|
Trichothecenes
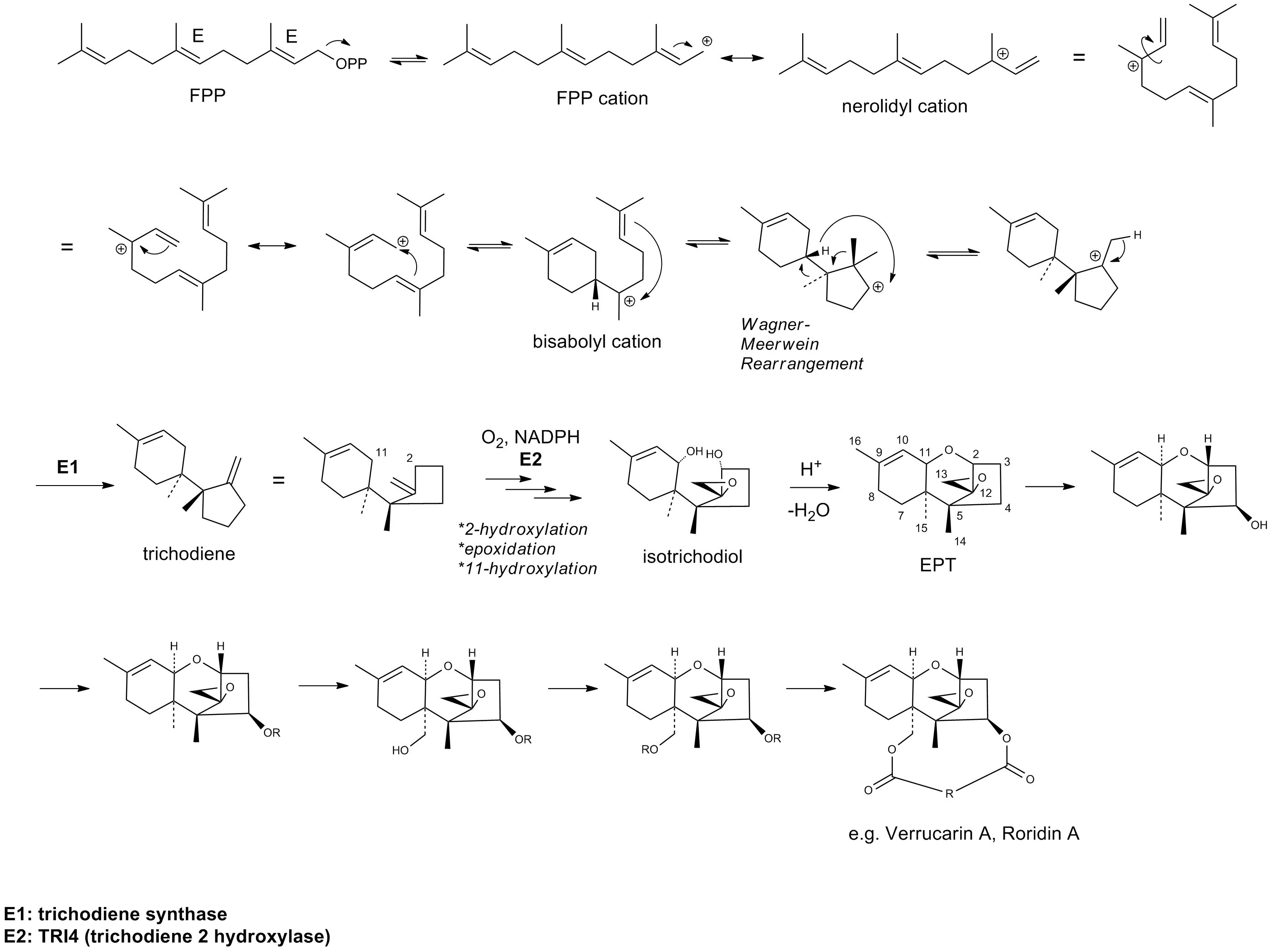
Trichothecenes constitute a large group of chemically related mycotoxins. They are produced by Fungus, fungi of the genera ''Fusarium'', ''Myrothecium'', ''Trichoderma'', ''Podostroma'', ''Trichothecium'', ''Cephalosporium'', ', ''Stachybotrys'' (most in Hypocreales) and possibly others. Chemically, trichothecenes are a class of sesquiterpenes. All trichothecenes share the Cyclic compound, cyclic sesquiterpene structure but differ in the type of functional group attached to the carbon backbone. They are produced on many different grains such as wheat, Oat, oats, or maize by various ''Fusarium'' species including ''Gibberella zeae, F. graminearum'', ''Fusarium sporotrichioides, F. sporotrichioides'', ''F. poae,'' and ''Fusarium equiseti, F. equiseti''. Some moulds that produce trichothecene mycotoxins, such as ''Stachybotrys chartarum'', can grow in damp indoor environments. It has been found that macrocyclic trichothecenes produced by ''Stachybotrys chartarum, S. chartarum'' can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roridin E
Roridin E is a mycotoxin of the trichothecene group. In nature it is mainly found in fungi of the ''Fusarium'' and ''Myrothecium'' species. The ''Fusarium'' and ''Myrothecium'' species belong to the most prevalent mycotoxin producing species in south-east Asia and Australia, therefore making them a considerable risk for the food crop production industry. The fungi are abundant in various agricultural products (cereal crops) and their further processed products such as bread. The ''Fusarium'' and ''Myrothecium'' species invade and grow on crops, and may produce roridin E under moist and cool conditions. In rats, the symptoms observed after exposure to roridin E and linoleic acid are increased blood glucose levels and a decrease in glutathione. This may attribute to the toxic effect of roridin E due to its ability to delay the absorption and elimination of the mycotoxin. Structure and reactivity Roridin E consists of a trichothecene core structure consisting of a six-membered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verrucarin A
Verrucarin A is a chemical compound that belongs in the class of trichothecenes, a group of sesquiterpene toxins produced by several fungi, namely from the ''Fusarium'' species, that are responsible for infecting food grains. It was first described in 1962. Within the skeleton of the basic trichothecene structure, the olefin and epoxide are crucial for toxicity; ester functionalities and hydroxyl groups often contribute to the toxicity, thereby rendering verrucarin A as one of the most lethal examples. The mechanism of action for this class of toxins mainly inhibits protein biosynthesis by preventing peptidyl transferase activity. Although initially thought to be potentially useful as anticancer therapeutics, numerous examples of trichothecene derivatives were shown to be too toxic for clinical use. Biosynthesis Verrucarin A is classified as a type D trichothecene based on its substitution pattern in the 12,13-epoxytrichothec-9-ene (EPT) core structure. Type D differs from types A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satratoxin H
Satratoxin-H, a trichothecene mycotoxin, is a naturally occurring toxin produced by the ascomycetes ''Stachybotrys chartarum'' and '' Trichoderma cornu-damae'' which is highly toxic and potentially fatal to humans and other animals. The clinical condition it causes is known as ''Stachybotrotoxicosis''. It is related to the mycotoxin T-2, but unlike T-2 has not been reported to have been used as a chemical weapon. Properties Satratoxin-H is almost completely insoluble in water, but is easily soluble in lower alcohols and polar solvents such as ethanol, methanol, 2-propanol, acetone and chloroform. Satratoxin-H is not officially classified as a chemical weapon. Effects Satratoxin-H is extremely versatile. Contact with the solution through ingestion, inhalation, or even prolonged physical contact produces symptoms similar to those listed below. * a rash that becomes a moist dermatitis * nosebleeds * chest pain * pulmonary hemorrhage Pulmonary hemorrhage (or pulmonary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichoderma Cornu-damae
, formerly ''Podostroma cornu-damae'' and also known as the poison fire coral, is a species of fungus in the family Hypocreaceae. The fruit bodies of the fungus are highly toxic if ingested, and have been responsible for several human fatalities as they contain an often fatal dose of the mycotoxin satratoxin-H. Taxonomy The species was originally described as ''Hypocrea cornu-damae'' by Narcisse Théophile Patouillard in 1895, and later transferred to the genus ''Podocrea'' in 1905 by Pier Andrea Saccardo. In 1994, Japanese mycologists Tsuguo Hongo and Masana Izawa placed the species in the genus ''Podostroma''. Range The fungus was once thought to be exclusive to South Korea and Japan, but recent discoveries have been made in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and Australia.Burt, Jemima and Mounter, Brendan (19 February 2021Deadly fungus, poison fire coral, sighted near Cairns, prompting warning for bushwalkers ''ABC News'', 2021-02-19. Description The conidiophores (specialized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gibberella Zeae
''Gibberella zeae'', also known by the name of its anamorph ''Fusarium graminearum'', is a fungus, fungal plant pathogen which causes fusarium head blight (FHB), a devastating disease on wheat and barley. The pathogen is responsible for billions of dollars in economic losses worldwide each year. Infection causes shifts in the amino acid composition of wheat, resulting in shriveled kernels and contaminating the remaining grain with mycotoxins, mainly deoxynivalenol (DON), which inhibits protein biosynthesis; and zearalenone, an estrogenic mycotoxin. These toxins cause vomiting, liver damage, and reproductive defects in livestock, and are harmful to humans through contaminated food. Despite great efforts to find resistance genes against ''F. graminearum'', no completely resistant variety is currently available. Research on the biology of ''F. graminearum'' is directed towards gaining insight into more details about the infection process and reveal weak spots in the life cycle of this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The Botanical nomenclature, botanical and Zoological nomenclature, zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In nomenclature, botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a Binomial nomenclature, scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different Binomial nomenclature, binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocyclic
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry. Synthesis The formation of macrocycles by ring-closure is called macrocyclization. The central challenge to macrocyclization is that ring-closing reactions do not favor the formation of large rings. Instead, medium sized rings or polymers tend to form. Early macrocyclizations were achieved ketonic decarboxylations for the preparation of terpenoid macrocycles. So, while Ružička was able to produce various macrocycles, the yields were low. This kinetic problem can be addressed by using high-dilution reactions, whereby intramolecular processes are favored relative to polymerizations. Reactions amenable to high dilution include Dieckmann condensation and related based-induced reactions of esters with remote halides. Some macrocyclizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |