|
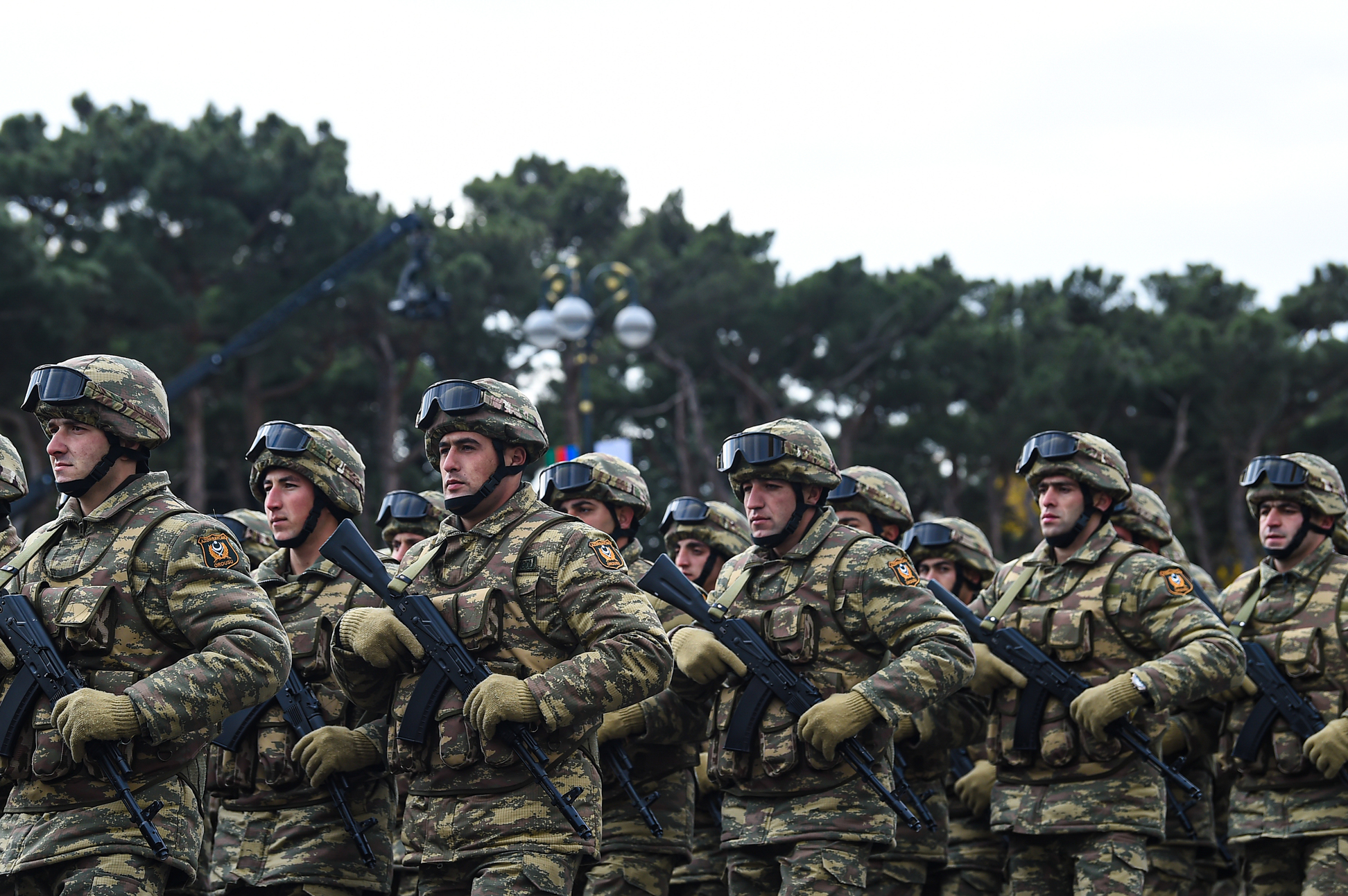
Venezuelan Army
The Bolivarian Army of Venezuela (), is the land arm of the National Bolivarian Armed Forces of Venezuela. Also known as Bolivarian Army (''Ejército Bolivariano'', EB), its role is to be responsible for land-based operations against external or internal threats that may put the sovereignty of the nation at risk. The army is the second largest military branch of Venezuela after the Bolivarian Militia (''Milicia Bolivariana'', MB). Its current commander is Major General José Murga Baptista. The army depends directly on the Ministry of Popular Power for Defense, under the orders of the general commander and the president of the Republic in his position as commander in chief of the National Bolivarian Armed Forces. It is divided into six combat arms and four commands; operations, logistics, education and Army Aviation. The command officers, troop officers, technicians and military surgeons belonging to the Venezuelan Army are graduates of the military academies of the Boliv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by possessing an army aviation component. Within a national military force, the word army may also mean a field army. Definition In some countries, such as France and China, the term "army", especially in its plural form "armies", has the broader meaning of armed forces as a whole, while retaining the colloquial sense of land forces. To differentiate the colloquial army from the formal concept of military force, the term is qualified, for example in France the land force is called , meaning Land Army, and the air and space force is called , meaning Air and Space Army. The naval force, although not using the term "army", is also included in the broad sense of the term "armies" — thus the French Navy is an integral component of the collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Gideon (2020)
:''This article uses Spanish naming customs: the paternal surname is first, and the maternal surname is second.'' Operation Gideon () was an unsuccessful attempt by the Active Coalition of the Venezuelan International Reserve, Venezuelan dissidents, and a private military company, private security firm, Jordan Goudreau's Silvercorp USA, to infiltrate Venezuela by sea and remove Nicolás Maduro from power. The plan executed from 3 to 4 May 2020 was for expatriate Venezuelan former military personnel living in Colombia to enter the country by boat at Macuto, Vargas, Macuto, take control of an airfield, capture Maduro and other high-level figures in his administration, and expel them from the country. A landing attempt to initiate the operation went forward despite its impracticality. Two boats were launched from eastern Colombia toward the Caribbean Sea, Caribbean coast of Venezuela north of Caracas, carrying approximately 60 Venezuelan dissidents and two American former Green B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivarian Militia Of Venezuela
The Bolivarian Militia of Venezuela is a militia branch of the National Bolivarian Armed Forces of Venezuela. Its headquarters is at the National Military Museum, Fort Montana, Caracas. The Commanding General of the National Militia is Major General Javier José Marcano Tábata, as of August 2024. The National Militia celebrates its anniversary every April 13 yearly. Mission According to the Article 46 of the organic law establishing the Militia, its functions are: * Enlist, organize, equip, instruct, train and retrain formed units of the National Bolivarian Militia; * Establish permanent links between the National Bolivarian Armed Forces and the Venezuelan people, in order to contribute to ensuring the overall defence of Venezuela; * Organize and train the Territorial Militia's personnel and unit to implement the comprehensive defense operations to ensure the defense of sovereignty and national independence; * Contribute to the Operational Strategic Command, in the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Warfare
Land warfare or ground warfare is the process of military operations eventuating in combat that takes place predominantly on the battlespace land surface of the planet. Land warfare is categorized by the use of large numbers of combat personnel employing a diverse set of combat skills, methods and a wide variety of weapon systems and equipment, conducted in diverse terrains and weather environments. Land warfare, by virtue of being conducted in defence of urban and rural population areas, dominates the study of war, and is a focus for most national defence policy planning and financial considerations. Land warfare in history has undergone several distinct transitions in conduct from a large concentration of largely untrained and irregularly armed populace used in frontal assaults to current employment of combined arms concepts with highly trained regular troops using a wide variety of organisational, weapon and information systems, and employing a variety of strategic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Bolivarian Army (Venezuela)
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countries. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlos Soublette
Carlos Valentín José de la Soledad Antonio del Sacramento de Soublette y Jerez de Aristeguieta (15 December 1789 – 11 February 1870) was a Venezuelan politician and military officer who was the 7th and 9th president of Venezuela from 1837 to 1839 and again from 1843 to 1847 and a hero of the Venezuelan War of Independence. Personal life Soublette was married to Olalla Buroz y Tovar, who served as List of First Ladies of Venezuela, First Lady of Venezuela from 1837 to 1839 and 1843 to 1847. File:Olaya Buroz y Tovar.jpg, Olalla Buroz y Tovar See also *List of ministers of foreign affairs of Venezuela *List of presidents of Venezuela References External links {{DEFAULTSORT:Soublette, Carlos People from La Guaira Presidents of Venezuela Vice presidents of Venezuela Ministers of foreign affairs of Venezuela People of the Venezuelan War of Independence Venezuelan soldiers 1789 births 1870 deaths Venezuelan people of Canarian descent Conservative Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santiago Mariño
Santiago Mariño Carige Fitzgerald (25 July 1788 in Valle Espíritu Santo, Margarita – 4 September 1854 in La Victoria, Aragua), was a nineteenth-century Venezuelan revolutionary leader and hero in the Venezuelan War of Independence (1811–1823). He became an important leader of eastern Venezuela and for a short while in 1835 seized power over the new state of Venezuela. Family His father was the captain of the "Santiago Mariño de Acuña" militias and "Lieutenant Greater Justice of the Gulf of Paria". His mother, Atanasia Carige Fitzgerald, of Creole and Irish descent, was from Chaguaramas in the island of Trinidad, where his parents resided while he was a boy. He had a sister, Concepción Mariño. Due to his parents' wealth he was well educated. After his father's death in 1808, he moved to the island of Margarita (about 250 km west of Trinidad, off the Venezuelan coast), to take possession of his inheritance. Masonry Mariño was also one of the greatest figures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Antonio Páez
José Antonio Páez Herrera (; 13 June 1790 – 6 May 1873) was a Venezuelan politician and military officer who served as the president of Venezuela three times. The first as the 5th president from 1830 to 1835, the second as the 8th president from 1839 to 1843, and the third as the 15th president from 1861 to 1863. He fought against the Spanish Crown for Simón Bolívar during the Venezuelan War of Independence. Páez later led Venezuela's independence from Gran Colombia. Páez dominated the country's politics for most of the next three decades once the country had achieved independence from Gran Colombia, serving either as president or as the power behind puppet presidents. He is considered a prime example of a 19th-century South American caudillo, saddling the country with a legacy of authoritarian rule that lasted with only a few breaks until 1958. He lived in Buenos Aires and New York City during his years in exile and died in the latter in 1873. Biography Early life P� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Crisóstomo Falcón
Juan Crisóstomo Falcón Zavarce (27 January 1820 – 29 April 1870) was the president of Venezuela from 1863 to 1868.Biography (Spanish) Biography Falcón was a member of the Liberal Venezuelan Federalist Party, and had been exiled to Curaçao after the Conservative March Revolution of 1858. At the outbreak of the , he returned to Venezuela as the supreme chief of the rebel movement in August 1859. When his military leader Ezequiel Zamora, was kill ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Tadeo Monagas
José Tadeo Monagas Burgos (28 October 1784 – 18 November 1868) was the president of Venezuela 1847–1851 and 1855–1858, and a hero of the Venezuelan War of Independence. Career Presidency In 1846, to head off the challenge from the Liberal Party, ex-President and caudillo José Antonio Páez selected Monagas as Conservative candidate. Páez thought Monagas could be controlled but he gravitated toward the Liberals, and eventually dispersed the Congress. In 1848 Páez led a rebellion against Monagas but was defeated by General Santiago Mariño in the 'Battle of the Araguatos', imprisoned, and eventually exiled. As a member of the Liberal Party, he abolished capital punishment for political crimes. The Liberal Party also passed laws that abolished slavery, extended suffrage, and limited interest rates. José Tadeo Monagas also supported his brother José Gregorio for the . José Tadeo Monagas and his brother José ''Gregorio'' Monagas combined rule 1847–1858 is commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francisco De Miranda
Sebastián Francisco de Miranda y Rodríguez de Espinoza (28 March 1750 – 14 July 1816), commonly known as Francisco de Miranda (), was a Venezuelan military leader and revolutionary who fought in the American Revolutionary War, the French Revolution and the Spanish American wars of independence. He is regarded as a precursor of South America's liberation from the Spanish Empire, and remains known as the "First Universal Venezuelan" and the "Great Universal American". Born in Caracas in the Viceroyalty of New Granada into a wealthy family, Miranda left to pursue an education in Madrid in 1771 and subsequently enlisted in the Spanish army. In 1780, following Spain's entry into the American Revolutionary War, he was sent to Cuba and fought the British at Siege of Pensacola, Pensacola. Accused of espionage and smuggling, he fled to the United States in 1783. Miranda returned to Europe in 1785 and travelled through the continent, gradually formulating his plans for Spanish Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |