|
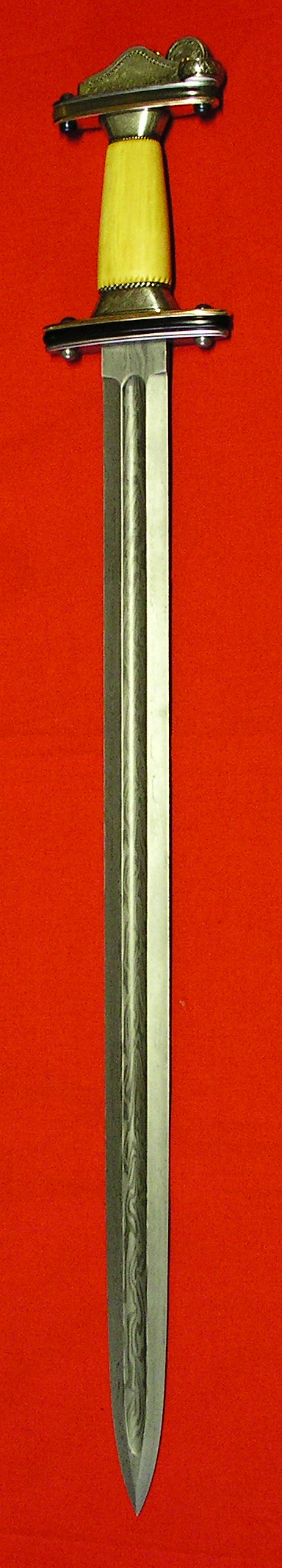
Quillons
On a sword, the crossguard, or cross-guard, the individual bars on either side known as quillon, is a bar of metal at right angles to the blade, placed between the blade and the hilt. The crossguard was developed in the European sword around the 10th century for the protection of the wielder's hand. The earliest forms were the crossguard variant of the Spatha used by the Huns, the so-called Pontic swords. There are many examples of crossguards on Sasanian Persian Swords beginning from the early 3rd century. They might be the oldest examples. The crossguards were not only used to counter enemy attacks, but also to get a better grip on the sword. They were later seen in late Viking swords, and is a standard feature of the Norman sword of the 11th century and of the knightly arming sword throughout the high and late medieval period. Early crossguards were straight metal bars, sometimes tapering towards the outer ends. While this simple type was never discontinued, more elaborate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilt
The hilt (rarely called a haft or shaft) of a knife, dagger, sword, or bayonet is its handle, consisting of a guard, grip and pommel. The guard may contain a crossguard or quillons. A tassel or sword knot may be attached to the guard or pommel. Pommel The pommel (Anglo-Norman "little apple") is an enlarged fitting at the top of the handle. They were originally developed to prevent the sword from slipping from the hand. From around the 11th century in Europe they became heavy enough to be a counterweight to the blade. This gave the sword a point of balance not too far from the hilt allowing a more fluid fighting style. Depending on sword design and swordsmanship style, the pommel may also be used to strike the opponent (e.g., using the Mordhau technique). Pommels have appeared in a wide variety of shapes, including oblate spheroids, crescents, disks, wheels, and animal or bird heads. They are often engraved or inlayed with various designs and occasionally gilt and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical arming sword with crossguard. The word '' sword'' conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
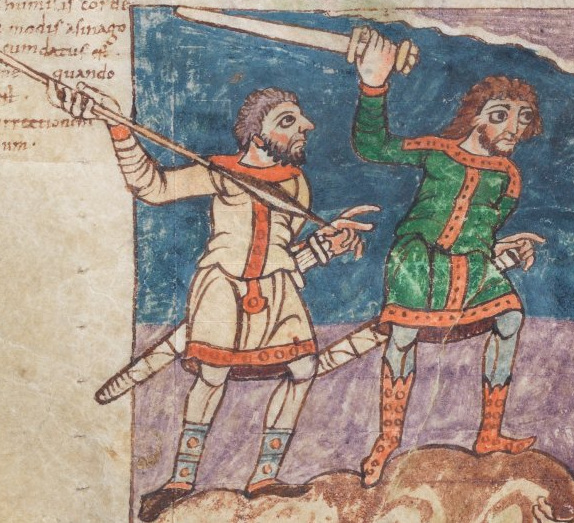
Spatha
The spatha was a type of straight and long sword, measuring between 0.5 and 1 m (19.7 and 39.4 in), with a handle length of between 18 and 20 cm (7.1 and 7.9 in), in use in the territory of the Roman Empire during the 1st to 6th centuries AD. Later swords, from the 7th to 10th centuries, like the Viking swords, are recognizable derivatives and sometimes subsumed under the term ''spatha''. The Roman ''spatha'' was used in war and in gladiatorial fights. The ''spatha'' of literature appears in the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD as a weapon used by presumably Celtic auxiliaries and gradually became a standard heavy infantry weapon, relegating the ''gladius'' to use as a light infantry weapon. The ''spatha'' apparently replaced the ''gladius'' in the front ranks, giving the infantry more reach when thrusting. While the infantry version had a long point, versions carried by the cavalry had a rounded tip that prevented accidental stabbing of the cavalryman's own foot or ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Sword
The Viking Age sword (also Viking sword) or Carolingian sword is the type of sword prevalent in Western and Northern Europe during the Early Middle Ages. The Viking Age or Carolingian-era sword developed in the 8th century from the Merovingian sword more specifically, the Frankish production of swords in the 6th to 7th century and during the 11th to 12th century in turn gave rise to the knightly sword of the Romanesque period. Terminology Although popularly called "Viking sword", this type of sword was produced in the Frankish Empire during the Carolingian era. The association of the name "Viking" with these swords is due to the disappearance of grave goods in Christian Francia in the 8th century, due to which the bulk of sword blades of Frankish manufacture of this period were found in pagan burials of Viking Age Scandinavia, imported by trade, ransom payment or looting, while continental European finds are mostly limited to stray finds in riverbeds. Swords of the 8th to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Sword
The spatha was a type of straight and long sword, measuring between 0.5 and 1 m (19.7 and 39.4 in), with a handle length of between 18 and 20 cm (7.1 and 7.9 in), in use in the territory of the Roman Empire during the 1st to 6th centuries AD. Later swords, from the 7th to 10th centuries, like the Viking swords, are recognizable derivatives and sometimes subsumed under the term ''spatha''. The Roman ''spatha'' was used in war and in gladiatorial fights. The ''spatha'' of literature appears in the Roman Empire in the 1st century AD as a weapon used by presumably Celtic auxiliaries and gradually became a standard heavy infantry weapon, relegating the ''gladius'' to use as a light infantry weapon. The ''spatha'' apparently replaced the ''gladius'' in the front ranks, giving the infantry more reach when thrusting. While the infantry version had a long point, versions carried by the cavalry had a rounded tip that prevented accidental stabbing of the cavalryman's own foot or ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arming Sword
In the European High Middle Ages, the typical sword (sometimes academically categorized as the knightly sword, arming sword, or in full, knightly arming sword) was a straight, double-edged weapon with a single-handed, cruciform (i.e., cross-shaped) hilt and a blade length of about . This type is frequently depicted in period artwork, and numerous examples have been preserved archaeologically. The high medieval sword of the Romanesque period (10th to 13th centuries) developed gradually from the Viking sword of the 9th century. In the Late Medieval period (14th and 15th centuries), late forms of these swords continued to be used, but often as a sidearm, at that point called "arming swords" and contrasting with the two-handed, heavier longswords. Though the majority of late-medieval arming swords kept their blade properties from previous centuries, there are also surviving specimens from the 15th century that took the form of a late-medieval estoc, specialised for use against mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rain-guard
A rain-guard or chappe is a piece of leather fitted to the crossguard of European swords of the later medieval period. The purpose of this leather is not entirely clear, but it seems to have originated as a part of the scabbard, functioning as a lid when the sword was in the scabbard. The rain-guard presumably originated in the 13th century but did not become universal until the 14th. Oakeshott (1960) is aware of one preserved specimen of c. 1250. The feature was ubiquitous throughout the 15th century and into the early 16th century, but they seem to fall out of use later in the 16th century. The main problem in researching the development of this feature is the fact that it is lost to decomposition in all swords recovered archaeologically. A few originals have survived from the late medieval period; otherwise, research is largely based on depictions in paintings or etchings (e.g. well represented in works by Albrecht Dürer) and effigies (a detailed specimen is shown in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
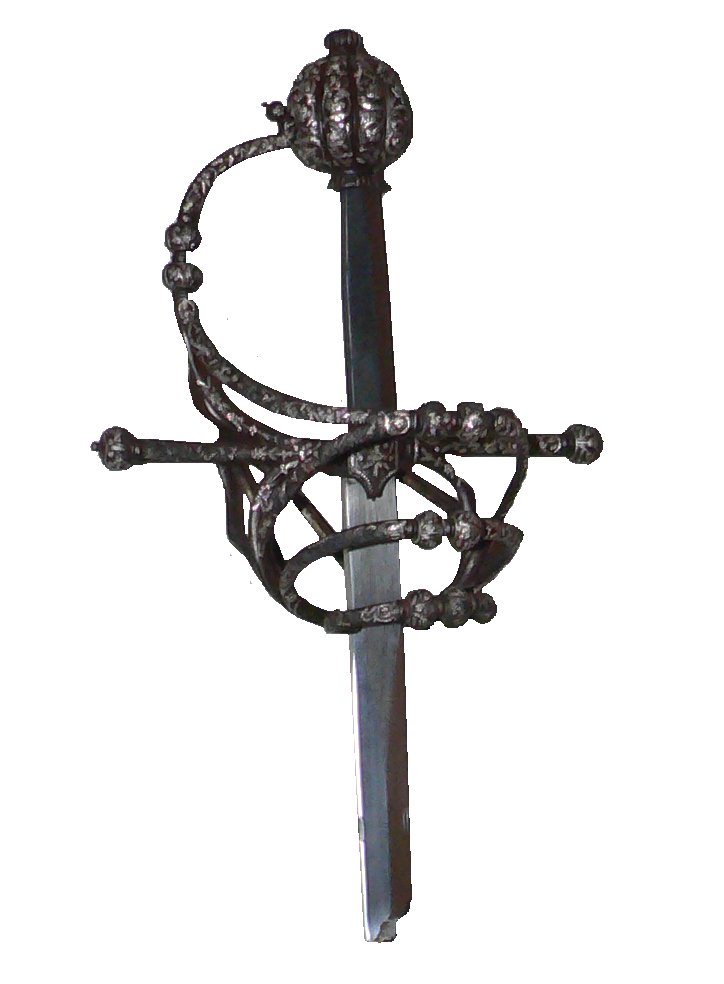
Basket Hilt
The basket-hilted sword is a sword type of the early modern era characterised by a basket-shaped guard that protects the hand. The basket hilt is a development of the quillons added to swords' crossguards since the Late Middle Ages. In modern times, this variety of sword is also sometimes referred to as the broadsword. The basket-hilted sword was generally in use as a military sword, in contrast with the rapier, the slim duelling sword worn with civilian dress during the same period, although each did find some use in both military and civilian contexts. A further distinction applied by arms historians and collectors is that a true broadsword possesses a double-edged blade, while similar wide-bladed swords with a single sharpened edge and a thickened back are called backswords. Various forms of basket-hilt were mounted on both broadsword and backsword blades. One of the weapon types in the modern German dueling sport of ("academic fencing") is the basket-hilted . Morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ewart Oakeshott
Ronald Ewart Oakeshott (25 May 1916 – 30 September 2002) was a British illustrator, collector, and amateur historian who wrote prodigiously on medieval arms and armour. He was a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries, a Founder Member of the Arms and Armour Society, and the Founder of the Oakeshott Institute. He created a classification system of the medieval sword, the Oakeshott typology, a systematic organization of medieval weaponry. Biography Ronald Ewart Oakeshott was born in 1916. His uncle Jeffery Farnol wrote romance novels and swashbucklers and also had a collection of antique swords, through which the young Oakeshott became interested in swords. After leaving Dulwich College, Oakeshott studied at the Central School of Art in London. He worked at Carlton Studios and at A.E. Johnson Ltd as a commercial artist, while still being interested in collecting arms and armour. During the 1930s and 1940s, antique swords could still be acquired relatively cheaply and Oakeshot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |