Angiogram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Angiography or arteriography is a
RadiologyInfo
for patients: Angiography procedures
from Angioplasty.Org
C-Arms types
Several types of C-Arms
Coronary CT angiography by Eugene Lin
{{Authority control Cardiac imaging Projectional radiography Vascular procedures
medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
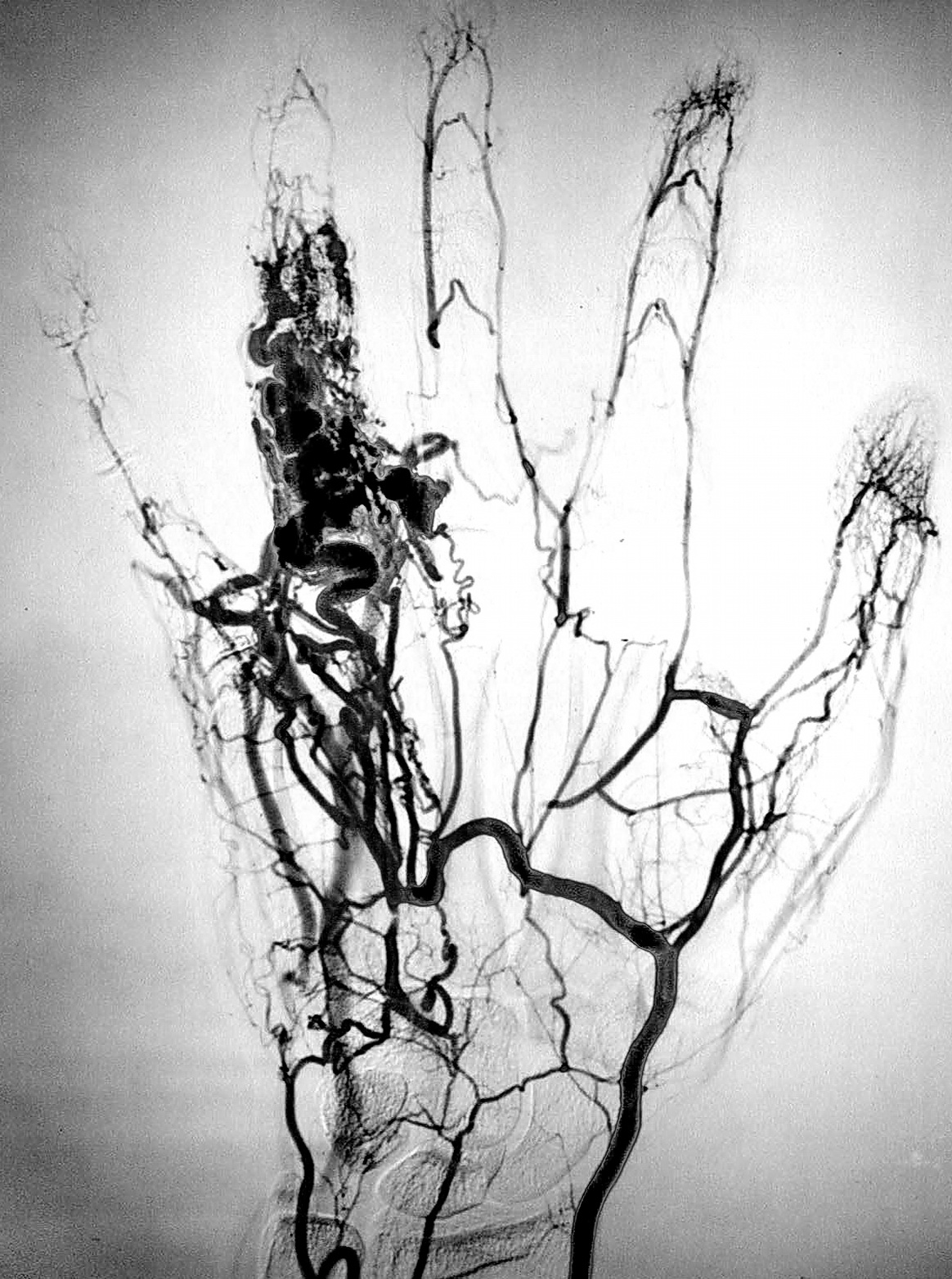
technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
, vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and feta ...
s, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
based techniques such as fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see t ...
. With time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance it is no longer necessary to use a contrast.
The word itself comes from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
words ἀνγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (bi ...
s is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely.
The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography
Radionuclide angiography is an area of nuclear medicine which specialises in imaging to show the functionality of the right and left ventricles of the heart, thus allowing informed diagnostic intervention in heart failure. It involves use of a ...
and newer vascular imaging techniques such as CO2 angiography, CT angiography and MR angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate ...
. The term ''isotope angiography'' has also been used, although this more correctly is referred to as isotope perfusion scanning.
History
The technique was first developed in 1927 by the Portuguese physician and neurologist Egas Moniz at theUniversity of Lisbon
The University of Lisbon (ULisboa; ) is a public university, public research university in Lisbon, and Portugal's largest university. It was founded in 1911, but the university's present structure dates to the 2013 merger of the former Universit ...
to provide contrasted X-ray cerebral angiography
Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms.
It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portugues ...
in order to diagnose several kinds of nervous diseases, such as tumors, artery disease and arteriovenous malformations. Moniz is recognized as the pioneer in this field. He performed the first cerebral angiogram in Lisbon in 1927, and Reynaldo dos Santos performed the first aortogram in the same city in 1929. In fact, many current angiography techniques were developed by the Portuguese at the University of Lisbon. For example, in 1932, Lopo de Carvalho performed the first pulmonary angiogram via venous puncture of the superior member. In 1948 the first cavogram was performed by Sousa Pereira. With the introduction of the Seldinger technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organ (anatomy), organs. It is eponym, named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Sweden, Swedish ...
in 1953, the procedure became markedly safer as no sharp introductory devices needed to remain inside the vascular lumen. Radial access technique for angiography can be traced back to 1989, when Lucien Campeau
Lucien Campeau (June 20, 1927March 15, 2010) was a Canadian cardiologist. He was a full professor at the Université de Montréal
The Université de Montréal (; UdeM; ) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, C ...
first cannulated the radial artery to perform a coronary angiogram.
Technique
Depending on the type of angiogram, access to the blood vessels is gained most commonly through thefemoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters ...
, to look at the left side of the heart and at the arterial system
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
; or the jugular
The jugular veins () are veins that take blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Struc ...
or femoral vein
In the human body, the femoral vein is the vein that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It is a deep vein that begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) as the continuation of the popliteal v ...
, to look at the right side of the heart and at the venous system. Using a system of guide wires and catheters
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are man ...
, a type of contrast agent
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
(which shows up by absorbing the X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s), is added to the blood to make it visible on the X-ray images.
The X-ray images taken may either be still, displayed on an image intensifier
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light proce ...
or film, or motion images. For all structures except the heart, the images are usually taken using a technique called digital subtraction angiography or DSA. Images in this case are usually taken at 2–3 frames per second, which allows the interventional radiologist to evaluate the flow of the blood through a vessel or vessels. This technique "subtracts" the bones and other organs so only the vessels filled with contrast agent can be seen. The heart images are taken at 15–30 frames per second, not using a subtraction technique. Because DSA requires the patient to remain motionless, it cannot be used on the heart. Both these techniques enable the interventional radiologist or cardiologist to see stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
(blockages or narrowings) inside the vessel which may be inhibiting the flow of blood and causing pain.
After the procedure has been completed, if the femoral technique is applied, the site of arterial entry is either manually compressed, stapled shut, or sutured in order to prevent access-site complications.
Uses
Coronary angiography
One of the most common angiograms performed is to visualize thecoronary arteries
The coronary arteries are the arteries, arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the Cardiac muscle, heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any ...
. A long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
is used to administer the X-ray contrast agent at the desired area to be visualized. The catheter is threaded into an artery in the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, techn ...
, and the tip is advanced through the arterial system into the major coronary artery. X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
images of the transient radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iod ...
distribution within the blood flowing inside the coronary arteries allows visualization of the size of the artery openings. The presence or absence of atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis, characterized by development of abnormalities called lesions in walls of arteries. This is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and is driven by eleva ...
or atheroma
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal accumulation of material in the tunica intima, inner layer of an arterial wall.
The material consists of mostly macrophage, macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variabl ...
within the walls of the arteries
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in ...
cannot be clearly determined.
Coronary angiography can visualize coronary artery stenosis
Stenosis () is the abnormal narrowing of a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing ...
, or narrowing of the blood vessel. The degree of stenosis can be determined by comparing the width of the lumen of narrowed segments of blood vessel with wider segments of adjacent vessel.
The coronary angiography is performed under local anaesthesia. The patient is awake during the procedure. An incision is made in the groin, wrist, or arm, and a catheter is inserted into the artery through it. An X-ray is used to guide the catheter to the area of blockage. A dye is inserted through the catheter to make the places of blockage visible.
When the catheter is in position, a thin wire with a balloon is guided to the place of blockage. The balloon is inflated to widen the artery, allowing the blood to flow freely. Often, a stent is used, and as the balloon is inflated, the stent in place expands and holds open the artery. The balloon is then deflated and removed, leaving the stent in place.
After the completion of the procedure, the catheter is removed, and the plug area is sealed using angio-seal.
The procedure takes around two hours, and the patient can be discharged after an overnight stay in the hospital, depending on the condition.
Cerebral angiography
Cerebral angiography provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain to detect abnormalities, includingarteriovenous malformation
An arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. Usually congenital, this vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually ...
s and aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward :wikt:bulge, bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also b ...
s. One common cerebral angiographic procedure is neuro-vascular digital subtraction angiography.
Pulmonary angiography
Pulmonary angiography is used to visualise the anatomy of pulmonary vessels. Pulmonary angiography may be used during embolization of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations. In addition, pulmonary angiography may be performed during treatment of pulmonary embolisms.Peripheral angiography
Angiography is also commonly performed to identify vessels narrowing in patients with leg claudication or ''cramps'', caused by reduced blood flow down the legs and to the feet; in patients with renal stenosis (which commonly causes high blood pressure) and can be used in the head to find and repair stroke. These are all done routinely through the femoral artery, but can also be performed through the brachial or axillary (arm) artery. Any stenoses found may be treated by the use of balloon angioplasty, stenting, oratherectomy
Atherectomy is a minimally invasive technique for removing atherosclerosis from blood vessels within the body. It is an alternative to angioplasty for the treatment of peripheral artery disease, but the studies that exist are not adequate to deter ...
.
Visceral angiography
A common indication for angiography is to evaluate and guide treatment for internal (e.g. gastrointestinal) bleeding. Angiography may also be used during hemorrhoidal artery embolization for treatment of symptomatic hemorrhoids.Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography (FA), fluorescent angiography (FAG), or fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid (parts of the fundus) using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. ...
is a medical procedure in which a fluorescent dye is injected into the bloodstream. The dye highlights the blood vessels in the back of the eye so they can be photographed. This test is often used to manage eye disorders.
OCT angiography
Optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a high-resolution imaging technique with most of its applications in medicine and biology. OCT uses coherent near-infrared light to obtain micrometer-level depth resolved images of biological tissue or oth ...
(OCT) is a technology using near-infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of ...
light to image the eye, in particular penetrate the retina to view the micro-structure behind the retinal surface.
Ocular OCT angiography (OCTA) is a method leveraging OCT technology to assess the vascular health of the retina.
Microangiography
Microangiography is commonly used to visualize tiny blood vessels.Post mortem CT angiography
Post mortem CT angiography for medicolegal cases is a method initially developed by a virtopsy group. Originating from that project, both watery and oily solutions have been evaluated. While oily solutions require special deposition equipment to collect waste water, watery solutions seem to be regarded as less problematic. Watery solutions also were documented to enhance post mortem CT tissue differentiation whereas oily solutions were not. Conversely, oily solutions seem to only minimally disturb ensuing toxicological analysis, while watery solutions may significantly impede toxicological analysis, thus requiring blood sample preservation before post mortem CT angiography.Complications
Angiography is a relatively safe procedure. But it does have some minor and very few major complications. After an angiogram, a sudden shock can cause a little pain at the surgery area, but heart attacks and strokes usually do not occur, as they may in bypass surgery. The risk of complications from angiography can be reduced with a prior CT scan by providing clinicians with more information about number and positioning of the clots in advance.Cerebral angiography
Major complications in cerebral angiography such as in digital subtraction angiography or contrast MRI are also rare but includestroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, an allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, alle ...
reaction to the anaesthetic
An anesthetic (American English) or anaesthetic (British English; see spelling differences) is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into t ...
other medication or the contrast medium, blockage or damage to one of the access veins in the leg, pseudoaneurysm at the puncture site; or thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
and embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (air embolism, gas embolism), amniotic ...
formation. Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethr ...
or bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
at the site where the contrast is injected are minor complications, delayed bleeding can also occur but is rare.
Additional risks
The contrast medium that is used usually produces a sensation of warmth lasting only a few seconds, but may be felt in a greater degree in the area of injection. If the patient is allergic to the contrast medium, much more serious side effects are inevitable; however, with new contrast agents the risk of a severe reaction is less than one in 80,000 examinations. Additionally, damage to blood vessels can occur at the site of puncture/injection, and anywhere along the vessel during passage of the catheter. If digital subtraction angiography is used instead, the risks are considerably reduced because the catheter does not need to be passed as far into the blood vessels; thus lessening the chances of damage or blockage.Infection
Antibiotic prophylaxis Antibiotic prophylaxis refers to, for humans, the prevention of infection complications using antimicrobial therapy (most commonly antibiotics). Antibiotic prophylaxis in domestic animal feed mixes has been employed in America since at least 1970 ...
may be given in those procedures that are not clean, or clean procedures that results in generation of infarcted or necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is ...
tissues such as embolisation. Routine diagnostic angiography is often considered a clean procedure. Prophylaxis is also given to prevent infection from infected space into blood stream.
Thrombosis
There are six risk factors causing thrombosis after arterial puncture: low blood pressure, small arterial diameter, multiple puncture tries, long duration of cannulation, administration of vasopressor/inotropic agents, and the usage of catheters with side holes.See also
* Acoustic angiography *Angiosarcoma
Angiosarcoma is a rare and aggressive cancer that starts in the endothelial cells that line the walls of blood vessels or lymphatic vessels. Since they are made from Endothelium, vascular lining, they can appear anywhere and at any age, but older ...
* Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath) is the insertion of a catheter into a heart chamber, chamber or Blood vessel, vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.
A common example of cardiac catheterization is c ...
* Computed tomography angiography
Computed tomography angiography (also called CT angiography or CTA) is a computed tomography technique used for angiography—the visualization of arteries and veins—throughout the human body. Using contrast injected into the blood vessels, im ...
* Contrast medium
A contrast agent (or contrast medium) is a substance used to increase the contrast of structures or fluids within the body in medical imaging. Contrast agents absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound, which is different from radiop ...
* Echocardiogram
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echo ...
* Electrocardiogram
* Fluorescein angiography
Fluorescein angiography (FA), fluorescent angiography (FAG), or fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) is a technique for examining the circulation of the retina and choroid (parts of the fundus) using a fluorescent dye and a specialized camera. ...
* Image intensifier
An image intensifier or image intensifier tube is a vacuum tube device for increasing the intensity of available light in an optical system to allow use under low-light conditions, such as at night, to facilitate visual imaging of low-light proce ...
* Interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultraso ...
* Intravascular ultrasound
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) or intravascular echocardiography is a medical imaging methodology using a specially designed catheter with a miniaturized ultrasound probe attached to the distal end of the catheter. The proximal end of the cathe ...
* Intravenous digital subtraction angiography
* Magnetic resonance angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate ...
* Peripheral artery occlusive disease
References
External links
RadiologyInfo
for patients: Angiography procedures
from Angioplasty.Org
C-Arms types
Several types of C-Arms
Coronary CT angiography by Eugene Lin
{{Authority control Cardiac imaging Projectional radiography Vascular procedures