|
Toyota E Engine
The Toyota E engine family is a straight-four piston engine series, and uses timing belts rather than chains. The E engines were the first multi-valve engines from Toyota designed with economy, practicality and everyday use in mind (rather than performance). Like many other Toyota engines from the era, the E engine series features a cast iron block, along with an aluminium cylinder head. E engines are lighter than earlier Toyota engines, due to the hollow crankshaft, thinned casting of the cylinder block, and several other reductions in auxiliaries as well as in the engine itself. Carbureted versions include a newly designed, variable-venturi carburetor. All of these changes improved economy and emissions. The members of the E engine family, range from 1.0 L to 1.5 L. The E family supplanted the '' K'' engines in most applications. A large number of parts in the E engine series are interchangeable between each other. 1E The 1E is a carbureted 12-valve SOHC engine. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 million vehicles per year. The company was originally founded as a spinoff of Toyota Industries, a machine maker started by Sakichi Toyoda, Kiichiro's father. Both companies are now part of the Toyota Group, one of the largest conglomerates in the world. While still a department of Toyota Industries, the company developed its first product, the Type A engine in 1934 and its first passenger car in 1936, the Toyota AA. After World War II, Toyota benefited from Japan's alliance with the United States to learn from American automakers and other companies, which would give rise to The Toyota Way (a management philosophy) and the Toyota Production System (a lean manufacturing practice) that would transform the small company into a leader i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a class of iron– carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloy constituents affect its color when fractured: white cast iron has carbide impurities which allow cracks to pass straight through, grey cast iron has graphite flakes which deflect a passing crack and initiate countless new cracks as the material breaks, and ductile cast iron has spherical graphite "nodules" which stop the crack from further progressing. Carbon (C), ranging from 1.8 to 4 wt%, and silicon (Si), 1–3 wt%, are the main alloying elements of cast iron. Iron alloys with lower carbon content are known as steel. Cast iron tends to be brittle, except for malleable cast irons. With its relatively low melting point, good fluidity, castability, excellent machinability, resistance to deformation and wear resistance, cast irons have become an engineering material with a wide range of applications a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
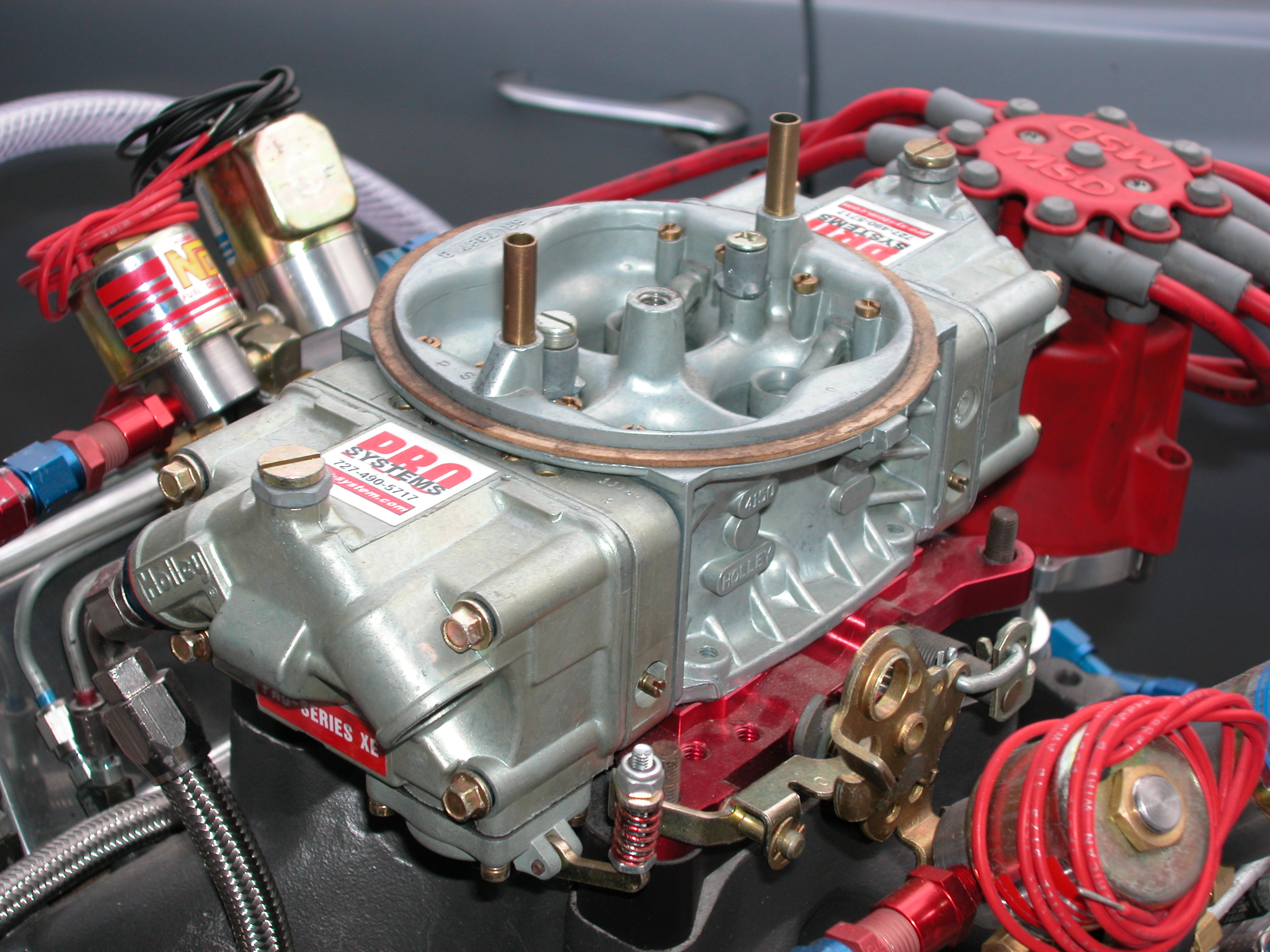
Toyota 2E Engine 2
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 million vehicles per year. The company was originally founded as a spinoff of Toyota Industries, a machine maker started by Sakichi Toyoda, Kiichiro's father. Both companies are now part of the Toyota Group, one of the largest conglomerates in the world. While still a department of Toyota Industries, the company developed its first product, the Type A engine in 1934 and its first passenger car in 1936, the Toyota AA. After World War II, Toyota benefited from Japan's alliance with the United States to learn from American automakers and other companies, which would give rise to The Toyota Way (a management philosophy) and the Toyota Production System (a lean manufacturing practice) that would transform the small company into a leader in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota Starlet
The is a subcompact car manufactured by Toyota from 1973 until 1999, replacing the Publica, but retaining the Publica's "P" code and generation numbering. The first generation Starlet was sold as the Publica Starlet in some markets. In Japan, it was exclusive to '' Toyota Corolla Store'' dealers. It is the first subcompact car from a Japanese automaker to offer a high-performance variant. These were available in three generations: the 1986–1989 Turbo S (EP71), the 1990–1995 GT Turbo (EP82), and the 1996–1999 Glanza V (EP91). Another variant was the Toyota Sera, a sport compact made in the early 1990s and officially sold only in Japan; the Sera had a unique two-door coupe body and butterfly doors but shared the Starlet's chassis and mechanicals. The Starlet was briefly exported to North America from 1981 to 1984. In 1999, the Starlet was replaced by the Vitz—sold as the Echo or Yaris in international markets—and the bB mini MPV, which was later sold as the Sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Transmission
An automatic transmission (sometimes abbreviated to auto or AT) is a multi-speed transmission used in internal combustion engine-based motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving conditions. It typically includes a transmission, axle, and differential in one integrated assembly, thus technically becoming a transaxle. The most common type of automatic transmission is the hydraulic automatic, which uses a planetary gearset, hydraulic controls, and a torque converter. Other types of automatic transmissions include continuously variable transmissions (CVT), automated manual transmissions (AMT), and dual-clutch transmissions (DCT). An electronic automatic transmission (EAT) may also be called an electronically controlled transmission (ECT), or electronic automatic transaxle (EATX). A hydraulic automatic transmission may also colloquially called a " slushbox" or simply a "torque converter", although the latter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota C Transmission
Toyota Motor Corporation's C family is a family of manual transmissions built for small to mid-sized front-wheel-drive vehicles (but also used in mid-engine applications). 4-speed transaxles C40 A 4-Speed manual transmission for FWD cars. Gear ratios for this transmission. Applications: * Toyota Corolla 1985 - 1988 Australian Market 'S' trim C140 A 4-Speed Manual Transmission for FWD cars. Gear ratios for this transmission. Applications: * Toyota Starlet * Toyota Tercel C141 A 4-Speed Manual Transmission for FWD cars. Gear ratios for this transmission. Applications: * Toyota Tercel 1991-2000 5-speed transaxles C50 A 5-speed manual transmission for FWD cars. This gearbox is known to develop a fifth gear pop-out problem as it ages. A version stamped C50X11a is found in the Australian market 2007 Yaris and it has the same ratios as listed for C54. A version stamped C50-M1 used in the 2000–02 MR2 Spyder model has the ratios as listed for C52 Gear ratios for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manual Gearbox
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle transmission system, where gear changes require the driver to manually select the gears by operating a gear stick and clutch (which is usually a foot pedal for cars or a hand lever for motorcycles). Early automobiles used ''sliding-mesh'' manual transmissions with up to three forward gear ratios. Since the 1950s, ''constant-mesh'' manual transmissions have become increasingly commonplace and the number of forward ratios has increased to 5-speed and 6-speed manual transmissions for current vehicles. The alternative to a manual transmission is an automatic transmission; common types of automatic transmissions are the hydraulic automatic transmission (AT), and the continuously variable transmission (CVT), whereas the automated manual transmission (AMT) and dual-clutch transmis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compression Ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values. A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the static compression ratio, calculated based on the relative volumes of the combustion chamber and the cylinder when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke, and the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at the top of its stroke. The dynamic compression ratio is a more advanced calculation which also takes into account gasses entering and exiting the cylinder during the compression phase. Effect and typical ratios A high compression ratio is desirable because it allows an engine to extract more mechanical energy from a given mass of air–fuel mixture due to its higher thermal efficiency. This occurs because internal combustion engines are heat engines, and higher compression ratios permit the same combustion temperature t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Overhead Cam
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. ''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam".) engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines. Design In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above the combustion chamber. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine (OHV) and flathead engine configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; however an OHV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin ''valva'', the moving part of a door, in turn from ''volvere'', to turn, roll. The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which swings down to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed up by the flow itself when the flow is moving in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. Modern control valves may regulate pressure or flow downstream and operate on sophisticated automation systems. Valves have many uses, including controlling water for irrigation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbureted
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main metering circuit, however various other components are also used to provide extra fuel or air in specific circumstances. Since the 1990s, carburetors have been largely replaced by fuel injection for cars and trucks, however carburetors are still used by some small engines (e.g. lawnmowers, generators and concrete mixers) and motorcycles. Diesel engines have always used fuel injection instead of carburetors. Etymology The name "carburetor" is derived from the verb ''carburet'', which means "to combine with carbon," or in particular, "to enrich a gas by combining it with carbon or hydrocarbons." Thus a carburetor mixes intake air with hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petrol or autogas (LPG). The name is spelled "carburetor" in American English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |