inverse agonist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 Like
Like
Inverse Agonists: An Illustrated Tutorial
Panesar K, Guzman F. Pharmacology Corner. 2012 {{Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Receptor agonists
pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur betwee ...
, an inverse agonist is a drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
that binds to the same receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
as an agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist.
A neutral antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of Receptor (biochemistry), receptor ligand (biochemistry), ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor rather than activating it like ...
has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either; they are in fact sometimes called ''blockers'' (examples include alpha blockers, beta blocker
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms ( arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ...
s, and calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s). Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists.
A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level.
The efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy.
Examples
Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the GABAA, melanocortin, mu opioid,histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
and beta adrenergic receptors. Both endogenous
Endogeny, in biology, refers to the property of originating or developing from within an organism, tissue, or cell.
For example, ''endogenous substances'', and ''endogenous processes'' are those that originate within a living system (e.g. an ...
and exogenous inverse agonists have been identified, as have drugs at ligand gated ion channels and at G protein-coupled receptors.
Ligand gated ion channel inverse agonists
An example of a receptor site that possesses basal activity and for which inverse agonists have been identified is the GABAA receptors. Agonists for GABAA receptors (such as muscimol) create a relaxant effect, whereas inverse agonists have agitation effects (for example, Ro15-4513) or even convulsive and anxiogenic effects (certain beta-carbolines).G protein-coupled receptor inverse agonists
Two known endogenous inverse agonists are the Agouti-related peptide (AgRP) and its associated peptide Agouti signalling peptide (ASIP). AgRP and ASIP appear naturally in humans and bind melanocortin receptors 4 and 1 ( Mc4R and Mc1R), respectively, with nanomolar affinities. The opioid antagonists naloxone and naltrexone act as neutral antagonists of the mu opioid receptors under basal conditions, but as inverse agonists when an opioid such asmorphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
is bound to the same channel. 6α-naltrexo, 6β-naltrexol, 6β-naloxol, and 6β-naltrexamine acted neutral antagonists regardless of opioid binding and caused significantly reduced withdrawal jumping when compared to naloxone and naltrexone.
Nearly all antihistamines acting at H1 receptors and H2 receptors have been shown to be inverse agonists.
The beta blockers carvedilol and bucindolol have been shown to be low level inverse agonists at beta adrenoceptors.
Mechanisms of action
 Like
Like agonists
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agon ...
, inverse agonists have their own unique ways of inducing pharmacological and physiological responses depending on many factors, such as the type of inverse agonist, the type of receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
, mutants of receptors, binding affinities and whether the effects are exerted acutely or chronically based on receptor population density. Because of this, they exhibit a spectrum of activity below the Intrinsic activity level. Changes in constitutive activity of receptors affect response levels from ligands like inverse agonists.
To illustrate, mechanistic models have been made for how inverse agonists induce their responses on G protein-coupled receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related ...
s (GPCRs). Many types of Inverse agonists for GPCRs have been shown to exhibit the following conventionally accepted mechanism.
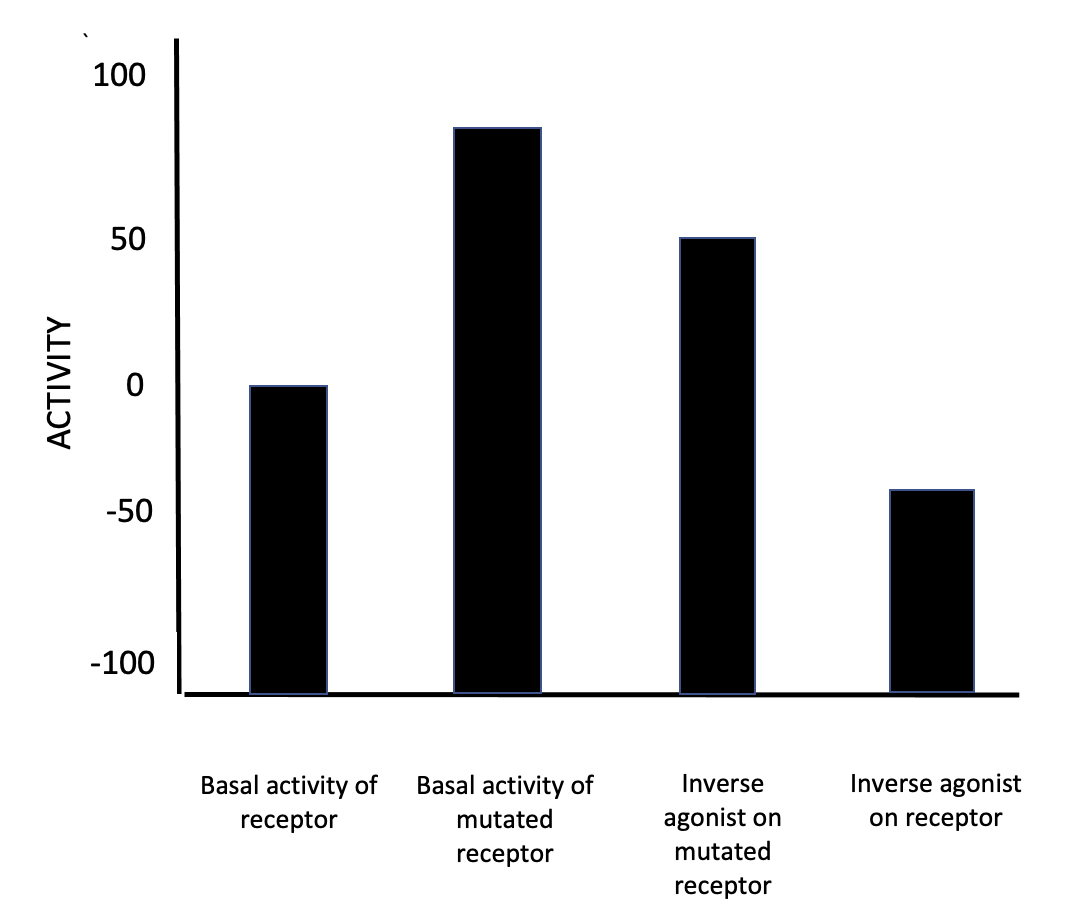
Based on the Extended Ternary complex model, the mechanism contends that inverse agonists switch the receptor from an active state to an inactive state by undergoing conformational changes. Under this model, current thinking is that the GPCRs can exist in a continuum of active and inactive states when no ligand is present. Inverse agonists stabilize the inactive states, thereby suppressing agonist-independent activity. However, the implementation of 'constitutively active mutants' of GPCRs change their intrinsic activity. Thus, the effect an inverse agonist has on a receptor depends on the basal activity of the receptor, assuming the inverse agonist has the same binding affinity (as shown in the figure 2).
See also
*Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
*Receptor antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of rec ...
* Autoreceptor
References
External links
*Inverse Agonists: An Illustrated Tutorial
Panesar K, Guzman F. Pharmacology Corner. 2012 {{Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Receptor agonists