|
Vladimir Sokolov (scientist)
Vladimir Sokolov (1 February 1928 – 19 April 1998) was a Russian scientist in the field of zoology and ecology. He was a member of the USSR Academy of Sciences, Russian Academy of Science and the Brundtland Commission. He was one of the pioneers of the Russian environmentalism movement and one of the early global sustainability advocates. Sokolov was professor and head of the Department of Vertebrate Zoology at the Faculty of Biology at Moscow State University; director of the Institute of Evolutionary Animal Morphology and Ecology at the Russian Academy of Sciences; and deputy chairman of Chemical, Technological and Biological Sciences at the USSR Academy of Sciences. He is the grandfather of Evgeny Lebedev, owner of the London ''Evening Standard'' and ''The Independent'' (with and after his father, Alexander Lebedev, an ex-KGB officer). Life Sokolov was born in Moscow, the son of a zoology professor. He graduated from Moscow State University in 1950 with aspirations to becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 19.1 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in Moscow metropolitan area, its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of , while the urban area covers , and the metropolitan area covers over . Moscow is among the world's List of largest cities, largest cities, being the List of European cities by population within city limits, most populous city entirely in Europe, the largest List of urban areas in Europe, urban and List of metropolitan areas in Europe, metropolitan area in Europe, and the largest city by land area on the European continent. First documented in 1147, Moscow became the capital of the Grand Principality of Moscow, which led the unification of the Russian lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
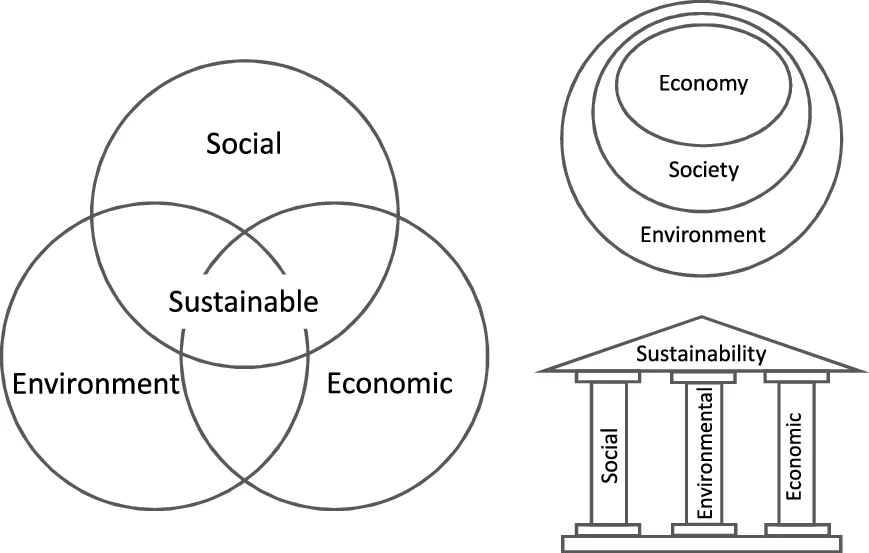
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Monitoring
Environmental monitoring is the processes and activities that are done to characterize and describe the state of the environment. It is used in the preparation of environmental impact assessments, and in many circumstances in which human activities may cause harmful effects on the natural environment. Monitoring strategies and programmes are generally designed to establish the current status of an environment or to establish a baseline and trends in environmental parameters. The results of monitoring are usually reviewed, analyzed statistics, statistically, and published. A monitoring programme is designed around the intended use of the data before monitoring starts. Environmental monitoring includes monitoring of Air pollution, air quality, soils and water quality. Many monitoring programmes are designed to not only establish the current state of the environment but also predict future conditions. In some cases this may involve collecting data related to events in the distant p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecotoxicology
Ecotoxicology is the study of the effects of toxic chemicals on biological organisms, especially at the population biology, population, biological community, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecotoxicology is a multidisciplinary field, which integrates toxicology and ecology. The ultimate goal of ecotoxicology is to reveal and predict the effects of pollution within the context of all other environmental factors. Based on this knowledge the most efficient and effective action to prevent or remediate any detrimental effect can be identified. In those ecosystems that are already affected by pollution, ecotoxicological studies can inform the choice of action to restore ecosystem services, structures, and functions efficiently and effectively. Ecotoxicology differs from environmental toxicology in that it integrates the effects of stressors across all levels of biological organisation from the molecular to whole communities and ecosystems, whereas environmental toxicology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', 'far off', and ''metron'', 'measure'. Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry: telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bionics
Bionics or biologically inspired engineering is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology. The word ''bionic'', coined by Jack E. Steele in August 1958, is a portmanteau from biology and electronics which was popularized by the 1970s U.S. television series ''The Six Million Dollar Man'' and ''The Bionic Woman'', both based on the novel ''Cyborg (novel), Cyborg'' by Martin Caidin. All three stories feature humans given various superhuman powers by their electromechanical implants. According to proponents of bionic technology, the technology transfer, transfer of technology between lifeforms and manufactured objects is desirable because evolutionary pressure typically forces living organisms—fauna and flora—to become optimized and efficient. For example, dirt- and water-repellent paint (coating) was inspired by the hydrophobic properties of the Nelumbo, lotus flower plant (the lotus e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrodynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion) and (the study of water and other liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space, understanding large scale geophysical flows involving oceans/atmosphere and modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves the calculation of various properties of the fluid, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Microscopy
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it to produce magnified images or electron diffraction patterns. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times smaller than that of visible light, electron microscopes have a much higher resolution of about 0.1 nm, which compares to about 200 nm for light microscopes. ''Electron microscope'' may refer to: * Transmission electron microscope (TEM) where swift electrons go through a thin sample * Scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) which is similar to TEM with a scanned electron probe * Scanning electron microscope (SEM) which is similar to STEM, but with thick samples * Electron microprobe similar to a SEM, but more for chemical analysis * Low-energy electron microscope (LEEM), used to image surfaces * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (anatomy)
Morphology (from Ancient Greek μορφή (morphḗ) "form", and λόγος (lógos) "word, study, research") is the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, color, pattern, size), as well as the form and structure of internal parts like bones and organs, i.e., anatomy. This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of the overall structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Bur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Academy Of Arts And Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (The Academy) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other Founding Fathers of the United States. It is headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Membership in the academy is achieved through a nominating petition, review, and election process. The academy's quarterly journal, '' Dædalus'', is published by the MIT Press on behalf of the academy, and has been open-access since January 2021. The academy also conducts multidisciplinary public policy research. Laurie L. Patton has served as President of the Academy since January 2025. History The Academy was established by the Massachusetts legislature on May 4, 1780, charted in order "to cultivate every art and science which may tend to advance the interest, honor, dignity, and happiness of a free, independent, and virtuous people." The sixty-tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalogist
In zoology, mammalogy is the study of mammals – a class of vertebrates with characteristics such as homeothermic metabolism, fur, four-chambered hearts, and complex nervous systems. The archive of number of mammals on earth is constantly growing, but is currently set at 6,495 different mammal species including recently extinct. There are 5,416 living mammals identified on earth and roughly 1,251 have been newly discovered since 2006. The major branches of mammalogy include natural history, taxonomy and systematics, anatomy and physiology, ethology, ecology, and management and control. Mammalogists are typically involved in activities such as conducting research, managing personnel, and writing proposals. Mammalogy branches off into other taxonomically oriented disciplines such as primatology (study of primates), and cetology (study of cetaceans). Like other studies, mammalogy is also a part of zoology which is also a part of biology, the study of all living things. Research p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |