facet joint on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
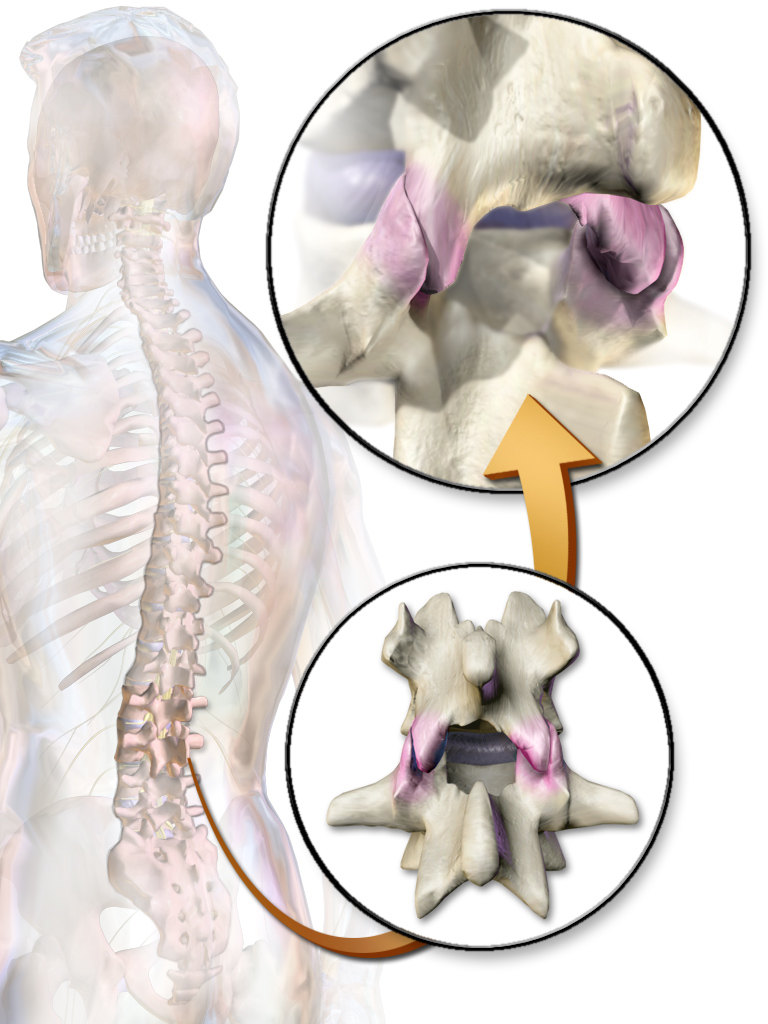 The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial,
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial,

Diagram at spineuniverse.com
Emedicine article on Lumbosacral Facet Syndrome
{{Authority control Bones of the vertebral column Joints Joints of the head and neck
 The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial,
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial, plane joint
A plane joint (arthrodial joint, gliding joint, plane articulation) is a synovial joint
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bone ...
s between the articular processes
The articular process or zygapophysis ( + apophysis) of a vertebra is a projection of the vertebra that serves the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. ...
of two adjacent vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
e. There are two facet joints in each spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the recurrent meningeal nerves.
Innervation
Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # The facet joint between C2 and C3 is innervated by the third occipital nerve and the C3 medial branch nerve. # The facet joint between C7 and T1 is innervated by the C7 and C8 medial branch nerves. In the thoracic and lumbar spine, the facet joints are innervated by the medial branch nerves from the vertebral segment above the upper segment and the upper segment. For example, the facet joint between T1 and T2 is innervated by C8 and T1 medial branch nerves. Facet joint between L1 and L2; the T12 and L1 medial branch nerves. However, the L5 and S1 facet joint is innervated by the L4 medial branch nerve and the L5 dorsal ramus. In this case, there is no L5 medial branch to innervate the facet joint.Function
The biomechanical function of each pair of facet joints is to guide and limit movement of the spinal motion segment. In thelumbar spine
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
, for example, the facet joints function to protect the motion segment from anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
shear forces, excessive rotation and flexion. Facet joints appear to have little influence on the range of side bending (lateral flexion). These functions can be disrupted by degeneration, dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
, fracture, injury, instability
In dynamical systems instability means that some of the outputs or internal states increase with time, without bounds. Not all systems that are not stable are unstable; systems can also be marginally stable or exhibit limit cycle behavior.
...
from trauma, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
, and surgery. In the thoracic spine the facet joints function to restrain the amount of flexion and anterior translation of the corresponding vertebral segment and function to facilitate rotation. Cavitation of the synovial fluid
Synovial fluid, also called synovia, elp 1/sup> is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articul ...
within the facet joints is responsible for the popping sound ( crepitus) associated with manual spinal manipulation, commonly referred to as "cracking the back."
The facet joints, both superior and inferior, are aligned in a way to allow flexion and extension, and to limit rotation. This is especially true in the lumbar spine.
Facet joint arthritis
In large part due to the mechanical nature of their function, all joints undergo degenerative changes with the wear and tear of age. This is particularly true for joints in the spine, and the facet joint in particular. This is commonly known as '' facet joint arthritis'' or ''facet arthropathy''. As with anyarthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
, the joint can become enlarged due to the degenerative process. Even small changes to the facet joint can narrow the intervertebral foramen
The intervertebral foramen (also neural foramen) (often abbreviated as IV foramen or IVF) is an opening between (the intervertebral notches of) two pedicles (one above and one below) of adjacent vertebra in the articulated spine. Each interve ...
, possibly impinging on the spinal nerve roots within. More advanced cases can involve severe inflammatory responses in the Z-joint, not unlike a swollen arthritic knee.
Diagnosis
Facet joint arthritis may not always have any symptoms, but often manifests as a dull ache across the back. However like many deep organs of the body it can be experienced by the patient in a variety of referral pain patterns. The location of facet joints, deep in the back and covered with large tracts of paraspinal muscles, further complicate the diagnostic approach. Typically facet joint arthritis is diagnosed with specializedphysical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of ...
by specialist physicians such as facet loading (also called Kemps test). However, this test has poor sensitivity (50-70%) and specificity (67.3%) for lumbar facet pain. Often providers perform diagnostic injections to determine if the facet joint is the underlying source of pain.
Treatment

Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment of facet joint arthritis involvesphysical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
or osteopathic medicine
Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO or D.O., or in Australia DO USA) is a medical degree conferred by the 38 osteopathic Medical school in the United States, medical schools in the United States. DO and Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Medicine (M ...
, with muscle strengthening, correction of posture, and biomechanics being the key.
Corticosteroid injections
Corticosteroid injections into the joint space may provide temporary pain relief anywhere from days to several months. With repeated injections, sometimes the patient may experience a more permanent improvement in their symptoms. Steroid injections are typically performed under image guidance to ensure accuracy given the complex shape and deep location of the facet. Some patients do not benefit from corticosteriod injections.Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium fre ...
or lesioning, also known as rhizolysis, can be used to give longer lasting relief by destroying the nerves that supply the facet joint ( medial branch nerves). Current guidelines as per the International Spine Intervention Society require two successful medial branch blocks before progressing to a radiofrequency ablation.
Surgery
Surgery, in the form of afacetectomy
Facetectomy is a surgical procedure
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabs ...
, can be performed in certain cases, particularly when the nerve root is affected.
Etymology
Ancient Greek: ' ("yoke") + ' ("out/from") + ' ("grow")See also
*Articular processes
The articular process or zygapophysis ( + apophysis) of a vertebra is a projection of the vertebra that serves the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. ...
* Artificial facet replacement
An artificial facet replacement is a joint prosthesis intended to replace the natural Zygapophysial joint, facets and other posterior elements of the spine, restoring normal (or near-normal) motion while providing stabilization of spinal segments. ...
* Facet joint injection
Facet joint injections are used to alleviate symptoms of Facet syndrome. The procedure is an outpatient surgery, so that the patient can go home on the same day. It usually takes 10–20 minutes, but may take up to 30 minutes if the patient needs ...
* Facet syndrome
Facet syndrome is a syndrome in which the facet joints (synovial joint, synovial diarthroses) cause painful symptoms. In conjunction with degenerative disc disease, a distinct but functionally related condition, facet arthropathy is believed to be ...
References
9. Shin-Tsu Chang, Chuan-Ching Liu, Wan-Hua Yang. Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography (hybrid imaging) in the diagnosis of unilateral facet joint arthritis after internal fixation for atlas fracture. HSOA Journal of Medicine: Study & Research 2019; 2: 010. 10. Zhu Wei Lim, Shih-Chuan Tsai, Yi-Ching Lin, Yuan-Yang Cheng, Shin-Tsu Chang. A worthwhile measurement of early vigilance and therapeutic monitor in axial spondyloarthritis: a literature review of quantitative sacroiliac scintigraphy. European Medical Journal (EMJ) Rheumatology 2021 July 15; 8 129-139.External links
Diagram at spineuniverse.com
Emedicine article on Lumbosacral Facet Syndrome
{{Authority control Bones of the vertebral column Joints Joints of the head and neck