or phosphor-converted white LEDs (pcLEDs). A fraction of the blue light undergoes the Stokes shift, which transforms it from shorter wavelengths to longer. Depending on the original LED's color, various color phosphors are used. Using several phosphor layers of distinct colors broadens the emitted spectrum, effectively raising the color rendering index
A color rendering index (CRI) is a quantitative measure of the ability of a light source to reveal the colors of various objects faithfully in comparison with a natural or standard light source.
''Color rendering'', as defined by the Internat ...
(CRI).
Phosphor-based LEDs have efficiency losses due to heat loss from the Stokes shift and also other phosphor-related issues. Their luminous efficacies compared to normal LEDs depend on the spectral distribution of the resultant light output and the original wavelength of the LED itself. For example, the luminous efficacy of a typical YAG yellow phosphor based white LED ranges from 3 to 5 times the luminous efficacy of the original blue LED because of the human eye's greater sensitivity to yellow than to blue (as modeled in the luminosity function
A luminous efficiency function or luminosity function represents the average spectral sensitivity of human visual perception of light. It is based on subjective judgements of which of a pair of different-colored lights is brighter, to describe re ...
).
Due to the simplicity of manufacturing, the phosphor method is still the most popular method for making high-intensity white LEDs. The design and production of a light source or light fixture using a monochrome emitter with phosphor conversion is simpler and cheaper than a complex RGB system, and the majority of high-intensity white LEDs presently on the market are manufactured using phosphor light conversion.
 Among the challenges being faced to improve the efficiency of LED-based white light sources is the development of more efficient phosphors. As of 2010, the most efficient yellow phosphor is still the YAG phosphor, with less than 10% Stokes shift loss. Losses attributable to internal optical losses due to re-absorption in the LED chip and in the LED packaging itself account typically for another 10% to 30% of efficiency loss. Currently, in the area of phosphor LED development, much effort is being spent on optimizing these devices to higher light output and higher operation temperatures. For instance, the efficiency can be raised by adapting better package design or by using a more suitable type of phosphor. Conformal coating process is frequently used to address the issue of varying phosphor thickness.
Some phosphor-based white LEDs encapsulate InGaN blue LEDs inside phosphor-coated epoxy. Alternatively, the LED might be paired with a remote phosphor, a preformed polycarbonate piece coated with the phosphor material. Remote phosphors provide more diffuse light, which is desirable for many applications. Remote phosphor designs are also more tolerant of variations in the LED emissions spectrum. A common yellow phosphor material is
Among the challenges being faced to improve the efficiency of LED-based white light sources is the development of more efficient phosphors. As of 2010, the most efficient yellow phosphor is still the YAG phosphor, with less than 10% Stokes shift loss. Losses attributable to internal optical losses due to re-absorption in the LED chip and in the LED packaging itself account typically for another 10% to 30% of efficiency loss. Currently, in the area of phosphor LED development, much effort is being spent on optimizing these devices to higher light output and higher operation temperatures. For instance, the efficiency can be raised by adapting better package design or by using a more suitable type of phosphor. Conformal coating process is frequently used to address the issue of varying phosphor thickness.
Some phosphor-based white LEDs encapsulate InGaN blue LEDs inside phosphor-coated epoxy. Alternatively, the LED might be paired with a remote phosphor, a preformed polycarbonate piece coated with the phosphor material. Remote phosphors provide more diffuse light, which is desirable for many applications. Remote phosphor designs are also more tolerant of variations in the LED emissions spectrum. A common yellow phosphor material is cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ...
- doped yttrium aluminium garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet (YAG, Yttrium, Y3Aluminium, Al5Oxygen, O12) is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group. It is a Crystal system, cubic yttrium aluminium oxide phase, with other examples being YAlO3 (YAP) in a Crystal system, ...
(Ce3+:YAG).
White LEDs can also be made by coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, or substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. powder coatings.
Paints ...
near-ultraviolet (NUV) LEDs with a mixture of high-efficiency europium
Europium is a chemical element; it has symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is a silvery-white metal of the lanthanide series that reacts readily with air to form a dark oxide coating. Europium is the most chemically reactive, least dense, and soft ...
-based phosphors that emit red and blue, plus copper and aluminium-doped zinc sulfide (ZnS:Cu, Al) that emits green. This is a method analogous to the way fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
s work. This method is less efficient than blue LEDs with YAG:Ce phosphor, as the Stokes shift is larger, so more energy is converted to heat, but yields light with better spectral characteristics, which render color better. Due to the higher radiative output of the ultraviolet LEDs than of the blue ones, both methods offer comparable brightness. A concern is that UV light may leak from a malfunctioning light source and cause harm to human eyes or skin.
A new style of wafers composed of gallium-nitride-on-silicon (GaN-on-Si) is being used to produce white LEDs using 200-mm silicon wafers. This avoids the typical costly sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire ...
substrate in relatively small 100- or 150-mm wafer sizes.Next-Generation GaN-on-Si White LEDs Suppress CostsElectronic Design, 19 November 2013 The sapphire apparatus must be coupled with a mirror-like collector to reflect light that would otherwise be wasted. It was predicted that since 2020, 40% of all GaN LEDs are made with GaN-on-Si. Manufacturing large sapphire material is difficult, while large silicon material is cheaper and more abundant. LED companies shifting from using sapphire to silicon should be a minimal investment.
Mixed white LEDs
 There are RGBW LEDs that combine RGB units with a phosphor white LED on the market. Doing so retains the extremely tunable color of RGB LED, but allows color rendering and efficiency to be optimized when a color close to white is selected.
Some phosphor white LED units are "tunable white", blending two extremes of color temperatures (commonly 2700K and 6500K) to produce intermediate values. This feature allows users to change the lighting to suit the current use of a multifunction room. As illustrated by a straight line on the chromaticity diagram, simple two-white blends will have a pink bias, becoming most severe in the middle. A small amount of green light, provided by another LED, could correct the problem. Some products are RGBWW, i.e. RGBW with tunable white.
A final class of white LED with mixed light is dim-to-warm. These are ordinary 2700K white LED bulbs with a small red LED that turns on when the bulb is dimmed. Doing so makes the color warmer, emulating an incandescent light bulb.
There are RGBW LEDs that combine RGB units with a phosphor white LED on the market. Doing so retains the extremely tunable color of RGB LED, but allows color rendering and efficiency to be optimized when a color close to white is selected.
Some phosphor white LED units are "tunable white", blending two extremes of color temperatures (commonly 2700K and 6500K) to produce intermediate values. This feature allows users to change the lighting to suit the current use of a multifunction room. As illustrated by a straight line on the chromaticity diagram, simple two-white blends will have a pink bias, becoming most severe in the middle. A small amount of green light, provided by another LED, could correct the problem. Some products are RGBWW, i.e. RGBW with tunable white.
A final class of white LED with mixed light is dim-to-warm. These are ordinary 2700K white LED bulbs with a small red LED that turns on when the bulb is dimmed. Doing so makes the color warmer, emulating an incandescent light bulb.
Other white LEDs
Experimental white light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have been developed using homoepitaxially grown zinc selenide (ZnSe) on ZnSe substrates. This approach eliminates the need for phosphors, distinguishing it from conventional white LEDs that typically combine blue or ultraviolet LEDs with phosphors to produce white light. In these ZnSe-based LEDs, the active region emits blue light, while the conductive ZnSe substrate emits yellow light. The combination of these emissions results in white light output. This method offers advantages such as lower operating voltage (approximately 2.7 V), reduced packaging complexity, and the potential for a broader range of color temperatures (3500–8500 K) compared to GaN-based devices. A study published in the Journal of Crystal Growth in 2000 demonstrated that these ZnSe-based white LEDs exhibited a color temperature around 3400 K and a color rendering index (CRI) of 68. At a forward current of 20 mA, the optical output power was 2.0 mW, and the luminous efficiency was estimated at 10.4 lm/W, comparable to incandescent lamps and commercial InGaN-based white LEDs. However, challenges remain, particularly concerning device degradation. Reports indicate that the lifetime of these ZnSe-based white LEDs is limited, with some studies suggesting a half-life of approximately 800 hours at 20°C . Additionally, the commercialization of these devices has been hindered by issues such as electron overflow and the need for enhanced p-type carrier concentration. Despite these challenges, the development of phosphor-free ZnSe-based white LEDs represents a significant step toward more efficient and versatile lighting solutions. Ongoing research aims to address the limitations and improve the performance and longevity of these devices.Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs)
In an organic light-emitting diode (OLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a type of light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is an organic compound film that emits light in respon ...
), the electroluminescent material composing the emissive layer of the diode is an organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
. The organic material is electrically conductive due to the delocalization
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref>
The term delocalization is general and can have slightly diff ...
of pi electrons
In chemistry, pi bonds (π bonds) are covalent chemical bonds, in each of which two lobes of an orbital on one atom overlap with two lobes of an orbital on another atom, and in which this overlap occurs laterally. Each of these atomic orbitals ...
caused by conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
*Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change o ...
over all or part of the molecule, and the material therefore functions as an organic semiconductor
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and – at times – heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals o ...
. The organic materials can be small organic molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s in a crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line phase, or polymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
s.
The potential advantages of OLEDs include thin, low-cost displays with a low driving voltage, wide viewing angle, and high contrast and color gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. cam ...
. Polymer LEDs have the added benefit of printable and flexible displays. OLEDs have been used to make visual displays for portable electronic devices such as cellphones, digital cameras, lighting and televisions.
Types
 LEDs are made in different packages for different applications. A single or a few LED junctions may be packed in one miniature device for use as an indicator or pilot lamp. An LED array may include controlling circuits within the same package, which may range from a simple
LEDs are made in different packages for different applications. A single or a few LED junctions may be packed in one miniature device for use as an indicator or pilot lamp. An LED array may include controlling circuits within the same package, which may range from a simple resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active e ...
, blinking or color changing control, or an addressable controller for RGB devices. Higher-powered white-emitting devices will be mounted on heat sinks and will be used for illumination. Alphanumeric displays in dot matrix or bar formats are widely available. Special packages permit connection of LEDs to optical fibers for high-speed data communication links.
Miniature

 These are mostly single-die LEDs used as indicators, and they come in various sizes from 1.8 mm to 10 mm, through-hole and surface mount packages. Typical current ratings range from around 1 mA to above 20 mA. LED's can be soldered to a flexible PCB strip to form LED tape popularly used for decoration.
Common package shapes include round, with a domed or flat top, rectangular with a flat top (as used in bar-graph displays), and triangular or square with a flat top. The encapsulation may also be clear or tinted to improve contrast and viewing angle. Infrared devices may have a black tint to block visible light while passing infrared radiation, such as the Osram SFH 4546.
5 V and 12 V LEDs are ordinary miniature LEDs that have a series resistor for direct connection to a 5V or 12V supply.
These are mostly single-die LEDs used as indicators, and they come in various sizes from 1.8 mm to 10 mm, through-hole and surface mount packages. Typical current ratings range from around 1 mA to above 20 mA. LED's can be soldered to a flexible PCB strip to form LED tape popularly used for decoration.
Common package shapes include round, with a domed or flat top, rectangular with a flat top (as used in bar-graph displays), and triangular or square with a flat top. The encapsulation may also be clear or tinted to improve contrast and viewing angle. Infrared devices may have a black tint to block visible light while passing infrared radiation, such as the Osram SFH 4546.
5 V and 12 V LEDs are ordinary miniature LEDs that have a series resistor for direct connection to a 5V or 12V supply.
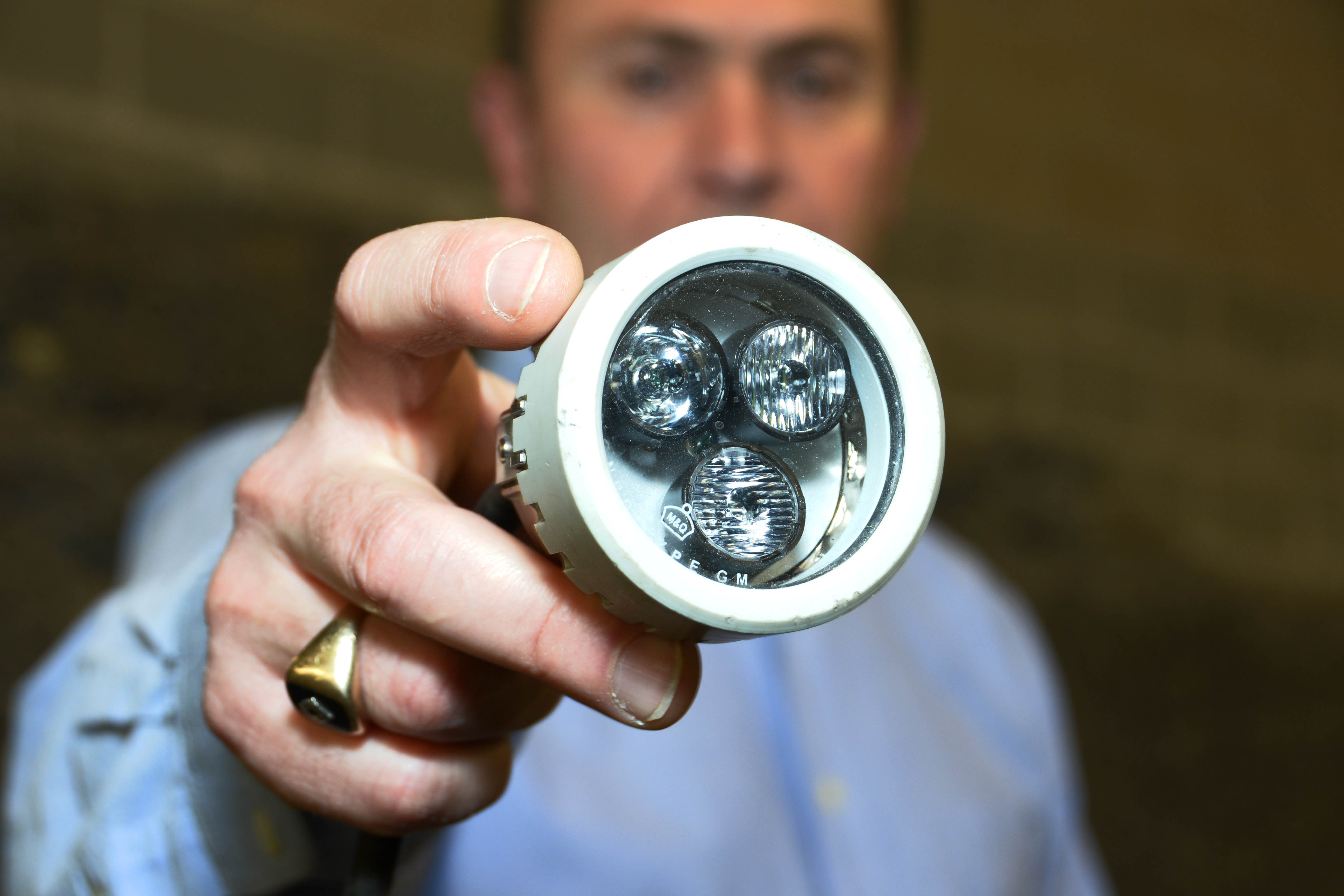
High-power
High-power LEDs (HP-LEDs) or high-output LEDs (HO-LEDs) can be driven at currents from hundreds of mA to more than an ampere, compared with the tens of mA for other LEDs. Some can emit over a thousand lumens. LED power densities up to 300 W/cm2 have been achieved. Since overheating is destructive, the HP-LEDs must be mounted on a heat sink to allow for heat dissipation. If the heat from an HP-LED is not removed, the device fails in seconds. One HP-LED can often replace an incandescent bulb in aflashlight
A flashlight (US English) or electric torch (Commonwealth English), usually shortened to torch, is a portable hand-held electric lamp. Formerly, the light source typically was a miniature incandescent light bulb, but these have been displaced ...
, or be set in an array to form a powerful LED lamp.
Some HP-LEDs in this category are the Nichia 19 series, Lumileds Rebel Led, Osram Opto Semiconductors Golden Dragon, and Cree X-lamp. As of September 2009, some HP-LEDs manufactured by Cree exceed 105 lm/W.
Examples for Haitz's law—which predicts an exponential rise in light output and efficacy of LEDs over time—are the CREE XP-G series LED, which achieved 105lm/W in 2009 and the Nichia 19 series with a typical efficacy of 140lm/W, released in 2010.
AC-driven
LEDs developed by Seoul Semiconductor can operate on AC power without a DC converter. For each half-cycle, part of the LED emits light and part is dark, and this is reversed during the next half-cycle. The efficiency of this type of HP-LED is typically 40lm/W. A large number of LED elements in series may be able to operate directly from line voltage. In 2009, Seoul Semiconductor released a high DC voltage LED, named 'Acrich MJT', capable of being driven from AC power with a simple controlling circuit. The low-power dissipation of these LEDs affords them more flexibility than the original AC LED design.Strip
There are many types of LED Strips each with different codenames and LED types. Each one can vary in input power, led spacing, color capability and more.Application-specific

 ; Flashing: Flashing LEDs are used as attention seeking indicators without requiring external electronics. Flashing LEDs resemble standard LEDs but they contain an integrated
; Flashing: Flashing LEDs are used as attention seeking indicators without requiring external electronics. Flashing LEDs resemble standard LEDs but they contain an integrated voltage regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. It may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism or electronic components. Depending on the ...
and a multivibrator
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state devices such as relaxation oscillators, timers, flip-flop (electronics), latches and flip-flops. The first multivibrator circuit, the astable multivibrator el ...
circuit that causes the LED to flash with a typical period of one second. In diffused lens LEDs, this circuit is visible as a small black dot. Most flashing LEDs emit light of one color, but more sophisticated devices can flash between multiple colors and even fade through a color sequence using RGB color mixing. Flashing SMD LEDs in the 0805 and other size formats have been available since early 2019.
; Flickering:  Simple electronic circuits integrated into the LED package have been around since at least 2011 which produce a random LED intensity pattern reminiscent of a flickering
Simple electronic circuits integrated into the LED package have been around since at least 2011 which produce a random LED intensity pattern reminiscent of a flickering candle
A candle is an ignitable candle wick, wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a Aroma compound, fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time. ...
. Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accompl ...
in 2024 has suggested that some flickering LEDs with automatic sleep and wake modes might be using an integrated 8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
for such functionally. Sometimes a flickering effect might happen due to an electric malfunction.
; Bi-color: Bi-color LEDs contain two different LED emitters in one case. There are two types of these. One type consists of two dies connected to the same two leads antiparallel to each other. Current flow in one direction emits one color, and current in the opposite direction emits the other color. The other type consists of two dies with separate leads for both dies and another lead for common anode or cathode so that they can be controlled independently. The most common bi-color combination is red/traditional green. Others include amber/traditional green, red/pure green, red/blue, and blue/pure green.
; RGB tri-color: Tri-color LEDs contain three different LED emitters in one case. Each emitter is connected to a separate lead so they can be controlled independently. A four-lead arrangement is typical with one common lead (anode or cathode) and an additional lead for each color. Others have only two leads (positive and negative) and have a built-in electronic controller. RGB LEDs consist of one red, one green, and one blue LED. By independently adjusting each of the three, RGB LEDs are capable of producing a wide color gamut. Unlike dedicated-color LEDs, these do not produce pure wavelengths. Modules may not be optimized for smooth color mixing.
; Decorative-multicolor: Decorative-multicolor LEDs incorporate several emitters of different colors supplied by only two lead-out wires. Colors are switched internally by varying the supply voltage.
; Alphanumeric: Alphanumeric LEDs are available in seven-segment, starburst, and dot-matrix
A dot matrix is a 2-dimensional patterned Array data structure, array, used to represent characters, symbols and images. Most types of modern technology use dot matrices for display of information, including mobile phones, televisions, and pri ...
format. Seven-segment displays handle all numbers and a limited set of letters. Starburst displays can display all letters. Dot-matrix displays typically use 5×7 pixels per character. Seven-segment LED displays were in widespread use in the 1970s and 1980s, but rising use of liquid crystal display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liq ...
s, with their lower power needs and greater display flexibility, has reduced the popularity of numeric and alphanumeric LED displays.
; Digital RGB: Digital RGB addressable LEDs contain their own "smart" control electronics. In addition to power and ground, these provide connections for data-in, data-out, clock and sometimes a strobe signal. These are connected in a daisy chain, which allows individual LEDs in a long LED strip light
An LED strip, tape, or ribbon light is a flexible printed circuit board, circuit board populated by surface-mount technology, surface-mount light-emitting diodes (SMD LEDs) and other components that usually comes with an adhesive backing. LED lam ...
to be easily controlled by a microcontroller. Data sent to the first LED of the chain can control the brightness and color of each LED independently of the others. They are used where a combination of maximum control and minimum visible electronics are needed such as strings for Christmas and LED matrices. Some even have refresh rates in the kHz range, allowing for basic video applications. These devices are known by their part numberWS2812
being common) or a brand name such as NeoPixel. ; Filament: An LED filament consists of multiple LED chips connected in series on a common longitudinal substrate that forms a thin rod reminiscent of a traditional incandescent filament. These are being used as a low-cost decorative alternative for traditional light bulbs that are being phased out in many countries. The filaments use a rather high voltage, allowing them to work efficiently with mains voltages. Often a simple rectifier and capacitive current limiting are employed to create a low-cost replacement for a traditional light bulb without the complexity of the low voltage, high current converter that single die LEDs need. Usually, they are packaged in bulb similar to the lamps they were designed to replace, and filled with inert gas at slightly lower than ambient pressure to remove heat efficiently and prevent corrosion. ; Chip-on-board arrays: Surface-mounted LEDs are frequently produced in chip on board (COB) arrays, allowing better heat dissipation than with a single LED of comparable luminous output. The LEDs can be arranged around a cylinder, and are called "corn cob lights" because of the rows of yellow LEDs.
Considerations for use
* Efficiency: LEDs emit more lumens per watt than incandescent light bulbs. The efficiency of LED lighting fixtures is not affected by shape and size, unlike fluorescent light bulbs or tubes. * Size: LEDs can be very small (smaller than 2 mm2) and are easily attached to printed circuit boards.Power sources
threshold voltage
The threshold voltage, commonly abbreviated as Vth or VGS(th), of a field-effect transistor (FET) is the minimum gate-to-source voltage (VGS) that is needed to create a conducting path between the source and drain terminals. It is an important s ...
and a current below their rating. Current and lifetime change greatly with a small change in applied voltage. They thus require a current-regulated supply (usually just a series resistor for indicator LEDs).
Efficiency droop: The efficiency of LEDs decreases as the electric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
increases. Heating also increases with higher currents, which compromises LED lifetime. These effects put practical limits on the current through an LED in high power applications.Stevenson, Richard (August 2009), "". ''IEEE Spectrum''.
Electrical polarity
Unlike a traditional incandescent lamp, an LED will light only when voltage is applied in the forward direction of the diode. No current flows and no light is emitted if voltage is applied in the reverse direction. If the reverse voltage exceeds thebreakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator (electrical), insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to experience electrical breakdown and become electrically Conductor (material), conductive.
For diodes, the breakdown vo ...
, which is typically about five volts, a large current flows and the LED will be damaged. If the reverse current is sufficiently limited to avoid damage, the reverse-conducting LED is a useful noise diode.
By definition, the energy band gap of any diode is higher when reverse-biased than when forward-biased. Because the band gap energy determines the wavelength of the light emitted, the color cannot be the same when reverse-biased. The reverse breakdown voltage is sufficiently high that the emitted wavelength cannot be similar enough to still be visible. Though dual-LED packages exist that contain a different color LED in each direction, it is not expected that any single LED element can emit visible light when reverse-biased.
It is not known if any zener diode could exist that emits light only in reverse-bias mode. Uniquely, this type of LED would conduct when connected backwards.
Appearance
* Color: LEDs can emit light of an intended color without using any color filters as traditional lighting methods need. This is more efficient and can lower initial costs. * Cool light: In contrast to most light sources, LEDs radiate very little heat in the form of IR that can cause damage to sensitive objects or fabrics. Wasted energy is dispersed as heat through the base of the LED. * Color rendition: Most cool- white LEDs have spectra that differ significantly from ablack body
A black body or blackbody is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence. The radiation emitted by a black body in thermal equilibrium with its environment is ...
radiator like the sun or an incandescent light. The spike at 460 nm and dip at 500 nm can make the color of objects appear differently under cool-white LED illumination than sunlight or incandescent sources, due to metamerism, red surfaces being rendered particularly poorly by typical phosphor-based cool-white LEDs. The same is true with green surfaces. The quality of color rendition of an LED is measured by the Color Rendering Index (CRI).
* Dimming: LEDs can be dimmed either by pulse-width modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), also known as pulse-duration modulation (PDM) or pulse-length modulation (PLM), is any method of representing a signal as a rectangular wave with a varying duty cycle (and for some methods also a varying peri ...
or lowering the forward current. This pulse-width modulation is why LED lights, particularly headlights on cars, when viewed on camera or by some people, seem to flash or flicker. This is a type of stroboscopic effect
The stroboscopic effect is a visual optical phenomenon, phenomenon caused by aliasing that occurs when continuous rotational or other cyclic motion is represented by a series of short or instantaneous samples (as opposed to a continuous view) at ...
.
Light properties
* Switch on time: LEDs light up extremely quickly. A typical red indicator LED achieves full brightness in under amicrosecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is to one second, ...
. LEDs used in communications devices can have even faster response times.
* Focus: The solid package of the LED can be designed to focus
Focus (: foci or focuses) may refer to:
Arts
* Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in East Australia Film
*Focus (2001 film), ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based on the Arthur Miller novel
*Focus (2015 ...
its light. Incandescent and fluorescent sources often require an external reflector to collect light and direct it in a usable manner. For larger LED packages total internal reflection
In physics, total internal reflection (TIR) is the phenomenon in which waves arriving at the interface (boundary) from one medium to another (e.g., from water to air) are not refracted into the second ("external") medium, but completely refl ...
(TIR) lenses are often used to the same effect. When large quantities of light are needed, many light sources such as LED chips are usually deployed, which are difficult to focus or collimate on the same target.
* Area light source: Single LEDs do not approximate a point source
A point source is a single identifiable ''localized'' source of something. A point source has a negligible extent, distinguishing it from other source geometries. Sources are called point sources because, in mathematical modeling, these sources ...
of light giving a spherical light distribution, but rather a lambertian distribution. So, LEDs are difficult to apply to uses needing a spherical light field. Different fields of light can be manipulated by the application of different optics or "lenses". LEDs cannot provide divergence below a few degrees.
Reliability
* Shock resistance: LEDs, being solid-state components, are difficult to damage with external shock, unlike fluorescent and incandescent bulbs, which are fragile. * Thermal runaway: Parallel strings of LEDs will not share current evenly due to the manufacturing tolerances in their forward voltage. Running two or more strings from a single current source may result in LED failure as the devices warm up. If forward voltage binning is not possible, a circuit is required to ensure even distribution of current between parallel strands. * Slow failure: LEDs mainly fail by dimming over time, rather than the abrupt failure of incandescent bulbs., US Department of Energy * Lifetime: LEDs can have a relatively long useful life. One report estimates 35,000 to 50,000 hours of useful life for white LEDs, though time to complete failure may be shorter or longer. Fluorescent tubes typically are rated at about 10,000 to 25,000 hours, depending partly on the conditions of use, and incandescent light bulbs at 1,000 to 2,000 hours. Several DOE demonstrations have shown that reduced maintenance costs from this extended lifetime, rather than energy savings, is the primary factor in determining the payback period for an LED product. * Cycling: LEDs are ideal for uses subject to frequent on-off cycling, unlike incandescent and fluorescent lamps that fail faster when cycled often, orhigh-intensity discharge lamp
High-intensity discharge lamps (HID lamps) are a type of electrical gas-discharge lamp which produces light by means of an electric arc between tungsten electrodes housed inside a translucent or transparent fused quartz or fused alumina arc ...
s (HID lamps) that require a long time to warm up to full output and to cool down before they can be lighted again if they are being restarted.
* Temperature dependence: LED performance largely depends on the ambient temperature of the operating environment – or thermal management properties. Overdriving an LED in high ambient temperatures may result in overheating the LED package, eventually leading to device failure. An adequate heat sink
A heat sink (also commonly spelled heatsink) is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant, where it is thermal management (electronics), ...
is needed to maintain long life. This is especially important in automotive, medical, and military uses where devices must operate over a wide range of temperatures, and require low failure rates.
Manufacturing
LED manufacturing involves multiple steps, including epitaxy, chip processing, chip separation, and packaging. In a typical LED manufacturing process, encapsulation is performed after probing, dicing, die transfer from wafer to package, and wire bonding or flip chip mounting, perhaps usingindium tin oxide
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a ternary composition of indium, tin and oxygen in varying proportions. Depending on the oxygen content, it can be described as either a ceramic or an alloy. Indium tin oxide is typically encountered as an oxygen-saturate ...
, a transparent electrical conductor. In this case, the bond wire(s) are attached to the ITO film that has been deposited in the LEDs.
Flip chip circuit on board (COB) is a technique that can be used to manufacture LEDs.
Colors and materials
Conventional LEDs are made from a variety of inorganicsemiconductor materials
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels ...
. The following table shows the available colors with wavelength range, voltage drop and material:
Applications
LED uses fall into five major categories: * Visual signals where light goes more or less directly from the source to the human eye, to convey a message or meaning * Illumination where light is reflected from objects to give visual response of these objects * Measuring and interacting with processes involving no human vision * Narrow band light sensors where LEDs operate in a reverse-bias mode and respond to incident light, instead of emitting light * Indoor cultivation, including cannabis. The application of LEDs in horticulture has revolutionized plant cultivation by providing energy-efficient, customizable lighting solutions that optimize plant growth and development. LEDs offer precise control over light spectra, intensity, and photoperiods, enabling growers to tailor lighting conditions to the specific needs of different plant species and growth stages. This technology enhances photosynthesis, improves crop yields, and reduces energy costs compared to traditional lighting systems. Additionally, LEDs generate less heat, allowing closer placement to plants without risking thermal damage, and contribute to sustainable farming practices by lowering carbon footprints and extending growing seasons in controlled environments. Light spectrum affects growth, metabolite profile, and resistance against fungal phytopathogens of '' Solanum lycopersicum'' seedlings. LEDs can also be used in micropropagation.Indicators and signs
The low energy consumption, low maintenance and small size of LEDs has led to uses as status indicators and displays on a variety of equipment and installations. Large-areaLED display
A LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as pixels for a video display. Their brightness allows them to be used outdoors where they are visible in the sun for store signs and billboards. I ...
s are used as stadium displays, dynamic decorative displays, and dynamic message signs on freeways. Thin, lightweight message displays are used at airports and railway stations, and as destination displays for trains, buses, trams, and ferries.
One-color light is well suited for traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – also known as robots in South Africa, Zambia, and Namibia – are signaling devices positioned at intersection (road), road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order t ...
s and signals, exit signs, emergency vehicle lighting
Emergency vehicle lighting, also known as simply emergency lighting or emergency lights, is a type of Automotive lighting, vehicle lighting used to visually announce a vehicle's presence to other road users. A sub-type of emergency vehicle equipme ...
, ships' navigation lights, and LED-based Christmas lights.
Because of their long life, fast switching times, and visibility in broad daylight due to their high output and focus, LEDs have been used in automotive brake lights and turn signals. The use in brakes improves safety, due to a great reduction in the time needed to light fully, or faster rise time, about 0.1 second faster than an incandescent bulb. This gives drivers behind more time to react. In a dual intensity circuit (rear markers and brakes) if the LEDs are not pulsed at a fast enough frequency, they can create a phantom array, where ghost images of the LED appear if the eyes quickly scan across the array. White LED headlamps are beginning to appear. Using LEDs has styling advantages because LEDs can form much thinner lights than incandescent lamps with parabolic reflector
A parabolic (or paraboloid or paraboloidal) reflector (or dish or mirror) is a Mirror, reflective surface used to collect or project energy such as light, sound, or radio waves. Its shape is part of a circular paraboloid, that is, the surface ge ...
s.
Due to the relative cheapness of low output LEDs, they are also used in many temporary uses such as glowsticks and throwies. Artists have also used LEDs for LED art.
Lighting
With the development of high-efficiency and high-power LEDs, it has become possible to use LEDs in lighting and illumination. To encourage the shift to LED lamps and other high-efficiency lighting, in 2008 theUS Department of Energy
US or Us most often refers to:
* Us (pronoun), ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we''
* US, an abbreviation for the United States
US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to:
Arts and entertainme ...
created the L Prize competition. The Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), simply branded Philips, is a Dutch multinational health technology company that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, its world headquarters have been situated in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarter ...
Lighting North America LED bulb won the first competition on August 3, 2011, after successfully completing 18 months of intensive field, lab, and product testing.
Efficient lighting is needed for sustainable architecture
Sustainable architecture is architecture that seeks to minimize the negative environmental impact of buildings through improved efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, development space and the ecosystem at large. Sometimes, su ...
. As of 2011, some LED bulbs provide up to 150 lm/W and even inexpensive low-end models typically exceed 50 lm/W, so that a 6-watt LED could achieve the same results as a standard 40-watt incandescent bulb. The lower heat output of LEDs also reduces demand on air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C (US) or air con (UK), is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior temperature, and in some cases, also controlling the humidity of internal air. Air c ...
systems. Worldwide, LEDs are rapidly adopted to displace less effective sources such as incandescent lamps
An incandescent light bulb, also known as an incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe, is an electric light that produces illumination by Joule heating a filament until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb that is either ...
and CFLs and reduce electrical energy consumption and its associated emissions. Solar powered LEDs are used as street light
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, streetlamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution b ...
s and in architectural lighting.
The mechanical robustness and long lifetime are used in automotive lighting
Automotive lighting is functional exterior lighting in vehicles. A motor vehicle has lighting and signaling devices mounted to or integrated into its front, rear, sides, and, in some cases, top. Various devices have the dual function of illumin ...
on cars, motorcycles, and bicycle lights. LED street lights are employed on poles and in parking garages. In 2007, the Italian village of Torraca was the first place to convert its street lighting to LEDs.
Cabin lighting on recent Airbus
Airbus SE ( ; ; ; ) is a Pan-European aerospace corporation. The company's primary business is the design and manufacturing of commercial aircraft but it also has separate Airbus Defence and Space, defence and space and Airbus Helicopters, he ...
and Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
jetliners uses LED lighting. LEDs are also being used in airport and heliport lighting. LED airport fixtures currently include medium-intensity runway lights, runway centerline lights, taxiway centerline and edge lights, guidance signs, and obstruction lighting.
LEDs are also used as a light source for DLP projectors, and to backlight
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) that provides light from the back or side of a display panel. LCDs do not produce light on their own, so they require illumination—either from available light, ambie ...
newer LCD
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liquid crystals do not em ...
television (referred to as LED TV), computer monitor (including laptop
A laptop computer or notebook computer, also known as a laptop or notebook, is a small, portable personal computer (PC). Laptops typically have a Clamshell design, clamshell form factor (design), form factor with a flat-panel computer scree ...
) and handheld device LCDs, succeeding older CCFL-backlit LCDs although being superseded by OLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a type of light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is an organic compound film that emits light in respon ...
screens. RGB LEDs raise the color gamut by as much as 45%. Screens for TV and computer displays can be made thinner using LEDs for backlighting.
LEDs are small, durable and need little power, so they are used in handheld devices such as flashlight
A flashlight (US English) or electric torch (Commonwealth English), usually shortened to torch, is a portable hand-held electric lamp. Formerly, the light source typically was a miniature incandescent light bulb, but these have been displaced ...
s. LED strobe light
A strobe light or stroboscopic lamp, commonly called a strobe, is a device used to produce regular flashes of light. It is one of a number of devices that can be used as a stroboscope. The word originated from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning ...
s or camera flashes operate at a safe, low voltage, instead of the 250+ volts commonly found in xenon
Xenon is a chemical element; it has symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
flashlamp-based lighting. This is especially useful in cameras on mobile phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This rad ...
s, where space is at a premium and bulky voltage-raising circuitry is undesirable.
LEDs are used for infrared illumination in night vision
Night vision is the ability to see in low-light conditions, either naturally with scotopic vision or through a night-vision device. Night vision requires both sufficient spectral range and sufficient intensity range. Humans have poor night v ...
uses including security cameras. A ring of LEDs around a video camera
A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other ...
, aimed forward into a retroreflective background, allows chroma keying in video production
Video production is the process of producing video content. It is the equivalent of filmmaking, but with video recorded either as analog signals on videotape, digitally in video tape or as computer files stored on optical discs, hard drives, SSDs, ...
s.

 LEDs are used in
LEDs are used in mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
operations, as cap lamps to provide light for miners. Research has been done to improve LEDs for mining, to reduce glare and to increase illumination, reducing risk of injury to the miners.
LEDs are increasingly finding uses in medical and educational applications, for example as mood enhancement. NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
has even sponsored research for the use of LEDs to promote health for astronauts.
Data communication and other signalling
Light can be used to transmit data and analog signals. For example, lighting white LEDs can be used in systems assisting people to navigate in closed spaces while searching necessary rooms or objects. Assistive listening devices in many theaters and similar spaces use arrays of infrared LEDs to send sound to listeners' receivers. Light-emitting diodes (as well as semiconductor lasers) are used to send data over many types offiber optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
cable, from digital audio over TOSLINK cables to the very high bandwidth fiber links that form the Internet backbone. For some time, computers were commonly equipped with IrDA
IrDA is a wireless standard designed for exchanging data using infrared (IR). Infrared ports for this purpose have been implemented in portable electronic devices such as mobile telephones, laptops, cameras, printers, and medical devices. The mai ...
interfaces, which allowed them to send and receive data to nearby machines via infrared.
Because LEDs can cycle on and off millions of times per second, very high data bandwidth can be achieved. For that reason, visible light communication (VLC) has been proposed as an alternative to the increasingly competitive radio bandwidth. VLC operates in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, so data can be transmitted without occupying the frequencies of radio communications.
Machine vision systems
Machine vision
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide image, imaging-based automation, automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision ...
systems often require bright and homogeneous illumination, so features of interest are easier to process. LEDs are often used.
Barcode scanner
A barcode reader or barcode scanner is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes and send the data they contain to computer. Like a flatbed scanner, it consists of a light source, a lens, and a light sensor for translating optical impulses ...
s are the most common example of machine vision applications, and many of those scanners use red LEDs instead of lasers. Optical computer mice use LEDs as a light source for the miniature camera within the mouse.
LEDs are useful for machine vision because they provide a compact, reliable source of light. LED lamps can be turned on and off to suit the needs of the vision system, and the shape of the beam produced can be tailored to match the system's requirements.
Biological detection
The discovery of radiative recombination in aluminum gallium nitride (AlGaN) alloys by U.S. Army Research Laboratory (ARL) led to the conceptualization of UV light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to be incorporated in light-inducedfluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colore ...
sensors used for biological agent detection. In 2004, the Edgewood Chemical Biological Center (ECBC) initiated the effort to create a biological detector named TAC-BIO. The program capitalized on semiconductor UV optical sources (SUVOS) developed by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA).
UV-induced fluorescence is one of the most robust techniques used for rapid real-time detection of biological aerosols. The first UV sensors were lasers lacking in-field-use practicality. In order to address this, DARPA incorporated SUVOS technology to create a low-cost, small, lightweight, low-power device. The TAC-BIO detector's response time was one minute from when it sensed a biological agent. It was also demonstrated that the detector could be operated unattended indoors and outdoors for weeks at a time.
Aerosolized biological particles fluoresce and scatter light under a UV light beam. Observed fluorescence is dependent on the applied wavelength and the biochemical fluorophores within the biological agent. UV induced fluorescence offers a rapid, accurate, efficient and logistically practical way for biological agent detection. This is because the use of UV fluorescence is reagentless, or a process that does not require an added chemical to produce a reaction, with no consumables, or produces no chemical byproducts.
Additionally, TAC-BIO can reliably discriminate between threat and non-threat aerosols. It was claimed to be sensitive enough to detect low concentrations, but not so sensitive that it would cause false positives. The particle-counting algorithm used in the device converted raw data into information by counting the photon pulses per unit of time from the fluorescence and scattering detectors, and comparing the value to a set threshold.
The original TAC-BIO was introduced in 2010, while the second-generation TAC-BIO GEN II, was designed in 2015 to be more cost-efficient, as plastic parts were used. Its small, light-weight design allows it to be mounted to vehicles, robots, and unmanned aerial vehicles. The second-generation device could also be utilized as an environmental detector to monitor air quality in hospitals, airplanes, or even in households to detect fungus and mold.
Other applications
LED costume for stage performers LED wallpaper by Meystyle A large LED display behind a disc jockey Seven-segment display that can display four digits and points LED panel light source used in an early experiment on potato growth during Shuttle mission STS-73 to investigate the potential for growing food on future long duration missions The light from LEDs can be modulated very quickly so they are used extensively in optical fiber and free space optics communications. This includes remote controls, such as for television sets, where infrared LEDs are often used. Opto-isolators use an LED combined with aphotodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
or phototransistor
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
to provide a signal path with electrical isolation between two circuits. This is especially useful in medical equipment where the signals from a low-voltage sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
circuit (usually battery-powered) in contact with a living organism must be electrically isolated from any possible electrical failure in a recording or monitoring device operating at potentially dangerous voltages. An optoisolator also lets information be transferred between circuits that do not share a common ground potential.
Many sensor systems rely on light as the signal source. LEDs are often ideal as a light source due to the requirements of the sensors. The Nintendo Wii's sensor bar uses infrared LEDs. Pulse oximeter
Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method for monitoring blood oxygen saturation. Peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2) readings are typically within 2% accuracy (within 4% accuracy in 95% of cases) of the more accurate (and invasive) reading of art ...
s use them for measuring oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the g ...
. Some flatbed scanners use arrays of RGB LEDs rather than the typical cold-cathode fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
as the light source. Having independent control of three illuminated colors allows the scanner to calibrate itself for more accurate color balance, and there is no need for warm-up. Further, its sensors only need be monochromatic, since at any one time the page being scanned is only lit by one color of light.
Since LEDs can also be used as photodiodes, they can be used for both photo emission and detection. This could be used, for example, in a touchscreen
A touchscreen (or touch screen) is a type of electronic visual display, display that can detect touch input from a user. It consists of both an input device (a touch panel) and an output device (a visual display). The touch panel is typically l ...
that registers reflected light from a finger or stylus
A stylus is a writing utensil or tool for scribing or marking into softer materials. Different styluses were used to write in cuneiform by pressing into wet clay, and to scribe or carve into a wax tablet. Very hard styluses are also used to En ...
. Many materials and biological systems are sensitive to, or dependent on, light. Grow lights use LEDs to increase photosynthesis
Photosynthesis ( ) is a system of biological processes by which photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical energy necessary to fuel their metabo ...
in plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s, and bacteria and viruses can be removed from water and other substances using UV LEDs for sterilization. LEDs of certain wavelengths have also been used for light therapy treatment of neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the white part of the eyes and skin in a newborn baby due to high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms may include excess sleepiness or poor feeding. Complications may include seizures, cerebral ...
and acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
.
UV LEDs, with spectra range of 220 nm to 395 nm, have other applications, such as water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
/air
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
purification, surface disinfection, glue curing, free-space non-line-of-sight communication, high performance liquid chromatography, UV curing dye printing, phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD), circ ...
(295nm Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, 308nm Excimer lamp or laser replacement), medical/ analytical instrumentation, and DNA absorption.
LEDs have also been used as a medium-quality voltage reference in electronic circuits. The forward voltage drop (about 1.7 V for a red LED or 1.2V for an infrared) can be used instead of a Zener diode
A Zener diode is a type of diode designed to exploit the Zener effect to affect electric current to flow against the normal direction from anode to cathode, when the voltage across its terminals exceeds a certain characteristic threshold, the ''Z ...
in low-voltage regulators. Red LEDs have the flattest I/V curve above the knee. Nitride-based LEDs have a fairly steep I/V curve and are useless for this purpose. Although LED forward voltage is far more current-dependent than a Zener diode, Zener diodes with breakdown voltages below 3 V are not widely available.
The progressive miniaturization of low-voltage lighting technology, such as LEDs and OLEDs, suitable to incorporate into low-thickness materials has fostered experimentation in combining light sources and wall covering surfaces for interior walls in the form of LED wallpaper.
Research and development
Key challenges
LEDs require optimized efficiency to hinge on ongoing improvements such as phosphor materials andquantum dot
Quantum dots (QDs) or semiconductor nanocrystals are semiconductor particles a few nanometres in size with optical and electronic properties that differ from those of larger particles via quantum mechanical effects. They are a central topic i ...
s.
The process of down-conversion (the method by which materials convert more-energetic photons to different, less energetic colors) also needs improvement. For example, the red phosphors that are used today are thermally sensitive and need to be improved in that aspect so that they do not color shift and experience efficiency drop-off with temperature. Red phosphors could also benefit from a narrower spectral width to emit more lumens and becoming more efficient at converting photons.
In addition, work remains to be done in the realms of current efficiency droop, color shift, system reliability, light distribution, dimming, thermal management, and power supply performance.
Early suspicions were that the LED droop was caused by elevated temperatures. Scientists showed that temperature was not the root cause of efficiency droop. The mechanism causing efficiency droop was identified in 2007 as Auger recombination, which was taken with mixed reaction. A 2013 study conclusively identified Auger recombination as the cause.
