|
Warao Language
Warao (also known as Guarauno, Guarao, Warrau) is the native language of the Warao people. A language isolate, it is spoken by about 33,000 people primarily in northern Venezuela, Guyana and Suriname. It is notable for its unusual object–subject–verb word order. The 2015 Venezuelan film ''Gone with the River'' was spoken in Warao. Classification Warao appears to be a language isolate, unrelated to any recorded language in the region or elsewhere. Terrence Kaufman (1994) included it in his hypothetical Macro-Paezan family, but the necessary supporting work was never done. Julian Granberry connected many of the grammatical forms, including nominal and verbal suffixes, of Warao to the Timucua language of North Florida, also a language isolate. However, he has also derived Timucua morphemes from Muskogean, Chibchan, Paezan, Arawakan, and other Amazonian languages, suggesting multi-language creolization as a possible explanation for these similarities. Waroid hypothesis Granberry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of States of Venezuela, 23 states, the Venezuelan Capital District, Capital District and Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. The territory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goajiro Language
Wayuu ( ), or Guajiro, is a major Arawakan language spoken by 400,000 indigenous Wayuu people in northwestern Venezuela and northeastern Colombia on the Guajira Peninsula and surrounding Lake Maracaibo. There were an estimated 300,000 speakers of Wayuunaiki in Venezuela in 2012 and another 120,000 in Colombia in 2008, approximately half the ethnic population of 400,000 in Venezuela (2011 census) and 400,000 in Colombia (2018 census). Smith (1995) reports that a mixed Wayuu—Spanish language is replacing Wayuunaiki in both countries. However, Campbell (1997) could find no information on this. Recent developments To promote bilingual education among Wayuu and other Colombians, the Kamusuchiwoꞌu Ethno-educative Center () came up with the initiative of creating the first illustrated Wayuunaiki–Spanish, Spanish–Wayuunaiki dictionary. In December 2011, the Wayuu Taya Foundation and Microsoft presented the first ever dictionary of technology terms in Wayuunaiki, after having de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
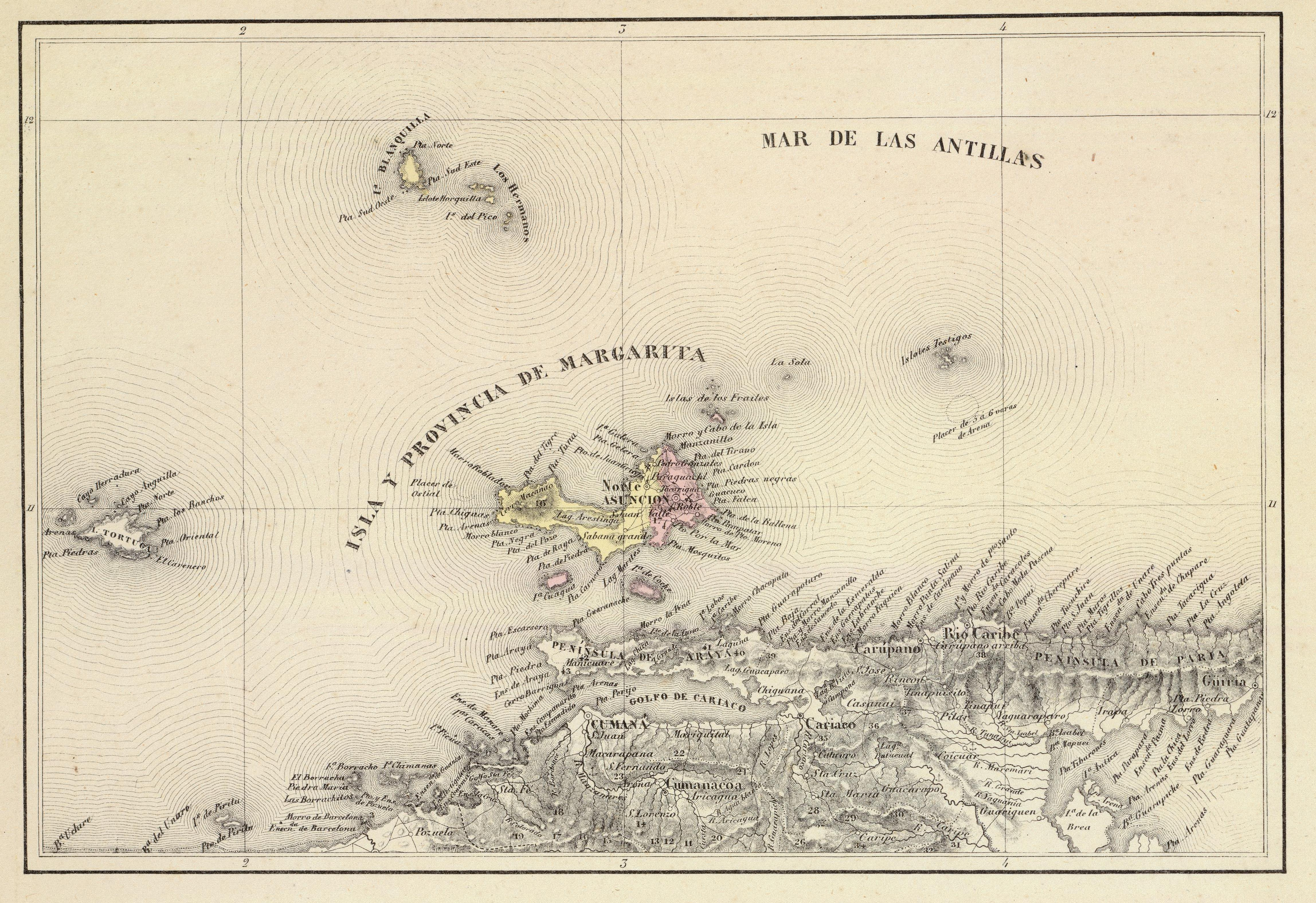
Margarita Island
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the States of Venezuela, Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the north west coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island. History Age of Exploration Christopher Columbus was the first European to arrive on Margarita Island in 1498. The local natives were the Guaiqueries people. The coast of the island was abundant in pearls, which represented almost a third of all New World tribute to the Spanish Crown. Margarita Island was fortified against the increasing threat of pirate attacks, and some fortifications remain today. It was the center of Spanish colonial Margarita Province, established in 1525. In 1561, the island was seized by Lope de Aguirre, a notoriously violent and rebellious conquistador who killed the governor Juan Villadrando. Around 1675, the island was captured again, this time by Red Legs Greaves, a pirate known for his humanity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayenne
Cayenne (; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and capital city of French Guiana, an overseas region and Overseas department, department of France located in South America. The city stands on a former island at the mouth of the Cayenne River on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. The city's motto is "fert aurum industria", which means "work brings wealth". Cayenne is the largest Francophone city of the South American continent. In the 2021 census, there were 151,103 inhabitants in the metropolitan area of Cayenne (as defined by INSEE), 63,468 of whom lived in the city (communes of France, commune) of Cayenne proper. History Ignored by Spanish explorers who found the region too hot and poor to be claimed, the region was not colonized until 1604, when the French founded a settlement. However, it was soon destroyed by the Portugal, Portuguese, determined to enforce the Treaty of Tordesillas. French colonists returned in 1643 and founded Cayenne, but were forced to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International security, security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 194 Member states of UNESCO, member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the Non-governmental organization, non-governmental, Intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 National Commissions for UNESCO, national commissions. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations' International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the events of World War II, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller islets. The capital city is Port of Spain, while its largest and most populous municipality is Chaguanas. Despite its proximity to South America, Trinidad and Tobago is generally considered to be part of the Caribbean. Trinidad and Tobago is located northeast off the coast of Venezuela, south of Grenada, and 288 kilometres (155 nautical miles) southwest of Barbados. Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples inhabited Trinidad for centuries prior to Spanish Empire, Spanish colonization, following the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1498. Spanish governor José María Chacón surrendered the island to a British fleet under Sir Ralph Abercromby's command in 1797. Trinidad and Tobago were ceded to Britain in 1802 under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger, more populous island of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the country. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is the southernmost island in the Caribbean. With an area of , it is also the fifth-largest in the Caribbean. Name The original name for the island in the Arawakan languages was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. Indo-Trinidadians called the island चीनीदत्त , 𑂒𑂲𑂢𑂲𑂠𑂞𑂹𑂞 , , ''Chinidat'' or ''Chinidad'' in Trinidadian Hindustani which translated to the land of sugar. The usage of the term goes back to the 19th century when recruiters from India would call the island ''Chinidat'' as a way of luring workers into indentureship. On Tuesday, 31 Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orinoco Delta
The Orinoco Delta is a vast river delta of the Orinoco River, located in eastern Venezuela. Location The Orinoco Delta is one of the eight natural regions of Venezuela. It covers the whole of Delta Amacuro State and a few square kilometers of Monagas State and Sucre State, comprising all the mouths of the Orinoco. It is divided into two sections: the principal, at the northernmost part of the system, located between Caño Manamo and the left shore of Caño Araguao, where the majority of villages are established, including the state capital Tucupita; and the secondary, between the right shore of Caño Araguao and Río Grande. The Warao people live in the region. Hydrology The delta is fan-shaped, formed by the Orinoco River as it splits into numerous distributaries, called ''caños'', which meander through the delta on their way to the sea. The main distributary is called the Rio Grande, which empties south-southeast through the southern portion of the delta, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiana Highlands
The Guianas, also spelled Guyanas or Guayanas, are a geographical region in north-eastern South America. Strictly, the term refers to the three Guianas: Guyana, Suriname, and French Guiana, formerly British, Dutch, and French Guiana respectively. Broadly, it refers to the South American coast from the mouth of the Orinoco to the mouth of the Amazon. Politically it is divided into: * Spanish or Venezuelan Guiana, now the Delta Amacuro State and Guayana Region of Venezuela. * Guyana, formerly British Guiana, independent since 1966. * Suriname, formerly Dutch Guiana, independent since 1975. * French Guiana, an overseas department and region of France. * Brazilian or Portuguese Guiana, now the Amapá State of Brazil. The three Guianas proper have a combined population of 1,718,651; Guyana: 804,567, Suriname: 612,985, and French Guiana: 301,099. Most of the population is along the coast. Due to the jungles to the south, the Guianas are one of the most sparsely populated regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sape Language
Sape, SAPE, Sapë, or Sapé may refer to: People * Janet Sape (died 2017), businesswoman from Papua New Guinea * Lauvale Sape, (born 1980), American football player Places * Roman Catholic Diocese of Sapë, Albania * Sapé, Paraíba, a municipality in Brazil * Sape, a municipality in Albania officially known as Vau i Dejës * Sape Strait, Indonesia Education and organizations * La Sape (''Société des Ambianceurs et des Personnes Élégantes''), a social movement centered in Brazzaville, Republic of Congo * , an ecological organization * Society of Avian Paleontology and Evolution, an international scientific society dedicated to the study of the evolution of birds; see '' Sapeornis'' Other uses * French destroyer ''Sape'' * Sapé language, a nearly extinct language spoken in Venezuela * Sape, a synonym for the Sarangesa genus of butterfly * Sape' or sapeh, a traditional lute in Borneo * SAPE, the stock symbol for Sapient Corporation Publicis Sapient is a digital c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Máku Language
Máku, also spelled ''Mako'' (Spanish ''Macú''), and in the language itself Jukude, is an unclassified language and likely language isolate once spoken on the Brazil–Venezuela border in Roraima along the upper Uraricoera and lower Auari rivers, west of Boa Vista, by the ''Jukudeitse'' ( or ) or 'people'. 300 years ago, the Jukude territory was between the Padamo and Cunucunuma rivers to the southwest. The last speaker, Sinfrônio Magalhães, died in 2000. There are currently no speakers or rememberers of Máku and no-one identifies as Jukude any longer. Aryon Rodrigues and Ernesto Migliazza, as well as Iraguacema Lima Maciel, worked on the language, and the data was collected into a grammar by Chris Rogers published in 2020. Name The people called themselves (person-PL) 'people'. When speaking to outsiders, they referred to themselves as or . ''Maku'' ~ ''Mako'' (in Spanish orthography ''Macu'' or ''Maco'') is an Arawakan term for unintelligible languages and people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arutani Language
Arutani (''Orotani, Urutani,'' also known as ''Awake, Auake, Auaqué, Aoaqui, Oewaku,'' ethnonym ''Uruak'') is a nearly extinct language spoken in Roraima, Brazil and in the Karum River area of Bolivar State, Venezuela. There are only around 6 speakers left. Documentation Arutani is one of the most poorly attested extant languages in South America, and may be a language isolate. Existing data is limited to a 1911 word list by Koch-Grünberg (1928: 308-313), a 1940 word list by Armellada & Matallana (1942: 101-110), and a 100-item Swadesh list by Migliazza (1978). There is also an unpublished Swadesh list by Fèlix Cardona i Puig from the 1930s-1940s, as well as an unpublished 200-item Swadesh list by Walter Coppens from 1970.Coppens, Walter. 2008. Los Uruak (Arutani). In W. Coppens, M. Á. Perera, R. Lizarralde & H. Seijas (eds.) ''Los aborígenes de Venezuela''. Volume 2, 747-770. Caracas: Fundación La Salle/Monte Avila Editores/Ediciones IVIC/Instituto Caribe de Antropolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |