|
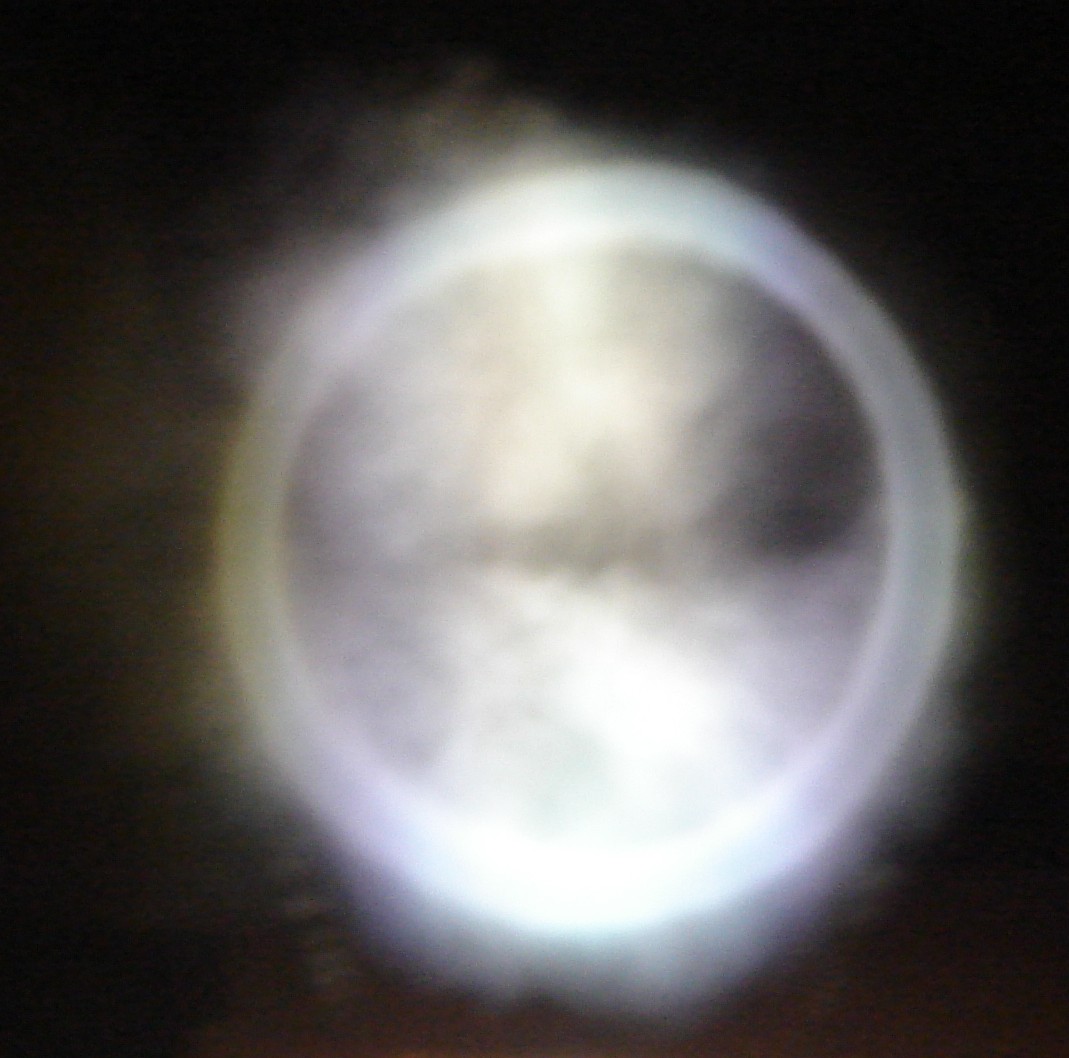
Vortex Ring
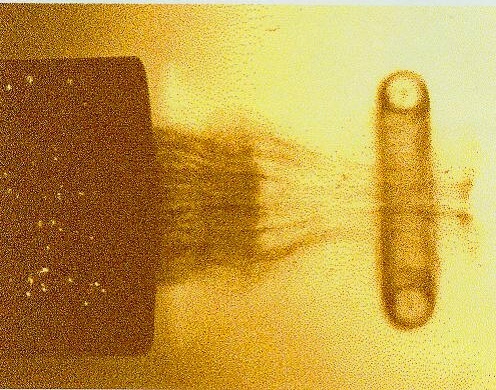
A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a fluid; that is, a region where the fluid mostly spins around an imaginary axis line that forms a closed loop. The dominant flow in a vortex ring is said to be toroidal, more precisely poloidal. Vortex rings are plentiful in turbulent flows of liquids and gases, but are rarely noticed unless the motion of the fluid is revealed by suspended particles—as in the smoke rings which are often produced intentionally or accidentally by smokers. Fiery vortex rings are also a commonly produced trick by fire eaters. Visible vortex rings can also be formed by the firing of certain artillery, in mushroom clouds, in microbursts, and rarely in volcanic eruptions. A vortex ring usually tends to move in a direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring and such that the inner edge of the ring moves faster forward than the outer edge. Within a stationary body of fluid, a vortex ring can travel for relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vortex Ring Gun Schlierin
In fluid dynamics, a vortex (: vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex carries so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Wave
In fluid dynamics, a wind wave, or wind-generated water wave, is a surface wave that occurs on the free surface of bodies of water as a result of the wind blowing over the water's surface. The contact distance in the direction of the wind is known as the '' fetch''. Waves in the oceans can travel thousands of kilometers before reaching land. Wind waves on Earth range in size from small ripples to waves over high, being limited by wind speed, duration, fetch, and water depth. When directly generated and affected by local wind, a wind wave system is called a wind sea. Wind waves will travel in a great circle route after being generated – curving slightly left in the southern hemisphere and slightly right in the northern hemisphere. After moving out of the area of fetch and no longer being affected by the local wind, wind waves are called '' swells'' and can travel thousands of kilometers. A noteworthy example of this is waves generated south of Tasmania during heavy wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lolliguncula Brevis
''Lolliguncula brevis'', or the Atlantic brief squid, is a small species of squid in the Loliginidae family. It is found in shallow parts of the western Atlantic Ocean. Distribution The Atlantic brief squid occurs most frequently in shallow waters along the eastern seaboard of the United States as far north as Delaware. It has also been found in Argentina, Brazil, the British Virgin Islands, Colombia, Mexico, Panama, Puerto Rico, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago and Venezuela. Description left, ''Lolliguncula brevis'' The female Atlantic brief squid is about 11 cm long and the male 9 cm. The maximum mantle length recorded was 12 cm. The basic colour is dark reddish-brown to yellow-brown and there are many chromatophores on the upper surface which enable the squid to change colour. The mantle is widest in the middle and tapers to a rounded point at the back. The fins are wider than they are long, rounded and about half the length of the mantle. The mantle has thick muscul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (26 June 182417 December 1907), was a British mathematician, Mathematical physics, mathematical physicist and engineer. Born in Belfast, he was the Professor of Natural Philosophy (Glasgow), professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, where he undertook significant research on the mathematical analysis of electricity, was instrumental in the formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and contributed significantly to unifying physics, which was then in its infancy of development as an emerging academic discipline. He received the Royal Society's Copley Medal in 1883 and served as its President of the Royal Society, president from 1890 to 1895. In 1892, he became the first scientist to be elevated to the House of Lords. Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in Lord Kelvin's honour. While the existence of a coldest possible temperature, absolute zero, was known before his work, Kelvin d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Jet
In fluid dynamics, a synthetic jet flow—is a type of jet flow, which is made up of the surrounding fluid. Synthetic jets are produced by periodic ejection and suction of fluid from an opening. This oscillatory motion may be driven by a piston or diaphragm inside a cavity among other ways. (http://www.crcpress.com/product/isbn/9781439868102 ) A ''synthetic jet flow'' was so named by Ari Glezer since the flow is "synthesized" from the surrounding or ambient fluid. Producing a convectional jet requires an external source of fluid, such as piped-in compressed air or plumbing for water. Synjet devices Synthetic jet flow can be developed in a number of ways, such as with an electromagnetic driver, a piezoelectric driver, or even a mechanical driver such as a piston. Each moves a membrane or diaphragm up and down hundreds of times per second, sucking the surrounding fluid into a chamber and then expelling it. Although the mechanism is fairly simple, extremely fast cycling require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vortex Ring Toy
An air vortex cannon is a toy that releases doughnut-shaped air vortices — similar to smoke rings but larger, stronger and invisible. The vortices can ruffle hair, disturb papers or blow out candles after travelling several metres. An air vortex cannon can be made easily at home, from just a cardboard box.The Vortex Cannon - Student Science at YouTube. Accessed February 2013. Air cannons are used in some s such as to spook or surprise visitors. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoke Rings
A smoke ring is a visible vortex ring formed by smoke in a clear atmosphere. Smokers may blow smoke rings from the mouth, intentionally or accidentally. Smoke rings may also be formed by sudden bursts of fire (such as lighting and immediately putting out a cigarette lighter), by shaking a smoke source (such as an incense stick) up and down, by firing certain types of artillery, or by the use of special devices, such as vortex ring guns and vortex ring toys. The head of a mushroom cloud is a large smoke ring. A smoke ring is commonly formed when a puff of smoke is suddenly injected into clear air, especially through a narrow opening. The outer parts of the puff are slowed by the still air (or by edges of the opening) relative to the central part, imparting it the characteristic poloidal flow pattern. The smoke makes the ring visible, but does not significantly affect the flow. The same phenomenon occurs with any fluid, producing vortex rings which are invisible but o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kutta Condition
The Kutta condition is a principle in steady-flow fluid dynamics, especially aerodynamics, that is applicable to solid bodies with sharp corners, such as the trailing edges of airfoils. It is named for German mathematician and aerodynamicist Martin Kutta. Kuethe and Schetzer state the Kutta condition as follows:A body with a sharp trailing edge which is moving through a fluid will create about itself a circulation of sufficient strength to hold the rear stagnation point at the trailing edge. In fluid flow around a body with a sharp corner, the Kutta condition refers to the flow pattern in which fluid approaches the corner from above and below, meets at the corner, and then flows away from the body. None of the fluid flows around the sharp corner. The Kutta condition is significant when using the Kutta–Joukowski theorem to calculate the lift created by an airfoil with a sharp trailing edge. The value of circulation of the flow around the airfoil must be that value which would c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear (fluid)
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress or force per unit area is: \tau = ,where is the force applied and is the cross-sectional area. The area involved corresponds to the material face (geometry), face parallel to the applied force vector, i.e., with surface normal vector perpendicular to the force. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as:\tau_w := \mu\left.\frac\_,where is the dynamic viscosity, is the flow velocity, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orifice Plate
An orifice plate is a device used for measuring flow rate, reducing pressure or restricting flow (in the latter two cases it is often called a '). Description An orifice plate is a thin plate with a hole in it, which is usually placed in a pipe. When a fluid (whether liquid or gaseous) passes through the orifice, its pressure builds up slightly upstream of the orifice but as the fluid is forced to converge to pass through the hole, the velocity increases and the fluid pressure decreases. A little downstream of the orifice the flow reaches its point of maximum convergence, the ''vena contracta'' (see drawing to the right) where the velocity reaches its maximum and the pressure reaches its minimum. Beyond that, the flow expands, the velocity falls and the pressure increases. By measuring the difference in fluid pressure across tappings upstream and downstream of the plate, the flow rate can be obtained from Bernoulli's equation using coefficients established from extensive research. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension (physics), tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. Gerridae, water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to Cohesion (chemistry), cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |