|
High-CRI LED Lighting
High-CRI LED lighting is a light-emitting diode (LED) lighting source that offers a high color rendering index (CRI). CRI is a quantitative measure of a light's ability to reproduce the colors of objects faithfully in comparison with an ideal or natural light source. In general terms, CRI is a measure of a light source's ability to show object colors "realistically" or "naturally" compared to a familiar reference source, either incandescent light or sunlight. Efficiently achieving an acceptable CRI has been the most difficult metric for more modern light bulbs attempting to replace older incandescent bulbs. It is therefore frequently ignored in marketing (the CRI value only occasionally appears on product packaging). Light bulbs with a high CRI can be acceptable replacements for incandescent bulbs. Most LED lamps do not have a CRI above 90. For example, the top bulbs listed in the 2016 Consumer Review have a CRI of 80. In 2008, the U.S. Department of Energy created the L Prize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
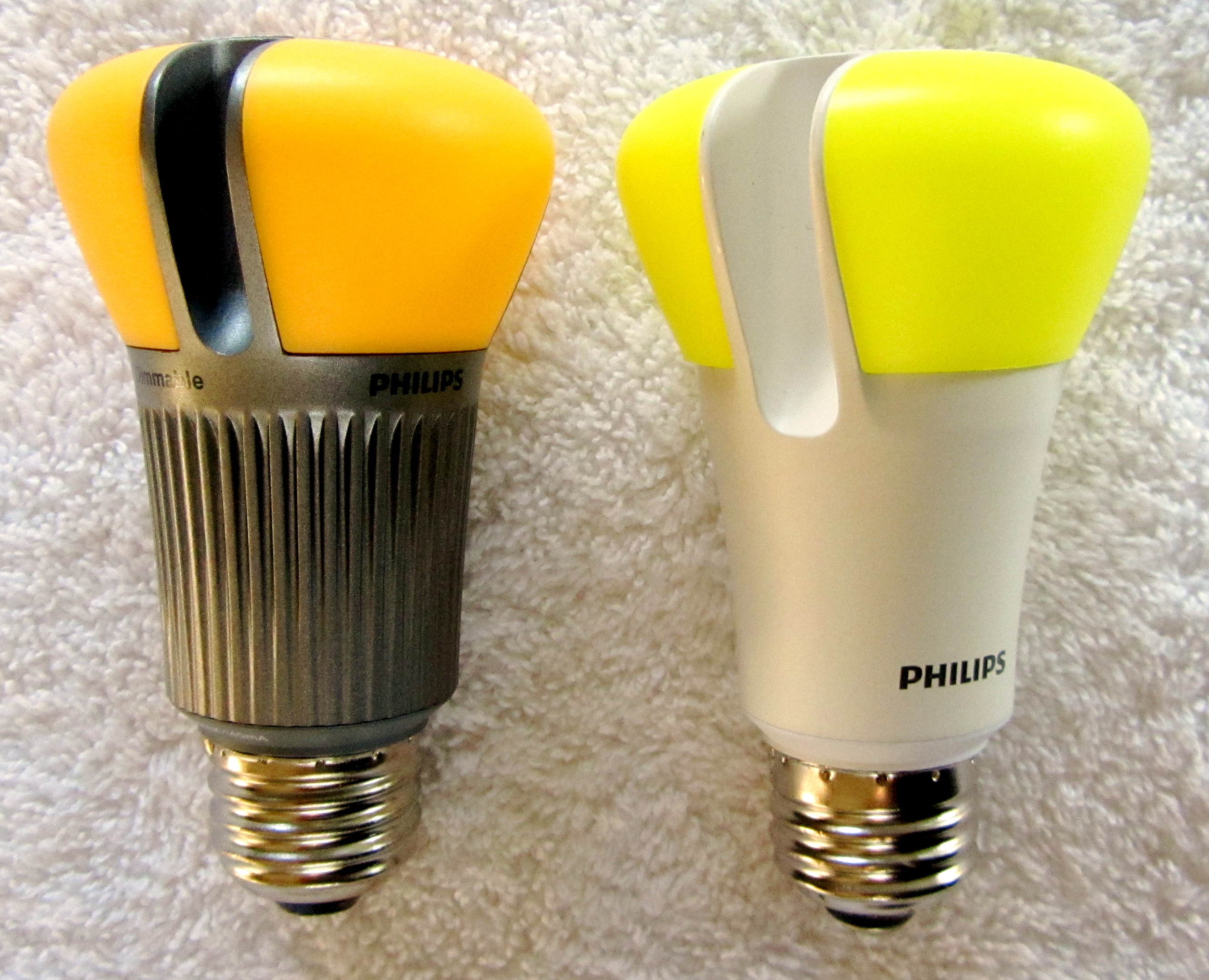
Philips LED Bulbs
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), simply branded Philips, is a Dutch multinational health technology company that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, its world headquarters have been situated in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is still in Eindhoven. The company gained its royal honorary title in 1998. Philips was founded by Gerard Philips and his father Frederik, with their first products being light bulbs. Through the 20th century, it grew into one of the world's largest electronics conglomerates, with global market dominance in products ranging from kitchen appliances and electric shavers to light bulbs, televisions, cassettes, and compact discs (both of which were invented by Philips). At one point, it played a dominant role in the entertainment industry (through PolyGram). However, intense competition from primarily East Asian competitors throughout the 1990s and 2000s led to a period of downsizing, including the divestment of its lighting and cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
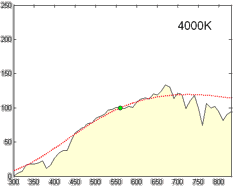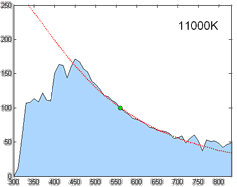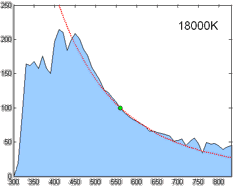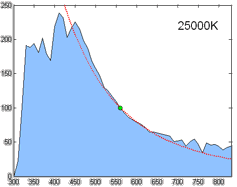
Correlated Color Temperature
Correlated color temperature (CCT, Tcp) refers to the "temperature of a Planckian radiator whose perceived color most closely resembles that of a given stimulus at the same brightness and under specified viewing conditions". The SI unit is the Kelvin (K). Motivation Black-body radiators are the reference by which the whiteness of light sources is judged. A black body is characterized by its temperature and emits light of a specific hue, which is referred to as color temperature. In practice, light sources that approximate Planckian radiators, such as certain fluorescent or high-intensity discharge lamps, are assessed based on their CCT, which is the temperature of a Planckian radiator whose color most closely resembles that of the light source. For light sources that do not follow the Planckian distribution, aligning them with a black body is not straightforward; thus, the concept of CCT is extended to represent these sources as accurately as possible on a one-dimensional col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. Daylighting (architecture), Daylighting (using windows, skylights, or Architectural light shelf, light shelves) is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings. Proper lighting can enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants. Indoor lighting is usually accomplished using light fixtures, and is a key part of interior design. Lighting can also be an intrinsic component of landscaping, landscape projects. History With the Control of fire by early humans, discovery of fire, the earliest form of artificial lighting used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Temperature
Color temperature is a parameter describing the color of a visible light source by comparing it to the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body. The temperature of the ideal emitter that matches the color most closely is defined as the color temperature of the original visible light source. The color temperature scale describes only the ''color'' of light emitted by a light source, which may actually be at a different (and often much lower) temperature. Color temperature has applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. In practice, color temperature is most meaningful for light sources that correspond somewhat closely to the color of some black body, i.e., light in a range going from red to orange to yellow to white to bluish white. Although the concept of correlated color temperature extends the definition to any visible light, the color temperature of a green or a purple light rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Motion Picture Arts And Sciences
The Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS, often pronounced ; also known as simply the Academy or the Motion Picture Academy) is a professional honorary organization in Beverly Hills, California, U.S., with the stated goal of advancing the arts and sciences of motion pictures. The Academy's corporate management and general policies are overseen by a board of governors, which includes representatives from each of the craft branches. As of April 2020, the organization was estimated to consist of around 9,921 motion picture professionals. The Academy is an international organization and membership is open to qualified filmmakers around the world. The Academy is known around the world for its annual Academy Awards, both officially and popularly known as "The Oscars". In addition, the Academy holds the Governors Awards annually for lifetime achievement in film; presents Academy Scientific and Technical Award, Scientific and Technical Awards annually; gives Student Aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Printer
An optical printer is a device consisting of one or more film projectors mechanically linked to a movie camera. It allows filmmakers to re-photograph one or more strips of film. The optical printer is used for making visual effects for motion pictures, or for copying and restoring film material. Common optical effects include fade outs and fade ins, dissolves, slow motion, fast motion, and matte work. More complicated work can involve dozens of elements, all combined into a single scene. History The first commercially available, although not mass produced, optical printer appeared in 1927 and was called the Depue & Vance Daylight Optical Printer. It was mainly used to reduce standard prints to 16mm and allowed for operation without a darkroom except for loading the positive film magazine. In 1918, the cinematographer Carl Gregory came upon a printer made by G. J. Badgley of New York, designed to produce copies of a standard film using domestic size film stock. Realizing the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlated Color Temperature
Correlated color temperature (CCT, Tcp) refers to the "temperature of a Planckian radiator whose perceived color most closely resembles that of a given stimulus at the same brightness and under specified viewing conditions". The SI unit is the Kelvin (K). Motivation Black-body radiators are the reference by which the whiteness of light sources is judged. A black body is characterized by its temperature and emits light of a specific hue, which is referred to as color temperature. In practice, light sources that approximate Planckian radiators, such as certain fluorescent or high-intensity discharge lamps, are assessed based on their CCT, which is the temperature of a Planckian radiator whose color most closely resembles that of the light source. For light sources that do not follow the Planckian distribution, aligning them with a black body is not straightforward; thus, the concept of CCT is extended to represent these sources as accurately as possible on a one-dimensional col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting. CIE illuminants The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name) is the body responsible for publishing all of the well-known standard illuminants. Each of these is known by a letter or by a letter-number combination. Illuminants A, B, and C were introduced in 1931, with the intention of respectively representing average incandescent light, direct sunlight, and average daylight. Illuminants D (1967) represent variations of daylight, illuminant E is the equal-energy illuminant, while illuminants F (2004) represent fluorescent lamps of various composition. There are instructions on how to experimentally produce light sources ("standard sources") corresponding to the older illuminants. For the relatively newer ones (such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminating Engineering Society
The Illuminating Engineering Society (IES), is an industry-backed, not-for-profit, learned society that was founded in New York City on January 10, 1906. The IES's stated mission is "to improve the lighted environment by bringing together those with lighting knowledge and by translating that knowledge into actions that benefit the public". Since 1906, when the IES was legally incorporated, the IES has always been known as the "IES". However, in 1981 the 6th edition IES Lighting Handbook published the phrase, "Illuminating Engineering Society of North America("IESNA"). The "IESNA" moniker persisted until it was removed in 2010 when the 10th Edition of Lighting Handbook was released. The IES is a global organization with sections worldwide and solely related to North America. The Society is headquartered in New York City. The IES is divided into approximately 100 local sections. Notably, the London-based Society of Light and Lighting (a part of the Chartered Institution of Bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Power Distribution
In radiometry, photometry (optics), photometry, and color science, a spectral power distribution (SPD) measurement describes the Power (physics), power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination (lighting), illumination (radiant exitance). More generally, the term ''spectral power distribution'' can refer to the concentration, as a function of wavelength, of any radiometric or photometric quantity (e.g. radiant energy, radiant flux, radiant intensity, radiance, irradiance, radiant exitance, Radiosity (heat transfer), radiosity, luminance, luminous flux, luminous intensity, illuminance, luminous emittance). Knowledge of the SPD is crucial for optical-sensor system applications. Optical properties such as transmittance, reflectivity, and absorbance as well as the sensor response are typically dependent on the incident wavelength. Physics Mathematically, for the spectral power distribution of a radiant exitance or irradiance one may write: : M(\lambda)=\frac\approx\fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphors
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, and cathodoluminescent substances which glow when struck by an electron beam (cathode rays) in a cathode-ray tube. When a phosphor is exposed to radiation, the orbital electrons in its molecules are excited to a higher energy level; when they return to their former level they emit the energy as light of a certain color. Phosphors can be classified into two categories: fluorescent substances which emit the energy immediately and stop glowing when the exciting radiation is turned off, and phosphorescent substances which emit the energy after a delay, so they keep glowing after the radiation is turned off, decaying in brightness over a period of milliseconds to days. Fluorescent materials are used in applications in which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |