|
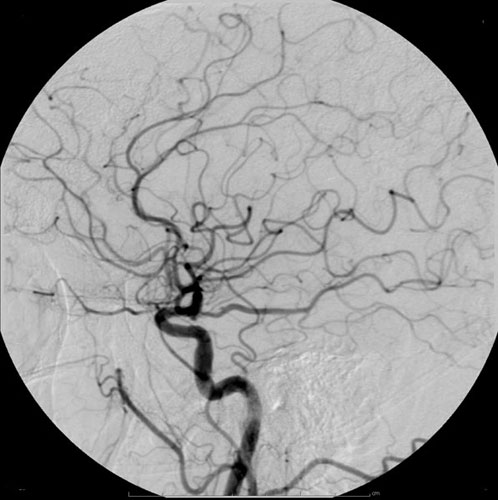
Angiogram
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. With time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance it is no longer necessary to use a contrast. The word itself comes from the Greek words ἀνγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessels is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely. The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography and newer vascular imaging t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure. Typically a catheter is inserted into a large artery (such as the femoral artery) and threaded through the circulatory system to the Common carotid artery, carotid artery, where a contrast agent is injected. A series of radiographs are taken as the contrast agent spreads through the brain's arterial system, then a second series as it reaches the venous system. For some applications, cerebral angiography may yield better images than less invasive methods such as computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography. In addition, cerebral angiography allows certain treatments to be performed immediately, based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computed Tomography Angiography
Computed tomography angiography (also called CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, images are created to look for blockages, aneurysms (dilations of walls), Dissection (medical), dissections (tearing of walls), and stenosis (narrowing of vessel). CTA can be used to visualize the vessels of the heart, the aorta and other large blood vessels, the lungs, the kidneys, the head and neck, and the arms and legs. CTA can also be used to localise arterial or venous bleed of the gastrointestinal system. Medical uses CTA can be used to examine blood vessels in many key areas of the body including the brain, kidneys, pelvis, and the lungs. Coronary CT angiography Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is the use of CT angiography to assess the coronary artery, arteries of the heart. The patient receives an intravenous injection of radiocont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radionuclide Angiography
Radionuclide angiography is an area of nuclear medicine which specialises in imaging to show the functionality of the right and left ventricles of the heart, thus allowing informed diagnostic intervention in heart failure. It involves use of a radiopharmaceutical, injected into a patient, and a gamma camera for acquisition. A MUGA scan (multigated acquisition) involves an acquisition triggered (gated) at different points of the cardiac cycle. MUGA scanning is also called equilibrium radionuclide angiocardiography, radionuclide ventriculography (RNVG), or gated blood pool imaging, as well as SYMA scanning (synchronized multigated acquisition scanning). This mode of imaging uniquely provides a cine type of image of the beating heart, and allows the interpreter to determine the efficiency of the individual heart valves and chambers. MUGA/Cine scanning represents a robust adjunct to the now more common echocardiogram. Mathematics regarding acquisition of cardiac output (''Q' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isotope Perfusion Scanning
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the lymphatic system or blood vessels to an organ or a tissue. The practice of perfusion scanning is the process by which this perfusion can be observed, recorded and quantified. The term perfusion scanning encompasses a wide range of medical imaging modalities.http://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/cardiac-perfusion-scan#1 www.webmd.com/ Applications With the ability to ascertain data on the blood flow to vital organs such as the heart and the brain, doctors are able to make quicker and more accurate choices on treatment for patients. Nuclear medicine has been leading perfusion scanning for some time, although the modality has certain pitfalls. It is often dubbed 'unclear medicine' as the scans produced may appear to the untrained eye as just fluffy and irregular patterns. More recent developments in CT and MRI have meant clearer images and solid data, such as graphs depicting blood flow, and blood volume charted over a fixed period of time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lucien Campeau
Lucien Campeau (June 20, 1927March 15, 2010) was a Canadian cardiologist. He was a full professor at the Université de Montréal The Université de Montréal (; UdeM; ) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university's main campus is located in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood of Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce on M .... He is best known for performing the world's first transradial coronary angiogram. Campeau was one of the founding staff of the Montreal Heart Institute, joining in 1957. He is also well known for developing the Canadian Cardiovascular Society grading of angina pectoris. Education Campeau received his M.D. degree from the University of Laval in 1953 and completed a fellowship in Cardiology at Johns Hopkins Hospital from 1956 to 1957. He later became a professor at University of Montreal in 1961 and was one of the co-founders of the Montreal Heart Institute. In his lifetime, Campeau was awarded the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arteriovenous Malformations
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. Usually congenital, this vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually as a cerebral AVM), but can appear anywhere in the body. The symptoms of AVMs can range from none at all to intense pain or bleeding, and they can lead to other serious medical problems. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of AVMs vary according to their location. Most neurological AVMs produce few to no symptoms. Often the malformation is discovered as part of an autopsy or during treatment of an unrelated disorder (an " incidental finding"); in rare cases, its expansion or a micro-bleed from an AVM in the brain can cause epilepsy, neurological deficit, or pain. The most general symptoms of a cerebral AVM include headaches and epileptic seizures, with more specific symptoms that normally depend on its location and the individual, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for intra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. The femoral artery proximal to the origin of the deep femoral artery is referred to as the ''common femoral artery'', whereas the femoral artery distal to this origin is referred to as the ''superficial femoral artery''. Structure The femoral artery represents the continuation of the external iliac artery beyond the inguinal ligament underneath which the vessel passes to enter the thigh. The vessel passes under the inguinal ligament just medial of the midpoint of this ligament, midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
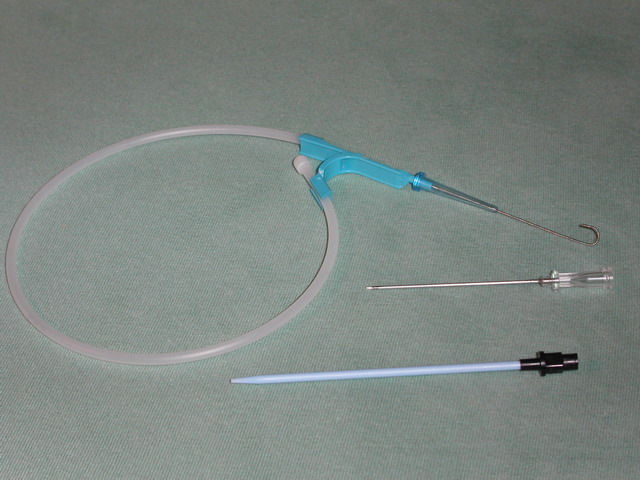
Seldinger Technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organ (anatomy), organs. It is eponym, named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Sweden, Swedish radiology, radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. Uses The Seldinger technique is used for angiography, insertion of chest drains and central venous catheters, insertion of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, PEG tubes using the push technique, insertion of the leads for an artificial pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and numerous other interventional medical procedures. Complications The initial puncture is with a sharp instrument, and this may lead to hemorrhage or perforation of the organ in question. Infection is a possible complication, and hence asepsis is practiced during most Seldinger procedures. Loss of the guidewire into the cavity or blood vessel is a significant and generally preventable com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sousa Pereira
Sousa refers to * John Philip Sousa (1854–1932), American composer of marches Sousa also may refer to: People * Sousa (surname), including other Portuguese variants such as Souza, de Sousa, D'Souza, etc. * João Sousa, Portuguese tennis player * Paulo Sousa, Portuguese football manager * Souza (footballer, born 1975), José Ivanaldo de Souza, Brazilian football attacking midfielder * Souza (footballer, born 1977), Sergio Roberto Pereira de Souza, Brazilian football midfielder * Souza (footballer, born 1979), Willamis de Souza Silva, Brazilian former football midfielder and television pundit * Souza (footballer, born 1982), Rodrigo de Souza Cardoso, Brazilian football striker * Souza (footballer, born 1988), Elierce Barbosa de Souza, Brazilian football defensive midfielder * Souza (footballer, born 2006), João Victor de Souza Menezes, Brazilian football left-back * Sousa (Brazilian footballer), Van Basty Sousa e Silva, (born 1994), Brazilian football midfielder * Daniel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fausto Lopo De Carvalho
Fausto Lopo Patrício de Carvalho (15 May 1890 – 23 May 1970), more commonly known as Fausto Lopo de Carvalho, was a Portuguese pulmonologist specialising in phthisiology, and the developer of pulmonary angiography in 1931, with Egas Moniz and Almeida Lima. He was the son of eminent phthisiologist Lopo de Carvalho (founder of the first sanatorium in Portugal, in Guarda), and his wife Leopoldina dos Anjos Patrício de Carvalho. He studied at the University of Coimbra, earning a degree in medicine with the highest possible grade (20 out of a possible 20) in 1916; after completing his medical studies he worked at the Guarda Sanatorium under his father's guidance, where he prepared his thesis for a doctorate, entitled '' Artificial Pneumothorax''. He taught Medical Propaedeutics, first at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra and later at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Lisbon, until 1934, when he was appointed to the newly created Chair of Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reynaldo Dos Santos
Reynaldo dos Santos (3 December 1880 – 6 May 1970) was a Portuguese physician, writer, and art historian. As a physician, he was a pioneer in the fields of vascular surgery and urology; as an art historian, he published numerous works on 15th-century Portuguese art, including on the Manueline style and on the paintings of Nuno Gonçalves. Biography Reynaldo dos Santos was born in 1880 to Clemente José dos Santos (himself a physician) and Maria Amélia Pinheiro Santos, in the family home in Rua das Varinas, Vila Franca de Xira, a town in the outskirts of Lisbon. He concluded his primary and secondary studies in this town, before enrolling at the Medico-Surgical School in Lisbon, from which he graduated in 1903. Between 1902 and 1905, he was abroad in Paris and the main surgical centres of the United States, in Boston, Chicago, Rochester, Baltimore, Philadelphia, and New York. He earned his doctorate in Medicine in 1906, with his thesis titled "''Aspectos Cirúrgicos das Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |