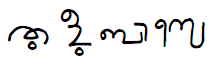|
Tulu Language
Tulu () in Kannada script, ml, തുളു ഭാഷെ in Malayalam script. ''bhāṣe'', , ''bhāśe'', and ''bāśe'' are alternative spellings for the Tulu word ''bāse'' in the Kannada script. The correct spelling for the word "language" in Kannada is kn, ಭಾಷೆ ''bhāṣe'', but that is not necessarily true in Tulu. Männer's ''Tulu-English and English-Tulu Dictionary'' (1886) says, " bāšè, bāsè, ''see'' ." (vol. 1, p. 478), " bhāšè, bhāshè, ''s''. Speech, language." (vol. 1, p. 508), meaning that the four spellings are more or less acceptable. The word is actually pronounced ''bāse'' in Tulu. Note that š and sh in his dictionary correspond to ''ś'' and ''ṣ'', respectively, in ISO 15919 is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Then, interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasaragod
Kasaragod () is a municipal town and administrative headquarters of Kasaragod district in the state of Kerala, India. Established in 1966, Kasaragod was the first municipal town in the district. It is the northernmost district of Kerala and is also known as ''Saptha Bhasha Sangama Bhoomi'' ('The Land of seven Languages'). Situated in the rich biodiversity of Western Ghats, it is known for the Chandragiri and Bekal Fort, Chandragiri River, historic Kolathiri Rajas, natural environment of Ranipuram and Kottancheri Hills, historical and religious sites like the Madiyan Kulom temple, Madhur Temple, Ananthapuram Lake Temple and Malik Deenar Mosque. The historic hill of Ezhimala is located on the southern portion of Kavvayi Backwaters of Nileshwaram. Kasaragod is located 50 km south of the major port city and a commercial hub Mangalore and 364 km north of the major port city Kochi. Kasaragod district has the maximum number of rivers in Kerala - 12. The town is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalasa
Kalasa is a tehsil located in Chikkamagaluru district in Karnataka. Kalasa is home to the Kalaseshwara Temple dedicated to Lord Shiva. Kalasa lies 92 Kilometres South-west of Chickmagalur and is located on the banks of the Bhadra River. Kannada and Tulu languages are spoken here. Santara dynasty The history of this region is also associated with the Santara dynasty, a medieval ruling dynasty located in present-day Karnataka, India. Edgar Thurston mentions that the Santaras were among the powerful Bunt Thurston, Edgar; K. Rangachari (1909). Castes and Tribes of Southern India Volume Pg. 152Madras: Government Press chiefs who seem to have exercised control over a greater part of the Tuluva country before the rise of the Vijayanagara Empire. The Santaras were Jains and had matrimonial relations with the Saivite Alupa royal family of the canara region. The Santaras built a number of Jain monuments and were responsible for the spread of Jainism in the Tulu Nadu and Malenadu regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udupi
Udupi (alternate spelling Udipi; also known as Odipu) is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. Udupi is situated about north of the educational, commercial and industrial hub of Mangalore and about west of state capital Bangalore by road. It is the administrative headquarters of Udupi district, and one of the fastest-growing cities in Karnataka. Udupi is one of the top tourist attractions in Karnataka and has various educational institutions. It is notable for the Krishna Temple and is also known as the temple city. It also lends its name to the popular Udupi cuisine, is also known as Parashurama Kshetra , and is famous for Kanakana kindi. A centre of pilgrimage, Udupi is known as Rajata Peetha and Shivalli (Shivabelle). Etymology The name ''Udupi'' is the stylized form of the city. History In the 13th century, Vaishnavite saint Madhvacharya founded the Sri Krishna Temple. He set up eight ''mathas'' - Ashta Mathas- In Kannada - ಅಷ್ಟ ಮಠಗಳು in Udupi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglutination
In linguistics, agglutination is a morphological process in which words are formed by stringing together morphemes, each of which corresponds to a single syntactic feature. Languages that use agglutination widely are called agglutinative languages. Turkish is an example of an agglutinative language. The Turkish word ("from your houses") consists of the morphemes ''ev-ler-iniz-den,'' literally translated morpheme-by-morpheme as ''house-plural-your(plural)-from''. Agglutinative languages are often contrasted with isolating languages, in which words are monomorphemic, and fusional languages, in which words can be complex, but morphemes may correspond to multiple features. Examples of agglutinative languages Although agglutination is characteristic of certain language families, this does not mean that when several languages in a certain geographic area are all agglutinative they are necessarily related phylogenetically. In the past, this assumption led linguists to propose the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries. It is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in Iberia after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. The oldest Latin texts with traces of Spanish come from mid-northern Iberia in the 9th century, and the first systematic written use of the language happened in Toledo, a prominent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also substratum, influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic languages, Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's French colonial empire, past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole language, Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Future Perfect
The future perfect is a verb form or construction used to describe an event that is expected or planned to happen before a time of reference in the future, such as ''will have finished'' in the English sentence "I will have finished by tomorrow." It is a grammatical combination of the future tense, or other marking of future time, and the perfect, a grammatical aspect that views an event as prior and completed. English In English, the future perfect construction consists of a future construction such as the auxiliary verb ''will'' (or ''shall'') or the going-to future and the perfect infinitive of the main verb (which consists of the infinitive of the auxiliary verb ''have'' and the past participle of the main verb). This parallels the construction of the "normal" future verb forms combining the same first components with the plain infinitive (e.g. ''She will fall'' / ''She is going to fall''). For example: * She will have fallen asleep by the time we get home. * I shall ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluperfect
The pluperfect (shortening of plusquamperfect), usually called past perfect in English, is a type of verb form, generally treated as a grammatical tense in certain languages, relating to an action that occurred prior to an aforementioned time in the past. Examples in English are: "we ''had'' arrived"; "they ''had'' written". The word derives from the Latin ''plus quam perfectum'', "more than perfect". The word "perfect" in this sense means "completed"; it contrasts with the "imperfect", which denotes uncompleted actions or states. In English grammar, the pluperfect (e.g. "had written") is now usually called the past perfect, since it combines past tense with perfect aspect. (The same term is sometimes used in relation to the grammar of other languages.) English also has a ''past perfect progressive'' (or ''past perfect continuous'') form: "had been writing". Meaning of the pluperfect The pluperfect is traditionally described as a tense; in modern linguistic terminology it ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil–Kannada Languages
Tamil–Kannada is an inner branch (Zvelebil 1990:56) of the Southern Dravidian I (SDr I) subfamily of the Dravidian languages that include Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam. (There have been slight differences in the way Dravidian languages are grouped by various Dravidian linguists: See Subrahmanyam 1983, Zvelebil 1990, Krishnamurthi 2003). Tamil–Kannada itself is designated as a branch of the South Dravidian subfamily and in turn branches off into Tamil–Malayalam and Kannada–Badaga. The languages that constitute the Tamil–Kannada branch are Tamil, Kannada, Malayalam, Irula, Toda, Kota, Kodava, and Badaga. (Zvelebil 1990:56) According to R. C. Hiremath, the separation of Tamil and Kannada into independent languages from the Tamil–Kannada inner branch started with the separation of Tulu in about 1500 BCE and completed in about 300 BCE. Kannada, Tamil and Malayalam are recognized among the official languages of India and are spoken mainly in South India. All three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Of India
The decennial Census of India has been conducted 16 times, as of 2021. While it has been undertaken every 10 years, beginning in 1872 under British Viceroy Lord Mayo, the first complete census was taken in 1881. Post 1949, it has been conducted by the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. All the censuses since 1951 were conducted under the 1948 Census of India Act. The last census was held in 2011, whilst the next was to be held in 2021. But it has been postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Historically, there has been a long time between collection of data and dissemination of data. Census of India during British Rule List of censuses conducted in India before independence: *1872 Census of india *1881 Census of India *1891 Census of India *1901 Census of India *1911 Census of India *1921 Census of India *1931 Census of India *1941 Census of India Census of Republic of India List of censuses conduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |