Baalbeck on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the
 A few miles from the swamp from which the Litani (the classical Leontes) and the Asi (the upper Orontes) flow, Baalbek may be the same as the ''manbaa al-nahrayn'' ("Source of the Two Rivers"), the abode of El in the
A few miles from the swamp from which the Litani (the classical Leontes) and the Asi (the upper Orontes) flow, Baalbek may be the same as the ''manbaa al-nahrayn'' ("Source of the Two Rivers"), the abode of El in the
Litani River
The Litani River ( ar, نهر الليطاني, Nahr al-Līṭānī), the classical Leontes ( grc-gre, Λέοντες, Léontes, lions), is an important water resource in southern Lebanon. The river rises in the fertile Beqaa Valley, west of B ...
in Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate french: Baalbek-Hermel
, settlement_type = Governorate
, image_skyline = Baalbek (4594513263).jpg
, image_caption = Baalbek
, image_flag =
, image_seal =
, image_shield =
, image_ ...
. In Greek and Roman times Baalbek was also known as Heliopolis (, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
for "Sun City"). In 1998 Baalbek had a population of 82,608, mostly Shia Muslims
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
, followed by Sunni Muslims and Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
.
It is home to the Baalbek temple complex which includes two of the largest and grandest Roman temple ruins: the Temple of Bacchus
The Temple of Bacchus is part of the Baalbek temple complex located in the broad Al-biqā (Bekaa Valley), Lebanon. The temple complex is considered an outstanding archaeological and artistic site of Imperial Roman Architecture and was inscribed a ...
and the Temple of Jupiter. It was inscribed in 1984 as an UNESCO World Heritage
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
site.
Name
 A few miles from the swamp from which the Litani (the classical Leontes) and the Asi (the upper Orontes) flow, Baalbek may be the same as the ''manbaa al-nahrayn'' ("Source of the Two Rivers"), the abode of El in the
A few miles from the swamp from which the Litani (the classical Leontes) and the Asi (the upper Orontes) flow, Baalbek may be the same as the ''manbaa al-nahrayn'' ("Source of the Two Rivers"), the abode of El in the Ugaritic
Ugaritic () is an extinct Northwest Semitic language, classified by some as a dialect of the Amorite language and so the only known Amorite dialect preserved in writing. It is known through the Ugaritic texts discovered by French archaeologist ...
Baal Cycle
The Baal Cycle is an Ugaritic cycle of stories about the Canaanite god Baʿal ( "Owner", "Lord"), a storm god associated with fertility. It is one of the Ugarit texts, dated to c. 1500-1300 BCE.
The text identifies Baal as the god Hadad, t ...
discovered in the 1920s and a separate serpent incantation.
Baalbek was called Heliopolis during the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
, a latinisation of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''Hēlioúpolis'' () used during the Hellenistic Period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
,
meaning "Sun City" in reference to the solar cult there. The name is attested under the Seleucids
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the M ...
and Ptolemies. However, Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae ...
notes that earlier " Assyrian" names of Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
ine towns continued to be used alongside the official Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
ones imposed by the Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
, who were successors of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. In Greek religion, Helios was both the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
in the sky and its personification as a god
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
. The local Semitic god Baʿal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", " lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied ...
Haddu was more often equated with Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek reli ...
or Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
or simply called the "Great God of Heliopolis", but the name may refer to the Egyptians' association of Baʿal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", " lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied ...
with their great god Ra. It was sometimes described as or Coelesyria ( la, Heliopolis Syriaca or ') to distinguish it from its namesake in Egypt. In Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, its titular see
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbis ...
is distinguished as , from its former Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
Phoenice
Phoenice or Phoenike ( el, Φοινίκη) was an ancient Greek city in Epirus and capital of the Chaonians.: "To the north the Chaonians had expelled the Corcyraeans from their holdings on the mainland and built fortifications at Buthrotum, K ...
. The importance of the solar cult is also attested in the name Biḳāʿ al-ʿAzīz borne by the plateau surrounding Baalbek, as it references an earlier solar deity and not later men, named Aziz
Aziz ( ar, عزيز, , is an Arabic male name. The feminine form of both the adjective and the given name is Aziza.
''Aziz'' in Arabic is derived from the root ''ʕ-z-z'' with a meaning of "strong, powerful" and the adjective has acquired its m ...
. In Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
antiquity, it was known as Heliopolis. It still possesses some of the best-preserved Roman ruins in Lebanon, including one of the largest temples of the empire. The gods that were worshipped there (Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, and Bacchus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; grc, wikt:Διόνυσος, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstas ...
) were equivalents of the Canaanite deities Hadad, Atargatis
Atargatis (; grc, Ἀτάργατις, translit=Atárgatis or arc, , translit=ʿtrʿth; syc, ܬܪܥܬܐ, translit=Tarʿaṯā) was the chief goddess of northern Syria in Classical antiquity. Ctesias also used the name Derketo ( grc-koi, Δε ...
. Local influences are seen in the planning and layout of the temples, as they vary from the classic Roman design.
The name is first attested in the Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Tor ...
, a second-century rabbinic text, as a geographic epithet for a kind of garlic, ''shum ba'albeki'' (שום בעלבכי). Two early 5th-century Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
manuscripts, a translation of Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Chris ...
's '' Theophania'' and a life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
of Rabbula, bishop of Edessa Early bishops
The following list is based on the records of the ''Chronicle of Edessa'' (to ''c''.540) and the ''Chronicle of Zuqnin''.
Jacobite (Syriac) bishops
These bishops belonged to the Syriac Orthodox Church. During the later period there ...
. It was pronounced as ''Baʿlabakk'' ( ar, بَعْلَبَكّ) in Classical Arabic. In Modern Standard Arabic
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Modern Written Arabic (MWA), terms used mostly by linguists, is the variety of standardized, literary Arabic that developed in the Arab world in the late 19th and early 20th centuries; occasionally, it also ref ...
, its vowels are marked as ''Baʿlabak'' () or ''Baʿlabekk''. It is ''Bʿalbik'' (, is ) in Lebanese Arabic
Lebanese Arabic ( ar, عَرَبِيّ لُبْنَانِيّ ; autonym: ), or simply Lebanese ( ar, لُبْنَانِيّ ; autonym: ), is a variety of North Levantine Arabic, indigenous to and spoken primarily in Lebanon, with significant ...
.
The etymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
of Baalbek has been debated indecisively since the 18th century. Cook took it to mean "Baʿal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", " lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied ...
(Lord) of the Beka" and Donne as "City of the Sun". Lendering asserts that it is probably a contraction of ''Baʿal Nebeq'' ("Lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are ...
of the Source" of the Litani River
The Litani River ( ar, نهر الليطاني, Nahr al-Līṭānī), the classical Leontes ( grc-gre, Λέοντες, Léontes, lions), is an important water resource in southern Lebanon. The river rises in the fertile Beqaa Valley, west of B ...
). Steiner proposes a Semitic adaption of "Lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the peerage in the United Kingdom, or are ...
Bacchus", from the classical temple complex.
On the basis of its similar name, several 19th-century Biblical archaeologists
Biblical archaeology is an academic school and a subset of Biblical studies and Levantine archaeology. Biblical archaeology studies archaeological sites from the Ancient Near East and especially the Holy Land (also known as Palestine, Land of ...
attempted to connect Baalbek to the "Baalgad A place in ancient Israel, Baal-Gad was a Canaanite town in the valley of Lebanon at the foot of Hermon, near the source of Jordan River (Josh. 13:5; 11:17; 12:7). It was the most northern point to which Joshua's conquests extended. It probably deri ...
" mentioned in the Hebrew Scripture
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''
''
Book of Joshua, the

 After
After
Bk. V, Ch. 15, §22
. and on

 Baalbek was occupied by the Muslim army in AD 634 ( 13), in 636, or under Abu ʿUbaidah following the
Baalbek was occupied by the Muslim army in AD 634 ( 13), in 636, or under Abu ʿUbaidah following the 
Tradition holds that many Christians quit the Baalbek region in the eighteenth century for the newer, more secure town of

 Baalbek was connected to the DHP, the French-owned railway concession in Ottoman Syria, on 19 June 1902. It formed a station on the
Baalbek was connected to the DHP, the French-owned railway concession in Ottoman Syria, on 19 June 1902. It formed a station on the 
 The Tell Baalbek temple complex, fortified as the town's citadel during the Middle Ages, was constructed from local stone, mostly white
The Tell Baalbek temple complex, fortified as the town's citadel during the Middle Ages, was constructed from local stone, mostly white  The Temple of Jupiter—once wrongly credited to Helios—lay at the western end of the Great Court, raised another on a platform reached by a wide staircase. Under the Byzantines, it was also known as the " Trilithon" from the three massive stones in its foundation and, when taken together with the forecourt and Great Court, it is also known as the Great Temple. The Temple of Jupiter proper was circled by a
The Temple of Jupiter—once wrongly credited to Helios—lay at the western end of the Great Court, raised another on a platform reached by a wide staircase. Under the Byzantines, it was also known as the " Trilithon" from the three massive stones in its foundation and, when taken together with the forecourt and Great Court, it is also known as the Great Temple. The Temple of Jupiter proper was circled by a
File:The Round Temple and the Temple of the Muses located outside the sanctuary complex, Heliopolis (Baalbek), Lebanon.jpg, The Round Temple and the Temple of the Muses located outside the sanctuary complex
File:Temple of Bacchus, Baalbek, Lebanon (49890013476).jpg, Temple of Bacchus
File:Propylaea of Baalbek temples complex 16062.JPG, Remains of the Propylaeum, the eastern entrance to the site
File:Great Court of Temples Complex in Baalbek (49856240571).jpg, The Great Court of Temples Complex
File:Temple of Venus, Baalbek 14114.JPG, Temple of Venus
File:Baalbeck Temple.jpg, Massive columns of the Temple of Jupiter
File:1873 Stieler Map of Asia Minor, Syria and Israel - Palestine (modern Turkey) - Geographicus - Klein-AsienSyrien-stieler-1873.jpg, An 1873 German map of Asia Minor & Syria, with relief illustrating the Beqaa (''El Bekaa'') valley
File:Baalbec. Panorama - Bonfils. LCCN93500455.jpg, Panorama, around 1870, by Félix Bonfils
File:Birdseye View of Baalbek and the Lebanons.jpg, Baalbek in 1910, after the arrival of
Google Maps satellite view
* Panoramas of the temples a
an
Discover Lebanon
from the
GCatholic – Latin titular see
Baalbeck International Festival
(2006) at ''Al Mashriq'' * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
volume I
volume II
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * & * * * * * * * * * * * Reprinted at Görlitz in 1591. * * * * * * * *
Baalath Baalath is the name of either one or two towns in the Hebrew Bible.For the existence of one or two Balaaths, see Its name is the female form of Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific ...
listed among Solomon's cities in the First Book of Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books ...
, the Baal-hamon
Baal Hammon, properly Baʿal Ḥammon or Baʿal Ḥamon ( Phoenician: ; Punic: ), meaning “Lord Hammon”, was the chief god of Carthage. He was a weather god considered responsible for the fertility of vegetation and esteemed as King of the ...
where he had a vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineya ...
, and the "Plain of Aven" in Amos
Amos or AMOS may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Amos Records, an independent record label established in Los Angeles, California, in 1968
* Amos (band), an American Christian rock band
* ''Amos'' (album), an album by Michael Ray
* ''Amos' ...
.
History
Prehistory
The hilltop of Tell Baalbek, part of a valley to the east of the northern Beqaa Valley ( la, Coelesyria), shows signs of almost continual habitation over the last 8–9000 years. It was well-watered both from a stream running from the ''Rās-el-ʿAin'' spring SE of the citadel and, during the spring, from numerous rills formed by meltwater from the Anti-Lebanons. Macrobius later credited the site's foundation to a colony of Egyptian or Assyrian priests. The settlement's religious, commercial, and strategic importance was minor enough, however, that it is never mentioned in any known Assyrian or Egyptian record, unless under another name. Its enviable position in a fertile valley, major watershed, and along the route from Tyre toPalmyra
Palmyra (; Palmyrene: () ''Tadmor''; ar, تَدْمُر ''Tadmur'') is an ancient city in present-day Homs Governorate, Syria. Archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first mention the city in the early secon ...
should have made it a wealthy and splendid site from an early age. During the Canaanite period, the local temples were largely devoted to the Heliopolitan Triad In early modern scholarship, a cult to a supposed Heliopolitan Triad of Jupiter, Venus and Mercury (or Dionysus) was thought to have originated in ancient Canaanite religion, adopted and adapted firstly by the Greeks, and then by the Romans when th ...
: a male god (Baʿal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", " lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied ...
), his consort (Astarte
Astarte (; , ) is the Hellenized form of the Ancient Near Eastern goddess Ashtart or Athtart ( Northwest Semitic), a deity closely related to Ishtar ( East Semitic), who was worshipped from the Bronze Age through classical antiquity. The name ...
), and their son ( Adon). The site of the present Temple of Jupiter was probably the focus of earlier worship, as its altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
was located at the hill's precise summit and the rest of the sanctuary raised to its level.
In Islamic mythology
Islamic mythology is the body of myths associated with Islam and the Quran. Islam is a religion that is more concerned with social order and law than with religious ritual or myths. ''The Oxford Companion to World Mythology'' identifies a numbe ...
, the temple complex was said to have been a palace of Solomon's which was put together by ''djinn
Jinn ( ar, , ') – also romanized as djinn or anglicized as genies (with the broader meaning of spirit or demon, depending on sources)
– are invisible creatures in early pre-Islamic Arabian religious systems and later in Islamic myt ...
'' and given as a wedding gift to the Queen of Sheba
The Queen of Sheba ( he, מַלְכַּת שְׁבָא, Malkaṯ Šəḇāʾ; ar, ملكة سبأ, Malikat Sabaʾ; gez, ንግሥተ ሳባ, Nəgśətä Saba) is a figure first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. In the original story, she bring ...
; its actual Roman origin remained obscured by the citadel's medieval fortifications as late as the 16th-century visit of the Polish prince Radziwiłł.
Antiquity

 After
After Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's conquest of Persia in the 330s BC, Baalbek (under its Hellenic name Heliopolis) formed part of the Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The War ...
kingdoms of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
& Syria. It was annexed by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
during their eastern wars. The settlers of the Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Character ...
Colonia Julia Augusta Felix Heliopolitana may have arrived as early as the time of Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
but were more probably the veterans
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military.
A military veteran that h ...
of the 5th
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five.
Fifth or The Fifth may refer to:
* Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth"
* Fifth column, a political term
* Fifth disease, a contagious rash tha ...
and 8th Legion
Legio VIII Augusta ("Augustus' Eighth Legion") was one of the oldest Roman legion, legions of the Imperial Roman army.
In republican service
They were ordered to Cisalpine Gaul around 58 BC by Julius Caesar and marched with him throughout the ...
s under Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, during which time it hosted a Roman garrison. From 15 BC to AD 193, it formed part of the territory of Berytus. It is mentioned in Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
, Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
, Strabo, and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
, '' Geogr.''Bk. V, Ch. 15, §22
. and on
coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
of nearly every emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
from Nerva to Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; c. 218 – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empi ...
. The 1st-century Pliny did not number it among the Decapolis
The Decapolis (Greek: grc, Δεκάπολις, Dekápolis, Ten Cities, label=none) was a group of ten Hellenistic cities on the eastern frontier of the Roman Empire in the Southern Levant in the first centuries BCE and CE. They formed a group ...
, the "Ten Cities" of Coelesyria, while the 2nd-century Ptolemy did. The population likely varied seasonally with market fairs and the schedules of the Indian monsoon
The Monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year fro ...
and caravans to the coast and interior.
During Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the city's temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
to Baʿal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", " lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied ...
Haddu was conflated first with the worship of the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
sun god Helios and then with the Greek and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
sky god under the name " Heliopolitan Zeus" or "Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
". The present Temple of Jupiter presumably replaced an earlier one using the same foundation; it was constructed during the mid- 1st century and probably completed around AD 60. His idol
Idol or Idols may refer to:
Religion and philosophy
* Cult image, a neutral term for a man-made object that is worshipped or venerated for the deity, spirit or demon that it embodies or represents
* Murti, a point of focus for devotion or medit ...
was a beardless golden
Golden means made of, or relating to gold.
Golden may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
*Golden, in the parish of Probus, Cornwall
* Golden Cap, Dorset
*Golden Square, Soho, London
*Golden Valley, a valley on the River Frome in Gloucestershi ...
god in the pose of a charioteer, with a whip raised in his right hand and a thunderbolt
A thunderbolt or lightning bolt is a symbolic representation of lightning when accompanied by a loud thunderclap. In Indo-European mythology, the thunderbolt was identified with the 'Sky Father'; this association is also found in later Hel ...
and stalks of grain in his left; its image appeared on local coinage and it was borne through the streets during several festivals throughout the year. Macrobius compared the rituals to those for Diva Fortuna
Fortuna ( la, Fortūna, equivalent to the Greek mythology, Greek goddess Tyche) is the goddess of fortune and the personification of luck in Religion in ancient Rome, Roman religion who, largely thanks to the Late Antique author Boethius, remaine ...
at Antium
Antium was an ancient coastal town in Latium, south of Rome. An oppidum was founded by people of Latial culture (11th century BC or the beginning of the 1st millennium BC), then it was the main stronghold of the Volsci people until it was conqu ...
and says the bearers were the principal citizens of the town, who prepared for their role with abstinence, chastity, and shaved heads. In bronze statuary attested from Byblos
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8 ...
in Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
and Tortosa
Tortosa (; ) is the capital of the '' comarca'' of Baix Ebre, in Catalonia, Spain.
Tortosa is located at above sea level, by the Ebro river, protected on its northern side by the mountains of the Cardó Massif, of which Buinaca, one of the hig ...
in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, he was encased in a pillarlike term
Term may refer to:
* Terminology, or term, a noun or compound word used in a specific context, in particular:
**Technical term, part of the specialized vocabulary of a particular field, specifically:
***Scientific terminology, terms used by scient ...
and surrounded (like the Greco-Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
Mithras
Mithraism, also known as the Mithraic mysteries or the Cult of Mithras, was a Roman mystery religion centered on the god Mithras. Although inspired by Iranian worship of the Zoroastrian divinity (''yazata'') Mithra, the Roman Mithras is link ...
) by busts representing the sun, moon, and five known planets. In these statues, the bust of Mercury is made particularly prominent; a marble stela
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), wh ...
at Massilia
Massalia (Greek: Μασσαλία; Latin: Massilia; modern Marseille) was an ancient Greek colony founded ca. 600 BC on the Mediterranean coast of present-day France, east of the river Rhône, by Ionian Greek settlers from Phocaea, in Western An ...
in Transalpine Gaul
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the ...
shows a similar arrangement but enlarges Mercury into a full figure. Local cults also revered the Baetylia, black conical stones considered sacred to Baʿal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", " lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied ...
. One of these was taken to Rome by the emperor Elagabalus
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Sextus Varius Avitus Bassianus, 204 – 11/12 March 222), better known by his nickname "Elagabalus" (, ), was Roman emperor from 218 to 222, while he was still a teenager. His short reign was conspicuous for s ...
, a former priest "of the sun" at nearby Emesa
ar, حمصي, Himsi
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_t ...
, who erected a temple for it on the Palatine Hill. Heliopolis was a noted oracle and pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
site, whence the cult spread far afield, with inscriptions to the Heliopolitan god discovered in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, Pannonia, Venetia, Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, and near the Wall
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or, is decorative. There are many kinds of walls, including:
* Walls in buildings that form a fundamental part of the sup ...
in Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. The Roman temple complex grew up from the early part of the reign of Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
in the late 1st century BC until the rise of Christianity in the 4th century. (The 6th-century chronicles of John Malalas of Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
, which claimed Baalbek as a " wonder of the world", credited most of the complex to the 2nd-century Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
, but it is uncertain how reliable his account is on the point.) By that time, the complex housed three temples on Tell Baalbek: one to Jupiter Heliopolitanus (Baʿal), one to Venus Heliopolitana
Venus (), , is a Roman goddess, whose functions encompass love, beauty, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity, and victory. In Roman mythology, she was the ancestor of the Roman people through her son, Aeneas, who survived the fall of Troy and fl ...
(Ashtart), and a third to Bacchus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; grc, wikt:Διόνυσος, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstas ...
. On a nearby hill, a fourth temple was dedicated to the third figure of the Heliopolitan Triad In early modern scholarship, a cult to a supposed Heliopolitan Triad of Jupiter, Venus and Mercury (or Dionysus) was thought to have originated in ancient Canaanite religion, adopted and adapted firstly by the Greeks, and then by the Romans when th ...
