|
Actinocenes
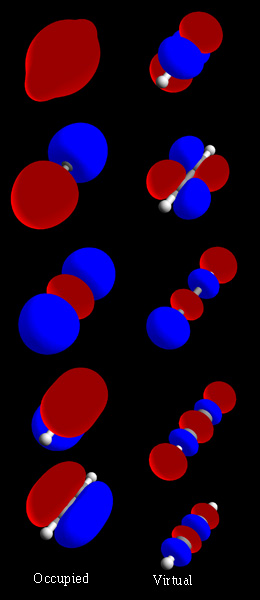
Actinocenes are a family of organoactinide compounds consisting of metallocenes containing elements from the actinide series. They typically have a sandwich structure with two dianionic cyclooctatetraenyl ligands (COT2-, which is ) bound to an actinide-metal center (An) in the oxidation state IV, resulting in the general formula An(C8H8)2. Characterised actinocenes The most studied actinocene is uranocene, U(C8H8)2, which in 1968 was the first member of this family to be synthesised and is still viewed as the archetypal example. Other actinocenes that have been synthesised are protactinocene (Pa(C8H8)2), thorocene (Th(C8H8)2), neptunocene (Np(C8H8)2), and plutonocene (Pu(C8H8)2). Especially the latter two, neptunocene and plutonocene, have not been extensively studied experimentally since the 1980s because of the radiation hazard they pose. Bonding The actinide-cyclooctatetraenyl bonding has been of interest for multiple theoretical studies. Computational chemistry metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonocene
Plutonocene, Pu(C8H8)2, is an organoplutonium compound composed of a plutonium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide (COT2-) rings. It is a dark red, very air-sensitive solid that is sparingly soluble in toluene and chlorocarbons. Plutonocene is a member of the actinocene family of metallocenes incorporating actinide elements in the +4 oxidation state. Compared to other actinocenes such as uranocene, plutonocene has been studied to a lesser degree since the 1980s due to the notable radiation hazard posed by the compound. Instead, it has mostly been the subject of theoretical studies relating to the bonding in the molecule. Structure and bonding The compound has been structurally characterised by single crystal XRD. The cyclooctatetraenide rings are eclipsed and assume a planar conformation with 8 equivalent C–C bonds of 1.41 Å length; the molecule possesses a centre of inversion at the position occupied by the plutonium atom. The Pu–COT distance (to the ring c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranocene
Uranocene, U(C8H8)2, is an organouranium compound composed of a uranium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide rings. It was one of the first organoactinide compounds to be synthesized. It is a green air-sensitive solid that dissolves in organic solvents. Uranocene, a member of the "actinocenes," a group of metallocenes incorporating elements from the actinide series. It is the most studied bis nnulene-metal system, although it has no known practical applications. Synthesis, structure and bonding Uranocene was first described in 1968 by the group of Andrew Streitwieser, when it was prepared by the reaction of dipotassium cyclooctatetraenide and uranium tetrachloride in THF at 0°C: : Uranocene is highly reactive toward oxygen, being pyrophoric in air but stable to hydrolysis. The x-ray crystal structure of uranocene was first elucidated by the group of Ken Raymond. Considering the molecule to be U4+(C8H82−)2, the η8- cyclooctatetraenide groups are planar, as ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptunocene
Neptunocene, Np(C8H8)2, is an organoneptunium compound composed of a neptunium atom sandwiched between two cyclooctatetraenide (COT2-) rings. As a solid it has a dark brown/red colour but it appears yellow when dissolved in chlorocarbons, in which it is sparingly soluble. The compound is quite air-sensitive. It was one of the first organoneptunium compounds to be synthesised, and is a member of the actinocene family of actinide-based metallocenes. Structure The sandwich structure of neptunocene has been determined by single crystal XRD. The COT2- rings are found to be planar with 8 equivalent C–C bonds of 1.385 Å length, and sit parallel in an eclipsed conformation. The Np–COT distance (to the ring centroid) is 1.909 Å and the individual Np–C distances are 2.630 Å. Neptunocene assumes a monoclinic crystal structure (''P''21/''n'' space group) which is isomorphous to uranocene and thorocene but not to plutonocene. Synthesis and properties Neptunocene was first syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoactinide Chemistry
Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond. Like most organometallic compounds, the organoactinides are air sensitive and need to be handled using the appropriate methods. Organometallic complexes with σ-bonding Most common organoactinide complexes involve π-bonding with ligands such as cyclopentadienyl, but there are a few exceptions with σ-bonding, namely in thorium and uranium chemistry as these are the most easily handleable elements of this group. Alkyl and aryl compounds Attempts to synthesize uranium alkyls were first made during the Manhattan project by Henry Gilman, inspired by the volatility of main group organometallics. However he noticed that these compounds tend to be highly unstable. Marks and Seyam attempted to synthesize them from UCl using organolithium reagents, but these decomposed quickly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoactinide
Organoactinide chemistry is the science exploring the properties, structure and reactivity of organoactinide compounds, which are organometallic compounds containing a carbon to actinide chemical bond. Like most organometallic compounds, the organoactinides are air sensitive and need to be handled using the appropriate methods. Organometallic complexes with σ-bonding Most common organoactinide complexes involve π-bonding with ligands such as cyclopentadienyl, but there are a few exceptions with σ-bonding, namely in thorium and uranium chemistry as these are the most easily handleable elements of this group. Alkyl and aryl compounds Attempts to synthesize uranium alkyls were first made during the Manhattan project by Henry Gilman, inspired by the volatility of main group organometallics. However he noticed that these compounds tend to be highly unstable. Marks and Seyam attempted to synthesize them from UCl using organolithium reagents, but these decomposed quickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly producing pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. It is generally regarded as having one of the most complex spectra of the elements. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach, who also discovered praseodymium. It is present in significant quantities in the minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Neodymium is fairly common—about as common as cobalt, nickel, or copper—and is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Most of the world's commercial neodymium is mined in China, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–71, from lanthanum through lutetium. These elements, along with the chemically similar elements scandium and yttrium, are often collectively known as the rare-earth elements or rare-earth metals. The informal chemical symbol Ln is used in general discussions of lanthanide chemistry to refer to any lanthanide. All but one of the lanthanides are f-block elements, corresponding to the filling of the 4f electron shell. There is some dispute on whether lanthanum or lutetium is a d-block element, but lutetium is usually considered so by those who study the matter; it is included due to its chemical similarities with the other 14. All lanthanide elements form trivalent cations, Ln3+, whose chemistry is largely determined by the ionic radius, which decreases steadily from lanthanum to lutetium. These elements are called lanthanides because the ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal–ligand Multiple Bond
In organometallic chemistry, a metal–ligand multiple bond describes the interaction of certain ligands with a metal with a bond order greater than one."Metal–Ligand Multiple Bonds: The Chemistry of Transition Metal Complexes Containing Oxo, Nitrido, Imido, Alkylidene, or Alkylidyne Ligands" W. A. Nugent and J. M. Mayer; Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1988. . Coordination complexes featuring multiply bonded ligands are of both scholarly and practical interest. Transition metal carbene complexes catalyze the olefin metathesis reaction. Metal oxo intermediates are pervasive in oxidation catalysis. : As a cautionary note, the classification of a metal ligand bond as being "multiple" bond order is ambiguous and even arbitrary because bond order is a formalism. Furthermore, the usage of multiple bonding is not uniform. Symmetry arguments suggest that most ligands engage metals via multiple bonds. The term 'metal ligand multiple bond" is often reserved for ligands of the type and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terbium
Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth metal that is malleable, and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with water, evolving hydrogen gas. Terbium is never found in nature as a free element, but it is contained in many minerals, including cerite, gadolinite, monazite, xenotime and euxenite. Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander discovered terbium as a chemical element in 1843. He detected it as an impurity in yttrium oxide, . Yttrium and terbium, as well as erbium and ytterbium, are named after the village of Ytterby in Sweden. Terbium was not isolated in pure form until the advent of ion exchange techniques. Terbium is used to dope calcium fluoride, calcium tungstate and strontium molybdate in solid-state devices, and as a crystal stabilizer of fuel cells that operate at elevated temperatures. As a component of Terfenol-D (an alloy that exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Orbitals
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an approximate solution to the Schrödi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term ''covalent bond'' dates from 1939. The prefix ''co-'' means ''jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, '' etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share " valence" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules, groups of molecules, and solids. It is essential because, apart from relatively recent results concerning the hydrogen molecular ion (dihydrogen cation, see references therein for more details), the quantum many-body problem cannot be solved analytically, much less in closed form. While computational results normally complement the information obtained by chemical experiments, it can in some cases predict hitherto unobserved chemical phenomena. It is widely used in the design of new drugs and materials. Examples of such properties are structure (i.e., the expected positions of the constituent atoms), absolute and relative (interaction) energies, electronic charge density distributions, dipoles and higher multipole moments, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
thorium(IV)-3D-balls.png)