|
Uranocene
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a green air-sensitive solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Uranocene, a member of the "actinocenes," a group of metallocenes incorporating elements from the actinide series. It is the most studied bis nnulene-metal system, although it has no known practical applications. Synthesis, structure and bonding Uranocene was first described in 1968 by the group of Andrew Streitwieser, when it was prepared by the reaction of dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide and uranium tetrachloride in THF at 0°C: : Uranocene is highly reactive toward oxygen, being pyrophoric in air but stable to hydrolysis. The x-ray crystal structure of uranocene was first elucidated by the group of Ken Raymond. Considering the molecule to be U4+(C8H82−)2, the η8- cyclooctatetraenide groups are planar, as ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranocene Synthesis
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a green air-sensitive solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Uranocene, a member of the " actinocenes," a group of metallocenes incorporating elements from the actinide series. It is the most studied bis nnulene-metal system, although it has no known practical applications. Synthesis, structure and bonding Uranocene was first described in 1968 by the group of Andrew Streitwieser, when it was prepared by the reaction of dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide and uranium tetrachloride in THF at 0°C: : Uranocene is highly reactive toward oxygen, being pyrophoric in air but stable to hydrolysis. The x-ray crystal structure of uranocene was first elucidated by the group of Ken Raymond. Considering the molecule to be U4+(C8H82−)2, the η8-cyclooctatetraenide groups are planar, as expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoactinide Chemistry
Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond. Like most organometallic compounds, the organoactinides are air sensitive and need to be handled using the appropriate methods. Organometallic complexes with σ-bonding Most common organoactinide complexes involve π-bonding with ligands such as cyclopentadienyl, but there are a few exceptions with σ-bonding, namely in thorium and uranium chemistry as these are the most easily handleable elements of this group. Alkyl and aryl compounds Attempts to synthesize uranium alkyls were first made during the Manhattan project by Henry Gilman, inspired by the volatility of main group organometallics. However he noticed that these compounds tend to be highly unstable. Marks and Seyam attempted to synthesize them from UCl using organolithium reagents, but these decomposed quickly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organouranium Compound
Organouranium chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure and reactivity of organouranium compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to uranium chemical bond. The field is of some importance to the nuclear industry and of theoretical interest in organometallic chemistry. History The development of organouranium compounds started in World War II when the Manhattan Project required volatile uranium compounds for 235U/238U isotope separation. For example, Henry Gilman attempted to synthesize compounds like tetramethyluranium, and others worked on uranium metal carbonyls, but none of the efforts met success due to organouranium instability. After the discovery of ferrocene in 1951, Todd Reynolds and Geoffrey Wilkinson in 1956 synthesized the uranium metallocene Cp3UCl from sodium cyclopentadienide and uranium tetrachloride as a stable but extremely air-sensitive compound. In it, the U-Cl bond is an ionic bond, while the bonds with the three C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinocenes
Actinocenes are a family of organoactinide compounds consisting of metallocenes containing elements from the actinide series. They typically have a sandwich structure with two dianionic cyclooctatetraenyl ligands (COT2-, which is ) bound to an actinide-metal center (An) in the oxidation state IV, resulting in the general formula An(C8H8)2. Characterised actinocenes The most studied actinocene is uranocene, U(C8H8)2, which in 1968 was the first member of this family to be synthesised and is still viewed as the archetypal example. Other actinocenes that have been synthesised are protactinocene (Pa(C8H8)2), thorocene (Th(C8H8)2), neptunocene (Np(C8H8)2), and plutonocene (Pu(C8H8)2). Especially the latter two, neptunocene and plutonocene, have not been extensively studied experimentally since the 1980s because of the radiation hazard they pose. Bonding The actinide-cyclooctatetraenyl bonding has been of interest for multiple theoretical studies. Computational chemistry metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to p2ZrCH3sup>+ catalyze olefin polymerization. Some metallocenes consist of metal plus two cyclooctatetraenide anions (, abbreviated cot2−), namely the lanthanocenes and the actinocenes ( uranocene and others). Metallocenes are a subset of a broader class of compounds called sandwich compounds. In the structure shown at right, the two pentagons are the cyclopentadienyl anions with circles inside them indicating they are aromatically stabilized. Here they are shown in a staggered conformation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Raymond
Kenneth Norman Raymond (born January 7, 1942) is a bioinorganic and coordination chemist. He is Chancellor's Professor of Chemistry at University of California, Berkeley, Professor of the Graduate School, the Director of the Seaborg Center in the Chemical Sciences Division at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and the President and Chairman of Lumiphore. Biography Early life and education Raymond was born on January 7, 1942, in Astoria, Oregon, and was raised in various towns in Oregon. After graduating from Clackamas High School in 1959, he spent a year in Germany where he worked as a test-driver for Volkswagen and developed a taste for German culture. He then attended Reed College in Portland, Oregon, where he majored in Chemistry and earned a Bachelor of Arts in 1964. Raymond then attended Northwestern University where he studied coordination chemistry and crystallography, under Fred Basolo, and also worked closely with James A. Ibers, earning his Ph.D. degree in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of its stoichiometric relationship to benzene, COT has been the subject of much research and some controversy. Unlike benzene, C6H6, cyclooctatetraene, C8H8, is not aromatic, although its dianion, ( cyclooctatetraenide), is. Its reactivity is characteristic of an ordinary polyene, i.e. it undergoes addition reactions. Benzene, by contrast, characteristically undergoes substitution reactions, not additions. History 1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene was initially synthesized by Richard Willstätter in Munich in 1905 using pseudopelletierine as the starting material and the Hofmann elimination as the key transformation: : Willstätter noted that the compound did not exhibit the expected aromaticity. Between 1939 and 1943, chemists throughout the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctatetraene
1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as nnulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of its stoichiometric relationship to benzene, COT has been the subject of much research and some controversy. Unlike benzene, C6H6, cyclooctatetraene, C8H8, is not aromatic, although its dianion, ( cyclooctatetraenide), is. Its reactivity is characteristic of an ordinary polyene, i.e. it undergoes addition reactions. Benzene, by contrast, characteristically undergoes substitution reactions, not additions. History 1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene was initially synthesized by Richard Willstätter in Munich in 1905 using pseudopelletierine as the starting material and the Hofmann elimination as the key transformation: : Willstätter noted that the compound did not exhibit the expected aromaticity. Between 1939 and 1943, chemists throughout the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipotassium Cyclooctatetraenide
Dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide, sometimes abbreviated K2COT, is an Organopotassium chemistry, organopotassium compound with the formula K2C8H8. It is a brown solid that is used as a precursor to cyclooctatetraenide complexes, such as uranocene (U(C8H8)2). Structural analog, Analogs of K2C8H8 are known with ring substituents, with different alkali metals, and with various complexants. Preparation and structure Potassium cyclooctatetraenide is formed by the reaction of cyclooctatetraene with potassium metal: :2 K + C8H8 → K2C8H8 The reaction entails 2-electron reduction of the polyene and is accompanied by a color change from colorless to brown. The structure of K2(diglyme)C8H8 has been characterized by X-ray crystallography of the derivatives with diglyme complexed to the potassium cations. The C8H8 unit is planar with an average C-C distance of 1.40 A.{{cite journal , author = J. H. Noordik, T. E. M. van den Hark, J. J. Mooij and A. A. K. Klaassen , title = Dipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Photoemission spectroscopy (PES), also known as photoelectron spectroscopy, refers to energy measurement of electrons emitted from solids, gases or liquids by the photoelectric effect, in order to determine the binding energies of electrons in the substance. The term refers to various techniques, depending on whether the ionization energy is provided by X-ray, XUV or UV photons. Regardless of the incident photon beam, however, all photoelectron spectroscopy revolves around the general theme of surface analysis by measuring the ejected electrons. Types X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was developed by Kai Siegbahn starting in 1957 and is used to study the energy levels of atomic core electrons, primarily in solids. Siegbahn referred to the technique as "electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis" (ESCA), since the core levels have small chemical shifts depending on the chemical environment of the atom that is ionized, allowing chemical structure to be determined. Siegbahn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
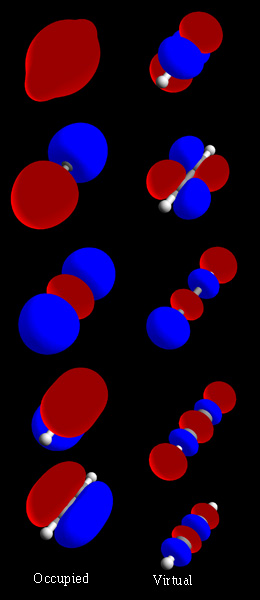
Molecular Orbitals
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an approximate solution to the Schrödi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, diamagnetic materials are repelled by magnetic fields and form induced magnetic fields in the direction opposite to that of the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials include most chemical elements and some compounds; they have a relative magnetic permeability slightly greater than 1 (i.e., a small positive magnetic susceptibility) and hence are attracted to magnetic fields. The magnetic moment induced by the applied field is linear in the field strength and rather weak. It typically requires a sensitive analytical balance to detect the effect and modern measurements on paramagnetic materials are often conducted with a SQUID magnetometer. Paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in the material, so most atoms w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
thorium(IV)-3D-balls.png)