, Mercury (Adon or Seimios). Ultimately, the site vied with Praeneste in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
as the two largest sanctuaries in the Western world.
The emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
consulted the site's oracle twice. The first time, he requested a written reply to his sealed and unopened question; he was favorably impressed by the god's blank reply as his own paper had been empty. He then inquired whether he would return alive from his wars against Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
and received in reply a centurion's vine staff
__NOTOC__
The vine staff, vine-staff, or centurion's staff ( la, vitis) was a vinewood rod of about in length used in the ancient Roman Army and Navy. It was the mark and tool of the centurion: both as an implement in the direction of drill and ...
, broken to pieces. In AD 193, Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
granted the city ''ius Italicum
''Ius Italicum'' (Latin, Italian or Italic law) was a law in the early Roman Empire that allowed the emperors to grant cities outside Italy the legal fiction that they were on Italian soil. This meant that the city would be governed under Roman la ...
'' rights. His wife Julia Domna
Julia Domna (; – 217 AD) was Roman empress from 193 to 211 as the wife of Emperor Septimius Severus. She was the first empress of the Severan dynasty. Domna was born in Emesa (present-day Homs) in Roman Syria to an Arab family of priests ...
and son Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor S ...
toured Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
and Syria in AD 215; inscriptions in their honour at the site may date from that occasion; Julia was a Syrian native whose father had been an Emesa
ar, حمصي, Himsi
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_t ...
n priest "of the sun" like Elagabalus
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Sextus Varius Avitus Bassianus, 204 – 11/12 March 222), better known by his nickname "Elagabalus" (, ), was Roman emperor from 218 to 222, while he was still a teenager. His short reign was conspicuous for s ...
.
The town became a battleground upon the rise of Christianity. Early Christian writers such as Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος ; 260/265 – 30 May 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilus (from the grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος τοῦ Παμφίλου), was a Greek historian of Christianity, exegete, and Chris ...
(from nearby Caesarea) repeatedly execrated the practices of the local pagans in their worship of the Heliopolitan Venus. In AD 297, the actor Gelasinus
Gelasinus ( grc-gre, Γελασινος, ''Gelasinos''; AD 297) was a reputed Christianity, Christian martyr (Christianity), martyr and saint (Christianity), saint. His feast day (saint), feast day is observed on August 26.
Gelasinus wa ...
converted in the middle of a scene mocking baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
; his public profession of faith provoked the audience to drag him from the theater and stone him to death. In the early 4th century, the deacon Cyril defaced many of the idols in Heliopolis; he was killed and (allegedly) cannibalised. Around the same time, Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
, though not yet a Christian, demolished the goddess' temple, raised a basilica in its place, and outlawed the locals' ancient custom of prostituting women before marriage. Bar Hebraeus
Gregory Bar Hebraeus ( syc, ܓܪܝܓܘܪܝܘܣ ܒܪ ܥܒܪܝܐ, b. 1226 - d. 30 July 1286), known by his Syriac ancestral surname as Bar Ebraya or Bar Ebroyo, and also by a Latinized name Abulpharagius, was an Aramean Maphrian (regional primat ...
also credited him with ending the locals' continued practice of polygamy
Crimes
Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is ...
. The enraged locals responded by raping and torturing Christian virgins. They reacted violently again under the freedom permitted to them by Julian the Apostate. The city was so noted for its hostility to the Christians that Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
ns were banished to it as a special punishment. The Temple of Jupiter, already greatly damaged by earthquakes, was demolished under Theodosius in 379 and replaced by another basilica (now lost), using stones scavenged from the pagan complex. The ''Easter Chronicle
''Chronicon Paschale'' (the ''Paschal'' or ''Easter Chronicle''), also called ''Chronicum Alexandrinum'', ''Constantinopolitanum'' or ''Fasti Siculi'', is the conventional name of a 7th-century Greek Christian chronicle of the world. Its name com ...
'' states he was also responsible for destroying all the lesser temples and shrines of the city. Around the year 400, Rabbula, the future bishop of Edessa Early bishops
The following list is based on the records of the ''Chronicle of Edessa'' (to ''c''.540) and the ''Chronicle of Zuqnin''.
Jacobite (Syriac) bishops
These bishops belonged to the Syriac Orthodox Church. During the later period there ...
, attempted to have himself martyred by disrupting the pagans of Baalbek but was only thrown down the temple stairs along with his companion. It became the seat of its own bishop as well. Under the reign of Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
, eight of the complex's Corinthian columns were disassembled and shipped to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
for incorporation in the rebuilt Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
sometime between 532 and 537. Michael the Syrian claimed the golden idol of Heliopolitan Jupiter was still to be seen during the reign of Justin II (560s & 570s), and, up to the time of its conquest by the Muslims, it was renowned for its palaces, monuments, and gardens.
Middle Ages

 Baalbek was occupied by the Muslim army in AD 634 ( 13), in 636, or under Abu ʿUbaidah following the
Baalbek was occupied by the Muslim army in AD 634 ( 13), in 636, or under Abu ʿUbaidah following the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
defeat at Yarmouk in 637 ( 16), either peacefully and by agreement or following a heroic defense and yielding of gold, of silver, 2000 silk vests, and 1000 swords. The ruined temple complex was fortified under the name ( " The Fortress") but was sacked with great violence by the Damascene caliph Marwan II in 748, at which time it was dismantled and largely depopulated. It formed part of the district of Damascus under the Umayyads Umayyads may refer to:
*Umayyad dynasty, a Muslim ruling family of the Caliphate (661–750) and in Spain (756–1031)
*Umayyad Caliphate (661–750)
:*Emirate of Córdoba (756–929)
:*Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ( ar, خ ...
and Abbasids before being conquered by Fatimid Egypt in 942. In the mid-10th century, it was said to have "gates of palaces sculptured in marble and lofty columns also of marble" and that it was the most "stupendous" and "considerable" location in the whole of Syria. It was sacked and razed by the Byzantines under John I in 974, raided by Basil II in 1000, and occupied by Salih ibn Mirdas
Abu Ali Salih ibn Mirdas ( ar, ابو علي صالح بن مرداس, Abū ʿAlī Ṣāliḥ ibn Mirdās), also known by his ''laqab'' (honorific epithet) Asad al-Dawla ('Lion of the State'), was the founder of the Mirdasid dynasty and emir of ...
, emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
of Aleppo, in 1025.
In 1075, it was finally lost to the Fatimids on its conquest by Tutush I, Seljuk emir of Damascus. It was briefly held by Muslim ibn Quraysh, emir of Aleppo, in 1083; after its recovery, it was ruled in the Seljuks' name by the eunuch Gümüshtegin until he was deposed for conspiring against the usurper Toghtekin
Toghtekin or Tughtekin (Modern tr, Tuğtekin; Arabicised epithet: ''Zahir ad-Din Tughtikin''; died February 12, 1128), also spelled Tughtegin, was a Turkic military leader, who was ''atabeg'' of Damascus from 1104 to 1128. He was the founder o ...
in 1110. Toghtekin then gave the town to his son Buri. Upon Buri's succession to Damascus on his father's death in 1128, he granted the area to his son Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
. After Buri's murder, Muhammad successfully defended himself against the attacks of his brothers Ismaʿil and Mahmud
Mahmud is a transliteration of the male Arabic given name (), common in most parts of the Islamic world. It comes from the Arabic triconsonantal root Ḥ-M-D, meaning ''praise'', along with ''Muhammad''.
Siam Mahmud
*Mahmood (singer) (born 1 ...
and gave Baalbek to his vizier
A vizier (; ar, وزير, wazīr; fa, وزیر, vazīr), or wazir, is a high-ranking political advisor or minister in the near east. The Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called '' katib'' (secretary), who was ...
Unur. In July 1139, Zengi, atabeg of Aleppo and stepfather of Mahmud, besieged Baalbek with 14 catapults. The outer city held until 10 October and the citadel until the 21st, when Unur surrendered upon a promise of safe passage. In December, Zengi negotiated with Muhammad, offering to trade Baalbek or Homs for Damascus, but Unur convinced the atabeg to refuse. Zengi strengthened its fortifications and bestowed the territory on his lieutenant Ayyub, father of Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
. Upon Zengi's assassination in 1146, Ayyub surrendered the territory to Unur, who was acting as regent for Muhammad's son Abaq. It was granted to the eunuch Ata al-Khadim, who also served as viceroy of Damascus.
In December 1151, it was raided by the garrison of Banyas as a reprisal for its role in a Turcoman raid on Banyas. Following Ata's murder, his nephew Dahhak, emir of the Wadi al-Taym Wadi al-Taym ( ar, وادي التيم, Wādī al-Taym), also transliterated as Wadi el-Taym, is a wadi (dry river) that forms a large fertile valley in Lebanon, in the districts of Rachaya and Hasbaya on the western slopes of Mount Hermon. It ad ...
, ruled Baalbek. He was forced to relinquish it to Nur ad-Din in 1154 after Ayyub had successfully intrigued against Abaq from his estates near Baalbek. Ayyub then administered the area from Damascus on Nur ad-Din's behalf. In the mid-12th century, Idrisi
TerrSet (formerly IDRISI) is an integrated geographic information system (GIS) and remote sensing software developed by Clark Labs at Clark University for the analysis and display of digital geospatial information. TerrSet is a PC grid-based syste ...
mentioned Baalbek's two temples and the legend of their origin under Solomon; it was visited by the Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
traveler Benjamin of Tudela in 1170.
Baalbek's citadel served as a jail for Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
taken by the Zengids as prisoners of war. In 1171, these captives successfully overpowered their guards and took possession of the castle from its garrison. Muslims from the surrounding area gathered, however, and entered the castle through a secret passageway shown to them by a local. The Crusaders were then massacred.
Three major earthquakes occurred in the 12th century, in 1139, 1157, and 1170. The one in 1170 ruined Baalbek's walls and, though Nur ad-Din repaired them, his young heir Ismaʿil was made to yield it to Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
by a 4-month siege in 1174. Having taken control of Damascus on the invitation of its governor Ibn al-Muqaddam, Saladin rewarded him with the following the Ayyubid victory at the Horns of Hama in 1175. Baldwin, the young leper king of Jerusalem
The King of Jerusalem was the supreme ruler of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, a Crusader state founded in Jerusalem by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade, when the city was conquered in 1099.
Godfrey of Bouillon, the first ruler of t ...
, came of age the next year, ending the Crusaders' treaty with Saladin. His former regent, Raymond of Tripoli, raided the Beqaa Valley from the west in the summer, suffering a slight defeat at Ibn al-Muqaddam's hands. He was then joined by the main army, riding north under Baldwin and Humphrey of Toron; they defeated Saladin's elder brother Turan Shah in August at Ayn al-Jarr
Anjar (meaning "unresolved or running river"; ar, عنجر / ALA-LC: ''‘Anjar''; also known as Hosh (architecture), Hosh Mousa ( ar, حوش موسى / ''Ḥawsh Mūsá''), is a town of Lebanon located in the Bekaa Valley. The population is 2,4 ...
and plundered Baalbek. Upon the deposition of Turan Shah for neglecting his duties in Damascus, however, he demanded his childhood home of Baalbek as compensation. Ibn al-Muqaddam did not consent and Saladin opted to invest the city in late 1178 to maintain peace within his own family. An attempt to pledge fealty to the Christians at Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
was ignored on behalf of an existing treaty with Saladin. The siege was maintained peacefully through the snows of winter, with Saladin waiting for the "foolish" commander and his garrison of "ignorant scum" to come to terms. Sometime in spring, Ibn al-Muqaddam yielded and Saladin accepted his terms, granting him Baʿrin, Kafr Tab, and al-Maʿarra. The generosity quieted unrest among Saladin's vassals through the rest of his reign but led his enemies to attempt to take advantage of his presumed weakness. He did not permit Turan Shah to retain Baalbek very long, though, instructing him to lead the Egyptian troops returning home in 1179 and appointing him to a sinecure in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
. Baalbek was then granted to his nephew Farrukh Shah
Al-Malik al-Mansur Izz ad-Din Abu Sa'id Farrukhshah Dawud was the Ayyubid Emir of Baalbek between 1179 and 1182 and ''Na'ib'' (Viceroy) of Damascus.
Biography
Farrukh was the son of Saladin's brother Nur ad-Din Shahanshah and the older brother ...
, whose family ruled it for the next half-century. When Farrukh Shah died three years later, his son Bahram Shah
Al-Malik al-Amjad Bahramshah was the List of Ayyubid rulers#Emirs of Baalbek, Ayyubid emir of Baalbek between 1182–1230 (578–627 AH).
Reign
Bahramshah succeeded his father Farrukh Shah, Farrukhshah as ruler of the minor emirate of Baalbek and ...
was only a child but he was permitted his inheritance and ruled til 1230. He was followed by al-Ashraf Musa, who was succeeded by his brother as-Salih Ismail, who received it in 1237 as compensation for being deprived of Damascus by their brother al-Kamil
Al-Kamil ( ar, الكامل) (full name: al-Malik al-Kamil Naser ad-Din Abu al-Ma'ali Muhammad) (c. 1177 – 6 March 1238) was a Muslim ruler and the fourth Ayyubid sultan of Egypt. During his tenure as sultan, the Ayyubids defeated the Fifth Cr ...
. It was seized in 1246 after a year of assaults by as-Salih Ayyub, who bestowed it upon Saʿd al-Din al-Humaidi. When as-Salih Ayyub's successor Turan Shah was murdered in 1250, al-Nasir Yusuf, the sultan of Aleppo
The rulers of Aleppo ruled as kings, emirs and sultans of the city and its surrounding region since the later half of the 3rd millennium BC, starting with the kings of Armi, followed by the Amorite dynasty of Yamhad. Muslim rule of the city end ...
, seized Damascus and demanded Baalbek's surrender. Instead, its emir did homage and agreed to regular payments of tribute.
The Mongolian general Kitbuqa
Kitbuqa Noyan (died 1260), also spelled Kitbogha, Kitboga, or Ketbugha, was an Eastern Christian of the Naimans, a group that was subservient to the Mongol Empire. He was a lieutenant and confidant of the Mongol Ilkhan Hulagu, assisting him ...
took Baalbek in 1260 and dismantled its fortifications. Later in the same year, however, Qutuz
Saif ad-Din Qutuz ( ar, سيف الدين قطز; died 24 October 1260), also romanized as Kutuz or Kotuz and fully al-Malik al-Muẓaffar Sayf ad-Dīn Quṭuz (), was a military leader and the third or fourth of the Mamluk Sultans of Egy ...
, the sultan of Egypt, defeated the Mongols and placed Baalbek under the rule of their emir in Damascus. Most of the city's still-extant fine mosque and fortress architecture dates to the reign of the sultan Qalawun
( ar, قلاوون الصالحي, – November 10, 1290) was the seventh Bahri Mamluk sultan; he ruled Egypt from 1279 to 1290.
He was called (, "Qalāwūn the Victorious").
Biography and rise to power
Qalawun was a Kipchak, ancient Turki ...
in the 1280s. By the early 14th century, Abulfeda
Ismāʿīl b. ʿAlī b. Maḥmūd b. Muḥammad b. ʿUmar b. Shāhanshāh b. Ayyūb b. Shādī b. Marwān ( ar, إسماعيل بن علي بن محمود بن محمد بن عمر بن شاهنشاه بن أيوب بن شادي بن مروان ...
the Hamathite was describing the city's "large and strong fortress". The revived settlement was again destroyed by a flood on 10 May 1318, when water from the east and northeast made holes wide in walls thick. 194 people were killed and 1500 houses, 131 shops, 44 orchards, 17 ovens, 11 mills, and 4 aqueducts were ruined, along with the town's mosque and 13 other religious and educational buildings. In 1400, Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kü ...
pillaged the town, and there was further destruction from a 1459 earthquake.

Early modernity
In 1516, Baalbek was conquered with the rest of Syria by the Ottoman sultan Selim the Grim. In recognition of their prominence among the Shiites of the Beqaa Valley, the Ottomans awarded thesanjak of Homs
The Homs Sanjak ( tr, Homs Sancağı) was a prefecture (sanjak) of the Ottoman Empire, located in modern-day Syria. The city of Homs was the Sanjak's capital. It had a population of 200,410 in 1914. The Sanjak of Homs shared same region with Sanja ...
and local ''iltizam
An Iltizām (Arabic التزام) was a form of tax farm that appeared in the 15th century in the Ottoman Empire. The system began under Mehmed the Conqueror and was abolished during the Tanzimat reforms in 1856.
Iltizams were sold off by the gov ...
'' concessions to Baalbek's Harfush family. Like the Hamadas, the Harfush emirs were involved on more than one occasion in the selection of Church officials and the running of local monasteries.Tradition holds that many Christians quit the Baalbek region in the eighteenth century for the newer, more secure town of
Zahlé
Zahlé ( ar, زَحْلة) is the capital and the largest city of Beqaa Governorate, Lebanon. With around 150,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city in Lebanon after Beirut and Tripoli and the fourth largest taking the whole urban area ...
on account of the Harfushes' oppression and rapacity, but more critical studies have questioned this interpretation, pointing out that the Harfushes were closely allied to the Orthodox Ma'luf family of Zahlé (where indeed Mustafa Harfush took refuge some years later) and showing that depredations from various quarters as well as Zahlé's growing commercial attractiveness accounted for Baalbek's decline in the eighteenth century. What repression there was did not always target the Christian community per se. The Shiite 'Usayran family, for example, is also said to have left Baalbek in this period to avoid expropriation by the Harfushes, establishing itself as one of the premier commercial households of Sidon
Sidon ( ; he, צִידוֹן, ''Ṣīḏōn'') known locally as Sayda or Saida ( ar, صيدا ''Ṣaydā''), is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate, of which it is the capital, on the Mediterranean coast. ...
and later even serving as consuls of Iran.
From the 16th century, European tourists
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mo ...
began to visit the colossal and picturesque ruins. Donne hyperbolised "No ruins of antiquity have attracted more attention than those of Heliopolis, or been more frequently or accurately measured and described." Misunderstanding the temple of Bacchus as the "Temple of the Sun", they considered it the best-preserved Roman temple
Ancient Roman temples were among the most important buildings in Roman culture, and some of the richest buildings in Roman architecture, though only a few survive in any sort of complete state. Today they remain "the most obvious symbol of ...
in the world. The Englishman Robert Wood's 1757 ''Ruins of Balbec'' included carefully measured engravings that proved influential on British and Continental Neoclassical architects
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing style ...
. For example, details of the Temple of Bacchus's ceiling inspired a bed and ceiling by Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his ...
and its portico inspired that of St George's in Bloomsbury.
During the 18th century, the western approaches were covered with attractive groves of walnut tree
Walnut trees are any species of tree in the plant genus ''Juglans'', the type genus of the family Juglandaceae, the seeds of which are referred to as walnuts. All species are deciduous trees, tall, with pinnate leaves , with 5–25 leafl ...
s, but the town itself suffered badly during the 1759 earthquakes, after which it was held by the Metawali
Lebanese Shia Muslims ( ar, المسلمون الشيعة اللبنانيين), historically known as ''matāwila'' ( ar, متاولة, plural of ''mutawālin'' ebanese pronounced as ''metouali'' refers to Lebanese people who are adherents ...
, who again feuded with other Lebanese tribes. Their power was broken by Jezzar Pasha
Ahmad Pasha al-Jazzar ( ar, أحمد باشا الجزّار; ota, جزّار أحمد پاشا; ca. 1720–30s7 May 1804) was the Acre-based Ottoman governor of Sidon Eyalet from 1776 until his death in 1804 and the simultaneous governor of D ...
, the rebel governor of Acre, in the last half of the 18th century. All the same, Baalbek remained no destination for a traveller unaccompanied by an armed guard. Upon the pasha's death in 1804, chaos ensued until Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt
Ibrahim Pasha ( tr, Kavalalı İbrahim Paşa; ar, إبراهيم باشا ''Ibrāhīm Bāshā''; 1789 – 10 November 1848) was an Ottoman Albanian general in the Egyptian army and the eldest son of Muhammad Ali, the Wāli and unrecognised Kh ...
occupied the area in 1831, after which it again passed into the hands of the Harfushes. In 1835, the town's population was barely 200 people. In 1850, the Ottomans finally began direct administration of the area, making Baalbek a kaza
A kaza (, , , plural: , , ; ota, قضا, script=Arab, (; meaning 'borough')
* bg, околия (; meaning 'district'); also Кааза
* el, υποδιοίκησις () or (, which means 'borough' or 'municipality'); also ()
* lad, kaza
, ...
under the Damascus Eyalet
ota, ایالت شام
, conventional_long_name = Damascus Eyalet
, common_name = Damascus Eyalet
, subdivision = Eyalet
, nation = the Ottoman Empire
, year_start = 1516
, year_end ...
and its governor a kaymakam
Kaymakam, also known by many other romanizations, was a title used by various officials of the Ottoman Empire, including acting grand viziers, governors of provincial sanjaks, and administrators of district kazas. The title has been retained a ...
.
Excavations

Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
Wilhelm II of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and his wife passed through Baalbek on 1 November 1898, on their way to Jerusalem. He noted both the magnificence of the Roman remains and the drab condition of the modern settlement. It was expected at the time that natural disasters, winter frosts, and the raiding of building materials by the city's residents would shortly ruin the remaining ruins. The archaeological team he dispatched began work within a month. Despite finding nothing they could date prior to Baalbek's Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
occupation, Otto Puchstein
Otto Puchstein (6 July 1856, Labes – 9 March 1911, Berlin) was a German classical archaeologist.
From 1875 to 1879 he studied philology, classical archaeology and Egyptology at the University of Strasbourg, where his instructors include ...
and his associates worked until 1904 and produced a meticulously researched and thoroughly illustrated series of volumes. Later excavations under the Roman flagstones in the Great Court unearthed three skeletons
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
and a fragment of Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
pottery dated to the 6th–4th centuries BC. The sherd featured cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
letters.
In 1977, Jean-Pierre Adam
Jean-Pierre Adam (born 24 November 1937 in Paris) is a French architect and archaeologist specialising in ancient architecture.
Biography
Adam was born in Paris. Following a special diploma from the School of Architecture in 1965, he entered th ...
made a brief study suggesting most of the large blocks could have been moved on rollers with machines using capstans and pulley blocks, a process which he theorised could use 512 workers to move a block. "Baalbek, with its colossal structures, is one of the finest examples of Imperial Roman architecture at its apogee", UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
reported in making Baalbek a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
in 1984. When the committee inscribed the site, it expressed the wish that the protected area include the entire town within the Arab walls, as well as the southwestern extramural quarter between Bastan-al-Khan, the Roman site and the Mameluk mosque of Ras-al-Ain. Lebanon's representative gave assurances that the committee's wish would be honoured. Recent cleaning operations at the Temple of Jupiter discovered the deep trench at its edge, whose study pushed back the date of Tell Baalbek's settlement to the PPNB
Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BC. It was typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon duri ...
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
. Finds included pottery sherds including a spout dating to the early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
. In the summer of 2014, a team from the German Archaeological Institute
The German Archaeological Institute (german: Deutsches Archäologisches Institut, ''DAI'') is a research institute in the field of archaeology (and other related fields). The DAI is a "federal agency" under the Federal Foreign Office of Germany ...
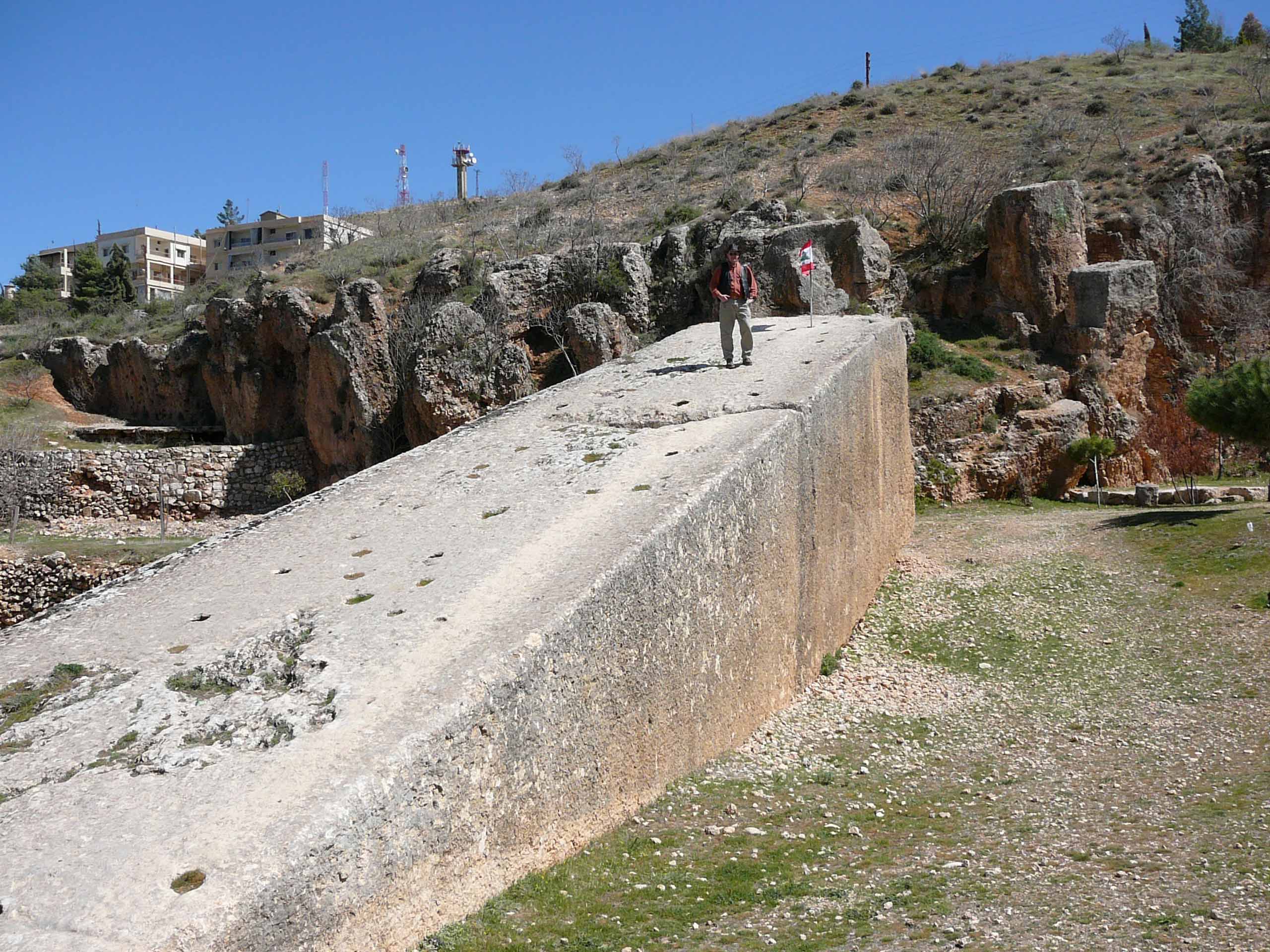
led by Jeanine Abdul Massih of the Lebanese University discovered a sixth, much larger stone suggested to be the world's largest ancient block
This is the list of ancient architectural records consists of record-making architectural achievements of the Classical antiquity, Greco-Roman world from c. 800 BC to 600 AD.
Bridges
*The highest bridge over the water or ground wa ...
. The stone was found underneath and next to the Stone of the Pregnant Woman ("Hajjar al-Hibla") and measures around . It is estimated to weigh .
20th century
 Baalbek was connected to the DHP, the French-owned railway concession in Ottoman Syria, on 19 June 1902. It formed a station on the
Baalbek was connected to the DHP, the French-owned railway concession in Ottoman Syria, on 19 June 1902. It formed a station on the standard-gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
line between Riyaq
Rayaq - Haouch Hala ( ar, رياق), also romanization of Arabic, romanized Rayak, is a Lebanon, Lebanese town in the Beqaa Governorate, Beqaa Mohafazat, Governorate near the city of Zahlé. In the early 20th century and up to 1975 and the outbrea ...
to its south and Aleppo (now in Syria) to its north. This Aleppo Railway connected to the Beirut–Damascus Railway
Rail transport in Lebanon began in the 1890s as French Third Republic, French projects under the Ottoman Empire but largely ceased in the 1970s owing to the country's Lebanese Civil War, civil war. The last remaining routes ended for economic reas ...
but—because that line was built to a 1.05-meter gauge
Gauge ( or ) may refer to:
Measurement
* Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments
* Gauge (firearms)
* Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire
** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, ...
—all traffic had to be unloaded and reloaded at Riyaq. Just before the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the population was still around 5000, about 2000 each of Sunnis and Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mo ...
Mutawalis and 1000 Orthodox and Maronites
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the larg ...
. The French general Georges Catroux proclaimed the independence of Lebanon in 1941 but colonial rule continued until 1943. Baalbek still has its railway station but service has been discontinued since the 1970s, originally owing to the Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ar, الحرب الأهلية اللبنانية, translit=Al-Ḥarb al-Ahliyyah al-Libnāniyyah) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities a ...
.
The Roman ruins have been the setting for the long running Baalbek International Festival.
In March 1974, Musa al-Sadr
Musa Sadr al-Din al-Sadr ( ar, موسى صدر الدين الصدر; 4 June 1928 – disappeared 31 August 1978) was an Iranian-born Lebanese scholar and political leader who founded the Amal Movement.
Born in the Chaharmardan neighborhood o ...
announced the launching of the " Movement of the Deprived" in front of a large rally in Baalbek. Its objective was to stand up for Lebanon's neglected Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mo ...
community. He also announced the setting up of military training camps to train villagers in southern Lebanon to protect their homes from Israeli attacks. These camps led to the creation of the Amal Militia. In 1982, at the height of the Israeli invasion, Amal split into two factions over Nabih Berri
Nabih Berri ( ar, نبيه مصطفى بري, translit=Nabīh Muṣṭafā Barriyy, links=hh; born 28 January 1938) is a Lebanese Shia politician who has been serving as Speaker of the Parliament of Lebanon since 1992. He heads the Amal Moveme ...
's acceptance of the American plan to evacuate Palestinians from West Beirut. A large number of dissidents, led by Amal's military commander Hussein Musawi
Husayn Al-Musawi (also Hussein Musawi) is a Lebanese who founded the now-dissolved pro-Iranian Islamist militia Islamic Amal in 1982. He was a Shia from Baalbek.
Musawi was a "chemistry teacher turned militia commander" who became the deputy ...
moved to Baalbek. Once established in the town the group, which was to evolve into Hizbollah
Hezbollah (; ar, حزب الله ', , also transliterated Hizbullah or Hizballah, among others) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and militant group, led by its Secretary-General Hassan Nasrallah since 1992. Hezbollah's paramili ...
, began to work with Iranian Revolutionary Guards, veterans of the Iran Iraq War. The following year the Iranians established their headquarters in the Sheikh Abdullah barracks in Baalbek. Ultimately there were between 1,500 to 2,000 Revolutionary Guards in Lebanon, with outposts further south in the Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mo ...
villages, such as Jebchit
Jebchit ( ar, جبشيت) is a village in the Nabatieh Governorate region of southern Lebanon located north of the Litani River.
History
In 1596, it was named as a village, ''Jibsid'', in the Ottoman empire, Ottoman ''nahiya'' (subdistrict) of S ...
.

Lebanon War
On the evening of 1 August 2006, hundreds of Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) soldiers raided Baalbek and the Dar al-Hikma or Hikmeh Hospital in Jamaliyeh to its north (" Operation Sharp and Smooth"). Their mission was to rescue two captured soldiers,Ehud Goldwasser
Ehud "Udi" Goldwasser ( he, אהוד גולדווסר; 18 July 1975 – 12 July 2006) was an Israeli soldier who was abducted in Israel by Hezbollah along with Eldad Regev on 12 July 2006, sparking the 2006 Lebanon War. His rank was First Sergeant ...
and Eldad Regev
Eldad Regev ( he, אלדד רגב, 16 August 1980 – 12 July 2006) was an Israeli soldier abducted by Hezbollah fighters along with Ehud Goldwasser on 12 July 2006 in Israel near the Lebanese border, sparking the 2006 Lebanon War. His rank ...
, who were abducted by Hezbollah on 12 July 2006. They were transported by helicopter and supported by Apache helicopter
The Boeing AH-64 Apache () is an American twin-turboshaft attack helicopter with a tailwheel-type landing gear arrangement and a tandem cockpit for a crew of two. It features a nose-mounted sensor suite for target acquisition and night visi ...
s and unmanned drones, The IDF was acting on information that Goldwasser and Regev were at the hospital. al-Jazeera and other sources claimed the IDF was attempting to capture senior Hezbollah officials, particularly Sheikh Mohammad Yazbek. The hospital had been empty for four days, the most unwell patients having been transferred and the rest sent home. No Israelis were killed; Five civilians were abducted and interrogated by the Israelis, presumably because one shared his name with Hassan Nasrallah
Hassan Nasrallah ( ar, حسن نصر الله ; born 31 August 1960) is a Lebanese cleric and political leader who has served as the 3rd secretary-general of Hezbollah since his predecessor, Abbas al-Musawi, was assassinated by the Israel De ...
, the secretary general of Hezbollah; they were released on August 21. Another 9 civilians were killed on 7 August by a strike in the middle of Brital
Brital ( ar, بريتال) is a village located in the Baalbek District of the Baalbek-Hermel Governorate in Lebanon. History
In 1838, Eli Smith noted Brital (under the name of ''Bereitan'') as a Metawileh village in the Baalbek area.
Brital has ...
, just south of Baalbek, and by the subsequent attack on the car leaving the scene for the hospital. On 14 August just before the ceasefire took effect, two Lebanese police and five Lebanese soldiers were killed by a drone strike while driving their van around the still-damaged road through Jamaliyeh.
Conservation work at Lebanon's historic sites began in October. The ruins at Baalbek were not directly hit but the effects of blasts during the conflict toppled a block of stones at the Roman ruins and existing cracks in the temples of Jupiter and Bacchus were feared to have widened. Frederique Husseini, director-general of Lebanon's Department of Antiquities, requested $550,000 from Europeans to restore Baalbek's souk and another $900,000 for repairs to other damaged structures.
Ruins
 The Tell Baalbek temple complex, fortified as the town's citadel during the Middle Ages, was constructed from local stone, mostly white
The Tell Baalbek temple complex, fortified as the town's citadel during the Middle Ages, was constructed from local stone, mostly white granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
and a rough white marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
. Over the years, it has suffered from the region's numerous earthquakes, the iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be conside ...
of Christian and Muslim lords, and the reuse of the temples' stone for fortification and other construction. The nearby Qubbat Duris
__NOTOC__
Duris (also Dūris, or Dûris ( ar, دورس), formally Doris and also known by its French language, French spelling Douris) is a village located approximately . southwest of Baalbek in the Bekaa Valley, Lebanon. It is the site of a 13th ...
, a 13th-century Muslim shrine on the old road to Damascus, is built out of granite columns, apparently removed from Baalbek. Further, the jointed columns were once banded together with iron; many were gouged open or toppled by the emirs of Damascus to get at the metal. As late as the 16th century, the Temple of Jupiter still held 27 standing columns out of an original 58; there were only nine before the 1759 earthquakes and six today.
The complex is located on an immense raised plaza erected over an earlier T-shaped base consisting of a podium, staircase, and foundation walls. These walls were built from about 24 monolith
A monolith is a geological feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock, such as some mountains. For instance, Savandurga mountain is a monolith mountain in India. Erosion usually exposes the geological formations, which are often ma ...
s, at their lowest level weighing approximately each. The tallest retaining wall, on the west, has a second course of monoliths containing the famous " Three Stones" ( grc-gre, Τρίλιθον, '' Trílithon''): a row of three stones, each over long, high, and broad, cut from limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
. They weigh approximately each. A fourth, still larger stone is called the Stone of the Pregnant Woman: it lies unused in a nearby quarry from the town. Its weight, often exaggerated, is estimated at . A fifth, still larger stone weighing approximately lies in the same quarry. This quarry was slightly higher than the temple complex, so no lifting was required to move the stones. Through the foundation there run three enormous passages the size of railway tunnels.
The temple complex was entered from the east through the Propylaea (, ''propýlaion'') or Portico, consisting of a broad staircase rising to an arcade of 12 columns flanked by 2 towers. Most of the columns have been toppled and the stairs were entirely dismantled for use in the nearby later wall, but a Latin inscription remains on several of their bases stating that Longinus, a lifeguard of the 1st Parthian Legion
Legio I ''Parthica'' (Latin language, Latin for "1st Parthian Legion") was a Roman legion, legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 197 by the emperor Septimius Severus (r. 193–211) for his forthcoming war against Parthia. The legion's ...
, and Septimius, a freedman, gilded their capitals with bronze in gratitude for the safety of Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
's son Antoninus Caracalla and empress Julia Domna
Julia Domna (; – 217 AD) was Roman empress from 193 to 211 as the wife of Emperor Septimius Severus. She was the first empress of the Severan dynasty. Domna was born in Emesa (present-day Homs) in Roman Syria to an Arab family of priests ...
.
Immediately behind the Propylaeum is a hexagonal forecourt reached through a threefold entrance that was added in the mid-3rd century by the emperor Philip the Arab
Philip the Arab ( la, Marcus Julius Philippus "Arabs"; 204 – September 249) was Roman emperor from 244 to 249. He was born in Aurantis, Arabia, in a city situated in modern-day Syria. After the death of Gordian III in February 244, Philip, ...
. Traces remain of the two series of columns which once encircled it, but its original function remains uncertain. Donne reckoned it as the town's forum. Badly preserved coins of the era led some to believe this was a sacred cypress grove, but better specimens show that the coins displayed a single stalk of grain instead.
The rectangular Great Court to its west covers around and included the main altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paga ...
for burnt offering, with mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
-floored lustration basins to its north and south, a subterranean chamber, and three underground passageways wide by high, two of which run east and west and the third connecting them north and south, all bearing inscriptions suggesting their occupation by Roman soldiers. These were surrounded by Corinthian Corinthian or Corinthians may refer to:
*Several Pauline epistles, books of the New Testament of the Bible:
**First Epistle to the Corinthians
**Second Epistle to the Corinthians
**Third Epistle to the Corinthians (Orthodox)
*A demonym relating to ...
porticoes, one of which was never completed. The columns' bases and capitals were of limestone; the shafts were monoliths of highly polished red Egyptian granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
high. Six remain standing, out of an original 128. Inscriptions attest that the court was once adorned by portraits of Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
's daughter Sabina Sabina may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions
* Sabina (region), region and place in Italy, and hence:
* the now Suburbicarian Diocese of Sabina (-Poggio Mirteto), Italy
* Magliano Sabina, city, Italy
* Pozzaglia Sabina, city, Italy
*Fara Sab ...
, Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
, Gordian, and Velius Rufus Velius may refer to:
* Norbertas Vėlius
Norbertas Vėlius (1 January 1938 in Gulbės, near Šilalė – 23 June 1996 in Vilnius, buried in the Antakalnis Cemetery) was a Lithuanian folklorist specializing in Lithuanian mythology
Lithuania ...
, dedicated by the city's Roman colonists. The entablature was richly decorated but is now mostly ruined. A westward-facing basilica was constructed over the altar during the reign of Theodosius; it was later altered to make it eastward-facing like most Christian churches.
 The Temple of Jupiter—once wrongly credited to Helios—lay at the western end of the Great Court, raised another on a platform reached by a wide staircase. Under the Byzantines, it was also known as the " Trilithon" from the three massive stones in its foundation and, when taken together with the forecourt and Great Court, it is also known as the Great Temple. The Temple of Jupiter proper was circled by a
The Temple of Jupiter—once wrongly credited to Helios—lay at the western end of the Great Court, raised another on a platform reached by a wide staircase. Under the Byzantines, it was also known as the " Trilithon" from the three massive stones in its foundation and, when taken together with the forecourt and Great Court, it is also known as the Great Temple. The Temple of Jupiter proper was circled by a peristyle
In ancient Greek and Roman architecture, a peristyle (; from Greek ) is a continuous porch formed by a row of columns surrounding the perimeter of a building or a courtyard. Tetrastoön ( grc, τετράστῳον or τετράστοον, lit=f ...
of 54 unfluted Corinthian columns: 10 in front and back and 19 along each side. The temple was ruined by earthquakes, destroyed and pillaged for stone under Theodosius, and 8 columns were taken to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
(Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
) under Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
for incorporation into the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
. Three fell during the late 18th century. 6 columns, however, remain standing along its south side with their entablature. Their capitals remain nearly perfect on the south side, while the Beqaa's winter winds have worn the northern faces almost bare. The architrave and frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor ...
blocks weigh up to each, and one corner block over , all of them raised to a height of above the ground. Individual Roman cranes were not capable of lifting stones this heavy. They may have simply been rolled into position along temporary earthen banks from the quarry or multiple cranes may have been used in combination. They may also have alternated sides a little at a time, filling in supports underneath each time. The Julio-Claudian emperors enriched its sanctuary in turn. In the mid-1st century, Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 unti ...
built the tower-altar opposite the temple. In the early 2nd century, Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
added the temple's forecourt, with porticos of pink granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergr ...
shipped from Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ar, أسوان, ʾAswān ; cop, Ⲥⲟⲩⲁⲛ ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the ...
at the southern end of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
.
The Temple of Bacchus
The Temple of Bacchus is part of the Baalbek temple complex located in the broad Al-biqā (Bekaa Valley), Lebanon. The temple complex is considered an outstanding archaeological and artistic site of Imperial Roman Architecture and was inscribed a ...
—once wrongly credited to Jupiter—may have been completed under Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
in the 190s, as his coins are the first to show it beside the Temple of Jupiter. It is the best preserved of the sanctuary's structures, as the other rubble from its ruins protected it. It is enriched by some of the most refined reliefs and sculpture to survive from antiquity. The temple is surrounded by forty-two columns—8 along each end and 15 along each side—nearly in height. These were probably erected in a rough state and then rounded, polished, and decorated in position. The entrance was preserved as late as Pococke and Wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin ...
, but the keystone of the lintel had slid following the 1759 earthquakes; a column of rough masonry was erected in the 1860s or '70s to support it. The 1759 earthquakes also damaged the area around the soffit
A soffit is an exterior or interior architectural feature, generally the horizontal, aloft underside of any construction element. Its archetypal form, sometimes incorporating or implying the projection of beams, is the underside of eaves (t ...
's famed inscription of an eagle, which was entirely covered by the keystone's supporting column. The area around the inscription of the eagle was greatly damaged by the 1759 earthquake. The interior of the temple is divided into a nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
and a adytum
The adyton ( , 'innermost sanctuary, shrine', ) or (Latin) was a restricted area within the cella of a Greek or Roman temple. The ''adyton'' was frequently a small area at the farthest end of the cella from the entrance: at Delphi it measured ...
or sanctuary on a platform raised above it and fronted by 13 steps. The screen between the two sections once held reliefs of Neptune, Triton, Arion and his dolphin, and other marine figures but these have been lost. The temple was used as a kind of donjon
A keep (from the Middle English ''kype'') is a type of fortified tower built within castles during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars have debated the scope of the word ''keep'', but usually consider it to refer to large towers in ...
for the medieval Arab and Turkish fortifications, although its eastern steps were lost sometime after 1688. Much of the portico was incorporated into a huge wall directly before its gate, but this was demolished in July 1870 by Barker on orders from Syria's governor Rashid Pasha. Two spiral staircases in columns on either side of the entrance lead to the roof.
The Temple of Venus—also known as the Circular Temple or Nymphaeum—was added under Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
in the early 3rd century but destroyed under Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
, who raised a basilica in its place. Jessup considered it the "gem of Baalbek". It lies about from the southeast corner of the Temple of Bacchus. It was known in the 19th century as ''El Barbara'' or ''Barbarat el-Atikah'' (St Barbara's), having been used as a Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
church into the 18th century.
The ancient walls of Heliopolis had a circumference of a little less than . Much of the extant fortifications around the complex date to the 13th century reconstruction undertaken by the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
sultan Qalawun
( ar, قلاوون الصالحي, – November 10, 1290) was the seventh Bahri Mamluk sultan; he ruled Egypt from 1279 to 1290.
He was called (, "Qalāwūn the Victorious").
Biography and rise to power
Qalawun was a Kipchak, ancient Turki ...
following the devastation of the earlier defenses by the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
army under Kitbuqa
Kitbuqa Noyan (died 1260), also spelled Kitbogha, Kitboga, or Ketbugha, was an Eastern Christian of the Naimans, a group that was subservient to the Mongol Empire. He was a lieutenant and confidant of the Mongol Ilkhan Hulagu, assisting him ...
. This includes the great southeast tower. The earliest round of fortifications were two walls to the southwest of the Temples of Jupiter and Bacchus. The original southern gateway with two small towers was filled in and replaced by a new large tower flanked by curtains, probably under Buri or Zengi. Bahramshah replaced that era's southwest tower with one of his own in 1213 and built another in the northwest in 1224; the west tower was probably strengthened around the same time. An inscription dates the barbican-like strengthening of the southern entrance to around 1240. Qalawun relocated the two western curtains nearer to the western tower, which was rebuilt with great blocks of stone. The barbican was repaired and more turns added to its approach. From around 1300, no alterations were made to the fortifications apart from repairs such as Sultan Barkuk
Al-Malik Az-Zahir Sayf ad-Din Barquq (Adyghe language, Circassian: Бэркъукъу аз-Захьир Сэфудин; ar, الملك الظاهر سيف الدين برقوق; ruled 1382–1389 and 1390–1399; born in Circassia) was the firs ...
's restoration of the moat in preparation for Timur's arrival.
Material from the ruins is incorporated into a ruined mosque north of downtown and probably also in the Qubbat Duris
__NOTOC__
Duris (also Dūris, or Dûris ( ar, دورس), formally Doris and also known by its French language, French spelling Douris) is a village located approximately . southwest of Baalbek in the Bekaa Valley, Lebanon. It is the site of a 13th ...
on the road to Damascus. In the 19th century, a "shell-topped canopy" from the ruins was used nearby as a mihrab, propped up to show locals the direction of Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow ...
for their daily prayers.
Tomb of Husayn's daughter
Under a white dome further towards town is the tomb of Khawla, daughter ofHussein
Hussein, Hussain, Hossein, Hossain, Huseyn, Husayn, Husein or Husain (; ar, حُسَيْن ), coming from the triconsonantal root Ḥ-S-i-N ( ar, ح س ی ن, link=no), is an Arabic name which is the diminutive of Hassan, meaning "good", " ...
and granddaughter of Ali, who died in Baalbek while Husayn's family was being transported as prisoners to Damascus.
Ecclesiastical history
Heliopolis (in Phoenicia; not to be confused with the Egyptian bishopricHeliopolis in Augustamnica
Heliopolis (I͗wnw, Iunu or 𓉺𓏌𓊖; egy, I͗wnw, 'the Pillars'; cop, ⲱⲛ; gr, Ἡλιούπολις, Hēlioúpοlis, City of the Sun) was a major city of ancient Egypt. It was the capital of the 13th or Heliopolite Nome of Lower Eg ...
) was a bishopric under Roman and Byzantine rule, but it disappeared due to the Islamic rule.
In 1701, Eastern Catholics ( Byzantine Rite) established anew an Eparchy of Baalbek, which in 1964 was promoted to the present Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Baalbek
Melkite Greek Catholic Archeparchy of Baalbek (in Latin: Archeparchia Heliopolitana Graecorum Melkitarum) is a diocese of the Catholic Church immediately subject to the Patriarchate of Antioch of the Melkites. It is currently governed by Archbisho ...
.
Titular see
In the Latin rite, the Ancient diocese was only nominally restored (no later than 1876) asTitular archbishopric
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbish ...
of Heliopolis (Latin) / Eliopoli (Curiate Italian), demoted in 1925 to Episcopal Titular bishopric
A titular see in various churches is an episcopal see of a former diocese that no longer functions, sometimes called a "dead diocese". The ordinary or hierarch of such a see may be styled a "titular metropolitan" (highest rank), "titular archbish ...
, promoted back in 1932, with its name changed (avoiding Egyptian confusion) in 1933 to (non-Metropolitan) Titular archbishopric of Heliopolis in Phoenicia.
The title has not been assigned since 1965. It was held by:
* Titular Archbishop: Luigi Poggi (1876.09.29 – death 1877.01.22) on emeritate (promoted) as former Bishop of Rimini
Rimini ( , ; rgn, Rémin; la, Ariminum) is a city in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy and capital city of the Province of Rimini. It sprawls along the Adriatic Sea, on the coast between the rivers Marecchia (the ancient ''Ariminu ...
(Italy) (1871.10.27 – 1876.09.29)
* Titular Archbishop: Mario Mocenni
Mario Mocenni (22 January 1823—14 November 1904) was an Italian Cardinal (Catholicism), Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church, who served both in Nuncio, the diplomatic service of the Holy See and in the Roman Curia, and was elevated to t ...
(1877.07.24 – 1893.01.16) as papal diplomat : Apostolic Delegate
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international o ...
to Colombia (1877.08.14 – 1882.03.28), Apostolic Delegate to Costa Rica, Nicaragua and Honduras (1877.08.14 – 1882.03.28), Apostolic Delegate to Ecuador (1877.08.14 – 1882.03.28), Apostolic Delegate to Peru and Bolivia (1877.08.14 – 1882.03.28), Apostolic Delegate to Venezuela (1877.08.14 – 1882.03.28), Apostolic Internuncio to Brazil (1882.03.28 – 1882.10.18), created Cardinal-Priest
A cardinal ( la, Sanctae Romanae Ecclesiae cardinalis, literally 'cardinal of the Holy Roman Church') is a senior member of the clergy of the Catholic Church. Cardinals are created by the ruling pope and typically hold the title for life. Col ...
of S. Bartolomeo all'Isola
S is the nineteenth letter of the English alphabet.
S may also refer to:
History
* an Anglo-Saxon charter's number in Peter Sawyer's, catalogue Language and linguistics
* Long s (ſ), a form of the lower-case letter s formerly used where "s ...
(1893.01.19 – 1894.05.18), promoted Cardinal-Bishop
A cardinal ( la, Sanctae Romanae Ecclesiae cardinalis, literally 'cardinal of the Holy Roman Church') is a senior member of the clergy of the Catholic Church. Cardinals are created by the ruling pope and typically hold the title for life. Col ...
of Sabina Sabina may refer to:
Places and jurisdictions
* Sabina (region), region and place in Italy, and hence:
* the now Suburbicarian Diocese of Sabina (-Poggio Mirteto), Italy
* Magliano Sabina, city, Italy
* Pozzaglia Sabina, city, Italy
*Fara Sab ...
(1894.05.18 – death 1904.11.14)
* Titular Archbishop: Augustinus Accoramboni (1896.06.22 – death 1899.05.17), without prelature
* Titular Archbishop: Robert John Seton (1903.06.22 – 1927.03.22), without prelature
*Titular Bishop: Gerald O'Hara
Gerald Patrick Aloysius O'Hara (May 4, 1895 – July 16, 1963) was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He served as an auxiliary bishop in the Archdiocese of Philadelphia (1929-1935), as bishop of the Diocese of Savannah in Georgia ...
(1929.04.26 – 1935.11.26) as Auxiliary Bishop of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city i ...
(Pennsylvania, USA) (1929.04.26 – 1935.11.26), later Bishop of Savannah (USA) (1935.11.26 – 1937.01.05), restyled (only) Bishop of Savannah–Atlanta (USA) (1937.01.05 – 1950.07.12), promoted Archbishop-Bishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
of Savannah (1950.07.12 – 1959.11.12), also Apostolic Nuncio
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international ...
(papal ambassador) to Ireland (1951.11.27 – 1954.06.08), Apostolic Delegate
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international o ...
to Great Britain (1954.06.08 – death 1963.07.16) and Titular Archbishop
A titular bishop in various churches is a bishop who is not in charge of a diocese.
By definition, a bishop is an "overseer" of a community of the faithful, so when a priest is ordained a bishop, the tradition of the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox an ...
of Pessinus
Pessinus ( el, Πεσσινούς or Πισσινούς) was an Ancient city and archbishopric in Asia Minor, a geographical area roughly covering modern Anatolia (Asian Turkey). The site of the city is now the modern Turkish village of Ballıhis ...
(1959.11.12 – 1963.07.16)
* Titular Archbishop: Alcide Marina Alcide Giuseppe Marina, Congregation of the Mission, C.M. (24 March 1887 – 17 September 1950) was an Italian prelate of the Catholic Church who worked as an educator and superior of the Congregation of the Mission, Vincentians until 1936 and then ...
, C.M. (1936.03.07 – death 1950.09.18), mainly as papal diplomat : Apostolic Delegate
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international o ...
to Iran (1936.03.07 – 1945), Apostolic Administrator
An Apostolic administration in the Catholic Church is administrated by a prelate appointed by the pope to serve as the ordinary for a specific area. Either the area is not yet a diocese (a stable 'pre-diocesan', usually missionary apostolic adm ...
of Roman Catholic Apostolic Vicariate of Constantinople
The Apostolic Vicariate of Istanbul ( la, Vicariatus Apostolicus Istanbulensis) is a Roman Catholic apostolic vicariate based in the city of Istanbul in Turkey.Apostolic Nuncio
An apostolic nuncio ( la, nuntius apostolicus; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international ...
to Lebanon (1947 – 1950.09.18)
* Titular Archbishop: Daniel Rivero Rivero (1951 – death 1960.05.23) (born Bolivia) on emeritate, formerly Titular Bishop of Tlous (1922.05.17 – 1931.03.30) as Coadjutor Bishop of Santa Cruz de la Sierra
Santa Cruz de la Sierra (; "Holy Cross of the Mountain Range"), commonly known as Santa Cruz, is the largest city in Bolivia and the capital of the Santa Cruz department.
Situated on the Pirai River in the eastern Tropical Lowlands of Bolivia ...
( Bolivia) (1922.05.17 – 1931.03.30) succeeding as Bishop of Santa Cruz de la Sierra (1931.03.30 – 1940.02.03), Metropolitan Archbishop of Sucre (Bolivia) (1940.02.03 – 1951)
* Titular Archbishop: Raffaele Calabria
Raffaele Calabria (11 December 1906–24 May 1982) was an Italian Catholic Church, Catholic bishop. During his career, he served as Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Otranto, Archbishop of Otranto and Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Benevento, Archbishop ...
(1960.07.12 – 1962.01.01) as Coadjutor Archbishop The term coadjutor (or coadiutor, literally "co-assister" in Latin) is a title qualifier indicating that the holder shares the office with another person, with powers equal to the other in all but formal order of precedence.
These include:
* Coad ...
of Benevento (Italy) (1960.07.12 – 1962.01.01), succeeding as Metropolitan Archbishop of Benevento (1962.01.01 – 1982.05.24); previously Titular Archbishop of Soteropolis
Soterioupolis ( el, Σωτηριούπολις; "City of the Saviour") or Soteropolis (Σωτηρόπολις) was a Byzantine fortress in the southeastern Black Sea coast during the 10th–12th centuries. The name has been suggested to apply to tw ...
(1950.05.06 – 1952.07.10) as Coadjutor Archbishop of Otranto
Otranto (, , ; scn, label=Salentino, Oṭṛàntu; el, label= Griko, Δερεντό, Derentò; grc, Ὑδροῦς, translit=Hudroûs; la, Hydruntum) is a coastal town, port and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce (Apulia, Italy), in a ferti ...
(Italy) (1950.05.06 – 1952.07.10), succeeding as Metropolitan Archbishop of Otranto (Italy) (1952.07.10 – 1960.07.12)
* Titular Archbishop: Ottavio De Liva
Ottavio De Liva (10 June 1911 – 23 August 1965) was an Italian prelate of the Catholic Church who worked in the diplomatic service of the Holy See. Early in his career, in 1950, he was expelled from Czechoslovakia as part of the young Communist ...
(1962.04.18 – death 1965.08.23) as papal diplomat : Apostolic Internuncio to Indonesia (1962.04.18 – 1965.08.23).
Climate
Baalbek has amediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
: ''Csa'') with significant continental influences. It is located in one of the drier regions of the country, giving it an average of 450mm of precipitation (compared with 800-850mm in coastal areas) annually, overwhelmingly concentrated in the months from November to April. Baalbek has hot rainless summers with cool (and occasionally snowy) winters. Autumn and spring are mild and fairly rainy.
Notable people
*Saint Barbara
Saint Barbara ( grc, Ἁγία Βαρβάρα; cop, Ϯⲁⲅⲓⲁ Ⲃⲁⲣⲃⲁⲣⲁ; ; ), known in the Eastern Orthodox Church as the Great Martyr Barbara, was an early Christian Lebanese and Greek saint and martyr. Accounts place her in t ...
(273–306)
* Callinicus of Heliopolis (c. 600 - c. 680), chemist and inventor
* Abd al-Rahman al-Awza'i
Abū ʿAmr ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ibn ʿAmr al-ʾAwzāʿī ( ar, أبو عمرو عبدُ الرحمٰن بن عمرو الأوزاعي) (707–774) was an Islamic scholar, traditionalist and the chief representative and eponym of the ʾAwzāʿī ...
(707–774)
*Qusta ibn Luqa
Qusta ibn Luqa (820–912) (Costa ben Luca, Constabulus) was a Syrian Melkite Christian physician, philosopher, astronomer, mathematician and translator. He was born in Baalbek. Travelling to parts of the Byzantine Empire, he brought back Greek te ...
(820–912), mathematician and translator
* Sheikh Adi ibn Musafir
‘Adī ibn Musāfir ( ku, شێخ ئادی, translit=Şêx Adî, ar, الشيخ عدي بن مسافر born 1072-1078, died 1162) was a Muslim sheikh of Arab origin, considered a Yazidi saint. The Yazidis consider him as an avatar of Tawûsê M ...
(1070s–1162)
* Bahāʾ al-dīn al-ʿĀmilī (1547–1621), Lebanese-Iranian scholar, philosopher, architect, mathematician, astronomer
* Rahme Haider (born 1886), American lecturer from Baalbek
* Khalil Mutran (1872–1949), poet and journalist
* Juliana Awada
María Juliana Awada (born 3 April 1974) is an Argentine businesswoman who served as the First Lady of Argentina from 2015 to 2019. She is the first woman in this role to have received the distinction of the Knight Grand Cross of the Order of I ...
, former First Lady of Argentina.
* Harfush dynasty
In popular culture
*Ameen Rihani
Ameen Rihani (Amīn Fāris Anṭūn ar-Rīḥānī) ( ar, أمين الريحاني / ALA-LC: ''Amīn ar-Rīḥānī''; Freike, Lebanon, November 24, 1876 – September 13, 1940), was a Lebanese American writer, intellectual and political a ...
's ''The Book of Khalid
''The Book of Khalid'' (1911) is a novel by Arab-American writer Ameen Rihani. Composed during a sojourn in the mountains of Lebanon, it is considered to be the first novel by an Arab-American writer in English. His contemporary, Khalil Gibran, i ...
'' (1911), the first English novel by an Arab-American, is set in Baalbek.
* The events of the 1984 novel ''Les fous de Baalbek'' (SAS, #74) by Gérard de Villiers take place in Baalbek.
Twin towns
Baalbek is twinned with: * Bari, Italy * L'Aquila, Italy *Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, Greece
* Yogyakarta
Yogyakarta (; jv, ꦔꦪꦺꦴꦒꦾꦏꦂꦠ ; pey, Jogjakarta) is the capital city of Special Region of Yogyakarta in Indonesia, in the south-central part of the island of Java. As the only Indonesian royal city still ruled by a monarchy, ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
.
Gallery
rail
Rail or rails may refer to:
Rail transport
*Rail transport and related matters
*Rail (rail transport) or railway lines, the running surface of a railway
Arts and media Film
* ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini
* ''Rail'' ( ...
File:Baalbek. General view 04956r.jpg , The ruins of Baalbek facing west from the hexagonal forecourt in the 19th century
File:Colossal Hewn Block, Ancient Quarries Baalbek.jpg , The " Stone of the Pregnant Woman" in the early 20th century, the Temple of Jupiter in the background
See also
*Cities of the ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by ...
* List of Catholic dioceses in Lebanon
* List of colossal sculpture in situ
A colossal statue is one that is more than twice life-size. This is a list of colossal statues and other sculptures that were created, mostly or all carved, and remain ''in situ''. This list includes two colossal stones that were intended to be m ...
* List of megalithic sites
Notes
References
Sources and external links
Google Maps satellite view
* Panoramas of the temples a
an
Discover Lebanon
from the
German Archaeological Institute
The German Archaeological Institute (german: Deutsches Archäologisches Institut, ''DAI'') is a research institute in the field of archaeology (and other related fields). The DAI is a "federal agency" under the Federal Foreign Office of Germany ...
GCatholic – Latin titular see
Baalbeck International Festival
(2006) at ''Al Mashriq'' * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
volume I
volume II
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * & * * * * * * * * * * * Reprinted at Görlitz in 1591. * * * * * * * *
Further reading
* * {{Authority control Lost ancient cities and towns Tourist attractions in Lebanon Populated places in Baalbek District World Heritage Sites in Lebanon Archaeological sites in Lebanon Great Rift Valley Phoenician cities Phoenician sites in Lebanon Coloniae (Roman) Populated places established in the 7th millennium BC Roman sites in Lebanon Tourism in Lebanon 7th-millennium BC establishments Sunni Muslim communities in Lebanon Pre-Pottery Neolithic B