|
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure. Typically a catheter is inserted into a large artery (such as the femoral artery) and threaded through the circulatory system to the Common carotid artery, carotid artery, where a contrast agent is injected. A series of radiographs are taken as the contrast agent spreads through the brain's arterial system, then a second series as it reaches the venous system. For some applications, cerebral angiography may yield better images than less invasive methods such as computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography. In addition, cerebral angiography allows certain treatments to be performed immediately, based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Plane
A transverse plane is a plane that is rotated 90° from two other planes. Anatomy The transverse plane is an anatomical plane that is perpendicular to the sagittal plane and the dorsal plane. It is also called the axial plane or horizontal plane, especially in human anatomy, but horizontal plane can be misleading with other animals. The plane splits the body into a cranial (head) side and caudal (tail) side, so in humans the plane will be horizontal (dividing the body into superior and inferior sections) but in quadrupeds it will be vertical. Human anatomy Clinically relevant anatomical planes * Transverse '' thoracic plane'' * '' Xiphosternal plane'' (or xiphosternal junction) * '' Transpyloric plane'' * '' Subcostal plane'' * '' Umbilical plane'' (or transumbilical plane) * '' Supracristal plane'' * '' Intertubercular plane'' (or transtubercular plane) * '' Interspinous plane'' Associated structures * The transverse '' thoracic plane'' ** Plane through T4 & T5 verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesoderm, the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leukocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ) was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningioma
Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur. Risk factors include exposure to ionizing radiation such as during radiation therapy, a family history of the condition, and neurofibromatosis type 2. They appear to be able to form from a number of different types of cells including arachnoid cells. Diagnosis is typically by medical imaging. If there are no symptoms, periodic observation may be all that is required. Most cases that result in symptoms can be cured by surgery. Following complete removal fewer than 20% recur. If surgery is not possible or all the tumor cannot be removed, radiosurgery may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embolisation
Embolization refers to the passage and lodging of an embolus within the bloodstream. It may be of natural origin ( pathological), in which sense it is also called embolism, for example a pulmonary embolism; or it may be artificially induced ( therapeutic), as a hemostatic treatment for bleeding or as a treatment for some types of cancer by deliberately blocking blood vessels to starve the tumor cells. In the cancer management application, the embolus, besides blocking the blood supply to the tumor, also often includes an ingredient to attack the tumor chemically or with irradiation. When it bears a chemotherapy drug, the process is called chemoembolization. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is the usual form. When the embolus bears a radiopharmaceutical for unsealed source radiotherapy, the process is called radioembolization or selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT). Uses Embolization involves the selective occlusion of blood vessels by purposely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
A dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) or malformation is an abnormal direct connection (fistula) between a meningeal artery and a meningeal vein or dural venous sinus. Signs and symptoms The most common signs/symptoms of DAVFs are: # Pulsatile tinnitus # Occipital bruit # Headache # Visual impairment # Papilledema Pulsatile tinnitus is the most common symptom in patients, and it is associated with transverse-sigmoid sinus DAVFs. Carotid-cavernous DAVFs, on the other hand, are more closely associated with pulsatile exophthalmos. DAVFs may also be asymptomatic (e.g. cavernous sinus DAVFs). Location Most commonly found adjacent to dural sinuses in the following locations: # Transverse (lateral) sinus, left-sided slightly more common than right # Intratentorial # From the posterior cavernous sinus, usually draining to the transverse or sigmoid sinuses # Vertebral artery (posterior meningeal branch) Causes It is still unclear whether DAVFs are congenital or acquired. Curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (cerebral AVM, CAVM, cAVM, brain AVM, or BAVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain—specifically, an arteriovenous malformation in the cerebrum. Signs and symptoms The most frequently observed problems related to a cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) are headaches and seizures, cranial nerve afflictions including pinched nerve and palsy, backaches, neckaches, and nausea from coagulated blood that has made its way down to be dissolved in the cerebrospinal fluid. Perhaps 15% of the population at detection are asymptomatic. Other common symptoms are a pulsing noise in the head, progressive weakness, numbness and vision changes as well as debilitating, excruciating pain. In serious cases, blood vessels rupture and cause bleeding within the brain (intracranial hemorrhage). In more than half of patients with AVM, this is the first symptom. Symptoms due to bleeding include loss of consciousness, sudden an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Vasospasm
Cerebral vasospasm is the prolonged, intense vasoconstriction of the larger conducting arteries in the subarachnoid space which is initially surrounded by a clot. Significant narrowing of the blood vessels in the brain develops gradually over the first few days after the aneurysmal rupture. This kind of narrowing usually is maximal in about a week's time following intracerebral haemorrhage. Vasospasm is one of the leading causes of death after the aneurysmal rupture along with the effect of the initial haemorrhage and later bleeding. Epidemiology Cerebral vasospasm is a common and severe complication following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, occurring in 50-90% of cases after aneurysm rupture. Moderate or severe vasospasm in one or more cerebral arteries develops in approximately two-thirds of patients with ruptured aneurysms. Of these, nearly half exhibit symptoms of cerebral ischemia. Infarction occurs in about half of the symptomatic patients and is significantly associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly. Signs and symptoms of stroke may include an hemiplegia, inability to move or feel on one side of the body, receptive aphasia, problems understanding or expressive aphasia, speaking, dizziness, or homonymous hemianopsia, loss of vision to one side. Signs and symptoms often appear soon after the stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than 24 hours, the stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also called a mini-stroke. subarachnoid hemorrhage, Hemorrhagic stroke may also be associated with a thunderclap headache, severe headache. The symptoms of stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and Urinary incontinence, loss of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
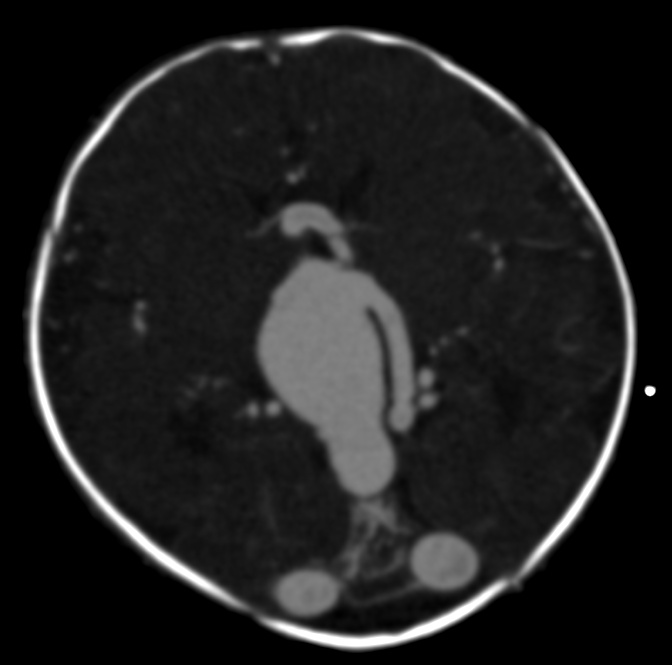
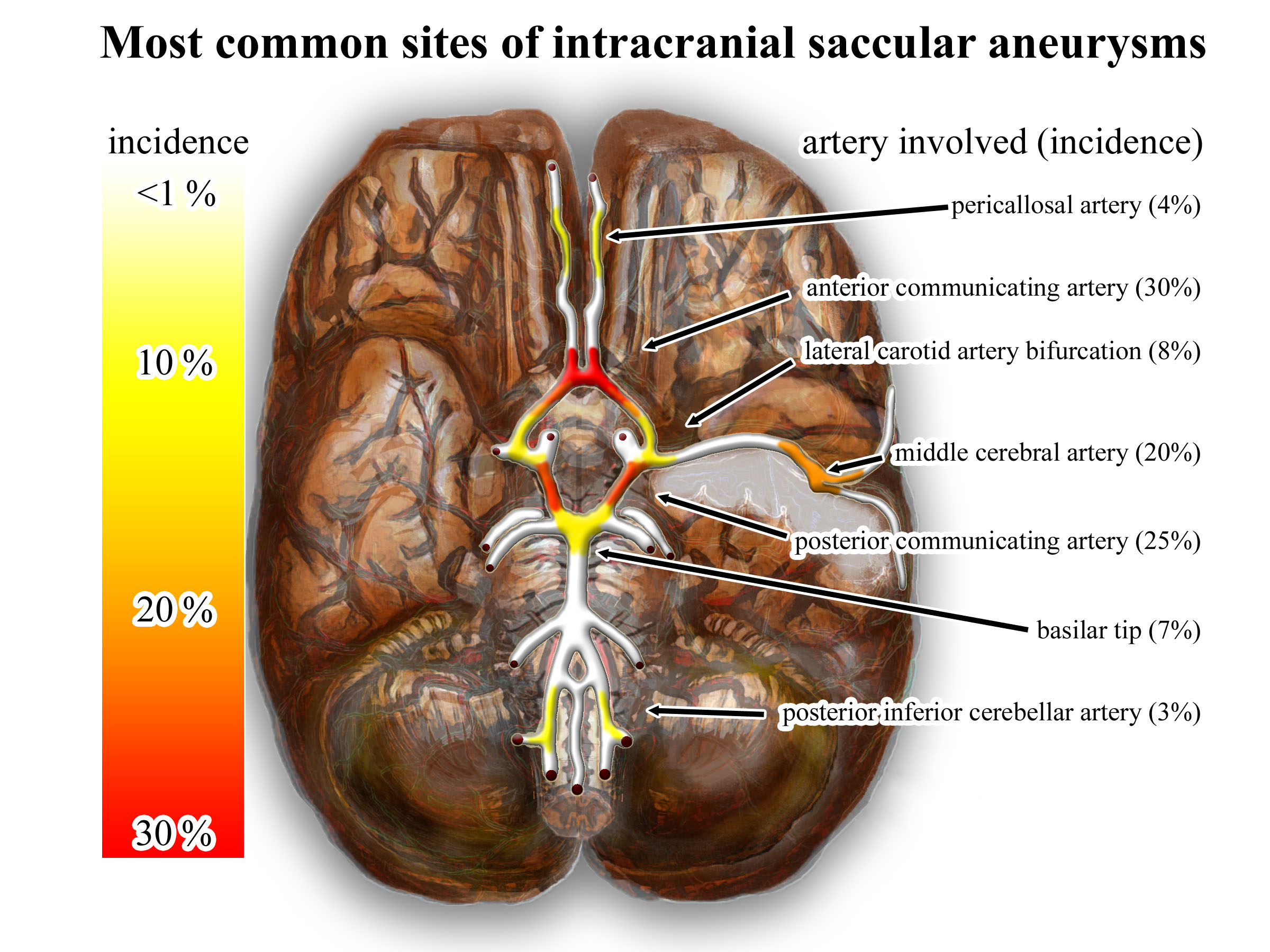
Intracranial Aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder characterized by a localized dilation or ballooning of a blood vessel in the brain due to a weakness in the vessel wall. These aneurysms can occur in any part of the brain but are most commonly found in the arteries of the cerebral arterial circle. The risk of rupture varies with the size and location of the aneurysm, with those in the posterior circulation being more prone to rupture. Cerebral aneurysms are classified by size into small, large, giant, and super-giant, and by shape into saccular (berry), fusiform, and microaneurysms. Saccular aneurysms are the most common type and can result from various risk factors, including genetic conditions, hypertension, smoking, and drug abuse. Symptoms of an unruptured aneurysm are often minimal, but a ruptured aneurysm can cause severe headaches, nausea, vision impairment, and loss of consciousness, leading to a subarachnoid hemorrhage. Treatm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracerebral Haemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as hemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain (i.e. the parenchyma), into its ventricles, or into both. An ICH is a type of bleeding within the skull and one kind of stroke (ischemic stroke being the other). Symptoms can vary dramatically depending on the severity (how much blood), acuity (over what timeframe), and location (anatomically) but can include headache, one-sided weakness, numbness, tingling, or paralysis, speech problems, vision or hearing problems, memory loss, attention problems, coordination problems, balance problems, dizziness or lightheadedness or vertigo, nausea/vomiting, seizures, decreased level of consciousness or total loss of consciousness, neck stiffness, and fever. Hemorrhagic stroke may occur on the background of alterations to the blood vessels in the brain, such as cerebral arteriolosclerosis, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cerebral arteriovenous malformation, brain trauma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain. Symptoms may include a severe headache of rapid onset, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness, fever, weakness, numbness, and sometimes seizures. Neck stiffness or neck pain are also relatively common. In about a quarter of people a small bleed with resolving symptoms occurs within a month of a larger bleed. SAH may occur as a result of a head injury or spontaneously, usually from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Risk factors for spontaneous cases include high blood pressure, smoking, family history, alcoholism, and cocaine use. Generally, the diagnosis can be determined by a CT scan of the head if done within six hours of symptom onset. Occasionally, a lumbar puncture is also required. After confirmation further tests are usually performed to determine the underlying cause. Treatment is by prompt neurosurgery or en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Effect (medicine)
In medicine, a mass effect is the effect of a growing mass that results in secondary pathological effects by pushing on or displacing surrounding tissue. In oncology, the mass typically refers to a tumor. For example, cancer of the thyroid gland may cause symptoms due to compressions of certain structures of the head and neck; pressure on the laryngeal nerves may cause voice changes, narrowing of the Vertebrate trachea, windpipe may cause stridor, pressure on the esophagus, gullet may cause dysphagia and so on. Surgery, Surgical removal or debulking is sometimes used to palliative care, palliate symptoms of the mass effect even if the underlying pathology is not curable. In neurology, a mass effect is the effect exerted by any mass, including, for example, hydrocephalus (cerebrospinal fluid buildup) or an evolving intracranial hemorrhage (bleeding within the skull) presenting with a clinically significant hematoma. The hematoma can exert a mass effect on the brain, increasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |