Single Overhead Cam on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
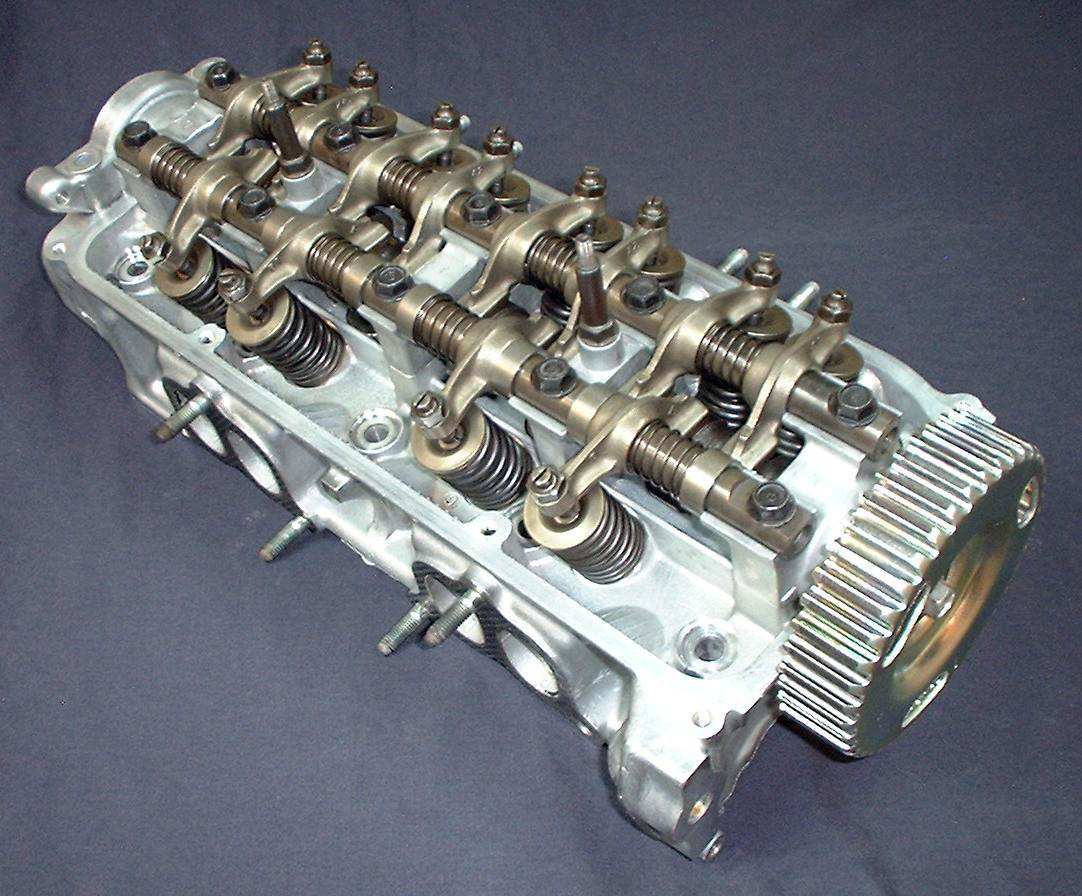 An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a
 The oldest configuration of overhead camshaft engine is the ''single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) design. A SOHC engine has one camshaft per bank of cylinders, therefore a
The oldest configuration of overhead camshaft engine is the ''single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) design. A SOHC engine has one camshaft per bank of cylinders, therefore a
 A ''dual overhead cam'', ''double overhead cam'', or ''twin-cam'' engine has two camshafts over each bank of the cylinder head, one for the intake valves and another for the exhaust valves. Therefore there are two camshafts for a straight engine and a total of four camshafts for a V engine or a flat engine.
A V engine or flat engine requires four camshafts to function as a DOHC engine, since having two camshafts in total would result in only a single camshaft per cylinder bank for these engine layouts. Some V engines with four camshafts have been marketed as "quad-cam" engines, however technically "quad-cam" would require four camshafts per cylinder bank (i.e. eight camshafts in total), therefore these engines are merely ''dual overhead camshaft'' engines.
Many DOHC engines have 4 valves per cylinder (sometimes 5,
A ''dual overhead cam'', ''double overhead cam'', or ''twin-cam'' engine has two camshafts over each bank of the cylinder head, one for the intake valves and another for the exhaust valves. Therefore there are two camshafts for a straight engine and a total of four camshafts for a V engine or a flat engine.
A V engine or flat engine requires four camshafts to function as a DOHC engine, since having two camshafts in total would result in only a single camshaft per cylinder bank for these engine layouts. Some V engines with four camshafts have been marketed as "quad-cam" engines, however technically "quad-cam" would require four camshafts per cylinder bank (i.e. eight camshafts in total), therefore these engines are merely ''dual overhead camshaft'' engines.
Many DOHC engines have 4 valves per cylinder (sometimes 5,
 The rotation of a camshaft is driven by a
The rotation of a camshaft is driven by a
 During World War I, both the Allied and
During World War I, both the Allied and
Hispano Suiza 8 A Brussel.jpg , 1914–1918
 An early American overhead camshaft production engine was the SOHC straight-eight engine used in the 1921–1926
An early American overhead camshaft production engine was the SOHC straight-eight engine used in the 1921–1926
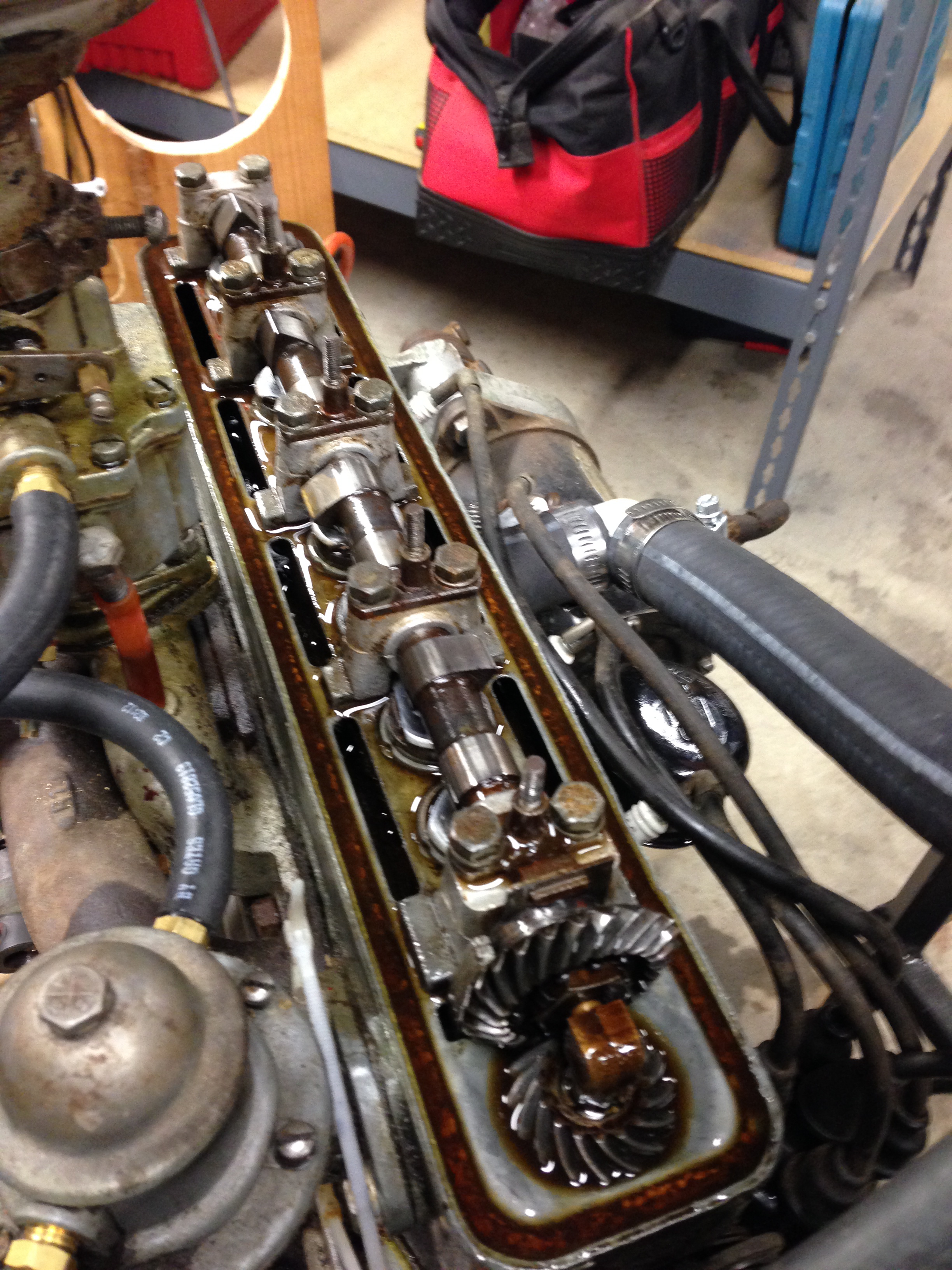 The 1946–1948 Crosley CC Four was arguably the first American mass-produced car to use an SOHC engine. This small mass-production engine powered the winner of the 1950
The 1946–1948 Crosley CC Four was arguably the first American mass-produced car to use an SOHC engine. This small mass-production engine powered the winner of the 1950
piston engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more Reciprocating motion, reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a Circular motion, rotating motion. This article ...
in which the camshaft
A camshaft is a shaft that contains a row of pointed cams in order to convert rotational motion to reciprocating motion. Camshafts are used in piston engines (to operate the intake and exhaust valves), mechanically controlled ignition syst ...
is located in the cylinder head
In a piston engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders, forming the roof of the combustion chamber. In sidevalve engines the head is a simple plate of metal containing the spark plugs and possibly heat dissipation fins. In more modern ...
above the combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a mo ...
. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block
In an internal combustion engine, the engine block is the structure that contains the cylinders and other components. The engine block in an early automotive engine consisted of just the cylinder block, to which a separate crankcase was attach ...
.
''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam") engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines.
Design
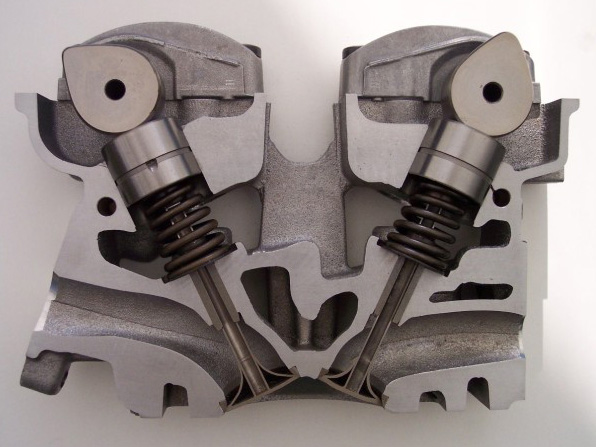
In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above thecombustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a mo ...
. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine
An overhead valve engine, abbreviated (OHV) and sometimes called a pushrod engine, is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with flathead (or "sidevalve") engines, where the v ...
(OHV) and flathead engine
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine, is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the engine block, instead of in the cylinder head, a ...
configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block
In an internal combustion engine, the engine block is the structure that contains the cylinders and other components. The engine block in an early automotive engine consisted of just the cylinder block, to which a separate crankcase was attach ...
. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; however an OHV engine requires pushrod
A valvetrain is a mechanical system that controls the operation of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. The intake valves control the flow of air/fuel mixture (or air alone for direct-injected engines) into the combu ...
s and rocker arm
A rocker arm is a valvetrain component that typically transfers the motion of a pushrod in an overhead valve engine, overhead valve internal combustion engine to the corresponding intake/exhaust poppet valve, valve.
Rocker arms in automobiles are ...
s to transfer the motion from the camshaft up to the valves, whereas an OHC engine has the valves directly actuated by the camshaft.
Compared with OHV engines with the same number of valves, there are fewer reciprocating components and less valvetrain inertia in an OHC engine. This reduced inertia in OHC engines results in less valve float at higher engine speeds (RPM). A downside is that the system used to drive the camshaft (usually a timing chain in modern engines) is more complex in an OHC engine, such as the 4-chain valvetrain of the Audi 3.2 or the 2 meter chain on Ford cammers. Another disadvantage of OHC engines is that during engine repairs where the removal of the cylinder head
In a piston engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders, forming the roof of the combustion chamber. In sidevalve engines the head is a simple plate of metal containing the spark plugs and possibly heat dissipation fins. In more modern ...
is required, the camshaft engine timing
In a spark ignition internal combustion engine, ignition timing is the timing, relative to the current piston position and crankshaft angle, of the release of a Electric spark, spark in the combustion chamber near the end of the compression strok ...
needs to be reset. In addition, an OHC engine has a large cylinder head to accommodate the camshaft or an extra set of valves to increase the volumetric efficiency
Volumetric efficiency (VE) in internal combustion engine engineering is defined as the ratio of the equivalent volume of the fresh air drawn into the cylinder during the intake stroke (if the gases were at the reference condition for density) to th ...
, so that with the same displacement as an OHV engine, the OHC engine will end up being the physically larger of the two mostly due to the enlarged cylinder head.
The other main advantage of OHC engines is that there is greater flexibility to optimise the size, location and shape of the intake and exhaust ports, since there are no pushrods that need to be avoided. This improves the gas flow through the engine, increasing power output and fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency (or fuel economy) is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical energy, chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or Mechanical work, w ...
.
Single overhead camshaft (SOHC)
 The oldest configuration of overhead camshaft engine is the ''single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) design. A SOHC engine has one camshaft per bank of cylinders, therefore a
The oldest configuration of overhead camshaft engine is the ''single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) design. A SOHC engine has one camshaft per bank of cylinders, therefore a straight engine
The straight engine (also called inline engine) is a configuration of multi-cylinder piston engine where all of the cylinders are arranged in a single row, rather than radially or in two or more cylinder banks.
Design
A straight engine is eas ...
has a total of one camshaft and a V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
or flat engine
A flat engine is a piston engine where the cylinders are located on either side of a central crankshaft. Flat engines are also known as horizontally opposed engines, however this is distinct from the less common opposed-piston engine design, ...
has a total of two camshafts (one for each cylinder bank).
Most SOHC engines have 2 valves per cylinder (sometimes 3 or 4), 1 intake valve and one exhaust valve. Motion of the camshaft is usually transferred to the valves either directly (using a tappet) or indirectly via a rocker arm
A rocker arm is a valvetrain component that typically transfers the motion of a pushrod in an overhead valve engine, overhead valve internal combustion engine to the corresponding intake/exhaust poppet valve, valve.
Rocker arms in automobiles are ...
.
Dual overhead camshaft (DOHC)
 A ''dual overhead cam'', ''double overhead cam'', or ''twin-cam'' engine has two camshafts over each bank of the cylinder head, one for the intake valves and another for the exhaust valves. Therefore there are two camshafts for a straight engine and a total of four camshafts for a V engine or a flat engine.
A V engine or flat engine requires four camshafts to function as a DOHC engine, since having two camshafts in total would result in only a single camshaft per cylinder bank for these engine layouts. Some V engines with four camshafts have been marketed as "quad-cam" engines, however technically "quad-cam" would require four camshafts per cylinder bank (i.e. eight camshafts in total), therefore these engines are merely ''dual overhead camshaft'' engines.
Many DOHC engines have 4 valves per cylinder (sometimes 5,
A ''dual overhead cam'', ''double overhead cam'', or ''twin-cam'' engine has two camshafts over each bank of the cylinder head, one for the intake valves and another for the exhaust valves. Therefore there are two camshafts for a straight engine and a total of four camshafts for a V engine or a flat engine.
A V engine or flat engine requires four camshafts to function as a DOHC engine, since having two camshafts in total would result in only a single camshaft per cylinder bank for these engine layouts. Some V engines with four camshafts have been marketed as "quad-cam" engines, however technically "quad-cam" would require four camshafts per cylinder bank (i.e. eight camshafts in total), therefore these engines are merely ''dual overhead camshaft'' engines.
Many DOHC engines have 4 valves per cylinder (sometimes 5, Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. A subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The origins of the compa ...
or Volkswagen
Volkswagen (VW; )English: , . is a German automotive industry, automobile manufacturer based in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Established in 1937 by German Labour Front, The German Labour Front, it was revitalized into the global brand it ...
for instance). The camshaft usually operates the valves directly via a bucket tappet. A DOHC design permits a wider angle between intake and exhaust valves than in SOHC engines, which improves the air-fuel mixture's flow through the engine. A further benefit is that the spark plug can be placed at the optimum location, which in turn improves combustion efficiency
Combustion efficiency refers to the effectiveness of the burning process in converting fuel into heat energy. It is measured by the proportion of fuel that is efficiently burned and converted into useful heat, while minimizing the emissions of po ...
. Another newer benefit of DOHC engine design is the ability to independently change/phase the timing between each camshaft and the crankshaft. This affords better fuel economy by allowing a broader torque curve. Although each major manufacturer has their own trade name for their specific system of variable cam phasing systems, overall they are all classified as variable valve timing
Variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a Poppet valve, valve lift event in an internal combustion engine, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combina ...
.
Components
Timing belt / timing chain
 The rotation of a camshaft is driven by a
The rotation of a camshaft is driven by a crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a reciprocating engine, piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating Shaft (mechanical engineering), shaft containing one or more crankpins, ...
. Many 21st century engines use a toothed ''timing belt'' made from rubber and kevlar to drive the camshaft. Timing belts are inexpensive, produce minimal noise and have no need for lubrication. A disadvantage of timing belts is the need for regular replacement of the belt; recommended belt life typically varies between approximately . If the timing belt is not replaced in time and fails and the engine is an interference engine, major engine damage is possible.
The first known automotive application of timing belts to drive overhead camshafts was the 1953 Devin-Panhard racing specials built for the SCCA H-modified racing series in the United States. These engines were based on Panhard OHV flat-twin engines, which were converted to SOHC engines using components from Norton motorcycle engines. The first production car to use a timing belt was the 1962 Glas 1004 compact coupe.
Another camshaft drive method commonly used on modern engines is a ''timing chain'', constructed from one or two rows of metal roller chains. By the early 1960s most production automobile overhead camshaft designs used chains to drive the camshaft(s). Timing chains do not usually require replacement at regular intervals, however the disadvantage is that they are noisier than timing belts.
Gear train
Agear train
A gear train or gear set is a machine element of a mechanical system formed by mounting two or more gears on a frame such that the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each oth ...
system between the crankshaft and the camshaft is commonly used in diesel overhead camshaft engines used in heavy trucks. Gear trains are not commonly used in engines for light trucks or automobiles.
Other camshaft drive systems
Several OHC engines up until the 1950s used a shaft with bevel gears to drive the camshaft. Examples include the 1908–1911 Maudslay 25/30, the Bentley 3 Litre, the 1917-?Liberty L-12
The Liberty L-12 is an American Water_cooling#Internal_combustion_engines, water-cooled 45° V12 engine, V-12 engine, displacing and making , designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It was designed principally as ...
, the 1929-1932 MG Midget, the 1925-1948 Velocette K series, the 1931-1957 Norton International and the 1947-1962 Norton Manx. In more recent times, the 1950-1974 Ducati Single, 1973-1980 Ducati L-twin engine, 1999-2007 Kawasaki W650 and 2011-2016 Kawasaki W800 motorcycle engines have used bevel shafts. The Crosley four cylinder was the last automotive engine to use the shaft tower design to drive the camshaft, from 1946 to 1952; the rights to the Crosley engine format were bought by a few different companies, including General Tire in 1952, followed by Fageol in 1955, Crofton in 1959, Homelite in 1961, and Fisher Pierce in 1966, after Crosley closed the automotive factory doors, and they continued to produce the same engine for several more years.
A camshaft drive using three sets of cranks and rods in parallel was used in the 1920–1923 Leyland Eight luxury car built in the United Kingdom. A similar system was used in the 1926-1930 Bentley Speed Six and the 1930-1932 Bentley 8 Litre. A two-rod system with counterweights at both ends was used by many models of the 1958-1973 NSU Prinz.
History
1900–1914
Among the first overhead camshaft engines were the 1902 Maudslay SOHC engine built in the United Kingdom and the 1903 Marr Auto Car SOHC engine built in the United States. The first DOHC engine was a Peugeot inline-four racing engine which powered the car that won the 1912 French Grand Prix. Another Peugeot with a DOHC engine won the 1913 French Grand Prix, followed by the ''Mercedes-Benz 18/100 GP'' with an SOHC engine winning the 1914 French Grand Prix. The Isotta Fraschini Tipo KM— built in Italy from 1910–1914— was one of the first production cars to use an SOHC engine.World War I
 During World War I, both the Allied and
During World War I, both the Allied and Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
; specifically those of the German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
's ''Luftstreitkräfte
The ''Deutsche Luftstreitkräfte'' (, German Air Combat Forces)known before October 1916 as (The Imperial German Air Service, lit. "The flying troops of the German Kaiser’s Reich")was the air arm of the Imperial German Army. In English-langu ...
'' air forces, sought to quickly apply the overhead camshaft technology of motor racing engines to military aircraft engines. The SOHC engine from the ''Mercedes 18/100 GP'' car (which won the 1914 French Grand Prix) became the starting point for both Mercedes' and Rolls-Royce's aircraft engines. Mercedes created a series of six-cylinder engines which culminated in the Mercedes D.III. Rolls-Royce reversed-engineered the Mercedes cylinder head design based on a racing car left in England at the beginning of the war, leading to the Rolls-Royce Eagle
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of oth ...
V12 engine. Other SOHC designs included the Spanish Hispano-Suiza 8
The Hispano-Suiza 8 is a Internal combustion engine cooling, water-cooled V8 engine, V8 SOHC aero engine introduced by Hispano-Suiza in 1914 that went on to become the most commonly used liquid-cooled engine in the aircraft of the Entente Powers ...
V8 engine (with a fully enclosed-drivetrain), the American Liberty L-12
The Liberty L-12 is an American Water_cooling#Internal_combustion_engines, water-cooled 45° V12 engine, V-12 engine, displacing and making , designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It was designed principally as ...
V12 engine, which closely followed the later Mercedes D.IIIa design's partly-exposed SOHC valvetrain design; and the Max Friz-designed; German BMW IIIa straight-six engine. The DOHC Napier Lion
The Napier Lion is a 12-cylinder, petrol-fueled 'broad arrow' W12 engine, W12 configuration aircraft engine built by D. Napier & Son from 1917 until the 1930s. A number of advanced features made it the most powerful engine of its day and kept ...
W12 engine was built in Great Britain beginning in 1918.
Most of these engines used a shaft to transfer drive from the crankshaft up to the camshaft at the top of the engine. Large aircraft engines— particularly air-cooled engines— experienced considerable thermal expansion, causing the height of the cylinder block to vary during operating conditions. This expansion caused difficulties for pushrod engines, so an overhead camshaft engine using a shaft drive with sliding spline was the easiest way to allow for this expansion. These bevel shafts were usually in an external tube outside the block, and were known as "tower shafts".
Hispano-Suiza 8A
The Hispano-Suiza 8 is a water-cooled V8 SOHC aero engine introduced by Hispano-Suiza in 1914 that went on to become the most commonly used liquid-cooled engine in the aircraft of the Entente Powers during the First World War. The original ...
SOHC aircraft engine
Hispano-suiza-V8 220PS.jpg , 1914–1918 Hispano-Suiza 8Be SOHC aircraft engine with "tower shafts" at the rear of each cylinder bank
Later Mercedes D III Valvetrain.jpg , Later production (1917-18) Mercedes D.III upper valvetrain details sketch, its design features copied by the BMW III and the Allied Liberty L-12
The Liberty L-12 is an American Water_cooling#Internal_combustion_engines, water-cooled 45° V12 engine, V-12 engine, displacing and making , designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It was designed principally as ...
engines
Liberty L-12-2.jpg , Detail closeup of a Liberty L-12
The Liberty L-12 is an American Water_cooling#Internal_combustion_engines, water-cooled 45° V12 engine, V-12 engine, displacing and making , designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It was designed principally as ...
's upper valvetrain, showing the similarity to the later-production Mercedes design
1919–1944
 An early American overhead camshaft production engine was the SOHC straight-eight engine used in the 1921–1926
An early American overhead camshaft production engine was the SOHC straight-eight engine used in the 1921–1926 Duesenberg Model A
The Duesenberg Model A was the first automobile in series production to have hydraulic brakes and the first automobile in series production in the United States with a straight-eight engine. Officially known as the Duesenberg Straight Eight, th ...
luxury car.
In 1926, the Sunbeam 3 litre Super Sports became the first production car to use a DOHC engine.
In the United States, Duesenberg added DOHC engines (alongside their existing SOHC engines) with the 1928 release of the Duesenberg Model J, which was powered by a DOHC straight-eight engine. The 1931–1935 Stutz DV32 was another early American luxury car to use a DOHC engine. Also in the United States, the DOHC Offenhauser racing engine was introduced in 1933. This inline-four engine dominated North American open-wheel racing from 1934 until the 1970s.
Other early SOHC automotive engines were the 1920–1923 Wolseley Ten, the 1928-1931 MG 18/80, the 1926–1935 Singer Junior and the 1928–1929 Alfa Romeo 6C Sport. Early overhead camshaft motorcycles included the 1925–1949 Velocette K Series and the 1927–1939 Norton CS1.
1945–present
 The 1946–1948 Crosley CC Four was arguably the first American mass-produced car to use an SOHC engine. This small mass-production engine powered the winner of the 1950
The 1946–1948 Crosley CC Four was arguably the first American mass-produced car to use an SOHC engine. This small mass-production engine powered the winner of the 1950 12 Hours of Sebring
The 12 Hours of Sebring is an annual motorsport Endurance racing (motorsport), endurance race for Sports car racing, sports cars held at Sebring International Raceway, on the site of the former Hendricks Army Airfield World War II air base in S ...
.
Use of a DOHC configuration gradually increased after World War II, beginning with sports cars. Iconic DOHC engines of this period include the 1948–1959 Lagonda straight-six engine, the 1949–1992 Jaguar XK
The Jaguar XK is a two-door 2+2 grand tourer manufactured and marketed by Jaguar Cars from 1996–2012 and by Jaguar Land Rover from 2013–2014 in hatchback coupé and convertible body styles, across two generations. The XK was intro ...
straight-six engine and the 1954–1994 Alfa Romeo Twin Cam inline-four engine. The 1966-2000 Fiat Twin Cam inline-four engine was one of the first DOHC engines to use a toothed timing belt instead of a timing chain.
In the 1980s, the need for increased performance while reducing fuel consumption and exhaust emissions saw increasing use of DOHC engines in mainstream vehicles, beginning with Japanese manufacturers. By the mid-2000s, most automotive engines used a DOHC layout.
See also
*Cam-in-block A cam-in-block engine is where the camshaft is located in the engine block
In an internal combustion engine, the engine block is the structure that contains the cylinders and other components. The engine block in an early automotive engine con ...
* Camless
* Overhead valve engine
An overhead valve engine, abbreviated (OHV) and sometimes called a pushrod engine, is a piston engine whose valves are located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with flathead (or "sidevalve") engines, where the v ...
* Variable valve timing
Variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a Poppet valve, valve lift event in an internal combustion engine, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combina ...
Footnotes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Overhead Camshaft Engine valvetrain configurations