American paddlefish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The American paddlefish (''Polyodon spathula''), also known as a Mississippi paddlefish, spoon-billed cat, or spoonbill, is a species of
 In 1797, French naturalist
In 1797, French naturalist
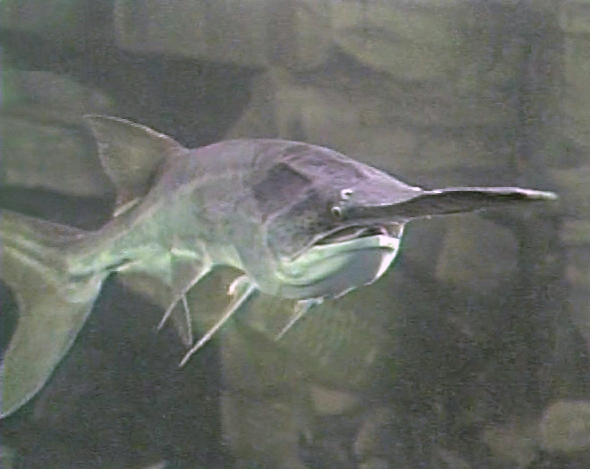
 American paddlefish are among the largest and longest-lived freshwater fishes in North America. They have a shark-like body, average in length, weigh , and can live in excess of thirty years. For most populations the median age is five to eight years and the maximum age is fourteen to eighteen years. The age of American paddlefish is best determined by
American paddlefish are among the largest and longest-lived freshwater fishes in North America. They have a shark-like body, average in length, weigh , and can live in excess of thirty years. For most populations the median age is five to eight years and the maximum age is fourteen to eighteen years. The age of American paddlefish is best determined by
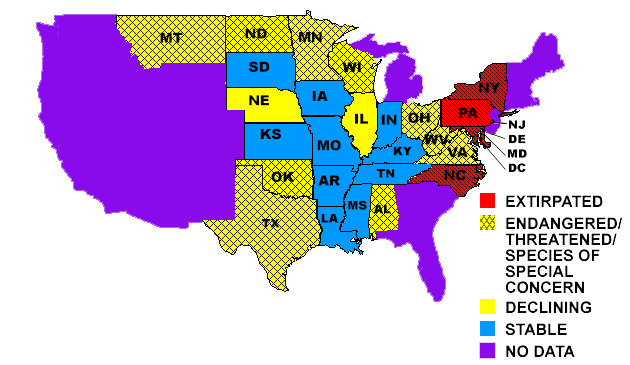 American paddlefish are highly mobile and well adapted to living in rivers. They inhabit many types of riverine habitats throughout much of the Mississippi Valley and adjacent Gulf slope drainages. They occur most frequently in deeper, low current areas such as side channels, oxbows, backwater lakes, bayous, and tailwaters below dams. They have been observed to move more than in a river system.
American paddlefish are endemic to the Mississippi River Basin, historically occurring from the
American paddlefish are highly mobile and well adapted to living in rivers. They inhabit many types of riverine habitats throughout much of the Mississippi Valley and adjacent Gulf slope drainages. They occur most frequently in deeper, low current areas such as side channels, oxbows, backwater lakes, bayous, and tailwaters below dams. They have been observed to move more than in a river system.
American paddlefish are endemic to the Mississippi River Basin, historically occurring from the
 Advancements in biotechnology have created a global commercial market for the
Advancements in biotechnology have created a global commercial market for the

The Paddlefish: An American Treasure
nbsp;– documentary chronicling the biology and life history of paddlefish
Study: 96 percent of vertebrates descended from common ancestor with 'sixth sense'
{{Authority control Polyodontidae Freshwater fish of the United States Fish of Canada Fish described in 1792 Articles containing video clips
ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ...
. It is the last living species of paddlefish
Paddlefish (family Polyodontidae) are a family of ray-finned fish belonging to order Acipenseriformes, and one of two living groups of the order alongside sturgeons (Acipenseridae). They are distinguished from other fish by their elongated rost ...
(Polyodontidae). This family is most closely related to the sturgeon
Sturgeon (from Old English ultimately from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European *''str̥(Hx)yón''-) is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the ...
s; together they make up the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Acipenseriformes
Acipenseriformes is an order (biology), order of basal (phylogenetics), basal Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes that includes living and fossil sturgeons and paddlefishes (Acipenseroidei), as well as the extinct family (biology), families C ...
, which are one of the most primitive living groups of ray-finned fish. Fossil records of other paddlefish species date back 125 million years to the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
, with records of ''Polyodon'' extending back 65 million years to the early Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), ...
. The American paddlefish is a smooth-skinned freshwater fish
Freshwater fish are fish species that spend some or all of their lives in bodies of fresh water such as rivers, lakes, ponds and inland wetlands, where the salinity is less than 1.05%. These environments differ from marine habitats in many wa ...
with an almost entirely cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
skeleton and a paddle-shaped rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
** podium
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ...
(snout), which extends nearly one-third its body length. It has been referred to as a freshwater shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
because of its heterocercal
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
tail or caudal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
resembling that of sharks, though it is not closely related. The American paddlefish is a highly derived fish because it has evolved specialised adaptations, such as filter feeding
Filter feeders are aquatic animals that acquire nutrients by feeding on organic matters, food particles or smaller organisms (bacteria, microalgae and zooplanktons) suspended in water, typically by having the water pass over or through a spe ...
. Its rostrum and cranium are covered with tens of thousands of sensory receptors for locating swarms of zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
, its primary food source. The only other species of paddlefish that survived to modern times was the Chinese paddlefish
The Chinese paddlefish (''Psephurus gladius''; : literal translation: "white sturgeon"), also known as the Chinese swordfish, is an Extinction, extinct species of fish that was formerly native to the Yangtze and Yellow River basins in China. Wit ...
(''Psephurus gladius''), last sighted in 2003 in the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
in China and considered to have gone extinct no later than 2010.
The American paddlefish is native to the Mississippi River basin and once moved freely under the relatively unaltered conditions that existed prior to the early 1900s. It commonly inhabited large, free-flowing rivers, braided channels, backwaters, and oxbow lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or stream pool, pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is meander cutoff, cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. The word "oxbow" can also refer to a U-shaped bend in a river or stream, whether ...
s throughout the Mississippi River drainage basin, and adjacent Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Tex ...
drainages. Its peripheral range extended into the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
, with occurrences in Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is shared on the north and east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the south and west by the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the lake is derived from early French ex ...
and Lake Helen in Canada until about 1917. American paddlefish populations have declined dramatically primarily because of overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
, habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
. Poaching
Poaching is the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set against the huntin ...
has also been a contributing factor to its decline and is liable to continue to be so as long as the demand for caviar
Caviar or caviare is a food consisting of salt-cured roe of the family Acipenseridae. Caviar is considered a delicacy and is eaten as a garnish or spread. Traditionally, the term caviar refers only to roe from wild sturgeon in the Caspi ...
remains strong. Naturally occurring American paddlefish populations have been extirpated
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinctions.
Local extinctions mark a chan ...
from most of their peripheral range, as well as from New York, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
. They have been reintroduced in the Allegheny, Monongahela and Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
river systems in western Pennsylvania. However, their current range has been reduced to the Mississippi and Missouri River
The Missouri River is a river in the Central United States, Central and Mountain states, Mountain West regions of the United States. The nation's longest, it rises in the eastern Centennial Mountains of the Bitterroot Range of the Rocky Moun ...
tributaries and Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. T ...
drainage basin. American paddlefish are currently found in twenty-two states in the U.S., and are protected under state, federal and international laws.
Taxonomy, etymology and evolution
 In 1797, French naturalist
In 1797, French naturalist Bernard Germain de Lacépède
Bernard-Germain-Étienne de La Ville-sur-Illon, comte de Lacépède or La Cépède (; 26 December 17566 October 1825) was a French natural history, naturalist and an active freemason. He is known for his contribution to the Comte de Buffon's g ...
established the genus ''Polyodon'' for paddlefish, which today includes a single extant species, ''Polyodon spathula''. Lacépède disagreed with Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre
Abbé Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre (1752, Aveyron – 20 September 1804, Saint-Geniez-d'Olt) was a French zoology, zoologist who contributed sections on cetaceans, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and insects to the ''Tableau encyclopéd ...
's description in (1788), which had suggested that paddlefish were a species of shark. When Lacépède established his binomial name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
''Polydon feuille'' he was unaware the species had already been described in 1792 by taxonomist Johann Julius Walbaum
Johann Julius Walbaum (30 June 1724 – 21 August 1799) was a German physician, natural history, naturalist and fauna taxonomist.
Works
Walbaum was from Greifswald. As an ichthyologist, he was the first to describe many previously unknown fish s ...
, who had named it as ''Squalus spathula''. Consequently ''spathula'' has priority as the specific name (and 'Walbaum, 1792' is the taxonomic authority to be cited). But Walbaum's generic name ''Squalus
''Squalus'' is a genus of dogfish sharks in the family (biology), family Squalidae. Commonly known as spurdogs, these sharks are characterized by smooth dorsal fin spines, teeth in upper and lower fish jaw, jaws similar in size, caudal peduncle ...
'' was already in use for dogfish, so Lacépède's ''Polyodon'' is the valid name for this paddlefish genus. Hence Polyodon spathula'' (Walbaum, 1792)' is the accepted full scientific name of the American paddlefish.
The American paddlefish is the sole surviving species in the paddlefish family, the Polyodontidae
Paddlefish (family Polyodontidae) are a family of ray-finned fish belonging to order Acipenseriformes, and one of two living groups of the order alongside sturgeons (Acipenseridae). They are distinguished from other fish by their elongated rost ...
. This is the sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
to the sturgeons
Sturgeon (from Old English ultimately from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European *''str̥(Hx)yón''-) is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the ...
(family Acipenseridae); evidence from DNA sequences suggest that their last common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
lived roughly 140 million years ago. Together these families compose the Acipenseriformes
Acipenseriformes is an order (biology), order of basal (phylogenetics), basal Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes that includes living and fossil sturgeons and paddlefishes (Acipenseroidei), as well as the extinct family (biology), families C ...
, an order of basal ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ...
es. Paddlefish have a long fossil record dating back to the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
125 million years ago. American paddlefish are often referred to as primitive fish, or relict species, because of morphological characteristics that they retain from some of their early fossil ancestors. These characteristics include a skeleton composed primarily of cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
, and a deeply forked heterocercal
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
(spine extending into the upper lobe) caudal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
similar to that of shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s, although they are not closely related.
The family Polyodontidae comprises six known species: three fossil species from western North America, one fossil species from China, one recently extinct species from China (the Chinese paddlefish
The Chinese paddlefish (''Psephurus gladius''; : literal translation: "white sturgeon"), also known as the Chinese swordfish, is an Extinction, extinct species of fish that was formerly native to the Yangtze and Yellow River basins in China. Wit ...
, ''Psephurus gladius''; last recorded 2003), and the single extant species, the American paddlefish, native to the Mississippi River Basin in the United States. DNA sequences suggest the Chinese and American paddlefishes diverged about 68 million years ago. The oldest fossils of paddlefish belonging to '' Polyodon'' are those of '' P. tuberculata'' from the Lower Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), ...
Tullock Member of the Fort Union Formation in Montana, dating to around 65 million years ago. An elongated rostrum is a morphological characteristic of Polyodontidae, but only the genus ''Polyodon'' has characteristics adapted specifically for filter feeding, including the jaw, gill arches, and cranium. The gill rakers of American paddlefish are composed of extensive comb-like filaments believed to have inspired the etymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of the genus name, ''Polyodon'', a Greek compound word meaning "many toothed". Adult American paddlefish are actually toothless, although numerous small teeth less than were found in a juvenile paddlefish measuring . The name ''spathula'' references the elongated, paddle-shaped snout or rostrum. Compared to Chinese paddlefish and fossil genera, American paddlefish (and the fossil relative ''P. tuberculata'') are considered to be highly derived because of their specialised adaptations.
Unlike the planktivorous American paddlefish, Chinese paddlefish were strong swimmers, grew larger, and were opportunistic piscivore
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that primarily eats fish. Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evolution (via water-bound amphibians during the Devonian period); insectivory came next; then in time, the more terrestrially adapted repti ...
s that fed on small fishes and crustaceans. Some distinct morphological differences of Chinese paddlefish include a narrower, sword-like rostrum, and a protrusible mouth. They also had fewer, thicker gill rakers than American paddlefish.
Description
 American paddlefish are among the largest and longest-lived freshwater fishes in North America. They have a shark-like body, average in length, weigh , and can live in excess of thirty years. For most populations the median age is five to eight years and the maximum age is fourteen to eighteen years. The age of American paddlefish is best determined by
American paddlefish are among the largest and longest-lived freshwater fishes in North America. They have a shark-like body, average in length, weigh , and can live in excess of thirty years. For most populations the median age is five to eight years and the maximum age is fourteen to eighteen years. The age of American paddlefish is best determined by dentary
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone ...
studies, a process which usually occurs on fish harvested during snagging season, a popular sport fishing activity in certain parts of the U.S. The dentary is removed from the lower jawbone, cleaned of any remaining soft tissue, and cross-sectioned to expose the annual rings. The dentary rings are counted in much the same way a tree is aged. Dentary studies suggest that some individuals can live 60 years or longer, and that females typically live longer and grow larger than males.
American paddlefish are smooth-skinned and almost entirely cartilaginous. Their eyes are small and directed laterally. They have a large, tapering operculum flap, a large mouth, and a flat, paddle-shaped rostrum that measures approximately one-third of their body length. During the initial stages of development from embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
to hatchling
In oviparous biology, a hatchling is a newly hatched fish, amphibian, reptile, or bird. A group of mammals called monotremes lay eggs, and their young are hatchlings as well.
Fish
Fish hatchlings generally do not receive parental care, similar t ...
, American paddlefish have no rostrum. It begins to form shortly after hatching. The rostrum is an extension of the cranium, not of the upper and lower jaws or olfactory system
The olfactory system, is the sensory nervous system, sensory system used for the sense of smell (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses directly associated with specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system ...
as with the long snouts of other fish. Other distinguishing characteristics include a deeply forked heterocercal caudal fin and dull coloration, often with mottling, ranging from bluish gray to black dorsally
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
grading to a whitish underbelly.
Feeding ecology and physiology
Scientists began to debate the function of the American paddlefish's rostrum when the species was described in the late 1700s. They had once believed it was used to excavate bottom substrate or functioned as a balancing mechanism and navigational aid. However, laboratory experiments in 1993 that utilized advanced technology in the field ofelectron microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing i ...
have established conclusively that the rostrum of American paddlefish is covered with tens of thousands of sensory receptors. These receptors are morphologically similar to the ampullae of Lorenzini
Ampullae of Lorenzini (: ''ampulla'') are electroreceptors, sense organs able to detect electric fields. They form a network of mucus-filled pores in the skin of Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish (sharks, Ray (fish), rays, and chimaeras) and of ...
of sharks and rays, and are indeed passive ampullary-type electroreceptors used by American paddlefish to detect plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
. Clusters of electroreceptors also cover the head and operculum flaps. The diet of the American paddlefish consists primarily of zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
. Examples of animals in the ''P. spathula'' diet are copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s, cladocerans such as ''Daphnia pulex
''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. ...
'', and ephemeropteran nymphs. Their electroreceptors can detect weak electrical fields that signal not only the presence of zooplankton, but also the individual feeding and swimming movements of zooplankton appendages. When a swarm of zooplankton is detected, the paddlefish swims forward continuously with its mouth wide open, forcing water over the gill rakers to filter out prey. Such feeding behavior is considered ram suspension-feeding. Further research has indicated that the electroreceptor of the paddlefish may serve as a navigational aid for obstacle avoidance.
American paddlefish have small undeveloped eyes that are directed laterally. Unlike most fishes, American paddlefish hardly respond to overhead shadows or changes in illumination. Electroreception appears to have largely replaced vision as a primary sensory modality, which indicates a reliance on electroreceptors for detecting prey. However, the rostrum is not their only means of food detection. Some reports suggest a damaged rostrum would render American paddlefish less capable of foraging efficiently to maintain good health, but laboratory experiments and field research indicate otherwise. As well as electroreceptors on the rostrum, American paddlefish have sensory pores covering nearly half of the skin surface extending from the rostrum to the top of the head down to the tips of the operculum flaps. Studies have indicated that American paddlefish with damaged or abbreviated rostrums are still able to forage and maintain good health.
Reproduction and life cycle
American paddlefish are long-lived, sexually late maturingpelagic fish
Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs. ...
. Females do not begin spawning
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is ...
until they are seven to ten years old, some as late as sixteen to eighteen years old. Females do not spawn every year; rather they spawn every second or third year. Males spawn more frequently, usually every year or every other year beginning around age seven, some as late as nine or ten years of age.
American paddlefish begin their upstream spawning migration sometime during early spring; some begin in late fall. They spawn on silt-free gravel bars that would otherwise be exposed to air or covered by very shallow water were it not for the rises in the river from snow melt and annual spring rains that cause flooding. Although availability of preferred spawning habitat is essential, there are three precise environmental events that must occur before American paddlefish will spawn. The water temperature must be from ; the lengthened photoperiod which occurs in spring triggers biological and behavioral processes that are dependent on increasing day length; and there must be a proper rise and flow in the river before a successful spawn can occur. Historically, American paddlefish did not spawn every year because the precise environmental events occurred just once every 4 or 5 years.
American paddlefish are broadcast spawners, also referred to as mass spawners or synchronous spawners. Gravid
In biology and medicine, gravidity and parity are the number of times a female has been pregnant (gravidity) and carried the pregnancies to a viable gestational age (parity). These two terms are usually coupled, sometimes with additional terms, t ...
females release their eggs into the water over bare rocks or gravel at the same time males release their sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
. Fertilization occurs externally. The eggs become sticky after they are released into the water and will attach to the bottom substrate. Incubation varies depending on water temperature, but in water the eggs will hatch into larval fish in about seven days. After hatching, the larval fish drift downstream into areas of low flow velocity where they forage on zooplankton.
Young American paddlefish are poor swimmers which makes them susceptible to predation. Therefore, rapid first-year growth is important to their survival. Fry can grow about per week, and by late July the fingerlings are around long. Their rate of growth is variable and highly dependent on food abundance. Higher growth rates occur in areas where food is not limited. The feeding behavior of fingerlings is quite different from that of older juveniles and adults. They capture individual plankton one by one, which requires detection and location of individual ''Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the Order (biology), order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their Saltation (gait), ...
'' on approach, followed by an intercept maneuver to capture the selected prey. By late September fingerlings have developed into juveniles, and are around long. After the 1st year their growth rate slows and is highly variable. Studies indicate that by age 5 their growth rate averages around per year depending on the abundance of food and other environmental influences.
Habitat and distribution
 American paddlefish are highly mobile and well adapted to living in rivers. They inhabit many types of riverine habitats throughout much of the Mississippi Valley and adjacent Gulf slope drainages. They occur most frequently in deeper, low current areas such as side channels, oxbows, backwater lakes, bayous, and tailwaters below dams. They have been observed to move more than in a river system.
American paddlefish are endemic to the Mississippi River Basin, historically occurring from the
American paddlefish are highly mobile and well adapted to living in rivers. They inhabit many types of riverine habitats throughout much of the Mississippi Valley and adjacent Gulf slope drainages. They occur most frequently in deeper, low current areas such as side channels, oxbows, backwater lakes, bayous, and tailwaters below dams. They have been observed to move more than in a river system.
American paddlefish are endemic to the Mississippi River Basin, historically occurring from the Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
and Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States located in the northwest corner of Wyoming, with small portions extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U ...
rivers in the northwest to the Ohio and Allegheny rivers of the northeast; the headwaters of the Mississippi River south to its mouth, from the San Jacinto River in the southwest to the Tombigbee and Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
rivers of the southeast. They were extirpated from New York, Maryland and Pennsylvania, as well as from much of their peripheral range in the Great Lakes region, including Lake Huron and Lake Helen in Canada. In 1991, Pennsylvania implemented a reintroduction program utilizing hatchery
A hatchery is a facility where eggs are hatched under artificial conditions, especially those of fish, poultry or even turtles. It may be used for ''ex situ'' conservation purposes, i.e. to breed rare or endangered species under controlled ...
-reared American paddlefish in an effort to establish self-sustaining populations in the upper Ohio and lower Allegheny rivers. In 1998, New York initiated a stocking program upstream in the Allegheny Reservoir above Kinzua Dam, and a second stocking in 2006 in Conewango Creek, a relatively unaltered section of their historic range. Reports of free ranging adults captured by gill nets have since been documented in Pennsylvania and New York, but there is no evidence of natural reproduction. They are currently found in 22 states in the US, and are protected under state and federal laws. There are 13 states that allow commercial or sport fishing for American paddlefish.
Human interaction
Propagation and culture
The artificial propagation of American paddlefish began with the efforts of the Missouri Department of Conservation during the early 1960s, and focused primarily on maintenance of the sport fishery. However, it was the growing importance of American paddlefish for their meat androe
Roe, ( ) or hard roe, is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooking, c ...
that became the catalyst for further development of culture techniques for aquaculture in the United States. Artificial propagation requires broodstock which, because of the late sexual maturation of American paddlefish, are initially obtained from the wild and brought into a hatchery
A hatchery is a facility where eggs are hatched under artificial conditions, especially those of fish, poultry or even turtles. It may be used for ''ex situ'' conservation purposes, i.e. to breed rare or endangered species under controlled ...
environment. The fish are injected with LH-RH hormone to stimulate spawning. The number of eggs a female may produce depends on the size of the fish and can range anywhere from 70,000 to 300,000 eggs. Unlike most teleosts, the oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
branches of American paddlefish and sturgeons are not directly attached to the ovaries
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocr ...
; rather, they open dorsally into the body cavity. To determine the status of progression toward maturation, ova staging is performed. The process begins with a minor procedure that involves a small abdominal incision from which to extract a few sample oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ger ...
s. The oocytes are boiled in water for a few minutes until the yolk is hardened, and then they are cut in half to expose the nucleus. The exposed nucleus is examined under a microscope to determine stage of maturity.
Once maturation is confirmed, one of three procedures is used to extract the eggs from a female paddlefish. The three procedures are:
# the traditional hand-stripping method, considered to be time-consuming and laborious;
# Caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because va ...
, a relatively quick surgical method of extracting eggs through a abdominal incision which, though considered faster than hand stripping, can involve time-consuming suturing and an incision resulting in muscular stress and poor suture retention which lowers survival rate; and;
# MIST (minimally invasive surgical technique), which is the fastest of the three procedures because it requires less handling of the fish and eliminates the need for suturing. A small internal incision is made in the dorsal area of the oviduct, which allows direct stripping of eggs from the body cavity through the gonopore
A gonopore, sometimes called a gonadopore, is a genital pore in many invertebrates. Hexapods, including insects, have a single common gonopore, except mayflies, which have a pair of gonopores. More specifically, in the unmodified female, it is ...
bypassing the oviductal funnels.
A spermiating male indicates successful production of mature spermatozoa
A spermatozoon (; also spelled spermatozoön; : spermatozoa; ) is a motile sperm cell (biology), cell produced by male animals relying on internal fertilization. A spermatozoon is a moving form of the ploidy, haploid cell (biology), cell that is ...
which results in the release of large volumes of milt over the course of three to four days. Milt is collected by inserting a short plastic tube with syringe attached into the urogenital opening of the male and applying light suction with the syringe to draw the milt. The collected milt is diluted in water just prior to adding it to the eggs and the combination is gently stirred for about a minute to achieve fertilization. Fertilized eggs are adhesive and demersal
The demersal zone is the part of the sea or ocean (or deep lake) consisting of the part of the water column near to (and significantly affected by) the seabed and the benthos. The demersal zone is just above the benthic zone and forms a layer o ...
, therefore if incubation is to take place in a flow-through hatching jar, the eggs must be treated to prevent clumping. Incubation usually takes anywhere from five to twelve days.
Hybridization
A 2020 paper reported that eggs from threeRussian sturgeon
The Russian sturgeon (''Huso gueldenstaedtii''), also known as the diamond sturgeon or Danube sturgeon, is a species of fish in the family Acipenseridae. It is found in Azerbaijan, Bulgaria, Georgia, Iran, Kazakhstan, Romania, Russia, Turkey, Tur ...
s were crossbred with American paddlefish using sperm from four male paddlefish, resulting in hybrids called sturddlefish
The sturddlefish is a hybrid of the American paddlefish (''Polyodon spathula'') and the Russian sturgeon (''Acipenser gueldenstaedtii''), accidentally created by researchers in 2019 and announced in 2020. Obtaining living hybrids through breedi ...
, a blend of the two names. The offspring had a survival rate of 62–74% and on average reached after a year of growth. This was the first time such fish from different families were successfully crossbred. Their last common ancestor is estimated to have lived 140 million years ago.
Global commercial market
 Advancements in biotechnology have created a global commercial market for the
Advancements in biotechnology have created a global commercial market for the polyculture
In agriculture, polyculture is the practice of growing more than one crop species together in the same place at the same time, in contrast to monoculture, which had become the dominant approach in developed countries by 1950. Traditional example ...
of American paddlefish. In 1970, American paddlefish were stocked in several rivers in Europe and Asia. Introduction
Introduction, The Introduction, Intro, or The Intro may refer to:
General use
* Introduction (music), an opening section of a piece of music
* Introduction (writing), a beginning section to a book, article or essay which states its purpose and g ...
began when five thousand hatched larvae from Missouri hatcheries in the United States were exported to the former Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
for aquacultural utilization. Reproduction was successful in 1988 and 1989, and resulted in the exportation of juveniles to Romania and Hungary. American paddlefish are now being raised in Ukraine, Germany, Austria, the Czech Republic, and the Plovdiv and Vidin regions in Bulgaria. In May 2006, specimens of different sizes and weights were caught by professional fisherman near Prahovo in the Serbian part of the Danube River
The Danube ( ; see also other names) is the second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important riv ...
.
In 1988, fertilized American paddlefish eggs and larvae from Missouri hatcheries were first introduced into China. Since that time, China imports approximately 4.5million fertilized eggs and larvae every year from hatcheries in Russia and the United States. Some American paddlefish are polycultured in carp ponds and sold to restaurants while others are cultured for brood stock and caviar
Caviar or caviare is a food consisting of salt-cured roe of the family Acipenseridae. Caviar is considered a delicacy and is eaten as a garnish or spread. Traditionally, the term caviar refers only to roe from wild sturgeon in the Caspi ...
production. China has also exported American paddlefish to Cuba, where they are farmed for caviar production.
Sport fishing
American paddlefish are a popular sport fish where their populations are sufficient to allow such activity. Areas where there are no self-sustaining populations rely on state and federal restocking programs to maintain a viable fishery. A 2009 report includes the following states as allowing American paddlefish sport fishing per their respective state and federal regulations: Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota and Tennessee. Since American paddlefish are filter-feeders, they will not take bait or lures, and must be caught by snagging. The official state record in Kansas is an American paddlefish snagged in 2004 that weighed . In Montana, an American paddlefish was snagged in 1973 weighing . In North Dakota, one snagged in 2024 weighed . The largest American paddlefish on record was captured in West Okoboji Lake, Iowa, in 1916 by a spear fisherman; it measured and weighed an estimated .Population declines

Overfishing and habitat destruction
American paddlefish populations have declined dramatically, primarily as a result of overfishing and habitat destruction. In 2004 they were listed as Vulnerable (VU A3de ver 3.1) on theIUCN Red List of Threatened Species
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological spe ...
. In 2022 the status category was changed to VU A2cd throughout their range as the result of a U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service assessment. The assessment concluded that "an overall population size reduction of at least 30% may occur within the next 10 years or three generations due to actual or potential levels of exploitation and the effects of introduced taxa, pollutants, competitors or parasites." American paddlefish are filter-feeding pelagic fish that require large, free-flowing rivers with braided channels, backwater areas, oxbow lakes that are rich in zooplankton, and gravel bars for spawning. Series of dams on rivers such as those constructed on the Missouri River
The Missouri River is a river in the Central United States, Central and Mountain states, Mountain West regions of the United States. The nation's longest, it rises in the eastern Centennial Mountains of the Bitterroot Range of the Rocky Moun ...
have impounded large populations of American paddlefish, and blocked their upstream migration to spawning shoals. Channelization and groyne
A groyne (in the U.S. groin) is a rigid aquatic structure built perpendicularly from an ocean shore (in coastal engineering) or a river bank, interrupting water flow and limiting the movement of sediment. It is usually made out of wood, concrete ...
s or wing dykes have caused the narrowing of rivers and altered flow, destroying crucial spawning and nursery habitat. As a result, most impounded populations are not self-sustaining and must be stocked to maintain a viable sport fishery.
Zebra mussels
Zebra mussel
The zebra mussel (''Dreissena polymorpha'') is a small freshwater mussel, an Aquatic animal, aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Dreissenidae. The species originates from the lakes of southern Russia and Ukraine, but has been accidentally Intro ...
infestations in the Mississippi River, Great Lakes and other Midwest rivers are also negatively affecting American paddlefish populations. Zebra mussels are an invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
well adapted for explosive population growth as a result of high rates of fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the capability to produc ...
and recruitment. As filter feeders, zebra mussels rely on plankton and can filter significant amounts of phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
and zooplankton from the water, altering the availability of an important food source for paddlefish and native unionidae
The Unionidae are a Family (biology), family of freshwater mussels, the largest in the order Unionida, the bivalve molluscs sometimes known as river mussels, or simply as unionids.
The range of distribution for this family is world-wide. It is a ...
. A few days after the fertilization of zebra mussel eggs, a microscopic larva emerges called a veliger
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of sea snails and freshwater snails, as well as most bivalve molluscs (clams) and tusk shells.
Description
The veliger is the characteristic larva of the gastropod, bivalve and scaphopod taxono ...
. During this initial stage of development, which usually lasts a few weeks, veligers are able to swim freely in the water column with other microscopic animals comprising zooplankton. Veligers are poor swimmers, making them susceptible to predation by any animal that feeds on zooplankton. However, natural predation of zebra mussels at any stage of development has not made a significant contribution to the long-term reduction of zebra mussel populations.
Poaching and overexploitation
Poaching
Poaching is the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights.
Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set against the huntin ...
has been a contributing factor to declining populations of American paddlefish in the states where they are commercially exploited, particularly while the demand for caviar
Caviar or caviare is a food consisting of salt-cured roe of the family Acipenseridae. Caviar is considered a delicacy and is eaten as a garnish or spread. Traditionally, the term caviar refers only to roe from wild sturgeon in the Caspi ...
remains strong. Since the 1980s, a trade embargo
Economic sanctions or embargoes are commercial and financial penalties applied by states or institutions against states, groups, or individuals. Economic sanctions are a form of coercion that attempts to get an actor to change its behavior throu ...
on Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
restricted imports of the highly sought after and most expensive beluga caviar from the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
, limiting U.S. sources of caviar. The most sought-after caviar is produced by sturgeons in the Northern Caspian Sea, but overfishing and poaching have exhausted the supply. American sturgeon and paddlefish populations were targeted as likely substitutes.
The roe
Roe, ( ) or hard roe, is the fully ripe internal egg masses in the ovaries, or the released external egg masses, of fish and certain marine animals such as shrimp, scallop, sea urchins and squid. As a seafood, roe is used both as a cooking, c ...
of American paddlefish can be processed into caviar similar in taste, color, size and texture to sevruga sturgeon caviar from the Caspian Sea. Several cases of mislabeled American paddlefish roe sold as Caspian Sea caviar have been prosecuted by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. State and federal regulations restricting the harvest of American paddlefish populations in the wild, and the illegal trafficking of their roe, are strictly enforced. Related violations such as the illegal transport of American paddlefish roe have resulted in convictions with substantial fines and prison sentences. American paddlefish are also protected under Appendix II of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
Convention may refer to:
* Convention (norm), a custom or tradition, a standard of presentation or conduct
** Treaty, an agreement in international law
** Convention (political norm), uncodified legal or political tradition
* Convention (meeting ...
(CITES) meaning international trade in the species (including parts and derivatives) is regulated.
Extinction of Chinese paddlefish
The primary reasons for the decline of the now-extinct Chinese paddlefish are similar to those of American paddlefish, which include overfishing, the construction of dams, and destruction of habitat. The last confirmed sighting of a live Chinese paddlefish was from theYangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
on January 24, 2003. From 2006 to 2008, scientists conducted surveys in an effort to locate the fish. They used several boats, deployed 4,762 setlines, 111 anchored setlines and 950 drift nets covering on the upper Yangtze River, most of which lies within the protected area of the Upper Yangtze National Nature Reserve. They did not catch a single fish. They also used hydroacoustic equipment to monitor sounds in the water, but were unable to confirm the presence of paddlefish. The species is believed to have gone extinct before 2005 and no later than 2010. The IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
assessed the species as extinct in 2019, formally publishing this categorisation in 2022.
References
External links
The Paddlefish: An American Treasure
nbsp;– documentary chronicling the biology and life history of paddlefish
Study: 96 percent of vertebrates descended from common ancestor with 'sixth sense'
{{Authority control Polyodontidae Freshwater fish of the United States Fish of Canada Fish described in 1792 Articles containing video clips