Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, consisting of a
continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
al landmass and many
islands and islets in the
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022.
The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of
Caracas
Caracas ( , ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas (CCS), is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern p ...
. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
and the
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, on the west by
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
,
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
on the south,
Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
to the north-east and on the east by
Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
. Venezuela is a
presidential republic
A presidential, strong-president, or single-executive system (sometimes also congressional system) is a form of government in which a head of government (usually titled " president") heads an executive branch that derives its authority and l ...
consisting of
23 states, the
Capital District and
federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America;
the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital.
The territory of Venezuela was
colonized by Spain in 1522 amid resistance from Indigenous peoples. In 1811, it became one of the first Spanish-American territories to
declare independence from the Spanish and to form part of the first federal Republic of Colombia (
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), also known as Greater Colombia and officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and parts of Central ...
). It separated as a full sovereign country in 1830. During the 19th century, Venezuela suffered political turmoil and autocracy, remaining dominated by regional
military dictators until the mid-20th century. From 1958, the country had a series of democratic governments, as an exception where most of the region was ruled by military dictatorships, and the period was characterized by economic prosperity.
Economic shocks in the
1980s and 1990s led to major political crises and widespread social unrest, including the deadly
Caracazo riots of 1989,
two attempted coups in 1992, and the
impeachment of a president for embezzlement of public funds charges in 1993. The collapse in confidence in the existing parties saw the
1998 Venezuelan presidential election, the catalyst for the
Bolivarian Revolution, which began with a
1999 Constituent Assembly, where a new
Constitution of Venezuela was imposed. The government's
populist social welfare policies were bolstered by soaring oil prices, temporarily increasing social spending, and reducing
economic inequality and poverty in the early years of the regime. However, poverty began to rapidly increase in the 2010s.
The
2013 Venezuelan presidential election was widely disputed leading to
widespread protest, which triggered another nationwide
crisis that continues to this day.
Venezuela has experienced
democratic backsliding, shifting into an
authoritarian state.
It
ranks low in international measurements of
freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic Media (communication), media, especially publication, published materials, shoul ...
and
civil liberties and has high levels of perceived
corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
.
Venezuela is a
developing country, has the world's
largest known oil reserves, and has been one of the world's leading
exporters of oil. Previously, the country was an underdeveloped exporter of agricultural commodities such as coffee and cocoa, but oil quickly came to dominate exports and government revenues. The excesses and poor policies of the incumbent government led to the collapse of Venezuela's entire economy.
The country struggles with record
hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real versus nominal value (economics), real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimiz ...
,
shortages of basic goods, unemployment, poverty, disease, high child mortality,
malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
,
environmental issues, severe crime and corruption.
US sanctions and the seizure of Venezuelan assets overseas have cost the country $24–30 billion. These factors have precipitated the
Venezuelan refugee crisis
The Venezuelan refugee crisis, the List of largest refugee crises, largest recorded refugee crisis in the Americas,
*
*
*
*
refers to the emigration of millions of Venezuelans from their native country during the presidencies of Hugo C ...
in which more than 7.7 million people had fled the country by June 2024. By 2017, Venezuela was declared to be in
default regarding debt payments by
credit rating agencies. The crisis in Venezuela has contributed to a rapidly deteriorating
human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
situation.
Etymology
According to the most popular and accepted version, in 1499, an expedition led by
Alonso de Ojeda
Alonso de Ojeda (; c. 1466 – c. 1515) was a Spanish explorer, governor and conquistador. He is famous for having named Venezuela, which he explored during his first two expeditions, for having been the first European to visit Guyana, Curaçao ...
visited the Venezuelan coast. The
stilt houses in the area of
Lake Maracaibo reminded the Italian navigator,
Amerigo Vespucci, of the city of
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, Italy, so he named the region ''Veneziola'', or "Little Venice". The Spanish version of ''Veneziola'' is .
Martín Fernández de Enciso, a member of the Vespucci and Ojeda crew, gave a different account. In his work , he states that the crew found
Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
who called themselves the ''Veneciuela.'' Thus, the name "Venezuela" may have evolved from the native word.
Previously, the official name was (1830–1856), (1856–1864), (1864–1953), and again (1953–1999).
History
Pre-Columbian history
Evidence exists of human habitation in the area now known as Venezuela from about 15,000 years ago. Tools have been found on the high
riverine terraces of the
Rio Pedregal in western Venezuela.
Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
hunting artifacts, including spear tips, have been found at a similar series of sites in northwestern Venezuela; according to
radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
, these date from 13,000 to 7,000 BC.
It is unknown how many people lived in Venezuela before the Spanish conquest; it has been estimated at one million. In addition to Indigenous peoples known today, the population included groups such as the
Kalina (Caribs),
Auaké,
Caquetio,
Mariche, and
Timoto–Cuicas. The Timoto–Cuica culture was the most complex society in Pre-Columbian Venezuela, with pre-planned permanent villages, surrounded by irrigated, terraced fields. Their houses were made of stone and wood with thatched roofs. They were peaceful and depended on growing crops. Regional crops included potatoes and
ullucos.
["Venezuela".]
''Friends of the Pre-Columbian Art Museum''. (retrieved 9 July 2011) They left behind art, particularly anthropomorphic ceramics, but no major monuments. They spun vegetable fibers to weave into textiles and mats for housing. They are credited with having invented the
arepa, a staple in
Venezuelan cuisine.
After the conquest, the population dropped markedly, mainly through the spread of infectious diseases from Europe. Two main north–south axes of pre-Columbian population were present, who cultivated maize in the west and
manioc in the east. Large parts of the ''
llanos'' were cultivated through a combination of
slash and burn and permanent settled agriculture.
Colonization

In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas,
Christopher Columbus sailed near the
Orinoco Delta and landed in the
Gulf of Paria. Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in a letter to Isabella and Ferdinand that he must have reached Heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
Spain's colonization of mainland Venezuela started in 1522, establishing its first permanent South American settlement in the city of
Cumaná.
German colonization
In the 16th century, the king of Spain granted a concession to the German
Welser family.
Klein-Venedig became the most extensive initiative in the
German colonization of the Americas from 1528 to 1546. The Welsers were bankers to the Habsburgs and financiers of
Charles V,
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (disambiguation), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and h ...
, who was King of Spain and had borrowed heavily from them to pay bribes for his
Imperial election
The election of a Holy Roman Emperor was generally a two-stage process whereby the King of the Romans was elected by a small body of the greatest princes of the realm, the prince-electors. This was then followed shortly thereafter by his coronati ...
.
In 1528, Charles V granted the Welsers the right to explore, rule and colonize the territory, as well as to seek the mythical golden town of
El Dorado. The first expedition was led by
Ambrosius Ehinger, who established
Maracaibo in 1529. After the deaths of first Ehinger (1533), then
Nikolaus Federmann, and
Georg von Speyer (1540),
Philipp von Hutten persisted in exploring the interior. In absence of von Hutten from the capital of the province, the crown of Spain claimed the right to appoint a governor. On Hutten's return to the capital,
Santa Ana de Coro, in 1546, the Spanish governor
Juan de Carvajal
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of '' John''. The name is of Hebrew origin and has the meaning "God has been gracious." It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking countries around the world and in the Phili ...
had Hutten and
Bartholomeus VI. Welser executed. Subsequently,
Charles V revoked Welser's concession. The Welsers transported German miners to the colony, in addition to 4,000 African
slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
to plant
sugar cane plantations. Many German colonists died from tropical diseases, to which they had no
immunity, or through wars with the
Indigenous inhabitants.
Late 15th century to early 17th century
Native ''
caciques'' (leaders) such as
Guaicaipuro () and
Tamanaco (died 1573) attempted to resist Spanish incursions, but the newcomers ultimately subdued them.
In the 16th century, during the Spanish colonization, indigenous peoples such as the
Mariches, themselves descendants of the Kalina, were converted to
Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
. Some resisting tribes or leaders are commemorated in place names, including Caracas,
Chacao and
Los Teques. The early colonial settlements focused on the northern coast, but in the mid-18th century, the Spanish pushed farther inland along the
Orinoco River. Here, the
Ye'kuana organized resistance in 1775–76.
Spain's eastern Venezuelan settlements were incorporated into
New Andalusia Province. Administered by the
Royal Audiencia of Santo Domingo from the early 16th century, most of Venezuela became part of the
Viceroyalty of New Granada in the early 18th century, and was then reorganized as an autonomous
Captaincy General starting in 1777. Caracas, founded in the central coastal region in 1567, was well-placed to become a key location, being near the coastal port of
La Guaira and in a valley, in a mountain range, providing defensive strength against
pirates and a more fertile and healthy climate.
Independence and 19th century
After unsuccessful uprisings, Venezuela, under the leadership of
Francisco de Miranda, a Venezuelan marshal who had fought in the
American and
French Revolutions,
declared independence as the
First Republic of Venezuela on 5 July 1811. This began the
Venezuelan War of Independence. A devastating
1812 Caracas earthquake, together with the rebellion of the Venezuelan ''
llaneros'', helped bring down the republic.
Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24July 178317December 1830) was a Venezuelan statesman and military officer who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama, and Bol ...
, new leader of the independentist forces, launched his
Admirable Campaign in 1813 from
New Granada, retaking most of the territory and being proclaimed as ''El Libertador'' ("The Liberator"). A
Second Republic of Venezuela was proclaimed on 7 August 1813, but lasted only a few months before being crushed by
royalist caudillo
José Tomás Boves and his personal army of ''llaneros''.
The end of the
French invasion of homeland Spain in 1814 allowed a large expeditionary force to come under general
Pablo Morillo, with the goal to regain the lost territory in Venezuela and New Granada. As the war reached a stalemate on 1817, Bolívar reestablished the
Third Republic of Venezuela
The Third Republic of Venezuela () was the reestablished Republic of Venezuela declared by Simón Bolívar in the year 1817, during the Venezuelan War of Independence.
The beginning of the Third Republic of Venezuela is attributed to the peri ...
on the territory still controlled by the patriots, mainly in the
Guayana and
Llanos regions. This republic was short-lived as only two years later, during the
Congress of Angostura of 1819, the union of Venezuela with New Granada was decreed to form the Republic of Colombia. The war continued until full victory and
sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
was attained after the
Battle of Carabobo on 24 June 1821. On 24 July 1823,
José Prudencio Padilla and
Rafael Urdaneta helped seal Venezuelan independence with their victory in the
Battle of Lake Maracaibo.
New Granada's congress gave Bolívar control of the Granadian army; leading it, he liberated several countries and founded the Republic of Colombia (
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), also known as Greater Colombia and officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and parts of Central ...
).

Sucre went on to liberate
Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contain ...
and become the second president of
Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
. Venezuela remained part of Gran Colombia until 1830, when a rebellion led by
José Antonio Páez allowed the proclamation of a newly independent Venezuela, on 22 September; Páez became the first president of the new
State of Venezuela. Between one-quarter and one-third of Venezuela's population was lost during these two decades of war (including about half the
Venezuelans of European descent), which by 1830, was estimated at 800,000.
[Venezuela – The Century of Caudillismo]
". Library of Congress Country Studies. In the
Flag of Venezuela, the yellow stands for land wealth, the blue for the sea that separates Venezuela from Spain, and the red for the blood shed by the heroes of independence.
Slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
in Venezuela was abolished in 1854.
Much of Venezuela's 19th-century history was characterized by political turmoil and dictatorial rule, including the Independence leader José Antonio Páez, who gained the presidency three times and served 11 years between 1830 and 1863. This culminated in the
Federal War (1859–63). In the latter half of the century,
Antonio Guzmán Blanco, another ''caudillo'', served 13 years, between 1870 and 1887, with three other presidents interspersed.

In 1895, a longstanding dispute with Great Britain about the Essequibo territory, which Britain claimed as part of
British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies. It was located on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first known Europeans to encounter Guia ...
and Venezuela saw as Venezuelan territory, erupted into the
Venezuela Crisis of 1895. The dispute became a diplomatic crisis when Venezuela's lobbyist,
William L. Scruggs, sought to argue that British behavior over the issue violated the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
'
Monroe Doctrine of 1823, and used his influence in Washington, D.C., to pursue the matter. Then, U.S. president
Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Hist ...
adopted a broad interpretation of the doctrine that declared an American interest in any matter within the hemisphere. Britain ultimately accepted arbitration, but in negotiations over its terms was able to persuade the U.S. on many details. A tribunal convened in Paris in 1898 to decide the issue and in 1899 awarded the bulk of the disputed territory to British Guiana.
In 1899,
Cipriano Castro, assisted by his friend
Juan Vicente Gómez, seized power in Caracas. Castro defaulted on Venezuela's considerable foreign debts and declined to pay compensation to foreigners caught up in Venezuela's
civil wars. This led to the
Venezuela Crisis of 1902–1903, in which Britain, Germany and Italy imposed a naval blockade before international arbitration at the new
Permanent Court of Arbitration was agreed. In 1908,
another dispute broke out with the Netherlands, which was resolved when Castro left for medical treatment in Germany and was promptly overthrown by
Juan Vicente Gómez (1908–35).
20th century
The discovery of massive
oil deposits in Lake Maracaibo during World War I proved pivotal for Venezuela and transformed its economy from a heavy dependence on agricultural exports. It prompted a boom that lasted into the 1980s; by 1935, Venezuela's per capita gross domestic product was Latin America's highest. Gómez benefited handsomely from this, as corruption thrived, but at the same time, the new source of income helped him centralize the state and develop its authority.
Gómez remained the most powerful man in Venezuela until his death in 1935. The ''gomecista'' dictatorship (1935–1945) system largely continued under
Eleazar López Contreras, but from 1941, under
Isaías Medina Angarita, was relaxed. Angarita granted a range of reforms, including the legalization of all political parties. After World War II, immigration from Southern Europe and poorer Latin American countries markedly diversified Venezuelan society.
In 1945, a civilian-military coup overthrew Medina Angarita and ushered in
a period of democratic rule (1945–1948) under the mass membership party
Democratic Action, initially under
Rómulo Betancourt, until
Rómulo Gallegos won the
1947 Venezuelan presidential election (the first free and fair elections in Venezuela). Gallegos governed until overthrown by a military junta led by the triumvirate ,
Marcos Pérez Jiménez, and Gallegos' Defense Minister,
Carlos Delgado Chalbaud, in the
1948 Venezuelan ''coup d'état''.
The most powerful man in the military ''junta'' (1948–58) was Pérez Jiménez and he was suspected of being behind the death of Chalbaud, who died in a bungled kidnapping in 1950. When the junta unexpectedly lost the
1952 presidential election, it ignored the results and Jiménez was installed as president. Jiménez was forced out on 23 January 1958.
In an effort to consolidate a young democracy, the three major political parties (
Acción Democrática (AD),
COPEI and
Unión Republicana Democrática (URD), with the notable exception of the
Communist Party of Venezuela), signed the
Puntofijo Pact power-sharing agreement. AD and COPEI dominated the political landscape for four decades.
During the presidencies of
Rómulo Betancourt (1959–64, his second term) and
Raúl Leoni (1964–69), substantial guerilla movements occurred. Most laid down their arms under
Rafael Caldera's first presidency (1969–74). Caldera had won the
1968 election for COPEI, the first time a party other than Democratic Action took the presidency through a democratic election. The new democratic order had its antagonists. Betancourt
suffered an attack planned by the Dominican dictator
Rafael Trujillo in 1960, and the leftists excluded from the Pact initiated an insurgency by organizing themselves into the Armed Forces of National Liberation, sponsored by the Communist Party and
Fidel Castro
Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruz (13 August 1926 – 25 November 2016) was a Cuban politician and revolutionary who was the leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008, serving as the prime minister of Cuba from 1959 to 1976 and President of Cuba, president ...
. In 1962 they tried to destabilize the military corps, with failed revolts. Betancourt promoted a foreign policy, the
Betancourt Doctrine, in which he only recognized elected governments by popular vote.

The
1973 Venezuelan presidential election of
Carlos Andrés Pérez coincided with an
oil crisis, in which Venezuela's income exploded as
oil prices soared; oil industries were nationalized in 1976. This led to massive increases in public spending, but also increases in external debts, until the collapse of oil prices during the 1980s crippled the economy. As the government started to devalue the currency in 1983 to face its financial obligations, standards of living fell dramatically. Failed economic policies and increasing corruption in government led to rising poverty and crime, worsening social indicators, and increased political instability.
In the 1980s, the Presidential Commission for State Reform (COPRE) emerged as a mechanism of political innovation. Venezuela decentralized its political system and diversified its economy, reducing the size of the state. COPRE operated as an innovation mechanism, also by incorporating issues into the political agenda, that were excluded from public deliberation by the main actors of the democratic system. The most discussed topics were incorporated into the public agenda: decentralization, political participation, municipalization, judicial order reforms and the role of the state in a new economic strategy. The social reality made the changes difficult to apply.
Economic crises in the 1980s and 1990s led to a political crisis. Hundreds of people were killed by security forces and the military in the ''
Caracazo'' riots of 1989, during the second presidential term of Carlos Andrés Pérez (1989–1993) and after the implementation of economic austerity measures.
Hugo Chávez, who in 1982 had promised to depose the bipartisanship governments, used the growing anger at economic austerity measures to justify a
coup attempt in February 1992;
a
second coup d'état attempt occurred in November.
President Carlos Andrés Pérez (re-elected in 1988) was impeached under embezzlement charges in 1993, leading to the interim presidency of
Ramón José Velásquez (1993–1994). Coup leader Chávez
was pardoned in March 1994 by president Rafael Caldera (1994–1999, his second term), with a clean slate and his political rights reinstated, allowing Chávez to win and maintain the presidency continuously from 1999 until his death in 2013. Chávez won the elections of 1998, 2000, 2006 and 2012 and the presidential referendum of 2004.
Bolivarian government under Chávez: 1999–2013

A collapse in confidence in the existing parties led to
Hugo Chávez being elected president in 1998 and the subsequent launch of a "Bolivarian Revolution", beginning with a 1999
constituent assembly to write a new Constitution. The Revolution refers to a
left-wing populism
Left-wing populism, also called social populism, is a Ideology#Political ideologies, political ideology that combines left-wing politics with populist rhetoric and themes. Its rhetoric often includes elements of anti-elitism, opposition to the E ...
social movement
A social movement is either a loosely or carefully organized effort by a large group of people to achieve a particular goal, typically a Social issue, social or Political movement, political one. This may be to carry out a social change, or to re ...
and political process led by Chávez, who founded the
Fifth Republic Movement in 1997 and the
United Socialist Party of Venezuela in 2007. The "Bolivarian Revolution" is named after
Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24July 178317December 1830) was a Venezuelan statesman and military officer who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama, and Bol ...
. According to Chávez and other supporters, the "Bolivarian Revolution" sought to build a mass movement to implement
Bolivarianism—
popular democracy, economic independence, equitable distribution of revenues, and an end to political corruption. They interpret Bolívar's ideas from a
populist perspective, using
socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
rhetoric. This led to formation of the Fifth Republic of Venezuela, commonly known as the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, that continues to the present day. Venezuela has been considered the Bolivarian Republic following the adoption of the new
Constitution of 1999. Following Chávez's election, Venezuela developed into a
dominant-party system, dominated by the
United Socialist Party of Venezuela. In April 2002, Chávez was briefly ousted from power in the
2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt following popular demonstrations by his opponents, but Chavez returned after two days as a result of demonstrations by poor Chávez supporters and actions by the military. Chávez remained in power after an all-out national strike that lasted
from December 2002 to February 2003, including a strike/lockout in the state oil company
PDVSA.
Capital flight before and during the strike led to the reimposition of
currency controls. In the subsequent decade, the government was forced into currency devaluations.
["Venezuela The homecoming"](_blank)
. Economist.com (23 February 2013). Retrieved on 20 April 2013.[Farzad, Roben. (15 February 2013]
"Venezuela's Double-Edged Devaluation"
Businessweek.com. Retrieved on 20 April 2013. These devaluations did not improve the situation of the people who rely on imported products or locally produced products that depend on imported inputs, while dollar-denominated oil sales account for the majority of exports. The profits of the oil industry have been lost to "social engineering" and corruption, instead of investments needed to maintain oil production.
Chávez survived further political tests, including an
August 2004 recall referendum. He was elected for another term
in December 2006 and for a third term in October 2012. However, he was never sworn in due to medical complications; he died in March 2013.
Bolivarian government under Maduro: 2013–present
The presidential election that took place in April 2013, was the first since Chávez took office in 1999 in which his name did not appear on the ballot.
Under the Bolivarian government, Venezuela went from being one of the richest countries in Latin America to one of the poorest.
of relying on oil sales and importing goods resulted in large amounts of debt, no change to
corruption in Venezuela and culminated into a
crisis in Venezuela
An ongoing socioeconomic and political crisis began in Venezuela during the presidency of Hugo Chávez and has worsened during the presidency of successor Nicolás Maduro. It has been marked by hyperinflation, escalating starvation, disease, c ...
.
As a result, the
Venezuelan refugee crisis
The Venezuelan refugee crisis, the List of largest refugee crises, largest recorded refugee crisis in the Americas,
*
*
*
*
refers to the emigration of millions of Venezuelans from their native country during the presidencies of Hugo C ...
, the largest emigration of people in Latin America's history,
occurred, with over 7 million – about 20% of the country's population – emigrating.
Chávez initiated
Bolivarian missions, programs aimed at helping the poor.
Poverty began to increase into the 2010s.
[Charlie Devereux & Raymond Colitt. 7 March 2013. ] Nicolás Maduro was picked by Chavez as his successor, appointing him vice president in 2013.
Maduro has been
president of Venezuela since 14 April 2013, when he won the
presidential election after Chavez' death, with 51% of the vote, against
Henrique Capriles on 49%. The
Democratic Unity Roundtable contested Maduro's election as fraud, but an audit of 56% of the vote showed no discrepancies,
and the
Supreme Court of Venezuela ruled Maduro was the legitimate president. Opposition leaders and some international media consider Maduro's government a dictatorship.
Since February 2014, hundreds of thousands have protested over high levels of criminal violence, corruption, hyperinflation, and chronic scarcity of basic goods due to government policies. Demonstrations and riots have resulted in over 40 fatalities in the unrest between Chavistas and opposition protesters
and opposition leaders, including
Leopoldo López and
Antonio Ledezma were arrested.
Human rights groups condemned the arrest of López. In the
2015 Venezuelan parliamentary election, the opposition gained a majority.
Venezuela devalued its currency in February 2013 due to rising shortages,
[ which included milk and other necessities. This led to an increase in malnutrition, especially among children.]Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
's administration imposed more economic sanctions
Economic sanctions or embargoes are Commerce, commercial and Finance, financial penalties applied by states or institutions against states, groups, or individuals. Economic sanctions are a form of Coercion (international relations), coercion tha ...
against PDVSA and Venezuelan officials. Economic problems, as well as crime, were the causes of the 2014–present Venezuelan protests. Since 2014, roughly 5.6 million people have fled Venezuela.
In January 2016, Maduro decreed an "economic emergency", revealing the extent of the crisis and expanding his powers. In July 2016, Colombian border crossings were temporarily opened to allow Venezuelans to purchase food and basic health items.food waste
The causes of food going uneaten are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during food production, production, food processing, processing, Food distribution, distribution, Grocery store, retail and food service sales, and Social clas ...
discarded by commercial establishments". 200 prison riots had occurred by October 2016. The Maduro-aligned Supreme Tribunal, which had been overturning
The Maduro-aligned Supreme Tribunal, which had been overturning National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
decisions since the opposition took control, took over the functions of the assembly, creating the 2017 Venezuelan constitutional crisis.enforced disappearance
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person with the support or acquiescence of a State (polity), state followed by a refusal to acknowledge the person's fate or whereabouts with the i ...
s that occurred in 2018–19. 724 enforced disappearances of political detainees were reported. The report stated that security forces subjected victims to torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons including corporal punishment, punishment, forced confession, extracting a confession, interrogational torture, interrogation for information, or intimid ...
. The report stated the government used enforced disappearances to silence opponents and other critical voices.
Maduro ran for a third consecutive term in the 2024 presidential election, while former diplomat Edmundo González Urrutia represented the Unitary Platform (; PUD), the main opposition political alliance.Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS or OEA; ; ; ) is an international organization founded on 30 April 1948 to promote cooperation among its member states within the Americas.
Headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, the OAS is ...
due to the lack of granular results, and disputed by the opposition, which claimed a landslide victory and released access to vote tallies collected by poll watchers from a majority of polling centers as proof.[
][ Also available fro]
MSN
.
In the aftermath of the announcement of results by the election authorities, protests broke out across the country.
Geography

 Venezuela is located in the north of South America; geologically, its mainland rests on the South American Plate. It has a total area of and a land area of , making Venezuela the 33rd largest country in the world. The territory it controls lies between latitudes 0° and 16°N and longitudes 59° and 74°W.
Shaped roughly like a triangle, the country has a coastline in the north, which includes numerous islands in the Caribbean and the northeast borders the northern Atlantic Ocean. Most observers describe Venezuela in terms of four fairly well defined topographical regions: the Maracaibo lowlands in the northwest, the northern mountains extending in a broad east–west arc from the Colombian border along the northern Caribbean coast, the wide plains in central Venezuela, and the Guiana Highlands in the southeast.
The northern mountains are the extreme northeastern extensions of South America's Andes mountain range. Pico Bolívar, the nation's highest point at , lies in this region. To the south, the dissected Guiana Highlands contain the northern fringes of the Amazon Basin and Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall, as well as '' tepuis'', large table-like mountains. The country's center is characterized by the ''llanos'', which are extensive plains that stretch from the Colombian border in the far west to the Orinoco River
Venezuela is located in the north of South America; geologically, its mainland rests on the South American Plate. It has a total area of and a land area of , making Venezuela the 33rd largest country in the world. The territory it controls lies between latitudes 0° and 16°N and longitudes 59° and 74°W.
Shaped roughly like a triangle, the country has a coastline in the north, which includes numerous islands in the Caribbean and the northeast borders the northern Atlantic Ocean. Most observers describe Venezuela in terms of four fairly well defined topographical regions: the Maracaibo lowlands in the northwest, the northern mountains extending in a broad east–west arc from the Colombian border along the northern Caribbean coast, the wide plains in central Venezuela, and the Guiana Highlands in the southeast.
The northern mountains are the extreme northeastern extensions of South America's Andes mountain range. Pico Bolívar, the nation's highest point at , lies in this region. To the south, the dissected Guiana Highlands contain the northern fringes of the Amazon Basin and Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall, as well as '' tepuis'', large table-like mountains. The country's center is characterized by the ''llanos'', which are extensive plains that stretch from the Colombian border in the far west to the Orinoco River delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
in the east. The Orinoco, with its rich alluvial soils, binds the largest and most important river system of the country; it originates in one of the largest watersheds in Latin America. The Caroní and the Apure are other major rivers.
 Venezuela borders Colombia to the west,
Venezuela borders Colombia to the west, Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
to the east, and Brazil to the south. Caribbean islands such as Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
, Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
, Curaçao
Curaçao, officially the Country of Curaçao, is a constituent island country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located in the southern Caribbean Sea (specifically the Dutch Caribbean region), about north of Venezuela.
Curaçao includ ...
, Aruba
Aruba, officially the Country of Aruba, is a constituent island country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, in the southern Caribbean Sea north of the Venezuelan peninsula of Paraguaná Peninsula, Paraguaná and northwest of Curaçao. In 19 ...
, and the Leeward Antilles lie near the Venezuelan coast. Venezuela has territorial disputes with Guyana, formerly United Kingdom, largely concerning the Essequibo area and with Colombia concerning the Gulf of Venezuela. In 1895, after years of diplomatic attempts to solve the border dispute, the dispute over the Essequibo River border flared up. It was submitted to a "neutral" commission (composed of British, American, and Russian representatives and without a direct Venezuelan representative), which in 1899 decided mostly against Venezuela's claim.
Climate
Venezuela is entirely located in the tropics over the Equator to around 12° N. Its climate varies from humid low-elevation plains, where average annual temperatures range as high as , to glaciers and highlands (the '' páramos'') with an average yearly temperature of . Annual rainfall varies from in the semiarid portions of the northwest to over in the Orinoco Delta of the far east and the Amazonian Jungle in the south. The precipitation level is lower in the period from August through April. These periods are referred to as hot-humid and cold-dry seasons. Another characteristic of the climate is this variation throughout the country by the existence of a mountain range called "Cordillera de la Costa" which crosses the country from east to west. The majority of the population lives in these mountains.
Biodiversity and conservation
 Venezuela lies within the
Venezuela lies within the Neotropical realm
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropics, tropical Ecoregion#Terrestrial, terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperat ...
; large portions of the country were originally covered by moist broadleaf forests. One of 17 megadiverse countries, Venezuela's habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
s range from the Andes Mountains in the west to the Amazon Basin rainforest in the south, via extensive ''llanos'' plains and Caribbean coast in the center and the Orinoco River Delta in the east. They include xeric scrublands in the extreme northwest and coastal mangrove forests in the northeast.rainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
s are particularly rich.
Animals
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a ...
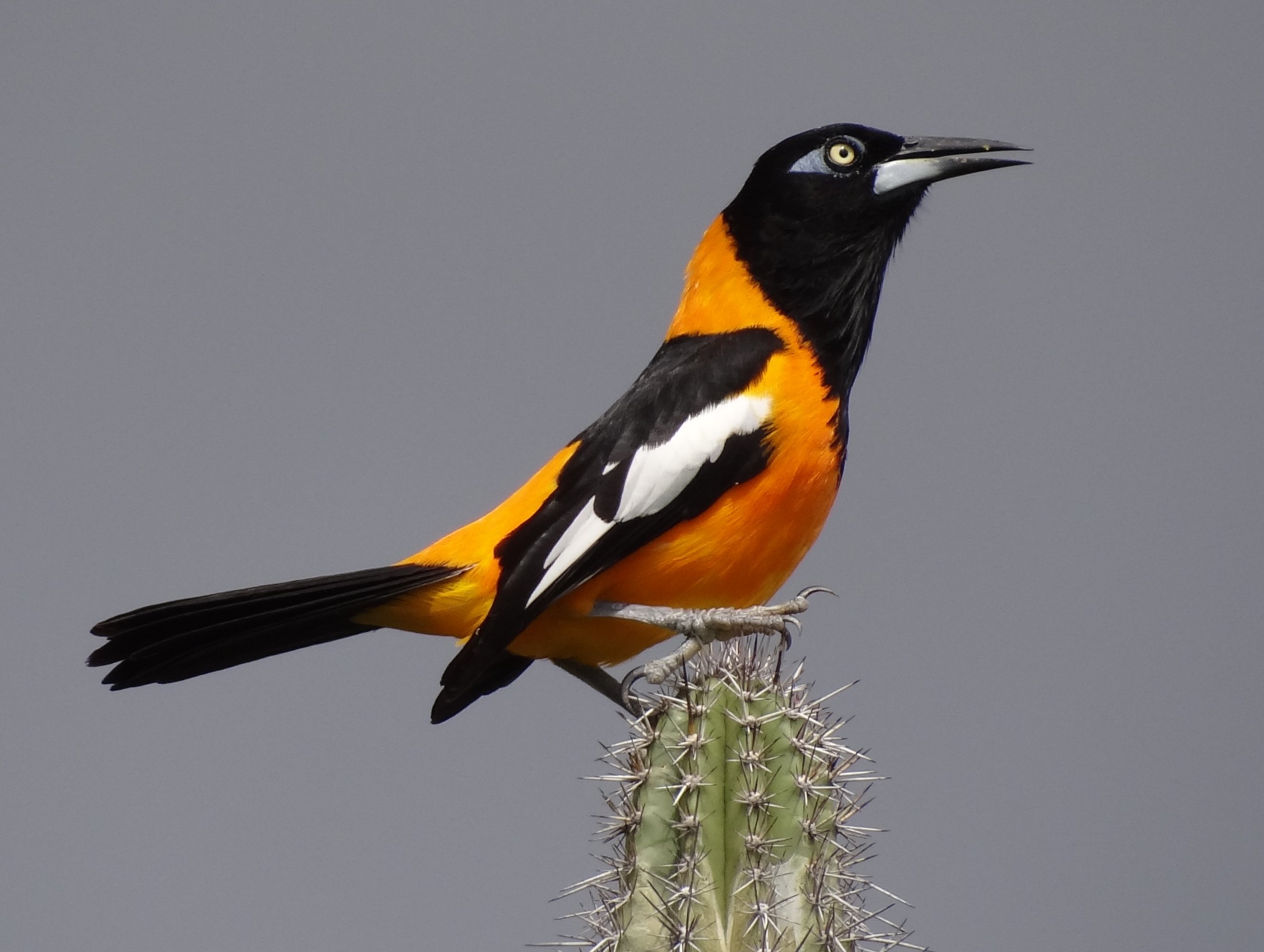
of Venezuela are diverse and include manatees, three-toed sloth, two-toed sloth, Amazon river dolphins, and Orinoco Crocodiles, which have been reported to reach up to in length. Venezuela hosts a total of 1,417 bird species, 48 of which are endemic. Important birds include ibises, ospreys, kingfishers, and the yellow-orange Venezuelan troupial, the national bird. Notable mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s include the giant anteater
The giant anteater (''Myrmecophaga tridactyla'') is an Insectivore, insectivorous mammal native to Central America, Central and South America. It is the largest of the four living species of anteaters, which are classified with sloths in the or ...
, jaguar, and the capybara, the world's largest rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
. More than half of Venezuelan avian and mammalian species are found in the Amazonian forests south of the Orinoco.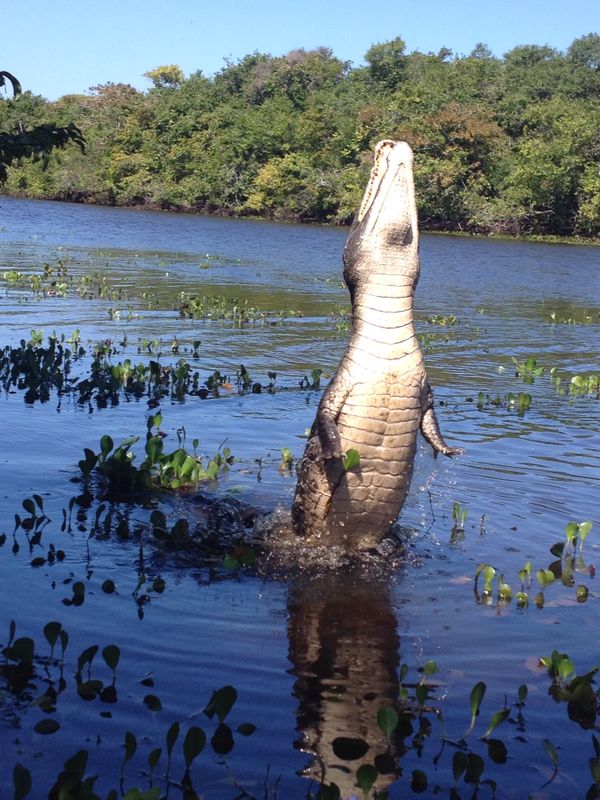 Among plants of Venezuela, over 25,000 species of orchids are found in the country's cloud forest and lowland rainforest ecosystems. These include the ''flor de mayo'' orchid ('' Cattleya mossiae''), the national flower. Venezuela's national tree is the araguaney. The tops of the tepuis are also home to several carnivorous plants including the marsh pitcher plant, Heliamphora, and the insectivorous bromeliad, Brocchinia reducta.
Venezuela is among the top 20 countries in terms of
Among plants of Venezuela, over 25,000 species of orchids are found in the country's cloud forest and lowland rainforest ecosystems. These include the ''flor de mayo'' orchid ('' Cattleya mossiae''), the national flower. Venezuela's national tree is the araguaney. The tops of the tepuis are also home to several carnivorous plants including the marsh pitcher plant, Heliamphora, and the insectivorous bromeliad, Brocchinia reducta.
Venezuela is among the top 20 countries in terms of endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
.amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
species, including the Trinidad poison frog, are endemic.wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
are registered under the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar site, Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on We ...
. In 2003, 70% of the nation's land was under conservation management in over 200 protected areas, including 43 national parks. Venezuela's 43 national parks include Canaima National Park, Morrocoy National Park, and Mochima National Park. In the far south is a reserve for the country's Yanomami tribes. Covering , the area is off-limits to farmers, miners, and all non-Yanomami settlers.
 Venezuela was one of the few countries that did not enter an INDC at COP21. Many terrestrial ecosystems are considered
Venezuela was one of the few countries that did not enter an INDC at COP21. Many terrestrial ecosystems are considered endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
, specially the dry forest in the northern regions of the country and the coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s in the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
coast.
Hydrography
The country is made up of three river basins: the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba ...
, the Atlantic Ocean and Lake Valencia, which forms an endorheic basin.
On the Atlantic side it drains most of Venezuela's river waters. The largest basin in this area is the extensive Orinoco basin whose surface area, close to one million km2, is greater than that of the whole of Venezuela, although it has a presence of 65% in the country.
The size of this basin - similar to that of the Danube - makes it the third largest in South America, and it gives rise to a flow of some 33,000 m3/s, making the Orinoco the third largest in the world, and also one of the most valuable from the point of view of renewable natural resources. The Rio or Brazo Casiquiare is unique in the world, as it is a natural derivation of the Orinoco that, after some 500 km in length, connects it to the Negro River, which in turn is a tributary of the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
.
 The Orinoco receives directly or indirectly rivers such as the Ventuari, the Caura, the Caroní, the Meta, the Arauca, the Apure and many others. Other Venezuelan rivers that empty into the Atlantic are the waters of the San Juan and Cuyuní basins. Finally, there is the Amazon River, which receives the Guainía, the Negro and others. Other basins are the Gulf of Paria and the Esequibo River.
The second most important watershed is the Caribbean Sea. The rivers of this region are usually short and of scarce and irregular flow, with some exceptions such as the Catatumbo, which originates in
The Orinoco receives directly or indirectly rivers such as the Ventuari, the Caura, the Caroní, the Meta, the Arauca, the Apure and many others. Other Venezuelan rivers that empty into the Atlantic are the waters of the San Juan and Cuyuní basins. Finally, there is the Amazon River, which receives the Guainía, the Negro and others. Other basins are the Gulf of Paria and the Esequibo River.
The second most important watershed is the Caribbean Sea. The rivers of this region are usually short and of scarce and irregular flow, with some exceptions such as the Catatumbo, which originates in Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
and drains into the Maracaibo Lake basin. Among the rivers that reach the Maracaibo lake basin are the Chama, the Escalante, the Catatumbo, and the contributions of the smaller basins of the Tocuyo, Yaracuy, Neverí and Manzanares rivers.
A minimum drains to the Lake Valencia basin. Of the total extension of the rivers, a total of 5400 km are navigable. Other rivers worth mentioning are the Apure, Arauca, Caura, Meta, Barima, Portuguesa, Ventuari and Zulia, among others.The country's main lakes are Lake Maracaibo -the largest in South America- open to the sea through the natural channel, but with fresh water, and Lake Valencia with its endorheic system. Other noteworthy bodies of water are the Guri reservoir, the Altagracia lagoon, the Camatagua reservoir and the Mucubají lagoon in the Andes.
Relief
The Venezuelan natural landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or human-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes th ...
 The relief of Venezuela has the following characteristics: coastline with several peninsulas and islands, adenas of the Andes mountain range (north and northwest), Lake Maracaibo (between the chains, on the coast);
The relief of Venezuela has the following characteristics: coastline with several peninsulas and islands, adenas of the Andes mountain range (north and northwest), Lake Maracaibo (between the chains, on the coast);Archean
The Archean ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan), in older sources sometimes called the Archaeozoic, is the second of the four geologic eons of Earth's history of Earth, history, preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic and t ...
rocks, with underlying layers of sandstone and shale clay.
The core of granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
and cordillera is, to a large extent, flanked by sedimentary layers from the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
, folded in an anticline structure. Between these orographic systems there are plains covered with tertiary and quaternary layers of gravel, sands and clayey marls. The depression contains lagoons and lakes, among which is that of Maracaibo, and presents, on the surface, alluvial deposits from the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
.
* Coastal Mountain Range
Also known as the Cordillera de la Costa, stretches along Venezuela's northern coast. This region is known for its lush tropical rainforests, stunning coastal views, and a rich variety of flora and fauna. The intermountain depressions, or valleys, between the mountain ranges are often home to fertile agricultural land and vibrant communities. These valleys offer a stark contrast to the rugged mountains that rise dramatically from the coast.
* Lara-Falcón Highlands
Situated in northwestern Venezuela, the Lara-Falcón Highlands exhibit a terrain defined by plateaus and rolling hills. These highlands provide a significant contrast to the surrounding lowlands and coastal areas. The relief is characterized by gently sloping plateaus that support agriculture, including coffee and cacao cultivation. This region's semi-arid climate and picturesque landscapes make it an important agricultural and tourism center.
* Lake Maracaibo Lowlands
Encompass the basin of Lake Maracaibo and the plains surrounding the Gulf of Venezuela. This region offers two distinct plains—the northern one is relatively dry, while the southern one is humid and dotted with swamps. The relief here is primarily characterized by flat terrain, with the exception of some elevated areas near the lake. Lake Maracaibo itself sits in a depression, surrounded by oil-rich lands and productive agricultural areas.Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
mountain range, offer a striking relief with towering peaks, deep valleys, and fertile intermontane basins. Dominated by these corpulent mountain ranges, including Venezuela's highest peak, Bolívar Peak, the region's rugged and picturesque landscapes are defined by its high-altitude terrain.
 The unique relief of this area finds its origins in the Last Glacial Period, where the interplay of repeated glacier advances and retreats sculpted the landscape, shaped by the cold, high-altitude climate. This glacial heritage has left a lasting imprint, with glaciers carving deep valleys and polishing rugged peaks, while sheltered intramontane valleys offer fertile soils and temperate microclimates, creating ideal conditions for agriculture and human settlement.
* Los Llanos
Los Llanos, or "the plains", are expansive sedimentary basins characterized by predominantly flat relief. However, the eastern Llanos feature low-plateaus and the Unare depression, created through mesa erosion, adding diversity to the terrain. This region is subject to seasonal flooding, transforming the flat plains into a vast wetland during the rainy season. The relief here influences the region's unique ecosystems, including extensive grasslands and abundant wildlife.
* Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield boasts a varied relief shaped by geological processes over millions of years. This region encompasses peneplains, rugged mountain ranges, foothills, and the iconic tepuis, or table-top mountains. The tepuis stand as isolated, flat-topped plateaus that rise dramatically from the surrounding terrain. This unique relief contributes to the region's remarkable biodiversity and scientific significance.
The unique relief of this area finds its origins in the Last Glacial Period, where the interplay of repeated glacier advances and retreats sculpted the landscape, shaped by the cold, high-altitude climate. This glacial heritage has left a lasting imprint, with glaciers carving deep valleys and polishing rugged peaks, while sheltered intramontane valleys offer fertile soils and temperate microclimates, creating ideal conditions for agriculture and human settlement.
* Los Llanos
Los Llanos, or "the plains", are expansive sedimentary basins characterized by predominantly flat relief. However, the eastern Llanos feature low-plateaus and the Unare depression, created through mesa erosion, adding diversity to the terrain. This region is subject to seasonal flooding, transforming the flat plains into a vast wetland during the rainy season. The relief here influences the region's unique ecosystems, including extensive grasslands and abundant wildlife.
* Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield boasts a varied relief shaped by geological processes over millions of years. This region encompasses peneplains, rugged mountain ranges, foothills, and the iconic tepuis, or table-top mountains. The tepuis stand as isolated, flat-topped plateaus that rise dramatically from the surrounding terrain. This unique relief contributes to the region's remarkable biodiversity and scientific significance.
Valleys
The valleys are undoubtedly the most important type of landscape
A landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or human-made features, often considered in terms of their aesthetic appeal.''New Oxford American Dictionary''. A landscape includes th ...
in the Venezuelan territory, not because of their spatial extension, but because they are the environment where most of the country's population and economic activities are concentrated. On the other hand, there are valleys throughout almost all the national space, except in the great sedimentary basins of the Llanos and the depression of the Maracaibo Lake, except also in the Amazonian peneplains.altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
. They are also the most picturesque in terms of their style of habitat, forms of land use, handicraft
A handicraft is a traditional main sector of craft making and applies to a wide range of creative and design activities that are related to making things with one's hands and skill, including work with textiles, moldable and rigid material ...
production and all the traditions linked to these activities.
Deserts
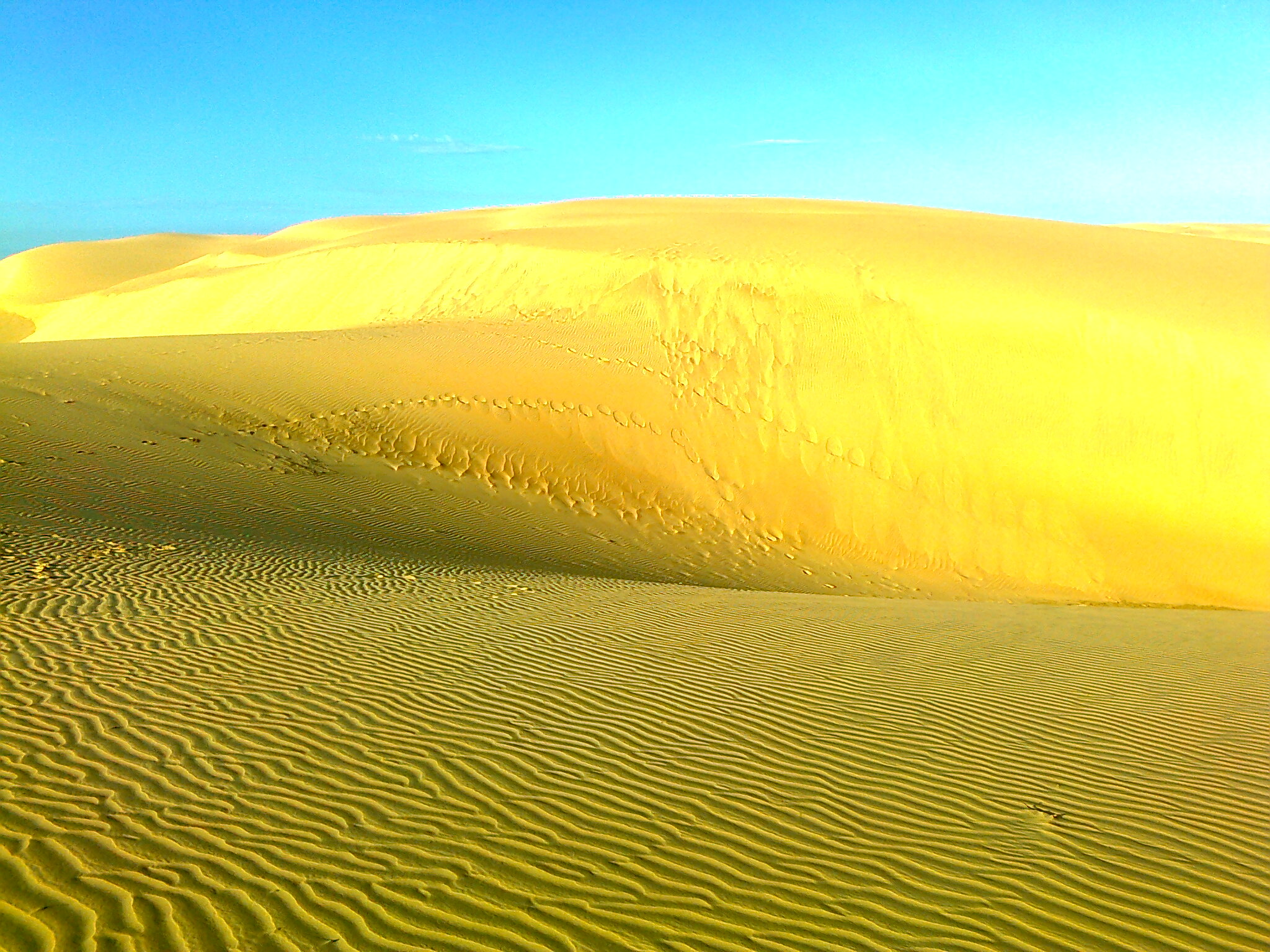 Venezuela has a great diversity of landscapes and climates, including arid and dry areas. The main
Venezuela has a great diversity of landscapes and climates, including arid and dry areas. The main desert
A desert is a landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions create unique biomes and ecosystems. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the la ...
in the country is in the state of Falcon near the city of Coro. It is now a protected park, the Médanos de Coro National Park. The park is the largest of its kind in Venezuela, covering 91 square kilometres. The landscape is dotted with cacti and other xerophytic plants that can survive in humidity-free conditions near the desert.
Desert wildlife includes mostly lizards, iguanas and other reptiles. Although less frequent, the desert is home to some foxes, giant anteaters and rabbits. There are also some native bird populations, such as the sparrowhawk, tropical mockingbird, scaly dove and crested quail.
Other desert areas in the country include part of the Guajira Desert in the Guajira Municipality in the north of Zulia State and facing the Gulf of Venezuela, the Médanos de Capanaparo in the Santos Luzardo National Park in Apure State, the Medanos de la Isla de Zapara in Zulia State, the so-called Hundición de Yay in the Andrés Eloy Blanco Municipality of Lara State, and the Urumaco Formation also in Falcón State.
Government and politics
 Two major blocs of
Two major blocs of political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
are in Venezuela: the incumbent leftist bloc United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV), its major allies Fatherland for All (PPT) and the Communist Party of Venezuela (PCV), and the opposition bloc grouped into the electoral coalition Mesa de la Unidad Democrática. This includes A New Era (UNT) together with allied parties Project Venezuela, Justice First, Movement for Socialism (MAS) and others.
The Venezuelan president is elected by a vote, with direct and universal suffrage
Universal suffrage or universal franchise ensures the right to vote for as many people bound by a government's laws as possible, as supported by the " one person, one vote" principle. For many, the term universal suffrage assumes the exclusion ...
, and is both head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...
and head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
. The term of office is six years, and (as of 15 February 2009) a president may be re-elected an unlimited number of times. The president appoints the vice president and decides the size and composition of the cabinet and makes appointments to it with the involvement of the legislature. The president can ask the legislature to reconsider portions of laws he finds objectionable, but a simple parliamentary majority can override these objections.
The president may ask the National Assembly to pass an enabling act granting the ability to rule by decree in specified policy areas; this requires a two-thirds majority in the Assembly. Since 1959, six Venezuelan presidents have been granted such powers.
The unicameral Venezuelan parliament is the ''Asamblea Nacional'' ("National Assembly"). The number of members is variable – each state and the Capital district elect three representatives plus the result of dividing the state population by 1.1% of the total population of the country. Three seats are reserved for representatives of Venezuela's Indigenous peoples. For the 2011–2016 period the number of seats is 165. All deputies serve five-year terms.
The voting age in Venezuela is 18. Voting is not compulsory.Continental Law
Civil law is a legal system rooted in the Roman Empire and was comprehensively codified and disseminated starting in the 19th century, most notably with France's Napoleonic Code (1804) and Germany's (1900). Unlike common law systems, which re ...
tradition. The highest judicial body is the Supreme Tribunal of Justice or ''Tribunal Supremo de Justicia'', whose magistrates are elected by parliament for a single twelve-year term. The National Electoral Council (''Consejo Nacional Electoral'', or ''CNE'') is in charge of electoral processes; it is formed by five main directors elected by the National Assembly. Supreme Court president Luisa Estela Morales said in December 2009 that Venezuela had moved away from "a rigid division of powers" toward a system characterized by "intense coordination" between the branches of government. Morales clarified that each power must be independent.
Administrative divisions
 Venezuela is divided into 23 states (''estados''), a capital district (''distrito capital'') corresponding to the city of Caracas, and the Federal Dependencies (''Dependencias Federales'', a special territory). Venezuela is further subdivided into 335 municipalities (''municipios''); these are subdivided into over one thousand parishes (''parroquias''). The states are grouped into nine administrative regions (''regiones administrativas''), which were established in 1969 by presidential decree.
The country can be further divided into ten geographical areas, some corresponding to climatic and biogeographical regions. In the north are the Venezuelan Andes and the Coro region, a mountainous tract in the northwest, holds several sierras and valleys. East of it are lowlands abutting Lake Maracaibo and the Gulf of Venezuela.
The Central Range runs parallel to the coast and includes the hills surrounding
Venezuela is divided into 23 states (''estados''), a capital district (''distrito capital'') corresponding to the city of Caracas, and the Federal Dependencies (''Dependencias Federales'', a special territory). Venezuela is further subdivided into 335 municipalities (''municipios''); these are subdivided into over one thousand parishes (''parroquias''). The states are grouped into nine administrative regions (''regiones administrativas''), which were established in 1969 by presidential decree.
The country can be further divided into ten geographical areas, some corresponding to climatic and biogeographical regions. In the north are the Venezuelan Andes and the Coro region, a mountainous tract in the northwest, holds several sierras and valleys. East of it are lowlands abutting Lake Maracaibo and the Gulf of Venezuela.
The Central Range runs parallel to the coast and includes the hills surrounding Caracas
Caracas ( , ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas (CCS), is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern p ...
; the Eastern Range, separated from the Central Range by the Gulf of Cariaco, covers all of Sucre
Sucre (; ) is the ''de jure'' capital city of Bolivia, the capital of the Chuquisaca Department and the sixth most populous city in Bolivia. Located in the south-central part of the country, Sucre lies at an elevation of . This relatively high ...
and northern Monagas. The Insular Region includes all of Venezuela's island possessions: Nueva Esparta and the various Federal Dependencies. The Orinoco Delta, which forms a triangle covering Delta Amacuro, projects northeast into the Atlantic Ocean.
The country maintains a claim on the territory it calls "Guayana Esequiba", the territory administered by Guyana west of the Esequibo River. In 1966 the British and Venezuelan governments signed the Geneva Agreement to resolve the conflict peacefully. The Port of Spain Protocol of 1970 set a deadline to try to resolve the issue, without success to date.
Largest cities
Suspension of constitutional rights
The 2015 parliamentary elections were held on 6 December 2015 to elect the 164 deputies and three Indigenous representatives of the National Assembly. In 2014, a series of protest and demonstrations began in Venezuela, attributed to inflation, violence and shortages in Venezuela. The protests were largely peaceful.Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
a day after the parliamentary elections,Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS or OEA; ; ; ) is an international organization founded on 30 April 1948 to promote cooperation among its member states within the Americas.
Headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, the OAS is ...
was considering the application of the Inter-American Democratic Charter sanctions for non-compliance to its own constitution.
In March 2017, the Venezuelan Supreme Court took over law making powers from the National Assembly but reversed its decision the following day.
Foreign relations
Throughout most of the 20th century, Venezuela maintained friendly relations with most Latin American and Western nations. Relations between Venezuela and the United States government worsened in 2002, after the 2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt during which the U.S. government recognized the short-lived interim presidency of Pedro Carmona. In 2015, Venezuela was declared a national security threat by U.S. president Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
. Correspondingly, ties to various Latin American and Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
ern countries not allied to the U.S. have strengthened.
Venezuela seeks alternative hemispheric integration via such proposals as the Bolivarian Alternative for the Americas trade proposal and the newly launched Latin American television network teleSUR. Venezuela is one of five nations in the world—along with Russia, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria—to have recognized the independence of Abkhazia and South Ossetia. Venezuela was a proponent of OAS's decision to adopt its Anti-Corruption Convention and is actively working in the Mercosur trade bloc to push increased trade and energy integration. Globally, it seeks a " multi-polar" world based on strengthened ties among undeveloped countries.
 On 26 April 2017, Venezuela announced its intention to withdraw from the OAS. Venezuelan Foreign Minister Delcy Rodríguez said that President Nicolás Maduro plans to publicly renounce Venezuela's membership on 27 April 2017. It will take two years for the country to formally leave. During this period, the country does not plan on participating in the OAS.
Venezuela is involved in a long-standing disagreement about the control of the
On 26 April 2017, Venezuela announced its intention to withdraw from the OAS. Venezuelan Foreign Minister Delcy Rodríguez said that President Nicolás Maduro plans to publicly renounce Venezuela's membership on 27 April 2017. It will take two years for the country to formally leave. During this period, the country does not plan on participating in the OAS.
Venezuela is involved in a long-standing disagreement about the control of the Guayana Esequiba
Guyana is a country in the Guianas, South America.
Guyana, Guiana, or Guayana may refer to:
* British Guiana, a British colony until 1966, now independent and known as Guyana
* French Guiana, an overseas department of France in the Guianas
* The ...
area.
Venezuela may suffer a deterioration of its power in international affairs if the global transition to renewable energy is completed. It is ranked 151 out of 156 countries in the index of Geopolitical Gains and Losses after energy transition (GeGaLo).
Venezuela is a charter member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
(UN), Organization of American States
The Organization of American States (OAS or OEA; ; ; ) is an international organization founded on 30 April 1948 to promote cooperation among its member states within the Americas.
Headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, the OAS is ...
(OAS), Union of South American Nations (UNASUR), Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America (ALBA), Mercosur, Latin American Integration Association (LAIA) and Organization of Ibero-American States
The Organization of Ibero-American States (, , ; abbreviated as OEI), formally the Organization of Ibero-American States for Education, Science and Culture, is an international organization made up of Member states of the Organization of Ibero-Am ...
(OEI).
Military
 The Bolivarian National Armed Forces (''Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana'', FANB) are the unified military forces of Venezuela. It includes over 320,150 men and women, under Article 328 of the Constitution, in five components of ground, sea and air. The components of the FANB are: the Venezuelan Army, the Venezuelan Navy, the Venezuelan Air Force, the Venezuelan National Guard, and the Venezuelan National Militia. , a further 600,000 soldiers were incorporated into a new branch, known as the Armed Reserve.
The president of Venezuela is the commander-in-chief of the FANB. Its main purposes are to defend the sovereign national territory of Venezuela, airspace, and islands, fight against drug trafficking, search and rescue and, in the case of a natural disaster, civil protection. All male citizens of Venezuela have a constitutional duty to register for the military service at 18, which is the
The Bolivarian National Armed Forces (''Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana'', FANB) are the unified military forces of Venezuela. It includes over 320,150 men and women, under Article 328 of the Constitution, in five components of ground, sea and air. The components of the FANB are: the Venezuelan Army, the Venezuelan Navy, the Venezuelan Air Force, the Venezuelan National Guard, and the Venezuelan National Militia. , a further 600,000 soldiers were incorporated into a new branch, known as the Armed Reserve.
The president of Venezuela is the commander-in-chief of the FANB. Its main purposes are to defend the sovereign national territory of Venezuela, airspace, and islands, fight against drug trafficking, search and rescue and, in the case of a natural disaster, civil protection. All male citizens of Venezuela have a constitutional duty to register for the military service at 18, which is the age of majority
The age of majority is the threshold of legal adulthood as recognized or declared in law. It is the moment when a person ceases to be considered a minor (law), minor, and assumes legal control over their person, actions, and decisions, thus te ...
.
Law and crime
In Venezuela, a person is murdered every 21 minutes. Violent crimes have been so prevalent in Venezuela that the government no longer produces the crime data. In 2013, the homicide rate was approximately 79 per 100,000, one of the world's highest, having quadrupled in the past 15 years with over 200,000 people murdered. By 2015, it had risen to 90 per 100,000.United States Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy of the United State ...
and the Government of Canada
The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federation, federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes Minister of t ...
have warned foreign visitors that they may be subjected to robbery, kidnapping and murder, and that their own diplomatic travelers are required to travel in armored vehicles. The United Kingdom's Foreign and Commonwealth Office has advised against all travel to Venezuela. Visitors have been murdered during robberies.
There are approximately 33 prisons holding about 50,000 inmates. Venezuela's prison system is heavily overcrowded; its facilities have capacity for only 14,000 prisoners.
Human rights
Human rights organizations such as Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Headquartered in New York City, the group investigates and reports on issues including War crime, war crimes, crim ...
and Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says that it has more than ten million members a ...
have increasingly criticized Venezuela's human rights record, with the former organization noting in 2017 that the Chavez and subsequently the Maduro government have increasingly concentrated power in the executive branch, eroded constitutional human rights protections and allowed the government to persecute and repress its critics and opposition. Other persistent concerns as noted by the report included poor prison conditions, the continuous harassment of independent media and human rights defenders by the government. In 2006, the Economist Intelligence Unit
The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) is the research and analysis division of the Economist Group, providing forecasting and advisory services through research and analysis, such as monthly country reports, five-year country economic forecasts ...
rated Venezuela a "hybrid regime" and the third least democratic regime in Latin America on the Democracy Index. The Democracy index downgraded Venezuela to an authoritarian regime in 2017, citing continued increasingly dictatorial behaviors by the Maduro government.
Corruption
Corruption in Venezuela is high by world standards and was so for much of the 20th century. The discovery of oil worsened political corruption. By the late 1970s, Juan Pablo Pérez Alfonso's description of oil as "the Devil's excrement" had become a common expression in Venezuela. The Corruption Perceptions Index has ranked Venezuela as one of the most corrupt countries since the survey started in 1995. The 2010 ranking placed Venezuela at number 164, out of 178 ranked countries in government transparency. By 2016, the rank had increased to 166 out of 178. The World Justice Project ranked Venezuela 99th out of 99 countries surveyed in its 2014 Rule of Law Index.
This corruption is shown with Venezuela's significant involvement in drug trafficking, with Colombian cocaine and other drugs transiting Venezuela towards the United States and Europe. In the period 2003–2008 Venezuelan authorities seized the fifth-largest total quantity of cocaine in the world, behind Colombia, the United States, Spain and Panama
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Latin America at the southern end of Central America, bordering South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and ...
. In 2006, the government's agency for combating illegal drug trade in Venezuela, '' ONA'', was incorporated into the office of the vice-president. However, many major government and military officials have been known for their involvement with drug trafficking.
Economy
Venezuela was "once among South America's wealthiest countries" before the economic meltdown under Maduro regime.mixed economy
A mixed economy is an economic system that includes both elements associated with capitalism, such as private businesses, and with socialism, such as nationalized government services.
More specifically, a mixed economy may be variously de ...
dominated by the petroleum sector, which accounts for roughly a third of GDP, around 80% of exports, and more than half of government revenues. Per capita GDP for 2016 was estimated to be US$15,100, ranking 109th in the world.monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
for the Venezuelan bolívar which is used as currency. The president of the Central Bank of Venezuela serves as the country's representative in the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution funded by 191 member countries, with headquarters in Washington, D.C. It is regarded as the global lender of las ...
. The U.S.-based conservative think tank The Heritage Foundation claims Venezuela has the weakest property rights in the world, scoring only 5.0 on a scale of 100; expropriation without compensation is not uncommon.
As of 2011, more than 60% of Venezuela's international reserves was in gold, eight times more than the average for the region. Most of Venezuela's gold held abroad was located in London. On 25 November 2011, the first of US$11 billion of repatriated gold bullion arrived in Caracas; Chávez called the repatriation of gold a "sovereign" step that will help protect the country's foreign reserves from the turmoil in the U.S. and Europe. However government policies quickly spent down this returned gold and in 2013 the government was forced to add the dollar reserves of state owned companies to those of the national bank to reassure the international bond market.
Manufacturing contributed 17% of GDP in 2006. Venezuela manufactures and exports heavy industry products such as steel, aluminium and cement, with production concentrated around Ciudad Guayana, near the Guri Dam, one of the largest in the world and the provider of about three-quarters of Venezuela's electricity. Other notable manufacturing includes electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
and automobiles, as well as beverages, and foodstuff
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is in ...
s. Agriculture in Venezuela accounts for approximately 3% of GDP, 10% of the labor force, and at least a quarter of Venezuela's land area. The country is not self-sufficient in most areas of agriculture.
Since the discovery of oil in the early 20th century, Venezuela has been one of the world's leading exporters of oil, and it is a founding member of OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC ) is an organization enabling the co-operation of leading oil-producing and oil-dependent countries in order to collectively influence the global oil market and maximize Profit (eco ...
. Previously an underdeveloped exporter of agricultural commodities, oil quickly came to dominate exports and government revenues. The 1980s oil glut led to an external debt crisis and a long-running economic crisis, which saw inflation peak at 100% in 1996. The 1990s also saw Venezuela experience a major banking crisis in 1994.
 The recovery of oil prices after 2001 boosted the Venezuelan economy and facilitated social spending. With social programs such as the Bolivarian Missions, Venezuela initially made progress in social development in the 2000s, particularly in areas such as health, education, and poverty. Many of the social policies pursued by Chávez and his administration were jump-started by the Millennium Development Goals, eight goals that Venezuela and 188 other nations agreed to in September 2000. The sustainability of the Bolivarian Missions has been questioned due to the Bolivarian state's overspending on public works and because the Chávez government did not save funds for future economic hardships, with economic issues and poverty rising as a result of their policies in the 2010s.
The recovery of oil prices after 2001 boosted the Venezuelan economy and facilitated social spending. With social programs such as the Bolivarian Missions, Venezuela initially made progress in social development in the 2000s, particularly in areas such as health, education, and poverty. Many of the social policies pursued by Chávez and his administration were jump-started by the Millennium Development Goals, eight goals that Venezuela and 188 other nations agreed to in September 2000. The sustainability of the Bolivarian Missions has been questioned due to the Bolivarian state's overspending on public works and because the Chávez government did not save funds for future economic hardships, with economic issues and poverty rising as a result of their policies in the 2010s.Great Recession
The Great Recession was a period of market decline in economies around the world that occurred from late 2007 to mid-2009. led to a renewed economic downturn. Despite controversial data shared by the Venezuelan government showing that the country had halved malnutrition following one of the UN's Millennium Development Goals, In early 2013, Venezuela devalued its currency due to growing shortages in the country.
In early 2013, Venezuela devalued its currency due to growing shortages in the country.[ Fears rose so high due to the toilet paper shortage that the government occupied a toilet paper factory, and continued plans to nationalize other industrial aspects like food distribution. Venezuela's bond ratings have also decreased multiple times in 2013 due to decisions by the president Nicolás Maduro. In 2016, consumer prices in Venezuela increased 800% and the economy declined by 18.6%, entering an ]economic depression
An economic depression is a period of carried long-term economic downturn that is the result of lowered economic activity in one or more major national economies. It is often understood in economics that economic crisis and the following recession ...
. Venezuela's outlook was deemed negative by most bond-rating services in 2017. For 2018 an inflation rate of 1,000,000 percent was projected, putting Venezuela in a similar situation to that in Germany in 1923 or Zimbabwe in the late 2000s.
Tourism
Tourism has been developed considerably in recent decades, particularly because of its favorable geographical position, the variety of landscapes, the richness of plant and wildlife, the culture and the tropical climate.
Margarita Island is one of the top tourist destinations. It is an island with a modern infrastructure, bordered by beaches suitable for extreme sports, and features castles, fortresses and churches of great cultural value.
Los Roques Archipelago is made up of a set of islands and keys that constitute one of the main tourist attractions in the country. With exotic crystalline beaches, Morrocoy is a national park, formed by small keys very close to the mainland, which have grown rapidly as one of the greatest tourist attractions in the Venezuelan Caribbean.
 Canaima National Park extends over 30,000 km2 to the border with Guyana and Brazil; due to its size it is considered the sixth largest national park in the world. Its steep cliffs and waterfalls (including Angel Falls, which is the highest waterfall in the world, at 1,002 m) form spectacular landscapes.
The state of Mérida is one of the main tourist centers of Venezuela. It has an extensive network of hotels not only in its capital city, but also throughout the state. Starting from the same city of Mérida is the longest and highest cable car in the world, which reaches the Pico Espejo of 4,765 m.
Canaima National Park extends over 30,000 km2 to the border with Guyana and Brazil; due to its size it is considered the sixth largest national park in the world. Its steep cliffs and waterfalls (including Angel Falls, which is the highest waterfall in the world, at 1,002 m) form spectacular landscapes.
The state of Mérida is one of the main tourist centers of Venezuela. It has an extensive network of hotels not only in its capital city, but also throughout the state. Starting from the same city of Mérida is the longest and highest cable car in the world, which reaches the Pico Espejo of 4,765 m.
Shortages
Shortages in Venezuela have been prevalent following the enactment of price controls and other policies during the economic policy of the Hugo Chávez government
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
.
Petroleum and other resources
Venezuela has the largest oil reserves, and the eighth largest natural gas reserves in the world. Compared to the preceding year another 40.4% in crude oil reserves were proven in 2010, allowing Venezuela to surpass Saudi Arabia as the country with the largest reserves of this type. The country's main petroleum deposits are located around and beneath Lake Maracaibo, the Gulf of Venezuela (both in Zulia), and in the Orinoco River basin ( eastern Venezuela), where the country's largest reserve is located. Besides the largest conventional oil reserves and the second-largest natural gas reserves in the Western Hemisphere,bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
and tar sands) approximately equal to the world's reserves of conventional oil.hydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, ...
, and includes the Guri Dam, one of the largest in the world.
In the first half of the 20th century, U.S. oil companies were heavily involved in Venezuela, initially interested only in purchasing concessions. In 1943 a new government introduced a 50/50 split in profits between the government and the oil industry. In 1960, with a newly installed democratic government, Hydrocarbons Minister Juan Pablo Pérez Alfonso led the creation of OPEC, the consortium of oil-producing countries aiming to support the price of oil.
 In 1973, Venezuela voted to nationalize its oil industry outright, effective 1 January 1976, with Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) taking over and presiding over a number of holding companies; in subsequent years, Venezuela built a vast refining and marketing system in the U.S. and Europe. In the 1990s PDVSA became more independent from the government and presided over an ''apertura'' (opening) in which it invited in foreign investment. Under Hugo Chávez a 2001 law placed limits on foreign investment. PDVSA played a key role in the December 2002 – February 2003 national strike. As a result of the strike, around 40% of the company's workforce (around 18,000 workers) were dismissed.
In 1973, Venezuela voted to nationalize its oil industry outright, effective 1 January 1976, with Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) taking over and presiding over a number of holding companies; in subsequent years, Venezuela built a vast refining and marketing system in the U.S. and Europe. In the 1990s PDVSA became more independent from the government and presided over an ''apertura'' (opening) in which it invited in foreign investment. Under Hugo Chávez a 2001 law placed limits on foreign investment. PDVSA played a key role in the December 2002 – February 2003 national strike. As a result of the strike, around 40% of the company's workforce (around 18,000 workers) were dismissed.
Infrastructure
Transport
Venezuela is connected to the world primarily via air ( Venezuela's airports include the Simón Bolívar International Airport in Maiquetía, near Caracas and La Chinita International Airport near Maracaibo) and sea (with major seaports at La Guaira, Maracaibo and Puerto Cabello). In the south and east the Amazon rainforest region has limited cross-border transport; in the west, there is a mountainous border of over shared with Colombia. The Orinoco River is navigable by oceangoing vessels up to inland and connects the major industrial city of Ciudad Guayana to the Atlantic Ocean.
Venezuela has a limited national railway system, which has no active rail connections to other countries. The government of Hugo Chávez tried to invest in expanding it, but Venezuela's rail project is on hold due to Venezuela not being able to pay the $7.5 billion and owing China Railway nearly $500 million.
Several major cities have metro systems; the Caracas Metro has been operating since 1983. The Maracaibo Metro and Valencia Metro were opened more recently. Venezuela has a road network of nearly , placing the country around 45th in the world; around a third of roads are paved.
Utilities
The electricity sector in Venezuela is heavily dependent on hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
, with this energy source accounting for 64% of the country's electricity generation in 2021.[
]
Demographics
Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America.conurbation
A conurbation is a region consisting of a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which, through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ...
. Other major cities include Barquisimeto, Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
, Maracay, Maracaibo, Barcelona-Puerto La Cruz, Mérida and San Cristóbal.
According to the total population was in . A 2014 study by sociologists of the Central University of Venezuela found over 1.5 million Venezuelans, or about 4% to 6% of the country's population, have left Venezuela since 1999.
Ethnicity
 The people of Venezuela come from a variety of ancestries. It is estimated that the majority of the population is of pardo, or mixed, ethnic ancestry. In the 2011 census, which Venezuelans were asked to identify themselves according to their customs and ancestry, the term ''pardo'' was excluded from the answers. The majority claimed to be moreno or
The people of Venezuela come from a variety of ancestries. It is estimated that the majority of the population is of pardo, or mixed, ethnic ancestry. In the 2011 census, which Venezuelans were asked to identify themselves according to their customs and ancestry, the term ''pardo'' was excluded from the answers. The majority claimed to be moreno or white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
—51.6% and 43.6%, respectively.Yanomami
The Yanomami, also spelled Yąnomamö or Yanomama, are a group of approximately 35,000 indigenous people of the Americas, indigenous people who live in some 200–250 villages in the Amazon rainforest on the border between Venezuela and Brazil. ...
; the remaining 9% consisted of other Indigenous nations.
According to an autosomal DNA study conducted in 2008 by the University of Brasília, the composition of Venezuela's population is 60.60% European, 23% Indigenous, and 16.30% African.
During the colonial period and until after the Second World War, many of the European immigrants to Venezuela came from the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
with a relevant amount of Galicians and Asturians. These immigrants from Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
had a significant cultural impact on the cuisine and customs of Venezuela. These influences on Venezuela have led to the nation being called the 8th island of the Canaries. With the start of oil exploitation in the early 20th century, companies from the United States began establishing operations in Venezuela, bringing with them U.S. citizens. Later, during and after the war, new waves of immigrants from other parts of Europe, the Middle East, and China began; many were encouraged by government-established immigration programs and lenient immigration policies.refugee
A refugee, according to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), is a person "forced to flee their own country and seek safety in another country. They are unable to return to their own country because of feared persecution as ...
and asylum seekers from Colombia numbering 252,200 in 2007, and 10,600 new asylum seekers entered Venezuela in 2007.Yanomami
The Yanomami, also spelled Yąnomamö or Yanomama, are a group of approximately 35,000 indigenous people of the Americas, indigenous people who live in some 200–250 villages in the Amazon rainforest on the border between Venezuela and Brazil. ...
installed in the south, and the Pemon which are mostly in the southeast of Venezuela.
Languages
Although most residents are monolingual Spanish speakers, many languages are spoken in Venezuela. In addition to Spanish, the Constitution recognizes more than thirty Indigenous languages, including Wayuu, Warao, Pemón, and many others for the official use of the Indigenous peoples, mostly with few speakers – less than 1% of the total population. Wayuu is the most spoken Indigenous language, with 170,000 speakers. Immigrants, in addition to Spanish, speak their own languages. Chinese (400,000), Portuguese (254,000),
Immigrants, in addition to Spanish, speak their own languages. Chinese (400,000), Portuguese (254,000),Puerto la Cruz
Puerto La Cruz () is a port city located in Anzoátegui State, in Venezuela. It is the seat of the Juan Antonio Sotillo Municipality. The city has road connections to the state capital, Barcelona, to Lecheria and to Guanta.
Geography
The cit ...
, El Tigre, Maracay, and Caracas. Portuguese is spoken not only by the Portuguese community in Santa Elena de Uairén but also by much of the population due to its proximity to Brazil. The German community speaks their native language, while the people of Colonia Tovar speak mostly an Alemannic dialect of German called ''alemán coloniero''.
English is the most widely used foreign language in demand and is spoken by many professionals, academics, and members of the upper and middle classes as a result of the oil exploration by foreign companies, in addition to its acceptance as a lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
. Culturally, English is common in southern towns like El Callao, and the native English-speaking (English-creole speaking) influence is evident in folk and calypso songs from the region. Various dialects of Eastern-Caribbean English-based creoles were brought to Venezuela by Trinidadian and other British West Indies immigrants, they are collectively referred to as Venezuelan English Creole. A variety of Antillean Creole
Antillean French Creole (also known as Lesser Antillean Creole, Kreyol, or Patois) is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles caribbean. Its grammar and vocabulary include ele ...
is spoken by a small community in El Callao and Paria. Italian language teaching is delivered by private Venezuelan schools and institutions. Other languages spoken by large communities in the country are Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
and Galician, among others.
Religion
According to a 2011 poll, 88% of the population is Christian, primarily Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
(71%), and the remaining 17% Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, primarily Evangelicals (in Latin America Protestants are usually called ''"evangélicos"''). 8% of Venezuelans are irreligious. Almost 3% of the population follow another religion (1% of these people practice Santería
Santería (), also known as Regla de Ocha, Regla Lucumí, or Lucumí, is an African diaspora religions, Afro-Caribbean religion that developed in Cuba during the late 19th century. It arose amid a process of syncretism between the traditional ...
).Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
,[.] Buddhist, and Jewish communities. The Muslim community of more than 100,000 is concentrated among persons of Lebanese and Syrian descent living in Nueva Esparta state, Punto Fijo and the Caracas
Caracas ( , ), officially Santiago de León de Caracas (CCS), is the capital and largest city of Venezuela, and the center of the Metropolitan Region of Caracas (or Greater Caracas). Caracas is located along the Guaire River in the northern p ...
area. Venezuela is home of the largest Druze communities outside the Middle East,Druze
The Druze ( ; , ' or ', , '), who Endonym and exonym, call themselves al-Muwaḥḥidūn (), are an Arabs, Arab Eastern esotericism, esoteric Religious denomination, religious group from West Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic ...
community are estimated around 60,000,[Annual Report 2004: Venezuela.]
Stephen Roth Institute
The Stephen Roth Institute for the Study of Contemporary Antisemitism and Racism is a research institute at Tel Aviv University in Israel.
It is a resource for information, provides a forum for academic discussion, and fosters research on issue ...
. Accessed 11 August 2006. with the population declining from 22,000 in 1999
Health
Venezuela has a national universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized a ...
system. The current government has created a program to expand access to health care known as Misión Barrio Adentro,malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
was 17%. Delta Amacuro and Amazonas had the nation's highest rates. According to the United Nations, 32% of Venezuelans lacked adequate sanitation, primarily those living in rural areas. Diseases ranging from diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacteria, bacterium ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild Course (medicine), clinical course, but in some outbreaks, the mortality rate approaches 10%. Signs a ...
, plague, malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
,typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by ''Salmonella enterica'' serotype Typhi bacteria, also called ''Salmonella'' Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often ther ...
fever, yellow fever, cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis D were present in the country.[Venezuela](_blank)
Guardian. 25 October 2006. Retrieved 20 September 2006. Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
was prevalent in approximately 30% of the adult population.
Education
 In 2008, 95.2% of the adult population was literate.
In 2008, 95.2% of the adult population was literate.
Culture
 The culture of Venezuela is a melting pot made up of three main groups: The Indigenous Venezuelans, the Africans, and the Spanish.
The Africans brought in many musical influences, especially introduction of the drum. The Spanish influence predominantes due to the colonization process and the socioeconomic structure it created. Spanish influences can be seen in the country's architecture, music, religion, and language.
Venezuela was also enriched by immigration streams of Indian and European origin in the 19th century, especially from France. Most recently, immigration from the United States, Spain, Italy, and Portugal has enriched the already complex cultural mosaic.
The culture of Venezuela is a melting pot made up of three main groups: The Indigenous Venezuelans, the Africans, and the Spanish.
The Africans brought in many musical influences, especially introduction of the drum. The Spanish influence predominantes due to the colonization process and the socioeconomic structure it created. Spanish influences can be seen in the country's architecture, music, religion, and language.
Venezuela was also enriched by immigration streams of Indian and European origin in the 19th century, especially from France. Most recently, immigration from the United States, Spain, Italy, and Portugal has enriched the already complex cultural mosaic.
Architecture
Carlos Raúl Villanueva was the most important Venezuelan architect of the modern era; he designed the Central University of Venezuela, (a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
) and its Aula Magna. Other notable architectural works include the Capitolio, the Baralt Theatre, the Teresa Carreño Cultural Complex, and the General Rafael Urdaneta Bridge. In Venezuela, prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
man began to build useful architecture from approximately 1000 BC to the 15th century AD, in the period known as the "Neo-Indian". Neo-Indian architecture consisted of incipient constructions, such as agricultural terraces and vaults lined by stones, called mintoyes, which were used as tombs and silos for the storage of agricultural products. The Indo-Hispanic architecture is the one that begins to develop from the year 1498 AD. Venezuelan colonial architecture is built from the 16th century, when Venezuela began to be a dependent colony of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
, until 1810, when the process of Venezuelan independence began.
The architecture of this period is characterized by its discreet modesty, with the exception of some cities. The explanation lies in the socioeconomic conditions of the country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, ...
. Venezuela did not offer then to the colonizers the immense riches kept by nature for later times. The simplification of technical problems, the renunciation of most of the decorative elements and variegated ostentations of fanciful baroque, the impossibility of using expensive materials and the consequent lack of craftsmen, contributed to establish a modest but well-defined physiognomy of the colonial architecture of Venezuela. During the colonial period, there were eventually confrontations between the Spanish conquerors and the barbarians and pirates that sailed along the Venezuelan coasts, in order to take over the provinces located on the coasts of the country.
Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
temples from the colonial era were constituted by an almost invariable, arrangement consisting of a rectangular plan, three naves separated by arches of alfarje roofing composed of religious architecture in colonial times. The Venezuelan society dedicated a great amount of resources to erect religious monuments comparable to those of other countries of the continent. The XVII century was of reconstruction of the Catholic churches that had been destroyed by the earthquake of 1641. In the 18th century, specifically between 1728 and 1785, the prosperity that Venezuela enjoyed due to the opening of the Compañía Guipuzcoana de Caracas was also reflected in the construction of new architecture, especially of a religious nature.
Art
 Venezuelan art was initially dominated by religious motifs. However, in the late 19th century, artists began emphasizing historical and heroic representations of the country's struggle for independence. This move was led by Martín Tovar y Tovar.
Venezuelan art was initially dominated by religious motifs. However, in the late 19th century, artists began emphasizing historical and heroic representations of the country's struggle for independence. This move was led by Martín Tovar y Tovar. Modernism
Modernism was an early 20th-century movement in literature, visual arts, and music that emphasized experimentation, abstraction, and Subjectivity and objectivity (philosophy), subjective experience. Philosophy, politics, architecture, and soc ...
took over in the 20th century. Notable Venezuelan artists include Arturo Michelena, Cristóbal Rojas, Armando Reverón, Manuel Cabré; the kinetic artists Jesús Soto, Gego and Carlos Cruz-Diez; and contemporary artists such as Marisol and Yucef Merhi.
Literature
Venezuelan literature originated soon after the Spanish conquest of the mostly pre-literate Indigenous societies. It was originally dominated by Spanish influences. Following the rise of political literature during the Venezuelan War of Independence, Venezuelan Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
, notably expounded by Juan Vicente González, emerged as the first important genre in the region. Although mainly focused on narrative writing, Venezuelan literature was advanced by poets such as Andrés Eloy Blanco and Fermín Toro.
Major writers and novelists include Rómulo Gallegos, Teresa de la Parra, Arturo Uslar Pietri, Adriano González León, Miguel Otero Silva, and Mariano Picón Salas. The great poet and humanist Andrés Bello was also an educator and intellectual (He was also a childhood tutor and mentor of Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24July 178317December 1830) was a Venezuelan statesman and military officer who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama, and Bol ...
). Others, such as Laureano Vallenilla Lanz and José Gil Fortoul, contributed to Venezuelan Positivism
Positivism is a philosophical school that holds that all genuine knowledge is either true by definition or positivemeaning '' a posteriori'' facts derived by reason and logic from sensory experience.John J. Macionis, Linda M. Gerber, ''Soci ...
.
Music
The Indigenous musical styles of Venezuela are exemplified by groups like Un Solo Pueblo and Serenata Guayanesa. The national musical instrument is the cuatro. Traditional musical styles and songs mainly emerged in and around the llanos region, including "Alma llanera" (by Pedro Elías Gutiérrez and Rafael Bolívar Coronado), "Florentino y el diablo" (by Alberto Arvelo Torrealba), "Concierto en la llanura" by Juan Vicente Torrealba, and "Caballo viejo" (by Simón Díaz).
The Zulian gaita is also a very popular genre, generally performed during Christmas. The national dance is the joropo. Venezuela has always been a melting pot of cultures and this can be seen in the richness and variety of its musical styles and dances: calipso, bambuco, fulía, cantos de pilado de maíz, cantos de lavanderas, sebucán, and maremare. Teresa Carreño
María Teresa Gertrudis de Jesús Carreño García (December 22, 1853June 12, 1917) was a Venezuelans, Venezuelan pianist, composer, soprano, and conductor. Over the course of her 54-year concert career, she became an internationally renowned v ...
was a world-famous 19th century piano virtuoso. Recently, great classical music performances have come out of Venezuela. The Simón Bolívar Youth Orchestra has hosted a number of excellent concerts in many European concert halls, most notably at the 2007 London Proms, and has received several honors. The orchestra is the pinnacle of El Sistema, a publicly financed, voluntary music education program now being emulated in other countries.
In the early 21st century, a movement known as "Movida Acústica Urbana" featured musicians trying to save some national traditions, creating their own original songs but using traditional instruments. Some groups following this movement are Tambor Urbano, Los Sinverguenzas, C4Trío, and Orozco Jam.
Afro-Venezuelan musical traditions are most intimately related to the festivals of the "black folk saints" San Juan and St. Benedict the Moor. Specific songs are related to the different stages of their festivals and processions, when the saints start their yearly "''paseo"'' – stroll – through the community.
Sport
The origins of baseball in Venezuela are unclear, although it is known that the sport was being played in the country by the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, North American immigrants who came to Venezuela to work in the nation's oil industry helped to popularize the sport in Venezuela. During the 1930s, baseball's popularity continued to rise in the country, leading to the foundation of the Venezuelan Professional Baseball League (LVBP) in 1945, and the sport would soon become the nation's most popular.
The popularity of baseball in the country makes Venezuela a rarity among its South American neighbors—association football is the dominant sport in the continent. However, football, as well as basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular Basketball court, court, compete with the primary objective of #Shooting, shooting a basketball (ball), basketball (appro ...
, are among the more popular sports played in Venezuela. Venezuela hosted the 2012 Basketball World Olympic Qualifying Tournament and the 2013 FIBA Basketball Americas Championship, which took place in the Poliedro de Caracas.
Although not as popular in Venezuela as the rest of South America, football, spearheaded by the Venezuela national football team is gaining popularity as well. The sport is also noted for having an increased focus during the World Cup. Venezuela is scheduled to host the Copa América every 40 years.
Venezuela is also home to former Formula 1 driver, Pastor Maldonado.2012 Summer Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012, were an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
, Rubén Limardo won a gold medal in fencing
Fencing is a combat sport that features sword fighting. It consists of three primary disciplines: Foil (fencing), foil, épée, and Sabre (fencing), sabre (also spelled ''saber''), each with its own blade and set of rules. Most competitive fe ...
.
See also
* Index of Venezuela-related articles
The following is an alphabetical list of topics related to Venezuela.
0–9
*.ve – Internet country code top-level domain for Venezuela
A
*Amazonas State, Venezuela
*Americas
**South America
***Islands of Venezuela
****North Atlantic Oce ...
* Outline of Venezuela
Notes
References
Bibliography
Articles
*
Books
*
*
* Carroll, Rory. ''Comandante: Hugo Chávez's Venezuela'' (Penguin Books, 2014).
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Schincariol, Vitor Eduardo. ''Society and Economy in Venezuela: An Overview of the Bolivarian Period (1998-2018).'' (2020).
*
* Straka, Tomás, Guillermo Guzmán Mirabal, and Alejandro E. Cáceres. ''Historical Dictionary of Venezuela'' (Rowman & Littlefield, 2017).
*
*
*
* Wilpert, Gregory. ''Changing Venezuela by taking power: the history and policies of the Chavez government'' (2007
online
*
*
*
*
*
Talks and interviews
*
External links
Official Government Website
Venezuela
''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
.
Venezuela
at ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
from the Library of Congress Country Studies (1990)
Venezuela profile
from the BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
*
Maps on Venezuela – Cartographic features
Key Development Forecasts for Venezuela
from International Futures
Venezuela and Tourism
from immigrationtovenezuela.com.ve
*
Venezuela situation - emergency appeal
{{Coord, 7, N, 65, W, type:country_region:VE, display=title
Countries in South America
Federal constitutional republics
Former Spanish colonies
G15 nations
Member states of OPEC
Member states of the United Nations
Member states of the Union of South American Nations
Spanish-speaking countries and territories
States and territories established in 1811
 In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus sailed near the Orinoco Delta and landed in the Gulf of Paria. Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in a letter to Isabella and Ferdinand that he must have reached Heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
Spain's colonization of mainland Venezuela started in 1522, establishing its first permanent South American settlement in the city of Cumaná.
In 1498, during his third voyage to the Americas, Christopher Columbus sailed near the Orinoco Delta and landed in the Gulf of Paria. Amazed by the great offshore current of freshwater which deflected his course eastward, Columbus expressed in a letter to Isabella and Ferdinand that he must have reached Heaven on Earth (terrestrial paradise):
Spain's colonization of mainland Venezuela started in 1522, establishing its first permanent South American settlement in the city of Cumaná.
 Sucre went on to liberate
Sucre went on to liberate  In 1895, a longstanding dispute with Great Britain about the Essequibo territory, which Britain claimed as part of
In 1895, a longstanding dispute with Great Britain about the Essequibo territory, which Britain claimed as part of  The 1973 Venezuelan presidential election of Carlos Andrés Pérez coincided with an oil crisis, in which Venezuela's income exploded as oil prices soared; oil industries were nationalized in 1976. This led to massive increases in public spending, but also increases in external debts, until the collapse of oil prices during the 1980s crippled the economy. As the government started to devalue the currency in 1983 to face its financial obligations, standards of living fell dramatically. Failed economic policies and increasing corruption in government led to rising poverty and crime, worsening social indicators, and increased political instability.
In the 1980s, the Presidential Commission for State Reform (COPRE) emerged as a mechanism of political innovation. Venezuela decentralized its political system and diversified its economy, reducing the size of the state. COPRE operated as an innovation mechanism, also by incorporating issues into the political agenda, that were excluded from public deliberation by the main actors of the democratic system. The most discussed topics were incorporated into the public agenda: decentralization, political participation, municipalization, judicial order reforms and the role of the state in a new economic strategy. The social reality made the changes difficult to apply.
Economic crises in the 1980s and 1990s led to a political crisis. Hundreds of people were killed by security forces and the military in the '' Caracazo'' riots of 1989, during the second presidential term of Carlos Andrés Pérez (1989–1993) and after the implementation of economic austerity measures. Hugo Chávez, who in 1982 had promised to depose the bipartisanship governments, used the growing anger at economic austerity measures to justify a coup attempt in February 1992; a second coup d'état attempt occurred in November. President Carlos Andrés Pérez (re-elected in 1988) was impeached under embezzlement charges in 1993, leading to the interim presidency of Ramón José Velásquez (1993–1994). Coup leader Chávez was pardoned in March 1994 by president Rafael Caldera (1994–1999, his second term), with a clean slate and his political rights reinstated, allowing Chávez to win and maintain the presidency continuously from 1999 until his death in 2013. Chávez won the elections of 1998, 2000, 2006 and 2012 and the presidential referendum of 2004.
The 1973 Venezuelan presidential election of Carlos Andrés Pérez coincided with an oil crisis, in which Venezuela's income exploded as oil prices soared; oil industries were nationalized in 1976. This led to massive increases in public spending, but also increases in external debts, until the collapse of oil prices during the 1980s crippled the economy. As the government started to devalue the currency in 1983 to face its financial obligations, standards of living fell dramatically. Failed economic policies and increasing corruption in government led to rising poverty and crime, worsening social indicators, and increased political instability.
In the 1980s, the Presidential Commission for State Reform (COPRE) emerged as a mechanism of political innovation. Venezuela decentralized its political system and diversified its economy, reducing the size of the state. COPRE operated as an innovation mechanism, also by incorporating issues into the political agenda, that were excluded from public deliberation by the main actors of the democratic system. The most discussed topics were incorporated into the public agenda: decentralization, political participation, municipalization, judicial order reforms and the role of the state in a new economic strategy. The social reality made the changes difficult to apply.
Economic crises in the 1980s and 1990s led to a political crisis. Hundreds of people were killed by security forces and the military in the '' Caracazo'' riots of 1989, during the second presidential term of Carlos Andrés Pérez (1989–1993) and after the implementation of economic austerity measures. Hugo Chávez, who in 1982 had promised to depose the bipartisanship governments, used the growing anger at economic austerity measures to justify a coup attempt in February 1992; a second coup d'état attempt occurred in November. President Carlos Andrés Pérez (re-elected in 1988) was impeached under embezzlement charges in 1993, leading to the interim presidency of Ramón José Velásquez (1993–1994). Coup leader Chávez was pardoned in March 1994 by president Rafael Caldera (1994–1999, his second term), with a clean slate and his political rights reinstated, allowing Chávez to win and maintain the presidency continuously from 1999 until his death in 2013. Chávez won the elections of 1998, 2000, 2006 and 2012 and the presidential referendum of 2004.
 A collapse in confidence in the existing parties led to Hugo Chávez being elected president in 1998 and the subsequent launch of a "Bolivarian Revolution", beginning with a 1999 constituent assembly to write a new Constitution. The Revolution refers to a
A collapse in confidence in the existing parties led to Hugo Chávez being elected president in 1998 and the subsequent launch of a "Bolivarian Revolution", beginning with a 1999 constituent assembly to write a new Constitution. The Revolution refers to a  The Maduro-aligned Supreme Tribunal, which had been overturning
The Maduro-aligned Supreme Tribunal, which had been overturning 
 Venezuela is located in the north of South America; geologically, its mainland rests on the South American Plate. It has a total area of and a land area of , making Venezuela the 33rd largest country in the world. The territory it controls lies between latitudes 0° and 16°N and longitudes 59° and 74°W.
Shaped roughly like a triangle, the country has a coastline in the north, which includes numerous islands in the Caribbean and the northeast borders the northern Atlantic Ocean. Most observers describe Venezuela in terms of four fairly well defined topographical regions: the Maracaibo lowlands in the northwest, the northern mountains extending in a broad east–west arc from the Colombian border along the northern Caribbean coast, the wide plains in central Venezuela, and the Guiana Highlands in the southeast.
The northern mountains are the extreme northeastern extensions of South America's Andes mountain range. Pico Bolívar, the nation's highest point at , lies in this region. To the south, the dissected Guiana Highlands contain the northern fringes of the Amazon Basin and Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall, as well as '' tepuis'', large table-like mountains. The country's center is characterized by the ''llanos'', which are extensive plains that stretch from the Colombian border in the far west to the Orinoco River
Venezuela is located in the north of South America; geologically, its mainland rests on the South American Plate. It has a total area of and a land area of , making Venezuela the 33rd largest country in the world. The territory it controls lies between latitudes 0° and 16°N and longitudes 59° and 74°W.
Shaped roughly like a triangle, the country has a coastline in the north, which includes numerous islands in the Caribbean and the northeast borders the northern Atlantic Ocean. Most observers describe Venezuela in terms of four fairly well defined topographical regions: the Maracaibo lowlands in the northwest, the northern mountains extending in a broad east–west arc from the Colombian border along the northern Caribbean coast, the wide plains in central Venezuela, and the Guiana Highlands in the southeast.
The northern mountains are the extreme northeastern extensions of South America's Andes mountain range. Pico Bolívar, the nation's highest point at , lies in this region. To the south, the dissected Guiana Highlands contain the northern fringes of the Amazon Basin and Angel Falls, the world's highest waterfall, as well as '' tepuis'', large table-like mountains. The country's center is characterized by the ''llanos'', which are extensive plains that stretch from the Colombian border in the far west to the Orinoco River  Venezuela was one of the few countries that did not enter an INDC at COP21. Many terrestrial ecosystems are considered
Venezuela was one of the few countries that did not enter an INDC at COP21. Many terrestrial ecosystems are considered  The unique relief of this area finds its origins in the Last Glacial Period, where the interplay of repeated glacier advances and retreats sculpted the landscape, shaped by the cold, high-altitude climate. This glacial heritage has left a lasting imprint, with glaciers carving deep valleys and polishing rugged peaks, while sheltered intramontane valleys offer fertile soils and temperate microclimates, creating ideal conditions for agriculture and human settlement.
* Los Llanos
Los Llanos, or "the plains", are expansive sedimentary basins characterized by predominantly flat relief. However, the eastern Llanos feature low-plateaus and the Unare depression, created through mesa erosion, adding diversity to the terrain. This region is subject to seasonal flooding, transforming the flat plains into a vast wetland during the rainy season. The relief here influences the region's unique ecosystems, including extensive grasslands and abundant wildlife.
* Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield boasts a varied relief shaped by geological processes over millions of years. This region encompasses peneplains, rugged mountain ranges, foothills, and the iconic tepuis, or table-top mountains. The tepuis stand as isolated, flat-topped plateaus that rise dramatically from the surrounding terrain. This unique relief contributes to the region's remarkable biodiversity and scientific significance.
* Orinoco Delta
The Orinoco Delta's relief is characterized by a complex system of lands and waters. It consists of numerous channels, islands, and shifting sedimentary deposits. While the relief may appear relatively uniform, it conceals a dynamic environment influenced by seasonal flooding and sediment deposition. This complex deltaic relief supports diverse aquatic life and the livelihoods of Indigenous communities adapted to its ever-changing landscapes.
The unique relief of this area finds its origins in the Last Glacial Period, where the interplay of repeated glacier advances and retreats sculpted the landscape, shaped by the cold, high-altitude climate. This glacial heritage has left a lasting imprint, with glaciers carving deep valleys and polishing rugged peaks, while sheltered intramontane valleys offer fertile soils and temperate microclimates, creating ideal conditions for agriculture and human settlement.
* Los Llanos
Los Llanos, or "the plains", are expansive sedimentary basins characterized by predominantly flat relief. However, the eastern Llanos feature low-plateaus and the Unare depression, created through mesa erosion, adding diversity to the terrain. This region is subject to seasonal flooding, transforming the flat plains into a vast wetland during the rainy season. The relief here influences the region's unique ecosystems, including extensive grasslands and abundant wildlife.
* Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield boasts a varied relief shaped by geological processes over millions of years. This region encompasses peneplains, rugged mountain ranges, foothills, and the iconic tepuis, or table-top mountains. The tepuis stand as isolated, flat-topped plateaus that rise dramatically from the surrounding terrain. This unique relief contributes to the region's remarkable biodiversity and scientific significance.
* Orinoco Delta
The Orinoco Delta's relief is characterized by a complex system of lands and waters. It consists of numerous channels, islands, and shifting sedimentary deposits. While the relief may appear relatively uniform, it conceals a dynamic environment influenced by seasonal flooding and sediment deposition. This complex deltaic relief supports diverse aquatic life and the livelihoods of Indigenous communities adapted to its ever-changing landscapes.
 Venezuela has a great diversity of landscapes and climates, including arid and dry areas. The main
Venezuela has a great diversity of landscapes and climates, including arid and dry areas. The main  Two major blocs of
Two major blocs of  On 26 April 2017, Venezuela announced its intention to withdraw from the OAS. Venezuelan Foreign Minister Delcy Rodríguez said that President Nicolás Maduro plans to publicly renounce Venezuela's membership on 27 April 2017. It will take two years for the country to formally leave. During this period, the country does not plan on participating in the OAS.
Venezuela is involved in a long-standing disagreement about the control of the
On 26 April 2017, Venezuela announced its intention to withdraw from the OAS. Venezuelan Foreign Minister Delcy Rodríguez said that President Nicolás Maduro plans to publicly renounce Venezuela's membership on 27 April 2017. It will take two years for the country to formally leave. During this period, the country does not plan on participating in the OAS.
Venezuela is involved in a long-standing disagreement about the control of the  The Bolivarian National Armed Forces (''Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana'', FANB) are the unified military forces of Venezuela. It includes over 320,150 men and women, under Article 328 of the Constitution, in five components of ground, sea and air. The components of the FANB are: the Venezuelan Army, the Venezuelan Navy, the Venezuelan Air Force, the Venezuelan National Guard, and the Venezuelan National Militia. , a further 600,000 soldiers were incorporated into a new branch, known as the Armed Reserve.
The president of Venezuela is the commander-in-chief of the FANB. Its main purposes are to defend the sovereign national territory of Venezuela, airspace, and islands, fight against drug trafficking, search and rescue and, in the case of a natural disaster, civil protection. All male citizens of Venezuela have a constitutional duty to register for the military service at 18, which is the
The Bolivarian National Armed Forces (''Fuerza Armada Nacional Bolivariana'', FANB) are the unified military forces of Venezuela. It includes over 320,150 men and women, under Article 328 of the Constitution, in five components of ground, sea and air. The components of the FANB are: the Venezuelan Army, the Venezuelan Navy, the Venezuelan Air Force, the Venezuelan National Guard, and the Venezuelan National Militia. , a further 600,000 soldiers were incorporated into a new branch, known as the Armed Reserve.
The president of Venezuela is the commander-in-chief of the FANB. Its main purposes are to defend the sovereign national territory of Venezuela, airspace, and islands, fight against drug trafficking, search and rescue and, in the case of a natural disaster, civil protection. All male citizens of Venezuela have a constitutional duty to register for the military service at 18, which is the  The recovery of oil prices after 2001 boosted the Venezuelan economy and facilitated social spending. With social programs such as the Bolivarian Missions, Venezuela initially made progress in social development in the 2000s, particularly in areas such as health, education, and poverty. Many of the social policies pursued by Chávez and his administration were jump-started by the Millennium Development Goals, eight goals that Venezuela and 188 other nations agreed to in September 2000. The sustainability of the Bolivarian Missions has been questioned due to the Bolivarian state's overspending on public works and because the Chávez government did not save funds for future economic hardships, with economic issues and poverty rising as a result of their policies in the 2010s. In 2003 the government of Hugo Chávez implemented currency controls after capital flight led to a devaluation of the currency. This led to the development of a parallel market of dollars in the subsequent years. The
The recovery of oil prices after 2001 boosted the Venezuelan economy and facilitated social spending. With social programs such as the Bolivarian Missions, Venezuela initially made progress in social development in the 2000s, particularly in areas such as health, education, and poverty. Many of the social policies pursued by Chávez and his administration were jump-started by the Millennium Development Goals, eight goals that Venezuela and 188 other nations agreed to in September 2000. The sustainability of the Bolivarian Missions has been questioned due to the Bolivarian state's overspending on public works and because the Chávez government did not save funds for future economic hardships, with economic issues and poverty rising as a result of their policies in the 2010s. In 2003 the government of Hugo Chávez implemented currency controls after capital flight led to a devaluation of the currency. This led to the development of a parallel market of dollars in the subsequent years. The  In early 2013, Venezuela devalued its currency due to growing shortages in the country. The shortages included, and still include, necessities such as toilet paper, milk, and flour. Fears rose so high due to the toilet paper shortage that the government occupied a toilet paper factory, and continued plans to nationalize other industrial aspects like food distribution. Venezuela's bond ratings have also decreased multiple times in 2013 due to decisions by the president Nicolás Maduro. In 2016, consumer prices in Venezuela increased 800% and the economy declined by 18.6%, entering an
In early 2013, Venezuela devalued its currency due to growing shortages in the country. The shortages included, and still include, necessities such as toilet paper, milk, and flour. Fears rose so high due to the toilet paper shortage that the government occupied a toilet paper factory, and continued plans to nationalize other industrial aspects like food distribution. Venezuela's bond ratings have also decreased multiple times in 2013 due to decisions by the president Nicolás Maduro. In 2016, consumer prices in Venezuela increased 800% and the economy declined by 18.6%, entering an  In 1973, Venezuela voted to nationalize its oil industry outright, effective 1 January 1976, with Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) taking over and presiding over a number of holding companies; in subsequent years, Venezuela built a vast refining and marketing system in the U.S. and Europe. In the 1990s PDVSA became more independent from the government and presided over an ''apertura'' (opening) in which it invited in foreign investment. Under Hugo Chávez a 2001 law placed limits on foreign investment. PDVSA played a key role in the December 2002 – February 2003 national strike. As a result of the strike, around 40% of the company's workforce (around 18,000 workers) were dismissed.
In 1973, Venezuela voted to nationalize its oil industry outright, effective 1 January 1976, with Petróleos de Venezuela (PDVSA) taking over and presiding over a number of holding companies; in subsequent years, Venezuela built a vast refining and marketing system in the U.S. and Europe. In the 1990s PDVSA became more independent from the government and presided over an ''apertura'' (opening) in which it invited in foreign investment. Under Hugo Chávez a 2001 law placed limits on foreign investment. PDVSA played a key role in the December 2002 – February 2003 national strike. As a result of the strike, around 40% of the company's workforce (around 18,000 workers) were dismissed.
 The people of Venezuela come from a variety of ancestries. It is estimated that the majority of the population is of pardo, or mixed, ethnic ancestry. In the 2011 census, which Venezuelans were asked to identify themselves according to their customs and ancestry, the term ''pardo'' was excluded from the answers. The majority claimed to be moreno or
The people of Venezuela come from a variety of ancestries. It is estimated that the majority of the population is of pardo, or mixed, ethnic ancestry. In the 2011 census, which Venezuelans were asked to identify themselves according to their customs and ancestry, the term ''pardo'' was excluded from the answers. The majority claimed to be moreno or  The culture of Venezuela is a melting pot made up of three main groups: The Indigenous Venezuelans, the Africans, and the Spanish.
The Africans brought in many musical influences, especially introduction of the drum. The Spanish influence predominantes due to the colonization process and the socioeconomic structure it created. Spanish influences can be seen in the country's architecture, music, religion, and language.
Venezuela was also enriched by immigration streams of Indian and European origin in the 19th century, especially from France. Most recently, immigration from the United States, Spain, Italy, and Portugal has enriched the already complex cultural mosaic.
The culture of Venezuela is a melting pot made up of three main groups: The Indigenous Venezuelans, the Africans, and the Spanish.
The Africans brought in many musical influences, especially introduction of the drum. The Spanish influence predominantes due to the colonization process and the socioeconomic structure it created. Spanish influences can be seen in the country's architecture, music, religion, and language.
Venezuela was also enriched by immigration streams of Indian and European origin in the 19th century, especially from France. Most recently, immigration from the United States, Spain, Italy, and Portugal has enriched the already complex cultural mosaic.