Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (HPV-positive OPC or HPV+OPC), is a
cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
(
squamous cell carcinoma) of the throat caused by the
human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and res ...
type 16 virus (HPV16). In the past, cancer of the
oropharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
(throat) was associated with the use of alcohol or tobacco or both, but the majority of cases are now associated with the HPV
virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsk ...
, acquired by having oral contact with the
genital
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
s (
oral-genital sex) of a person who has a genital HPV infection. Risk factors include having a large number of sexual partners, a history of oral-genital sex or
anal–oral sex, having a female partner with a history of either an abnormal
Pap smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in t ...
or
cervical dysplasia, having chronic
periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cau ...
, and, among men, younger age at first intercourse and a history of
genital warts
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). They are generally pink in color and project out from the surface of the skin. Usually they cause few symptoms, but can occasionally be pai ...
. HPV-positive OPC is considered a separate disease
from HPV-negative
oropharyngeal cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer (OPC), also known as oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) and tonsil cancer, is a disease in which abnormal cells with the potential to both grow locally and spread to other parts of the body are found in the oral ca ...
(also called HPV negative-OPC and HPV-OPC).
HPV-positive OPC presents in one of four ways: as an asymptomatic abnormality in the mouth found by the patient or a health professional such as a dentist; with local symptoms such as pain or infection at the site of the tumor; with difficulties of speech, swallowing, and/or breathing; or as a swelling in the neck if the cancer has spread to local lymph nodes. Detection of a
tumour suppressor protein, known as
p16
p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S p ...
, is commonly used to diagnose an HPV associated OPC. The extent of disease is described in the standard cancer
staging system
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that ha ...
, using the
AJCC TNM system, based on the T stage (size and extent of tumor), N stage (extent of involvement of regional
lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
) and M stage (whether there is
spread of the disease outside the region or not), and combined into an overall stage from I–IV. In 2016, a separate staging system was developed for HPV+OPC, distinct from HPV-OPC.
Whereas most
head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms ...
s have been declining as smoking rates have declined, HPV-positive OPC has been increasing. Compared to HPV-OPC patients, HPV-positive patients tend to be younger, have a higher
socioeconomic status and are less likely to smoke. In addition, they tend to have smaller tumours, but are more likely to have involvement of the cervical lymph nodes. In the United States and other countries, the number of cases of oropharyngeal cancer has been increasing steadily, with the incidence of HPV-positive OPC increasing faster than the decline in HPV-negative OPC. The increase is seen particularly in young men in
developed countries, and HPV-positive OPC now accounts for the majority of all OPC cases. Efforts are being made to reduce the incidence of HPV-positive OPC by introducing
vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
that includes HPV types 16 and 18, found in 95% of these cancers, prior to exposure to the virus. Early data suggest a reduction in infection rates.
In the past, the treatment of OPC was radical surgery, with an approach through the neck and splitting of the
jaw bone
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serv ...
, which resulted in morbidity and poor survival rates. Later,
radiotherapy with or without the addition of
chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
, provided a less disfiguring alternative, but with comparable poor outcomes. Now, newer
minimally invasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass Surgery, surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by d ...
surgical techniques through the mouth have improved outcomes; in high risk cases, this surgery is often followed by radiation and/or chemotherapy. In the absence of
high quality evidence regarding which treatment provides the best outcomes, management decisions are often based on one or more of the following: technical factors, likely functional loss, and patient preference. The presence of HPV in the tumour is associated with a better response to treatment and a better outcome, independent of the treatment methods used, and a nearly 60% reduced risk of dying from the cancer. Most recurrence occurs locally and within the first year after treatment. The use of tobacco decreases the chances of survival.
Signs and symptoms
HPV+OPC presents in one of four ways: as an asymptomatic abnormality in the mouth found by the patient or a health professional such as a dentist; with local symptoms such as pain or infection at the site of the tumor; with difficulties of speech, swallowing, and/or breathing; or as a swelling in the neck (if the cancer has spread to lymph nodes). These may be accompanied by more general symptoms such as loss of appetite, weight loss, and weakness.
Cause

Most
mucosal squamous cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
head and neck cancers, including
oropharyngeal cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer (OPC), also known as oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) and tonsil cancer, is a disease in which abnormal cells with the potential to both grow locally and spread to other parts of the body are found in the oral ca ...
(OPC), have historically been attributed to tobacco and alcohol use. However this pattern has changed considerably since the 1980s. It was realised that some cancers occur in the absence of these risk factors and
an association between
human papilloma virus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and r ...
(HPV) and various squamous cell cancers, including OPC, was first described in 1983. Since then both
molecular and
epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
evidence has been accumulating, with the
International Agency for Research on Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC; french: Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer, CIRC) is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organization of the United Nations.
Its role is to conduct and ...
(IARC) stating that high-risk HPV types 16 and 18 are carcinogenic in humans, in 1995, and In 2007 that HPV was a cause for oral cancers.
Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and res ...
(HPV)-positive cancer (HPV+OPC)
incidence has been increasing while HPV-negative (HPV-OPC) cancer incidence is declining, a trend that is estimated to increase further in coming years. Since there are marked differences in
clinical presentation and
treatment relative to HPV status, HPV+OPC is now viewed as a distinct biologic and clinical condition.
Human HPV has long been implicated in the
pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
of several anogenital cancers including those of the
anus,
vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulv ...
,
vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
,
cervix, and
penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
. In 2007 it was also implicated by both
molecular and
epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidenc ...
evidence in cancers arising outside of the anogenital tract, namely oral cancers. HPV infection is common among healthy individuals, and is acquired through
oral sex
Oral sex, sometimes referred to as oral intercourse, is sexual activity involving the stimulation of the genitalia of a person by another person using the mouth (including the lips, tongue, or teeth) and the throat. Cunnilingus is oral sex p ...
. Although less data is available, prevalence of HPV infection is at least as common among men as among women, with 2004 estimates of about 27% among US women aged 14–59.
HPV oral infection precedes the development of HPV+OPC. Slight injuries in the
mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
serve as an entry gate for HPV, which thus works into the
basal layer of the
epithelium. People testing positive for HPV type 16 virus (HPV16) oral infection have a 14 times increased risk of developing HPV+OPC.
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
seems to be an increased risk factor for HPV+OPC. Individuals with
TGF-β1 genetic variations, specially T869C, are more likely to have HPV16+OPC. TGF-β1 plays an important role in controlling the immune system. In 1993 it was noted that patients with human papillomavirus (HPV)-associated anogenital cancers had a 4-fold increased risk of tonsillar squamous-cell carcinoma. Although evidence suggests that HPV16 is the main cause of OPC in humans not exposed to smoking and alcohol, the degree to which tobacco and/or alcohol use may contribute to increase the risk of HPV+OPC has not always been clear but it appears that both smoking and HPV infection are independent and additive risk factors for developing OPC. The connection between HPV-infection and oropharyngeal cancer is stronger in regions of lymphoepithelial tissue (base of tongue and palatine tonsils) than in regions of stratified squamous epithelium (soft palate and uvula).
Human herpesvirus-8 infection can potentiate the effects of HPV-16.
Risk factors
Risk factors
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
include a high number of sexual partners (25% increase >= 6 partners), a history of
oral-genital sex (125% >= 4 partners), or
anal–oral sex, a female partner with a history of either an abnormal
Pap smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in t ...
or
cervical dysplasia, chronic
periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cau ...
, and, among men, decreasing age at first intercourse and history of
genital warts
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). They are generally pink in color and project out from the surface of the skin. Usually they cause few symptoms, but can occasionally be pai ...
.
Pathology

Cancers of the oropharynx primarily arise in lingual and palatine tonsil
lymphoid
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
tissue that is lined by respiratory
squamous
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellula ...
mucosal epithelium, which may be
invaginated within the lymphoid tissue. Therefore, the tumour first arises in hidden crypts. OPC is graded on the basis of the degree of squamous and
keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
differentiation into well, moderate or poorly (high) differentiated grades. Other pathological features include the presence of finger-like invasion,
perineural invasion
In pathology, perineural invasion, abbreviated PNI, refers to the invasion of cancer to the space surrounding a nerve. It is common in head and neck cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer.
Unlike perineurial spread (PNS), which is defined ...
, depth of invasion and distance of the tumour from resection margins. Phenotypic variants include
basaloid squamous carcinoma, a high grade form (''see'' Chung Fig. 35-3(C) and illustration here). They are most commonly non-keratinising. HPV+OPC also differs from HPV-OPC in being focal rather than multifocal and not being associated with pre-malignant
dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs ( macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopi ...
. HPV+OPC patients are therefore at less risk of developing other malignancies in the head and neck region, unlike other head and neck primary tumours that may have associated second neoplasms, that may occur at the same time (synchronous) or a distant time (metachronous), both within the head and neck region or more distantly. This suggests that the oncogenic alterations produced by the virus are spatially limited rather than related to a field defect.
Anatomy
The
oropharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struc ...
, at the back of the
mouth, forms a circle and includes the
base of the tongue (posterior third) below, the
tonsils
The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play a ...
on each side, and the
soft palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. ...
above, together with the walls of the
pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
, including the anterior
epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food in ...
,
epiglottic valleculae and
branchial cleft
A pharyngeal groove (or branchial groove, or pharyngeal cleft) is made up of ectoderm unlike its counterpart the pharyngeal pouch on the endodermal side.
The first pharyngeal groove produces the external auditory meatus (ear canal). The rest (2, ...
at its base. The oropharynx is one of three divisions of the interior of the pharynx based on their relation to adjacent structures (nasal pharynx (
nasopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
), oral pharynx (oropharynx) and laryngeal pharynx (
laryngopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
- also referred to as the hypopharynx), from top to bottom). The pharynx is a semicircular fibromuscular tube joining the
nasal cavities
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal c ...
above to the
larynx (voice box) and
oesophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to th ...
(gullet), below, where the larynx is situated in front of the oesophagus.
The oropharynx lies between the mouth (oral cavity) to the front, and the laryngopharynx below, which separates it from the larynx. The upper limit of the oropharynx is marked by the soft palate, and its lower limit by the epiglottis and root of the tongue. The oropharynx communicates with the mouth, in front through what is known as the oropharyngeal isthmus, or
isthmus of the fauces. The
isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus ...
(i.e. connection) is formed above by the soft palate, below by the posterior third of the tongue, and at the sides by the
palatoglossal arches. The posterior third of the tongue, or tongue base contains numerous
follicles of
lymphatic tissue
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid o ...
that form the
lingual tonsils
The lingual tonsils are a collection of lymphatic tissue located in the lamina propria of the root of the tongue. This lymphatic tissue consists of the lymphatic nodules rich in cells of the immune system (immunocytes). The immunocytes initiate th ...
. Adjacent to the tongue base, the lingual surface of the epiglottis, which curves forward, is attached to the tongue by median and lateral
glossoepiglottic folds. The folds form small troughs known as the epiglottic valleculae. The lateral walls are marked by two vertical pillars on each side, the pillars of the fauces, or palatoglossal arches. More properly they are separately named the palatoglossal arch anteriorly and the
palatopharyngeal arch posteriorly. The anterior arch is named from the
palatoglossal muscle
The palatoglossus or palatoglossal muscle is a muscle of the soft palate and extrinsic muscle of the tongue. Its surface is covered by oral mucosa and forms the visible palatoglossal arch.
Structure
Palatoglossus arises from the palatine aponeu ...
within, running from the soft palate to the
tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
(
glossus), while the posterior arch similarly contains the
palatopharyngeal muscle running from the soft palate to the lateral pharynx. Between the arches lies a triangular space, the
tonsillar fossa in which lies the
palatine tonsil
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present a ...
, another lymphoid organ.
The external pharyngeal walls consisting of the four constrictor muscles form part of the mechanism of
swallowing. The microscopic anatomy is composed of four layers, being from the
lumen outwards, the
mucosa,
submucosa, muscles and the fibrosa, or fibrous layer. The mucosa consists of stratified squamous epithelium, that is generally non-keratinised, except when exposed to chronic irritants such as tobacco smoke. The submucosa contains aggregates of lymphoid tissue.
Patterns of spread
Cancers arising in the tonsillar fossa spread to the
cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammati ...
, primarily the subdigastric (upper jugular) lymph nodes (level II), with secondary involvement of the mid (level III) and low (level IV)
jugular nodes and sometimes the posterior cervical nodes (level V). Base of tongue cancers spread to the subdigastric and mid jugular nodes, and occasionally posterior cervical nodes but being closer to the midline are more likely to have bilateral nodal disease. Tonsillar cancers rarely spread to the contralateral side unless involving the midline.
Mechanism
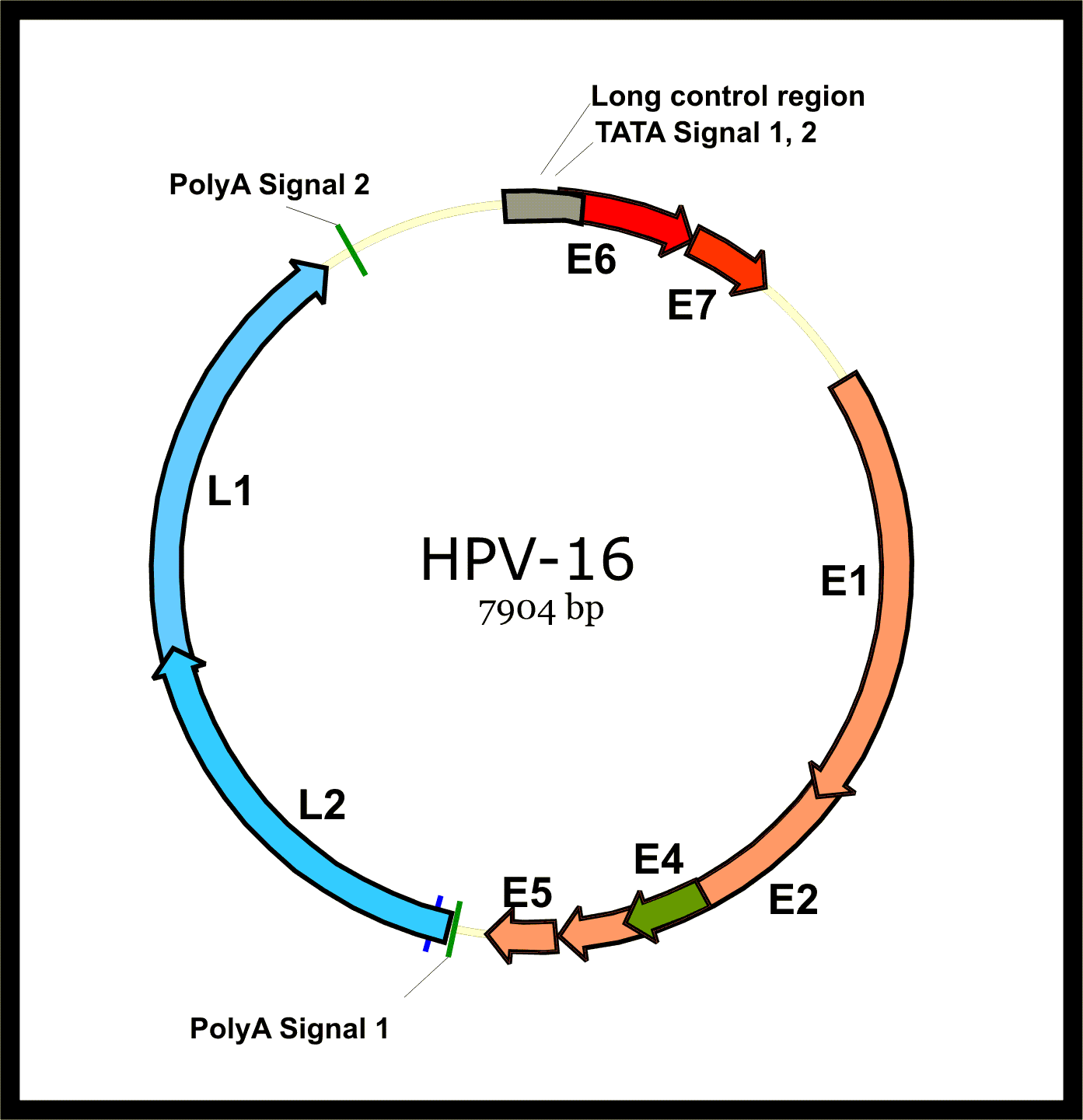
Virology
HPV associated cancers are caused by high-risk strains of HPV, mainly HPV-16 and HPV-18. HPV is a small
non-enveloped DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and ...
of the
papillomavirus
''Papillomaviridae'' is a family of non- enveloped DNA viruses whose members are known as papillomaviruses. Several hundred species of papillomaviruses, traditionally referred to as "types", have been identified infecting all carefully inspected ...
family. Its
genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
encodes the early (E)
oncoproteins
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels. E5, E6 and E7 and the late (L)
capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
proteins L1 and L2. The virus gains access to the mucosa through microlesions, where it infects the
basal layer of cells, which are still able to proliferate. While the virus does not replicate in these cells,
expression
Expression may refer to:
Linguistics
* Expression (linguistics), a word, phrase, or sentence
* Fixed expression, a form of words with a specific meaning
* Idiom, a type of fixed expression
* Metaphorical expression, a particular word, phrase, o ...
of its early genes stimulates proliferation and lateral expansion of the basal cells. As this moves the virus particles into the overlying suprabasal layers, late viral gene expression occurs, enabling replication of the circular viral genome (''see'' figure) and structural proteins. As these are pushed into the most superficial mucosal layers, complete viral particles are assembled and released.
Oncogenesis
An increased risk of HPV+OPC is observed more than 15 years after HPV exposure, pointing to a slow development of the disease, similar to that seen in cervical cancer. Relative to HPV-OPC, the
oncogenic molecular progression of HPV+OPC is poorly understood. The two main viral
oncoproteins
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels. of the high risk HPV types are E6 and E7. These are consistently expressed in malignant cell lines, and if their expression is inhibited the malignant
phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological pr ...
of the cancer cells is blocked. Either of these oncoproteins can
immortalise cell lines, but are more efficient when both are expressed, since their separate molecular roles are
synergistic. The E6 and E7
oncogenes
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels. become integrated into host-cell DNA, and the oncoproteins they express interfere with a variety of predominantly
antiproliferative cellular regulatory mechanisms. They bind to and inactivate the best known of these mechanisms, the
tumor suppressor proteins p53
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often s ...
and
retinoblastoma protein
The retinoblastoma protein (protein name abbreviated pRb; gene name abbreviated ''Rb'', ''RB'' or ''RB1'') is a proto-oncogenic tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in several major cancers. One function of pRb is to prevent excessive ...
pRB (pRb) leading to genomic instability and then
cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and sub ...
deregulation (''see'' Chung et al., 2016 Fig. 35.2). Further, yet to be elicited, mechanisms are required for the final steps of
malignant transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor.
Causes
There are ...
of HPV infected cells.
HPV- and HPV+OPC are distinguishable at the molecular level. The naturally occurring (
wild type
The wild type (WT) is the phenotype of the typical form of a species as it occurs in nature. Originally, the wild type was conceptualized as a product of the standard "normal" allele at a locus, in contrast to that produced by a non-standard, "m ...
) p53 is widely involved in
cellular processes
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and ...
, including
autophagy, response to DNA damage, cell cycle regulation and
senescence,
apoptosis and the generation of
adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms o ...
(ATP) through
oxidative phosphorylation. The gene encoding p53 is inactivated by E6 at the protein level and is found as the wild type in HPV+OPC but mutated in HPV-OPC. In HPV+OPC
p53
p53, also known as Tumor protein P53, cellular tumor antigen p53 (UniProt name), or transformation-related protein 53 (TRP53) is a regulatory protein that is often mutated in human cancers. The p53 proteins (originally thought to be, and often s ...
protein undergoes accelerated degradation by E6, drastically reducing its levels, while in HPV-OPC it undergoes
genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
, which may result in
synthesis of an abnormal p53 protein, that may not only be inactive as a tumour suppressor, but can also bind and inactivate any non-mutated wild type p53, with an increase in oncogenic activity. Although p53 mutations occur in HPV+OPC, they are far less common than in HPV-OPC (26% ''vs'' 48%), and do not appear to affect clinical outcome.
The pRb protein is inactivated by E7 in HPV+OPC, but in HPV-OPC it is the p16 tumour suppressor part of the pRb tumour suppressor network that is inactivated. Also the pRb pathway is inactivated by E7 instead of
Cyclin D1 amplification. ''
CDKN2A'' is a
tumour suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or red ...
that encodes a tumor suppressor protein,
p16
p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S p ...
(cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A) and inhibits the
kinase activity of the cyclin-dependent kinases
CDK4 and
CDK6
Cell division protein kinase 6 (CDK6) is an enzyme encoded by the ''CDK6'' gene. It is regulated by cyclins, more specifically by Cyclin D proteins and Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor proteins. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of th ...
, which in turn induce cell cycle arrest. p16 expression is cell cycle dependent and is expressed focally in only about 5–10% of normal squamous epithelium. Like most HPV+ cancers, HPV+OPC express p16 but the latter does not function as a tumour-suppressor, because the mechanism by which this is achieved, pRb, has been inactivated by E7. p16 is
upregulated (over-expressed) due to E7-related loss of pRB with reduced negative feedback, whereas it is downregulated in up to 90% of HPV-OPC. This diffuse over-expression in the tumour cells provides a diagnostic marker for HPV involvement. Although HPV E6 and E7 reduce tumour suppressor activity, they do so less than genetic and
epigenetic processes do in HPV-OPC.
The tonsillar epithelia (
palatine
A palatine or palatinus (in Latin; plural ''palatini''; cf. derivative spellings below) is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman times. and
lingual) share similar
nonkeratinization characteristics with the
cervix, where HPV infection plays the major role in cases of
cervical cancer. Also E6 and E7 may make HPV+OPC more
immunogenic
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted:
* Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injectio ...
than HPV-OPC, since anti-E6 and E7
antibodies may be detected in these patients. This in turn could restrict the malignant behaviour of HPV+OPC and the presence of antibodies has been associated with a better prognosis, while treatment may enhance the immunogenicity of the tumour, and hence improve response, although to what extent is not clear. Outcomes are also associated with improved
adaptive immunity
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
.
Diagnosis

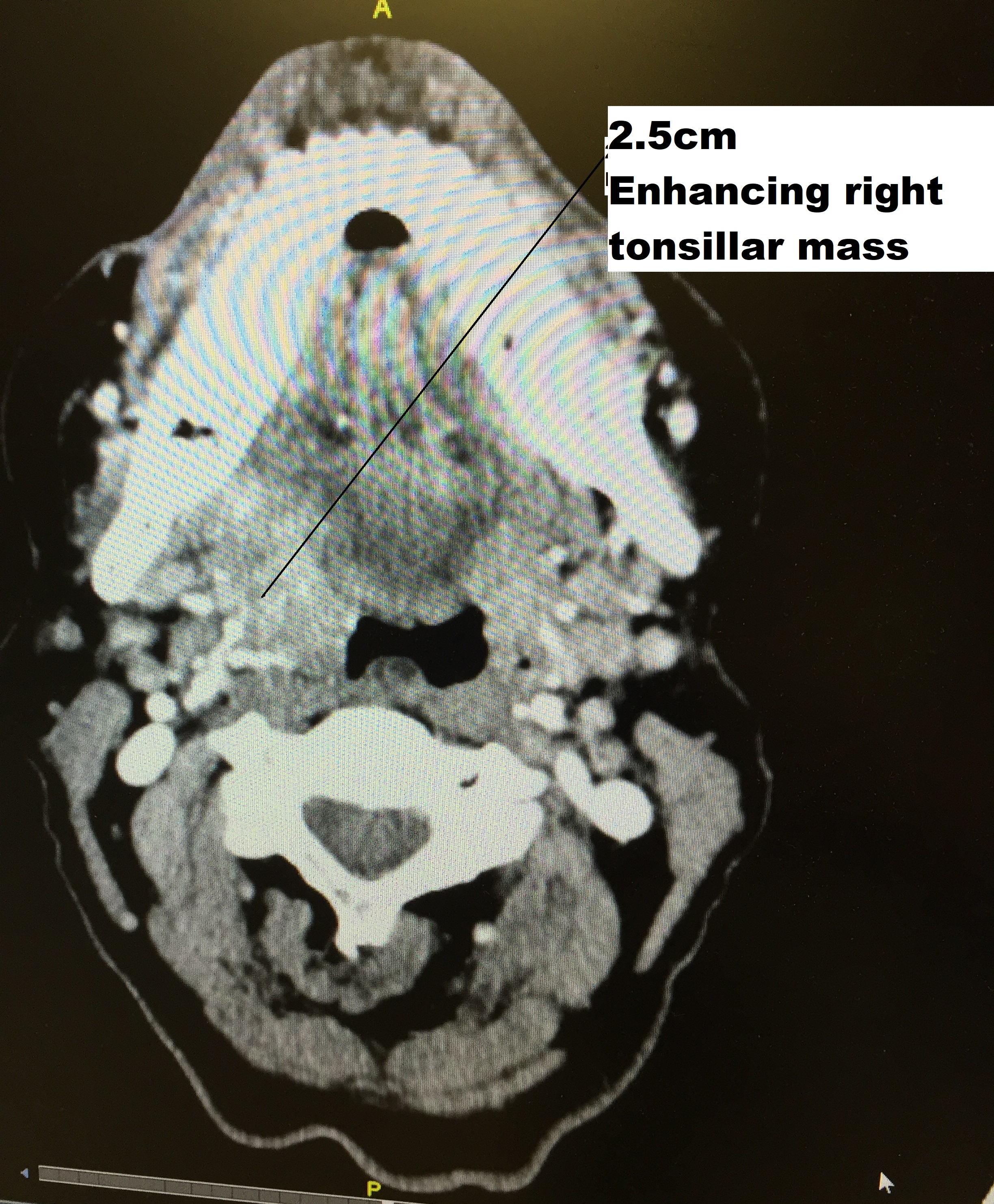
Biopsy
Initial diagnosis requires visualisation of the tumour either through the mouth or
endoscopically
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
through the nose using a
rhinoscope, illustrated to the right, followed by
biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
.
Differentiating HPV+OPC from HPV-OPC
HPV+OPC is usually diagnosed at a more advanced
stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
than HPV-OPC, with 75–90% having involvement of regional lymph nodes. Furthermore, HPV+OPC is more likely to be poorly differentiated with nonkeratinized or basaloid cells.
Genetic signatures of HPV+ and HPV- OPC are different. HPV+OPC is associated with expression level of the
E6/E7 mRNAs and of
p16
p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S p ...
. HPV16 E6/E7-positive cases are
histopathologically
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spec ...
characterized by their
verrucous or papillary (
nipple
The nipple is a raised region of tissue on the surface of the breast from which, in females, milk leaves the breast through the lactiferous ducts to feed an infant. The milk can flow through the nipple passively or it can be ejected by smooth m ...
like) structure and
koilocytosis of the adjacent mucosa. Approximately 15% of HNSCCs are caused by HPV16 infection and the subsequent constitutive expression of E6 and E7, and some HPV-initiated tumors may lose their original characteristics during
tumor progression
Tumor progression is the third and last phase in tumor development. This phase is characterised by increased growth speed and invasiveness of the tumor cells. As a result of the progression, phenotypical changes occur and the tumor becomes more agg ...
. High-risk HPV types may be associated with oral carcinoma, by
cell-cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subse ...
control dysregulation, contributing to oral
carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
and the overexpression of mdm2, p27 and cathepsin B.
HPV+OPC is not merely characterized by the presence of HPV-16: only the expression of viral oncogenes within the tumor cells plus the serum presence of E6 or E7 antibodies is unambiguously conclusive for HPV+OPC.
There is not a standard HPV testing method in head and neck cancers, both
in situ hybridization
''In situ'' hybridization (ISH) is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA or modified nucleic acids strand (i.e., probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (''in situ'') o ...
(ISH) and
polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) ...
(PCR) are commonly used. Both methods have comparable performance for HPV detection, however it is important to use appropriate
sensitivity controls.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
staining of the tissue for p16 is frequently used as a cost-effective surrogate for HPV in OPC, compared to ISH or PCR but there is a small incidence of HPV-negative p16-positive disease accounting for about 5% of HPV-OPC.
Staging
Staging
Staging may refer to:
Computing
* Staging (cloud computing), a process used to assemble, test, and review a new solution before it is moved into production and the existing solution is decommissioned
* Staging (data), intermediately storing data b ...
is generally by the
UICC/
AJCC TNM (Tumour, Nodes, Metastases) system. Staging is based on
clinical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patie ...
,
diagnostic imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues ( physiology). Medical imaging seeks to r ...
, and pathology. On imaging, involved lymph nodes may appear
cystic
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); ...
, a characteristic of HPV+OPC.
HPV+OPC has been treated similarly to stage-matched and site-matched HPV unrelated OPC, but its unique features, which contrast smoking-related HPV-OPC head and neck cancers, for which patients' demographics, comorbidities, risk factors, and carcinogenesis differ markedly, suggest that a distinct staging system be developed to more appropriately represent the severity of the disease and its prognosis. Standard AJCC TNM staging, such as the seventh edition (2009) while predictive for HPV-OPC has no prognostic value in HPV+OPC. The 8th edition of the
AJCC TNM Staging Manual (2016) incorporates this specific staging for HPV+OPC. As of 2018, treatment
guidelines
A guideline is a statement by which to determine a course of action. A guideline aims to streamline particular processes according to a set routine or sound practice. Guidelines may be issued by and used by any organization (governmental or pri ...
are evolving to account for the different outcomes observed in HPV+OPC. Consequently, less intensive (de-intensification) use of radiotherapy or chemotherapy, as well as specific therapy, is under investigation, enrolling HPV+OPC in
clinical trials to preserve disease control and minimise
morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
in selected groups based on modified TNM staging and smoking status.
HPV+ cancer of the oropharynx are staged as (AJCC 8th ed. 2016):
Tumour stage
* T0 no primary identified
* T1 2 cm or less in greatest dimension
* T2 2–4 cm
* T3 >4 cm, or extension to lingual surface of epiglottis
* T4 moderately advanced local disease, invading larynx, extrinsic muscle of tongue, medial pterygoid, hard palate, or mandible or beyond
Nodal stage
* Nx regional
lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
cannot be assessed
* N0 no regional lymph nodes involved
* N1 one or more ipsilateral nodes involved, less than 6 cm
* N2 contralateral or bilateral lymph nodes, less than 6 cm
* N3 lymph node(s) larger than 6 cm
Clinical stage
* Stage I: T0N1, T1–2N0–1
* Stage II: T0N2, T1–3N2, T3N0–2
* Stage III: T0–3N3, T4N0-3
* Stage IV: any
metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
(M1)
However, the published literature and ongoing clinical trials use the older seventh edition that does not distinguish between HPV+OPC and HPV-OPC - see
Oropharyngeal Cancer - Stages. The T stages are essentially similar between AJCC 7 and AJCC 8. with two exceptions. Tis (
carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma ''in situ'' (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells. While they are a form of neoplasm, there is disagreement over whether CIS should be classified as cancer. This controversy also depends on the exact CIS in question (i.e. cervical, skin, bre ...
) has been eliminated and the division of T4 into substages (e.g. T4a) has been removed. The major changes are in the N stages, and hence the overall clinical stage. N0 remains the same, but as with the T stage, substages such as N2a have been eliminated. Extracapsular extension (ECE), also referred to as extranodal extension (ENE), which is invasion by the tumour beyond the capsule of the lymph node has been eliminated as a staging criterion.
This results in a HPV+OPC tumour being given a lower stage than if it were HPV-OPC. For instance, a 5 cm tumour with one ipsilateral node involved that is 5 cm in size but has ECE would be considered T3N3bM0 Stage IVB if HPV- but T3N1M0 Stage II if HPV+.
Prevention

Avoiding exposure
Prevention of HPV+OPC involves avoiding or reducing exposure to risk factors where possible.
Vaccination
About 90% of HPV+OPC carry HPV 16, and another 5% type 18. These two types are both targets of available vaccines.
HPV vaccines given prior to exposure can prevent persistent genital infection and the consequent precancerous state. Therefore, they have a theoretical potential to prevent oral HPV infection. A 2010 review study has found that HPV16 oral infection was rare (1.3%) among the 3,977 healthy subjects analyzed.
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to optimise survival and locoregional disease control, and prevent spread to distant areas of the body (
metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
), while minimising short- and long-term
morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
. There is no high quality
Level I evidence from prospective clinical trials in HPV+OPC, therefore treatment guidelines must rely on data from treatment of OPC in general and from some retrospective unplanned
subsetting of those studies, together with data for head and neck cancer in general. Treatment for OPC has traditionally relied on
radiotherapy,
chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
and/or other systemic treatments, and surgical resection. Depending on stage and other factors treatment may include a combination of
modalities. The mainstay has been radiotherapy in most cases. a pooled analysis of published studies suggested comparable disease control between radiation and surgery, but higher complication rates for surgery +/- radiation. Ideally a single modality approach is preferred, since triple modality is associated with much more toxicity, and a multidisciplinary team in a large centre with high patient volumes is recommended.
Differences in response to treatment between HPV-OPC and HPV+OPC may include differences in the extent and manner in which cellular growth-regulatory pathways are altered in the two forms of OPC. For instance in HPV+OPC the HPV E6 and E7 oncogenes merely render the p53 and pRb pathways dormant, leaving open the possibility of reactivation of these pathways by
down-regulating (reducing) expression of the oncogenes. This is in contrast to the mutant form of p53 found in HPV-OPC that is associated with treatment resistance. Furthermore, it is suggested that the effects of E6 and E7 on these pathways renders the tumour more radiosensitive, possibly by interference with mechanisms such as
DNA repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
, repopulation signalling, and cell-cycle redistribution. The microenvironment is also important, with radiation increasing host
immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
to viral
antigens expressed on the tumour. Also, there is an association between an increase in
tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) are white blood cells that have left the bloodstream and migrated towards a tumor. They include T cells and B cells and are part of the larger category of ‘tumor-infiltrating immune cells’ which consist ...
and in circulating
white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
in HPV+OPC patients and better prognosis. This implies a role for an
adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
in suppressing
tumour progression.
Surgery
Historically, surgery provided the single approach to head and neck cancer. Surgical management of OPC carried significant morbidity with a transcervical (through the neck) approach, often involving mandibulotomy, in which the jawbone (
mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
) is split. This is referred to as an open surgical technique. Consequently, surgical approaches declined in favour of radiation. In the United States, the use of surgery declined from 41% of cases in 1998 to 30% by 2009, the year that the
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
approved the use of the newer techniques.
These improvements in surgical techniques have allowed many tumours to be
resected (removed) by transoral (through the mouth) surgical approaches (TOS), using transoral
endoscopic
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
head and neck surgery (HNS). Consequently, surgery became used more, increasing to 35% of cases by 2012. This approach has proven safety, efficacy and tolerability, and includes two main
minimally invasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass Surgery, surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by d ...
techniques,
transoral robotic surgery (TORS) and
transoral laser microsurgery (TLM). No direct comparisons of these two techniques have been conducted, and clinical trials in head and neck cancer such as ECOG 3311 allow either. They are associated with substantial postoperative morbidity, depending on extent of resection but compared to older techniques have shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, less pain, and less need for
gastrostomy or
tracheostomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision (cut) on the anterior aspect (front) of the neck and opening a direct airway through an incision in the trachea (windpipe). The r ...
, and less long-term effects, which are minimal in the absence of postoperative radiation (RT), or chemoradiation (CRT). TORS has the practical advantage that angled telescopes and rotating robotic surgical arms provide better line of sight. Outcomes of minimally invasive procedures also compare favourably with more invasive ones. In early stage disease, including involvement of neck nodes, TORS produces a 2-year survival of 80–90%. TLM similarly, is reported to have a five-year survival of 78% and local control rates of 85–97%. In addition to early disease, minimally invasive surgery has been used in advanced cases, with up to 90% local control and disease specific survival. Postoperative swallowing was excellent in 87%, but long-term dysphagia was associated with larger (T4) cancers, especially if involving the base of the tongue.
The details of the surgical approach depend on the location and size of the primary tumour and its N stage.
Neck dissection to examine the draining lymph nodes may be carried out simultaneously or as a second staging procedure. For tumours of the tonsil and lateral pharyngeal wall, and clinically node negative (N0) disease, dissection of the neck typically involves levels 2–4 (''see
diagram in Dubner 2017'')
ipsilaterally. Where nodes are involved clinically, dissection will depend on the location and size of the node or nodes. In the case of tongue base primaries, close to the
midline, bilateral dissection is recommended.
Pathological staging
An advantage of a primary surgical approach is the amount of
pathological
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in th ...
information made available, including grade,
margin status, and degree of involvement of lymph nodes. This may change the staging, as up to 40% of patients may have a different postoperative pathological stage compared to their preoperative clinical stage. In one study, 24% had their stage reduced (downstaged), which may impact subsequent decision making, including reduction in intensity and morbidity. In the United Kingdom, the
Royal College of Pathologists
The Royal College of Pathologists (RCPath) is a professional membership organisation.
Its main function is the overseeing of postgraduate training, and its Fellowship Examination (FRCPath) is recognised as the standard assessment of fitness to pr ...
(1998) has standardised the reporting of surgical margins, with two categories, "mucosal" and "deep", and for each created groups based on the microscopic distance from invasive cancer to the margin, as follows: more than 5 mm (clear), 1–5 mm (close) and less than 1 mm (involved).
Adjuvant postoperative therapy
Data on the use of postoperative
radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radi ...
(PORT) is largely confined to historical or retrospective studies rather than high quality
randomized clinical trials
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical t ...
and are based on the overall population of patients with head and neck cancer, rather than specific studies of HPV+OPC, which would have formed a very small proportion of the population studied. Despite surgical excision, in the more advanced cases local and regional recurrence of the cancer, together with spread outside of the head and neck region (
metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
) are frequent. The risk of subsequent recurrent disease has been considered highest in those tumours where the pathology shows tumour at the margins of the resection (positive margins), multiple involved regional lymph nodes and extension of the tumour outside of the capsule of the lymph node (extracapsular extension), based on historical experience with head and neck cancer. PORT was introduced in the 1950s in an attempt to reduce treatment failure from surgery alone. Although never tested in a controlled setting, PORT has been widely adopted for this purpose. In an analysis of surgical treatment failure at
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK or MSKCC) is a cancer treatment and research institution in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, founded in 1884 as the New York Cancer Hospital. MSKCC is one of 52 National Cancer Institute� ...
, patients treated with surgery alone between 1960 and 1970 had failure rates of 39 and 73% for those with negative and positive surgical margins respectively. These were compared to those who received PORT (with or without chemotherapy) from 1975 to 1980. The latter group had lower failure rates of 2% and 11% respectively. In addition, one randomised study from the 1970s (RTOG 73–03) compared preoperative radiation to PORT, and found lower failure rates with the latter.
The addition of another modality of treatment is referred to as
adjuvant (literally helping) therapy, compared to its use as the initial (primary) therapy, also referred to as radical therapy. Consequently, many of these patients have been treated with adjuvant radiation, with or without chemotherapy. In the above series of reports of minimally invasive surgery, many (30–80%) patients received adjuvant radiation. However, functional outcomes were worse if radiation was added to surgery and worst if both radiation and chemotherapy were used. Radiation dosage has largely followed that derived for all head and neck cancers, in this setting, based on risk. Historically only one randomised clinical trial has addressed optimal dosage, allocated patients to two dosage levels, stratified by risk, but showed no difference in cancer control between the low and high doses (63 and 68.4 Gy), but a higher incidence of complications at the higher doses. Consequently, the lower dose of 57.6
Gy was recommended. Because the authors used a fractionation scheme of 1.8 Gy per treatment, this dosage was not widely adopted, practitioners preferring a larger fraction of 2 Gy to produce a shorter treatment time, and a slightly higher dose of 60 Gy in 2 Gy fractions (30 daily treatments). Yet 57.6 Gy in 1.8 Gy fractions is equivalent (iso-effective dose) to only 56 Gy in 2 Gy fractions. 60 Gy corresponds to the 63 Gy used as the low dose in the high risk group. 60 Gy was also the dose used in RTOG 73–03. Subsequently, there was a tendency to intensify treatment in head and neck cancer, and a number of centres adopted a dose of 66 Gy, at least for those patients with adverse tumour features. The effectiveness of PORT in HPV+OPC receives some support from a
cohort study
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort (a group of people who share a defining characteristic, typically those who experienced a common event in a selected period, such as birth or graduation), performing ...
(Level 2b), although the number of patients was low, and the number of events (recurrent disease or death) only 7%. Another retrospective population-level study (Level 4) of the
SEER
In the United States, the efficiency of air conditioners is often rated by the seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) which is defined by the Air Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute, a trade association, in its 2008 standard AHR ...
database (1998–2011) concluded that there was an overall survival but not disease-specific survival effect of radiation in 410 patients with a single lymph node involved, but used only
univariate
In mathematics, a univariate object is an expression, equation, function or polynomial involving only one variable. Objects involving more than one variable are multivariate. In some cases the distinction between the univariate and multivariate ...
statistical analysis and contained no information on HPV status. A subsequent much larger study on a similar population in the National Cancer Database (2004–2013) of over 9,000 patients found a survival advantage but this was only in HPV-OPC, not in 410 HPV+OPC patients, and a subsequent study of 2,500 low and intermediate risk HPV+OPC patients showed similar overall survival whether PORT was given or not.
= Deintensification
=
While less studies have been completed examining deintensification (de-escalation) in this setting, than in primary radical radiation for this cancer (see below), it is an area of active investigation. In one single institution study, a decision was made to reduce the radiation dose in high risk patients with HPV+OPC from 66 to 60 Gy, corresponding to the actual evidence, and follow up has shown no decrease in cancer control. Current trials, both in North America and Europe (such as ECOG 3311 and PATHOS) use 50 Gy as the comparison arm. The comparator of 50 Gy was chosen on the grounds of (i) the exquisite sensitivity of HPV+OPC to radiation, both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo''; ECOG 1308 showing excellent disease control at 54 Gy; and data suggesting that 50 Gy in 1.43 Gy (iso-effective dose 43 Gy in 2.0 Gy) was sufficient to electively treat the neck. Other studies, such as MC1273 and DART-HPV have evaluated doses as low as 30–36 Gy. Lowering the radiation dose to 54 Gy was identified as one of the important Clinical Cancer Advances of 2018 by the
American Society of Clinical Oncology, under the general theme of "Less Is More: Preserving Quality of Life With Less
Treatment".
Chemotherapy has been used concurrently with radiation in this setting, as in primary treatment with radical radiation, particularly where pathological features indicated a higher risk of cancer recurrence. A number of studies have suggested that this does not improve local control, although adding toxicity.
Radiotherapy

Concerns over the morbidity associated with traditional open surgical en-bloc resection, led to exploring alternative approaches using radiation. Intensity modulated radiation therapy (
IMRT
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
) can provide good control of primary tumours while preserving excellent control rates, with reduced toxicity to salivary and pharyngeal structures relative to earlier technology. HPV+OPC has shown increased sensitivity to radiation with more rapid regression, compared to HPV-OPC. Generally, radiation can safely be delivered to the involved side alone (ipsilateral), due to the low rate of recurrent cancer on the opposite side (contralateral), and significantly less toxicity compared to bilateral treatment. IMRT has a two-year disease free survival between 82 and 90%, and a two-year disease specific survival up to 97% for stage I and II.
Reported
toxicities include dry mouth (
xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side eff ...
) from
salivary gland
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary ...
damage, 18% (grade 2); difficulty swallowing (
dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liq ...
) from damage to the constrictor muscles, larynx and oesophageal sphincter, 15% (grade 2);
subclinical aspiration up to 50% (reported incidence of aspiration pneumonia approximately 14%);
hypothyroidism 28–38% at three years (may be up to 55% depending on amount of the thyroid gland exposed to over 45
Gy radiation;
esophageal stenosis 5%;
osteonecrosis
Avascular necrosis (AVN), also called osteonecrosis or bone infarction, is death of bone tissue due to interruption of the blood supply. Early on, there may be no symptoms. Gradually joint pain may develop which may limit the ability to move. Co ...
of the
mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
2.5%; and need for a
gastrostomy tube to be placed at some point during or up to one year after treatment 4% (up to 16% with longer follow up). Concerns have been expressed regarding excessive short- and long-term toxicity, especially dysphagia and xerostomia, and hence whether standard doses expose patients with better prognoses are being exposed to overtreatment and unnecessary side effects.
Dosimetry
The probability of xerostomia at one year increases by 5% for every 1Gy increase in dose to the
parotid gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the ma ...
. Doses above 25–30 Gy are associated with moderate to severe xerostomia. Similar considerations apply to the
submandibular gland, but xerostomia is less common if only one parotid gland is included in the radiated field and the contralateral submandibular gland is spared (less than 39 Gy) In the same manner, radiation dose to the
pharyngeal constrictor muscles
The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity.
The pharyngeal muscles (involunta ...
,
larynx, and
cricopharyngeal inlet determine the risk of dysphagia (and hence dependence on
gastrostomy tube feeds). The threshold for this toxicity is volume-dependent at 55–60 Gy, with moderate to severe impairment of swallowing, including aspiration, stricture and feeding tube dependence above a mean dose of 47 Gy, with a recommended dose to the inferior constrictor of less than 41 Gy. Dose-toxicity relationships for the superior and middle constrictors are steep, with a 20% increase in the probability of dysphagia for each 10 Gy. For late dysphagia, threshold mean total constrictor doses, to limit rates of greater than or equal to grade 2 and 3 below 5% were 58 and 61 Gy respectively. For grade 2 dysphagia, the rate increased by 3.4% per Gy. Doses above 30 Gy to the thyroid are associated with moderate to severe hypothyroidism. Subjective, patient-reported outcomes of
quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
also correlate with radiation dose received.
Altered
fractionation
Fractionation is a separation process in which a certain quantity of a mixture (of gases, solids, liquids, enzymes, or isotopes, or a suspension) is divided during a phase transition, into a number of smaller quantities (fractions) in which the ...
schemes, such as RTOG 9003 and RTOG 0129 have not conferred additional benefit. Radiation dose recommendations were largely determined
empirically
In philosophy, empiricism is an epistemological theory that holds that knowledge or justification comes only or primarily from sensory experience. It is one of several views within epistemology, along with rationalism and skepticism. Empir ...
in clinical studies with few HPV+OPC patients, and have remained unchanged for half a century, making it difficult to determine the optimum dose for this subgroup. A common approach uses 70 Gy bilaterally and anteriorly, such as RTOG 9003 (1991–1997) and RTOG 0129 (2002–2005). For lateralized tonsil cancer unilateral neck radiation is usually prescribed, but for tongue base primaries bilateral neck radiation is more common, but unilateral radiation may be used where tongue base lesions are lateralised.
Deintensification
Concerns have been expressed regarding excessive short- and long-term toxicity, especially dysphagia and xerostomia, and hence whether standard doses expose patients with better prognoses to overtreatment and unnecessary side effects. Current toxicities have been described as "not tolerable", and hence an intense interest in de-escalation.
While comparison with historical controls has limited value compared to randomised clinical trials (
phase III),
phase II studies using reduced doses of radiation compared to the historical standard of 70 Gy have been carried out. A study using 54–60 Gy (a 15–20% reduction, stratified by response to initial induction chemotherapy) demonstrated comparable levels of disease control with much lower complication rates, when compared to similar studies, using 70 Gy, such as ECOG 2399. The percentage of patients alive after 2 years were 95% at the higher dose and 98% at the lower dose. Similarly for the percentage free of disease (86 and 92%). Toxicities were greatly reduced from an incidence of grade 3 or greater dysphagia and mucositis of 54 and 53% respectively, to 9%. A lower incidence and severity of dysphagia also means that less patients require gastrostomy feeding. A similar comparison can be made with the pooled data from two RTOG studies which utilized 70 Gy (0129 and 0522).
No new guidelines dealing specifically with HPV+OPC have yet been developed, outside of clinical trials. Indirect data suggests the efficacy of less intense treatment. A retrospective analysis of advanced (N+) HPV+OPC suggested 96% 5 year local control with de-intensified radiation of 54 Gy and concurrent
cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, breast cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, ...
based chemotherapy. The conclusions of the above pair of similar phase II trials have been supported by several other phase II trials. A prospective trial (
ECOG 1308) demonstrated similar locoregional control with 54 Gy, and another study, a high pathological complete response rate at 60 Gy. The Quarterback trial showed comparable outcomes between 56 and 70 Gy. and was followed by Quarterback 2, comparing 50 to 56 Gy. Similarly, the Optima trial showed good disease control with doses between 45 and 50 Gy. Ongoing studies, following the experience of the
Mayo Clinic trial (MC1273), such as that the
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK or MSKCC) is a cancer treatment and research institution in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, founded in 1884 as the New York Cancer Hospital. MSKCC is one of 52 National Cancer Institute– ...
are exploring doses as low as 30Gy. These studies all used well below the previous standard dose of 70 Gy. Since long-term toxicity is associated with radiation dose, determining the efficacy of lower and hence less morbid doses of radiation is a priority, since many HPV+ patients can be expected to have long-term survival.
Radiation is commonly utilised in combination with chemotherapy, but also may be used as a single modality, especially in earlier stages, e.g. T1-T2, N0-1, and its use in later stages is being explored in clinical trials such as RTOG 1333 which compares radiation alone to radiation with reduced chemotherapy, in non or light smokers.
Chemotherapy
As with the radiotherapy data, most of the available knowledge on the efficacy of chemotherapy derives from the treatment of advanced head and neck cancer rather than specific studies of HPV+OPC. Since 1976, many clinical studies have compared CRT to RT alone in the primary management of locally advanced head and neck cancers and have demonstrated an advantage to CRT in both survival and locoregional control. Cisplatin is considered the standard agent, and a survival advantage was seen for those patients who received radiation with concurrent cisplatin. Despite this no trials directly comparing cisplatin with other agents in this context have been conducted. The other agent that is widely used is
Cetuximab
Cetuximab, sold under the brand name Erbitux, is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor medication used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer. Cetuximab is a chimeric (mouse/human) monoclonal a ...
, a
monoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodies ...
directed at the
epidermal growth factor receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF family) of extracellular protein ligands.
The epidermal growth factor rece ...
(EGFR). A 10% survival advantage at three years was noted when cetuximab was given concurrently with radiation (bioradiation). Cetuximab trials were completed prior to knowledge of HPV status. Laboratory and clinical studies on the utility of cetuximab in this context are conflicting. The main toxicity is an
acneiform rash, but it had not been compared directly to cisplatin in HPV+OPC, until RTOG 1016 (''
see Talk'') addressed this question. Analysis of the results three years after the trial was completed demonstrate that cetuximab is inferior to cisplatin. Concurrent chemotherapy is also superior to chemotherapy alone (
induction chemotherapy) followed by radiation. Cetuximab shows no advantage when added to cisplatin in combination with radiation. Although chemoradiation became a treatment standard based on clinical trials and in particular,
meta-analyses
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting m ...
, a subsequent
population based study of patients with OPC, indicated no advantage to the addition of chemotherapy to radiation in either HPV+OPC or HPV-OPC, and significant concerns about added toxicity.
Chemotherapy also has a role, combined with radiation, in the postoperative setting (adjuvant therapy). Generally it is used where the
pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
of the resected specimen indicates features associated with high risk of locoregional recurrence (e.g. extracapsular extension through involved lymph nodes or very close margins). It has shown improved disease-free survival and locoregional control in two very similar clinical trials in such high risk patients,
EORTC 22931 (1994–2000) and RTOG 9501 (1995–2000). However, for HPV+OPC patients, such extracapsular spread does not appear to be an adverse factor and the addition of chemotherapy to radiation in this group provided no further advantage. Since the
sample size
Sample size determination is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a populatio ...
to detect a survival advantage is large, given the small number of events in this group, these studies may have been
underpowered and the question of the utility of adding chemotherapy is being addressed in a randomized clinical trial (ADEPT) with two year locoregional control and disease free survival as the endpoint. The addition of chemotherapy to radiation increases acute and late toxicity. In the GORTEC trial, chemotherapy with
docetaxel
Docetaxel (DTX or DXL), sold under the brand name Taxotere among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes breast cancer, head and neck cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer and non-small-cell ...
provided improved survival and locoregional control in locally advanced OPC, but was associated with increased mucositis and need for feeding by gastrostomy. Chemotherapy and radiation are associated with a risk of death of 3–4% in this context. It is unclear whether the added toxicity of adding chemotherapy to radiation is offset by significant clinical benefit in disease control and survival.
It is thought that HPV+OPC patients benefit better from radiotherapy and concurrent
cetuximab
Cetuximab, sold under the brand name Erbitux, is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor medication used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer. Cetuximab is a chimeric (mouse/human) monoclonal a ...
treatment than HPV-OPC patients receiving the same treatment, and that radiation and cisplatin induce an immune response against an
antigenic tumour which enhances their effect on the cancer cells. Although the incidence of HPV positivity is low (10–20%), an advantage for HPV+OPC was seen in trials of both cetuximab and
panitumumab, a similar anti-EGFR agent, but not a consistent interaction with treatment, although HPV+OPC appears not to benefit to the same extent as HPV-OPC to second line anti-EGFR therapy, possibly due to lower EGFR expression in HPV+OPC.
Choice of treatment approach
In the absence of high quality evidence comparing a primary surgical approach to other modalities, decisions are based on consideration of factors such as adequate surgical exposure and anatomically favourable features for adequate resection, post treatment function and
quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
. Such patient selection may enable them to avoid the morbidity of additional adjuvant treatment. In the absence of favourable surgical features the primary treatment of choice remains radiation with or without chemotherapy. Tumor characteristics which favour a non-surgical approach include invasion of the base of the tongue to the extent of requiring resection of 50% or more of the tongue, pterygoid muscle involvement, extension into the
parapharyngeal fat abutting the
carotid
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) (Entry "carotid"
in
maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. T ...
or invasion of the
prevertebral space.
The adequacy of surgical
resection is a major factor in determining the role of postoperative adjuvant therapy. In the presence of a
positive margin
A resection margin or surgical margin is the margin of apparently non-tumorous tissue around a tumor that has been surgically removed, called " resected", in surgical oncology. The resection is an attempt to remove a cancer tumor so that no portio ...
on pathological examination, most radiation oncologists recommend radiation to the primary site, and concurrent chemotherapy. A negative margin is more likely to be treated with lower doses and a smaller treatment volume. Also the removal of a bulky tumour may allow reduced dosage to adjacent uninvolved pharyngeal structures and hence less effect on normal
swallowing.
The cancer outcomes (local control, regional control, and survival) for transoral resection followed by adjuvant therapy are comparable to primary chemoradiation, so that treatment decisions depend more on treatment-related morbidity, functional outcome, and quality of life. Patient factors also need to be taken into account, including general baseline functionality, smoking history, anesthesia risk, oropharyngeal function, swallowing and airway protection and potential for rehabilitation. Patient preference is equally important. Many clinical trials are under way focussing on deintensification, often with risk
stratification
Stratification may refer to:
Mathematics
* Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols
* Data stratification in statistics
Earth sciences
* Stable and unstable stratification
* Stratification, or st ...
, e.g. Low, Intermediate and High risk (''see Fundakowski and Lango, Table I'').
Clinical decisions also take into account morbidities, particularly if cancer outcomes are comparable for instance surgery is associated with a risk of bleeding between 5–10%, and a 0.3% risk of fatal postoperative haemorrhage. Surgery may also be complicated by
dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liq ...
, and while most patients can tolerate a diet on the first postoperative day, long-term use of a feeding tube has been reported as high as 10%. Patients with larger tumours, involvement of base of tongue and requiring postoperative adjuvant therapy are more likely to require a long-term feeding tube. Overall, function and quality of life appear relatively similar between surgery with postoperative radiation, and primary chemoradiation, but HPV+OPC patients tend to have better quality of life at diagnosis than HPV-OPC but may sustain greater loss following treatment.
Anatomical considerations may also dictate preference for surgical or non-surgical approaches. For instance
trismus
Trismus, commonly called ''lockjaw'' as associated with tetanus, is a condition of limited jaw mobility. It may be caused by spasm of the muscles of mastication or a variety of other causes. Temporary trismus occurs much more frequently than perma ...
, a bulky tongue, limited extension of the neck, prominent teeth,
torus mandibularis
Torus mandibularis is a bony growth in the mandible along the surface nearest to the tongue. Mandibular tori are usually present near the premolars and above the location of the mylohyoid muscle's attachment to the mandible. In 90% of cases, ther ...
(a bony growth on the mandible) or limited width of the mandible would all be relative contraindications to surgery. Tumour related considerations include invasion of the mandible,
base of skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria.
Structure
Structures found at the base of the skull are for ...
and extensive involvement of the larynx or more than half of the base of tongue. Technical considerations in offering surgery as a primary modality include the presumed ability to achieve adequate margins in the resected specimen and the degree of resulting defect, since close or positive margins are likely to result in subsequent adjuvant therapy to achieve disease control, with resultant increased morbidity. Costs are difficult to estimate but one US study, based on estimates of 25% of all OPC patients receiving surgery alone and 75% surgery followed by adjuvant therapy, using the criteria of the
NCCN, found that this approach was less expensive than primary chemoradiation.
Early stage disease is associated with a relatively favourable outcome, for which single modality therapy is recommended, the choice depending on tumour location and accessibility. For instance unilateral tonsil or tongue base tumours will generally be treated with transoral resection and selective ipsilateral neck dissection. On the other hand, a large midline tongue lesion would require bilateral neck dissection, but in the absence of what are considered adverse pathology (positive margins, extracapsular extension) will likely be treated by surgery alone or radiation including ipsilateral or bilateral neck radiation fields, with surgery for those instances where the likelihood of adjuvant therapy is low.
But many HPV+OPC present with involvement of the lymph nodes in the neck, and hence a higher stage of disease, generally referred to as locally advanced disease. This group is mostly treated with multimodality therapy, with the exception of one of the more favourable subgroups with small primary tumours and lymph node involvement confined to a single node no larger than 3 cm in size, which as noted are considered early stage disease. The three main options for locally advanced but operable disease are resection, neck dissection and adjuvant therapy; chemoradiation (with possible
salvage surgery); induction chemotherapy followed by radiation or chemoradiation. However the last option has not been supported in clinical trials that tested it. The primary consideration of surgery for locally advanced disease is to obtain adequate negative margins and spare the patient postoperative chemoradiation. But this must be balanced against the morbidity and functional loss from extensive resection, particularly where the tongue base is involved. To avoid such morbidity, primary chemoradiation is preferred. The management of disease within the cervical lymph nodes has to be taken into account in treating locally advanced disease. Guidelines for all OPC dictate that ectracapsular extension be given postoperative chemoradiation. Where gross neck disease is evident initially primary chemoradiation is usually given.
Patient preferences
Current guidelines are based on data for OPC as a whole, so that patients are generally being treated regardless of HPV status, yet many clinicians and researchers are considering deintensification. It is likely that treatment of this condition will continue to evolve in the direction of deintensification, in order to minimize loss of function but maintain disease control. In the absence of specific clinical trials and guidelines, patient preferences need to be taken into consideration to minimise short- and long-term toxicity and functional loss and optimize quality of life, given the prolonged survival frequently seen. This may involve exploring patients' values regarding
trade-offs of disease control against adverse effects of treatment. Patients who have received CRT as primary treatment for OPC place a high value on survival, and although agreeing that deintensification is desirable, were reluctant to trade off much survival advantage for lower toxicity, though would be more likely to forgo chemotherapy than accept reduced radiation.
Carcinoma of unknown primary
In some situations HPV+OPC may present with cervical lymph nodes but no evident disease of a primary tumour (T0 N1-3) and is therefore classed as
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Unknown Primary Origin. The occurs in 2-4% of patients presenting with metastatic cancer in the cervical nodes. The incidence of HPV positivity is increasing at a similar rate to that seen in OPC. In such situations, resection of the lingual and palatine tonsils together with neck dissection may be diagnostic and constitute sufficient intervention, since recurrence rates are low.
Prognosis
The presence of HPV within the tumour has been realised to be an important factor for predicting survival since the 1990s.
Comparison with HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer
Tumor HPV status is strongly associated with positive therapeutic response and survival compared with HPV-negative cancer, independent of the treatment modality chosen and even after adjustment for stage. While HPV+OPC patients have a number of favourable
demographic features compared to HPV-OPC patients, such differences account for only about ten per cent of the survival difference seen between the two groups. Response rates of over 80% are reported in HPV+ cancer and three-year progression free survival has been reported as 75–82% and 45–57%, respectively, for HPV+ and HPV- cancer, and improving over increasing time. It is likely that HPV+OPC is inherently less malignant than HPV-OPC, since patients treated by surgery alone have a better survival after adjustment for stage.
Determinants of survival
In
RTOG
"The Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) was initially organized in 1968 under the direction of Dr. Simon Kramer as a national cooperative group for the purpose of conducting radiation therapy research and clinical investigations. Funding fro ...
clinical trial 0129, in which all patients with advanced disease received radiation and chemotherapy, a retrospective analysis (
recursive-partitioning analysis Recursive partitioning is a statistical method for multivariable analysis. Recursive partitioning creates a decision tree that strives to correctly classify members of the population by splitting it into sub-populations based on several dichotomous ...
, or RPA) at three years identified three risk groups for survival (low, intermediate, and high) based on HPV status, smoking, T stage and N stage (''see'' Ang et al., Fig. 2). HPV status was the major determinant of survival, followed by smoking history and stage. 64% were HPV+ and all were in the low and intermediate risk group, with all non-smoking HPV+ patients in the low risk group. 82% of the HPV+ patients were alive at three years compared to 57% of the HPV- patients, a 58% reduction in the risk of death. Locoregional failure is also lower in HPV+, being 14% compared to 35% for HPV-.
Determinants of disease progression
HPV positivity confers a 50–60% lower risk of disease progression and death, but the use of tobacco is an independently negative prognostic factor. A pooled analysis of HPV+OPC and HPV-OPC patients with disease progression in RTOG trials 0129 and 0522 showed that although less HPV+OPC experienced disease progression (23 v. 40%), the
median time to disease progression following treatment was similar (8 months). The majority (65%) of recurrences in both groups occurred within the first year after treatment and were locoregional. Although the rate of failure in the opposite neck following treatment of only one side, is 2.4%, the rate of an isolated recurrence in the opposite neck is 1.7%, and these were mainly where the primary tumour involved the midline. However the rate of failure in the contralateral neck is also greater for HPV+. Of those that recur in this site, nearly all were successfully treated (salvaged) by further local treatment to the opposite neck.
Determinants of metastasis rates
HPV+ did not reduce the rate of metastases (about 45% of patients experiencing progression), which are predominantly to the lungs (70%), although some studies have reported a lower rate. with 3-year distant recurrence rates of about 10% for patients treated with primary radiation or chemoradiation. Even if recurrence or metastases occur, HPV positivity still confers an advantage.
By contrast tobacco usage is an independently negative prognostic factor, with decreased response to therapy, increased disease recurrence rates and decreased survival. The negative effects of smoking, increases with amount smoked, particularly
if greater than 10
pack-years
A pack-year is a clinical quantification of cigarette smoking used to measure a person's exposure to tobacco. This is used to assess their risk of developing lung cancer or other pathologies related to tobacco use. However, it is difficult to re ...
.
Predictors of survival
After chemoradiation
For patients such as those treated on RTOG 0129 with primary chemoradiation, detailed
nomograms
A nomogram (from Greek , "law" and , "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart, or abac, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function ...
have been derived from that
dataset A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
combined with RTOG 0522, enabling prediction of outcome based on a large number of
variables. For instance, a 71 year old married non-smoking high school graduate with a
performance status
In medicine (oncology and other fields), performance status is an attempt to quantify cancer patients' general well-being and activities of daily life. This measure is used to determine whether they can receive chemotherapy, whether dose adjustment ...
(PS) of 0, and no weight loss or
anaemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
and a T3N1 HPV+OPC would expect to have a
progression-free survival Progression-free survival (PFS) is "the length of time during and after the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, that a patient lives with the disease but it does not get worse". In oncology, PFS usually refers to situations in which a tumor is p ...
of 92% at 2 years and 88% at 5 years. A 60 year old unmarried nonsmoking high school graduate with a PS of 1, weight loss and anaemia and a T4N2 HPV+OPC would expect to have a survival of 70% at two years and 48% at five years.
After surgery
Less detailed information is available for those treated primarily with surgery, for whom less patients are available, as well as low rates of recurrence (7–10%), but features that have traditionally been useful in predicting prognosis in other head and neck cancers, appear to be less useful in HPV+OPC. These patients are frequently stratified into three risk groups:
* Low risk: No adverse pathological features
* Intermediate risk: T3–T4 primary, perineural or lymphovascular invasion, N2 (AJCC 7)
* High risk: Positive margins, ECE
Development of other cancers
HPV+OPC patients are less likely to develop other cancers, compared to other head and neck cancer patients. A possible explanation for the favourable impact of HPV+ is "the lower probability of occurrence of 11q13 gene amplification, which is considered to be a factor underlying faster and more frequent recurrence of the disease" Presence of TP53 mutations, a marker for HPV- OPC, is associated with worse prognosis. High grade of p16 staining is thought to be better than HPV PCR analysis in predicting radiotherapy response.
Regional recurrence after surgery
The risk of regional cancer recurrence after neck dissection is often estimated from a large series based on all upper aerodigestive squamous cell cancers. In this series, the overall risks at three years by pathological stage (AJCC 7) were:
*pN0 4.7%
*pN1 4.9%
*pN2 12.1%
Epidemiology
In 2015, squamous cell cancer of the head and neck region was the fifth most common cancer other than skin cancer, globally, with an annual incidence of 600,000 cases and about 60,000 cases annually in the United States and Europe. The global
incidence of pharyngeal cancer in 2013 was estimated at 136,000 cases. For 2008 the
Global Burden of Disease for OPC in 2008 is estimated at 85,000 cases, of which 22,000 were attributable to HPV, a
population attributable fraction In epidemiology, attributable risk or excess risk is a term synonymous to risk difference, that has also been used to denote attributable fraction among the exposed and attributable fraction for the population.
See also
* Population Impact Measur ...
(PAF) of 26%. Of these, 17,000 were males and 4,400 females, 13,000 (60%) were aged between 50 and 69 years of age, and the majority of cases (15,000) were in
developed regions compared to
developing regions
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
(6,400).
Age Standardised Incidence Rates (ASR) differ considerably by region and country (''see'' de Martel et al., 2017 Fig. 2b). ASRs for 2012 were highest in Europe (Hungary 3.0) and North America (United States 1.7) but much lower in Africa (≤ 0.3), Asia (≤ 0.6), Latin America (≤ 0.4) and
Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
(≤ 0.2) (other than
Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologi ...
, Australia 0.9). Estimated average numbers of cases and ASR for the US in the period 2008–2012 were 15,738 and 4.5 respectively. HPV+OPC was much more common in males than females (12,638, 7.6 and 3,100, 1.7). The highest incidence age group was 60–69, and was higher in
Caucasians than in other races.
HPV+OPC patients tend to be younger than HPV- patients in general. The clinical presentation is also changing from the "typical" head and neck cancer patient with advanced age and major
substance usage. By contrast patients with HPV+ cancer are younger (4th–6th decades), male (ratio 8:1) with no or only a minimum history of smoking, generally Caucasian, reached higher education levels, are married, and have higher income. The risk factors for HPV-OPC and HPV+OPC tend to be independent, with the exception of smoking which has an adverse effect on both. The presenting features are also different between HPV+ and HPV- OPC. HPV+ tumours have smaller primary lesions (less than 4 cm) but more advanced nodal disease resulting in higher TNM staging. This in turn may overestimate the severity of the disease status.
Trends
There has been a global trend in increasing OPC incidence, particularly in North America and northern Europe, but even in Taiwan, which has a very high rate for all cancers of the head and neck region, OPC rates increased more rapidly between 1995 and 2009 than any other cancer site. The Global Burden of HPV+OPC increased from 22,000 in 2008 to 29,000 by 2012, and the PAF from 26% to 31%, and is considered an
epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
. In the United States the estimated number of cases was 12,410 in 2008, 13,930 in 2013 and 17,000 for 2017. Of these cases, HPV+ cancer has been increasing compared to HPV- cancer, but the increase in HPV+OPC exceeds the decline in HPV-OPC resulting an overall increase in OPC. The rise in pharyngeal cancer incidence contrasts with a marginal decline in other head and neck cancers. As a result, the commonest head and neck cancer has shifted from
larynx to oropharynx. A survey of 23 countries between 1983 and 2002 showed an increase in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma that was particularly noticeable in young men in economically
developed countries. In the United Kingdom the incidence of oral and oropharyngeal cancer in men rose 51%, from 7/100,000 to 11/100,000 between 1989 and 2006. In the US there is a growing incidence of HPV associated oropharyngeal cancers, In the early 1980s HPV+ accounted for only 7.5% of cases in the US but by 2016 this was 70%, perhaps as a result of changing sexual behaviors, decreased popularity of tonsillectomies, improved radiologic and pathologic evaluation, and changes in classification. Tonsil and oropharyngeal cancers increased in male predominance between 1975 and 2004, despite reductions in smoking. HPV-OPC decreased with decreasing smoking rates from 1988 to 2004, while HPV+OPC increased by almost 7.5% per year from about 16% of all cases of OPC in the early 1980s to almost 70% in 2004. The decline in smoking may be linked to the decreasing proportion of HPV negative cancers, while changes in sexual activity may be reflected in increasing proportion of HPV positive cancers. Recently, in the US, HPV associated OPC represent about 60% of OPC cases compared with 40% in the previous decade. By 2007, in the US, incidence of general OPC, including non-HPV associated, is 3.2 cases per 100,000 males/year and 1.9 per 100,000 all-sexes/year. This makes HPV+OPC one of only five cancers that have increased in incidence in the US since 1975. The largest increase in incidence has occurred in patients under age 50.
The increase in incidence of HPV associated OPC is also seen in other countries, like
Sweden, with a 2007 incidence of over 80% for cancer in the tonsils,
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
and the
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
. Partners of patients with HPV positive oropharyngeal cancer do not seem to have elevated oral HPV infection compared with the general population. In Australia the incidence of HPV associated OPC was 1.56 cases per 100,000 males/year (2001–2005), rising from 19% (1987–90), to 47% (2001–05) and 63.5% (2006–2010). In Canada the percentage of cases of OPC attributable to HPV increased from 47% in 2000 to 74% in 2012.
See also
*
HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer awareness and prevention
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
Articles
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and molecular biology
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Diagnosis and staging
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Treatment
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
=Surgery
=
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
=Radiation
=
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
=Chemotherapy and chemoradiation
=
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
=Deintensification
=
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Prognosis
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Epidemiology
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Books and conference proceedings
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* , see also
Gray's Anatomy
Chapters, monographs, reports and theses
* , in
* , in
* , in
*
* , in
*
* , in
* . ''excerpt'
here* , in (''additional extract'
here
*
*
*
Websites
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Treatment guidelines
*
* , in
* , in
*
*
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hpv-Positive Oropharyngeal Cancer
Head and neck cancer
Sexually transmitted diseases and infections
Papillomavirus-associated diseases
Otorhinolaryngology
 Most mucosal
Most mucosal 



 Concerns over the morbidity associated with traditional open surgical en-bloc resection, led to exploring alternative approaches using radiation. Intensity modulated radiation therapy (
Concerns over the morbidity associated with traditional open surgical en-bloc resection, led to exploring alternative approaches using radiation. Intensity modulated radiation therapy (