Potential technology
A new family of LEDs are based on the semiconductors calledperovskites
A perovskite is a crystalline material of formula ABX3 with a crystal structure similar to that of Perovskite, the mineral perovskite, this latter consisting of calcium titanium oxide (CaTiO3). The mineral was first discovered in the Ural Moun ...
. In 2018, less than four years after their discovery, the ability of perovskite LEDs (PLEDs) to produce light from electrons already rivaled those of the best performing OLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a type of light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is an organic compound film that emits light in respon ...
s. They have a potential for cost-effectiveness as they can be processed from solution, a low-cost and low-tech method, which might allow perovskite-based devices that have large areas to be made with extremely low cost. Their efficiency is superior by eliminating non-radiative losses, in other words, elimination of recombination pathways that do not produce photons; or by solving outcoupling problem (prevalent for thin-film LEDs) or balancing charge carrier injection to increase the EQE (external quantum efficiency). The most up-to-date PLED devices have broken the performance barrier by shooting the EQE above 20%.
In 2018, Cao et al. and Lin et al. independently published two papers on developing perovskite LEDs with EQE greater than 20%, which made these two papers a mile-stone in PLED development. Their device have similar planar structure, i.e. the active layer (perovskite) is sandwiched between two electrodes. To achieve a high EQE, they not only reduced non-radiative recombination, but also utilized their own, subtly different methods to improve the EQE.
In the work of Cao ''et al.'', researchers targeted the outcoupling problem, which is that the optical physics of thin-film LEDs causes the majority of light generated by the semiconductor to be trapped in the device. To achieve this goal, they demonstrated that solution-processed perovskites can spontaneously form submicrometre-scale crystal platelets, which can efficiently extract light from the device. These perovskites are formed via the introduction of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
additives into the perovskite precursor solutions. In addition, their method is able to passivate perovskite surface defects and reduce nonradiative recombination. Therefore, by improving the light outcoupling and reducing nonradiative losses, Cao and his colleagues successfully achieved PLED with EQE up to 20.7%.
Lin and his colleague used a different approach to generate high EQE. Instead of modifying the microstructure of perovskite layer, they chose to adopt a new strategy for managing the compositional distribution in the device—an approach that simultaneously provides high luminescence
Luminescence is a spontaneous emission of radiation from an electronically or vibrationally excited species not in thermal equilibrium with its environment. A luminescent object emits ''cold light'' in contrast to incandescence, where an obje ...
and balanced charge injection. In other words, they still used flat emissive layer, but tried to optimize the balance of electrons and holes injected into the perovskite, so as to make the most efficient use of the charge carriers. Moreover, in the perovskite layer, the crystals are perfectly enclosed by MABr additive (where MA is CH3NH3). The MABr shell passivates the nonradiative defects that would otherwise be present perovskite crystals, resulting in reduction of the nonradiative recombination. Therefore, by balancing charge injection and decreasing nonradiative losses, Lin and his colleagues developed PLED with EQE up to 20.3%.
Health and safety
Certain blue LEDs and cool-white LEDs can exceed safe limits of the so-called blue-light hazard as defined in eye safety specifications such as "ANSI/IESNA RP-27.1–05: Recommended Practice for Photobiological Safety for Lamp and Lamp Systems". One study showed no evidence of a risk in normal use at domestic illuminance, and that caution is only needed for particular occupational situations or for specific populations. In 2006, theInternational Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC; ) is an international standards organization that prepares and publishes international standards for all electrical, electronics, electronic and related technologies. IEC standards cover a va ...
published ''IEC 62471 Photobiological safety of lamps and lamp systems'', replacing the application of early laser-oriented standards for classification of LED sources.
While LEDs have the advantage over fluorescent lamp
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor ...
s, in that they do not contain mercury, they may contain other hazardous metals such as lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
and arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
.
In 2016 the American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is an American professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. This medical association was founded in 1847 and is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was 271,660 ...
(AMA) issued a statement concerning the possible adverse influence of blueish street light
A street light, light pole, lamp pole, lamppost, streetlamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or path. Similar lights may be found on a railway platform. When urban electric power distribution b ...
ing on the sleep-wake cycle
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural oscillation that repeats roughly every 24 hours. Circadian rhythms can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to the environment (is entrai ...
of city-dwellers. Critics in the industry claim exposure levels are not high enough to have a noticeable effect.
Environmental issues
*Light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of any unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive artificial Visible spectrum, lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting sources, during the ...
: Because white LEDs emit more short wavelength light than sources such as high-pressure sodium vapor lamp
A sodium-vapor lamp is a gas-discharge lamp that uses sodium in an excited state to produce light at a characteristic wavelength near 589 nm.
Two varieties of such lamps exist: low pressure, and high pressure. Low-pressure sodium lamps ar ...
s, the increased blue and green sensitivity of scotopic vision
In the study of visual perception, scotopic vision (or scotopia) is the vision of the eye under low-light conditions. The term comes from the Greek ''skotos'', meaning 'darkness', and ''-opia'', meaning 'a condition of sight'. In the human eye, c ...
means that white LEDs used in outdoor lighting cause substantially more sky glow.
* Impact on wildlife: LEDs are much more attractive to insects than sodium-vapor lights, so much so that there has been speculative concern about the possibility of disruption to food web
A food web is the natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what-eats-what in an ecological community. Position in the food web, or trophic level, is used in ecology to broadly classify organisms as autotrophs or he ...
s. LED lighting near beaches, particularly intense blue and white colors, can disorient turtle hatchlings and make them wander inland instead. The use of "turtle-safe lighting" LEDs that emit only at narrow portions of the visible spectrum is encouraged by conservancy groups in order to reduce harm.
* Use in winter conditions: Since they do not give off much heat in comparison to incandescent lights, LED lights used for traffic control can have snow obscuring them, leading to accidents.
See also
* High-CRI LED lighting * Hiroshi Amano * Isamu Akasaki *List of light sources
This is a list of sources of light, the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light sources produce photons from another energy source, such as heat, chemical reactions, or conversion of mass or a different frequency of electromagnetic ener ...
* LED tattoo
* MicroLED
MicroLED, also known as micro-LED, mLED or μLED is an emerging flat-panel display technology consisting of arrays of microscopic Light-emitting diode, LEDs forming the individual pixel elements. Inorganic semiconductor microLED (μLED) technol ...
* Perovskite light-emitting diode
* Shuji Nakamura
* Superluminescent diode
* LED Strip Light
An LED strip, tape, or ribbon light is a flexible printed circuit board, circuit board populated by surface-mount technology, surface-mount light-emitting diodes (SMD LEDs) and other components that usually comes with an adhesive backing. LED lam ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
*Color cycling LED in a single two pin package
* {{Use mdy dates, date=March 2013 LED lamps Optical diodes Display technology Signage 20th-century inventions