|
Toroidal Reflector
Toroidal describes something which resembles or relates to a torus or toroid: Mathematics * Toroidal coordinates, a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system * Toroidal and poloidal coordinates, directions for a three-dimensional system which follows a circular ring around the surface * Toroidal graph, a graph whose vertices can be placed on a torus such that no edges cross *Toroidal grid network, an n-dimensional grid connected circularly in more than one dimension *Toroidal polyhedron, partition of a toroidal surface into polygons Engineering * Toroidal engine, an internal combustion engine with pistons that rotate inside a ring-shaped cylinder *Toroidal expansion joint, a metallic assembly consisting of a series of circular tubes used in high pressure applications *Toroidal inductors and transformers, a type of electrical device using magnetic cores with a ring or donut shape *Toroidal propeller, a loop-shaped propeller used in aviation and maritime transport * Toroidal r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus
In geometry, a torus (: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanarity, coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses include ring toruses, horn toruses, and spindle toruses. A ring torus is sometimes colloquially referred to as a donut or doughnut. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution, also known as a ring torus. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a Lemon (geometry), spindle torus (or ''self-crossing torus'' or ''self-intersecting torus''). If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a ''toroid'', as in a square toroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Inductors And Transformers
Toroidal inductors and transformers are inductors and transformers which use magnetic cores with a toroidal (ring or donut) shape. They are passivity (engineering), passive electronic components, consisting of a circular ring or donut shaped magnetic core of ferromagnetic material such as laminated core, laminated iron, iron powder, or Ferrite (magnet), ferrite, around which wire is wound. Although closed-core inductors and transformers often use cores with a rectangular shape, the use of toroidal-shaped cores sometimes provides superior electrical performance. The advantage of the toroidal shape is that, due to its symmetry, the amount of magnetic flux that escapes outside the core (leakage flux) can be made low, potentially making it more efficient and making it emit less electromagnetic interference (EMI). Toroidal inductors and transformers are used in a wide range of electronic circuits: power supply, power supplies, inverters, and amplifiers, which in turn are used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
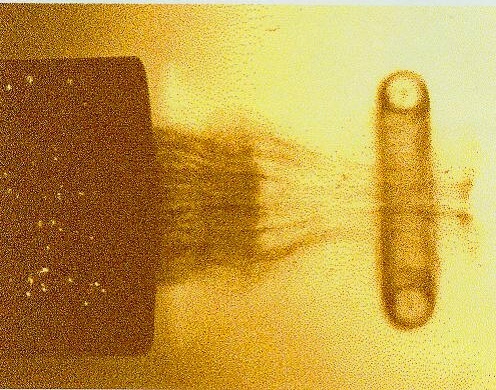
Vortex Ring
A vortex ring, also called a toroidal vortex, is a torus-shaped vortex in a fluid; that is, a region where the fluid mostly spins around an imaginary axis line that forms a closed loop. The dominant flow in a vortex ring is said to be toroidal, more precisely poloidal. Vortex rings are plentiful in turbulent flows of liquids and gases, but are rarely noticed unless the motion of the fluid is revealed by suspended particles—as in the smoke rings which are often produced intentionally or accidentally by smokers. Fiery vortex rings are also a commonly produced trick by fire eaters. Visible vortex rings can also be formed by the firing of certain artillery, in mushroom clouds, in microbursts, and rarely in volcanic eruptions. A vortex ring usually tends to move in a direction that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring and such that the inner edge of the ring moves faster forward than the outer edge. Within a stationary body of fluid, a vortex ring can travel for relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Solenoid
The toroidal solenoid was an early 1946 design for a fusion power device designed by George Paget Thomson and Moses Blackman of Imperial College London. It proposed to confine a deuterium fuel plasma to a toroidal (donut-shaped) chamber using magnets, and then heating it to fusion temperatures using radio frequency energy in the fashion of a microwave oven. It is notable for being the first such design to be patented, filing a secret patent on 8 May 1946 and receiving it in 1948. A critique by Rudolf Peierls noted several problems with the concept. Over the next few years, Thomson continued to suggest starting an experimental effort to study these issues, but was repeatedly denied as the underlying theory of plasma diffusion was not well developed. When similar concepts were suggested by Peter Thonemann that included a more practical heating arrangement, John Cockcroft began to take the concept more seriously, establishing small study groups at Harwell. Thomson adopted Thonema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Ring Model
The toroidal ring model, known originally as the Parson magneton or magnetic electron, is a physical model of subatomic particles. It is also known as the plasmoid ring, vortex ring, or helicon ring. This physical model treated electrons and protons as elementary particles, and was first proposed by Alfred Lauck Parson in 1915. Theory Instead of a single orbiting charge, the toroidal ring was conceived as a collection of infinitesimal charge elements, which orbited or circulated along a common continuous path or " loop". In general, this path of charge could assume any shape, but tended toward a circular form due to internal repulsive electromagnetic forces. In this configuration the charge elements circulated, but the ring as a whole did not radiate due to changes in electric or magnetic fields since it remained stationary. The ring produced an overall magnetic field (" spin") due to the current of the moving charge elements. These elements circulated around the ring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Planet
A toroidal planet is a hypothetical type of terrestrial planet, telluric exoplanet with a Torus, toroidal or doughnut shape. While no firm theoretical understanding as to how toroidal planets could Planetary formation, form naturally is necessarily known, the shape itself is potentially wiktionary:quasistable, quasistable, and is analogous to the physical parameters of a speculatively constructible megastructure in self-suspension, such as a Dyson sphere, ringworld, Stanford torus or Bishop Ring (habitat), Bishop Ring. Physical description At sufficiently large enough scales, rigid matter such as the typical silicate-ferrous composition of rocky planets Lane–Emden equation, behaves fluidly, and satisfies the condition for evaluating the mechanics of toroidal self-gravitating fluid bodies in context. A rotating mass in the form of a torus allows an effective balance between the gravitational attraction and the force due to centrifugal acceleration, when the angular momentum is ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Reflector
Toroidal describes something which resembles or relates to a torus or toroid: Mathematics * Toroidal coordinates, a three-dimensional orthogonal coordinate system * Toroidal and poloidal coordinates, directions for a three-dimensional system which follows a circular ring around the surface * Toroidal graph, a graph whose vertices can be placed on a torus such that no edges cross *Toroidal grid network, an n-dimensional grid connected circularly in more than one dimension *Toroidal polyhedron, partition of a toroidal surface into polygons Engineering * Toroidal engine, an internal combustion engine with pistons that rotate inside a ring-shaped cylinder *Toroidal expansion joint, a metallic assembly consisting of a series of circular tubes used in high pressure applications *Toroidal inductors and transformers, a type of electrical device using magnetic cores with a ring or donut shape *Toroidal propeller, a loop-shaped propeller used in aviation and maritime transport * Toroidal r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Propeller
A toroidal propeller is a type of propeller that is ring-shaped with each blade forming a closed loop. The propellers are significantly quieter at audible frequency ranges, between 20 Hz and 20 kHz, while generating comparable thrust to traditional propellers. In practice, toroidal propellers reduce noise pollution in both aviation and maritime transport. History In the centuries after Archimedes invented the Archimedes' screw, developments of propeller design led to the torus marine propeller, then described as a propeller featuring "double blades". It was invented in the early 1890s by Charles Myers from Manchester affiliated with Fawcett, Preston and Company. The design was successfully trialed on several English steam tugboats and passenger ferries at the time. In the 1930s, Friedrich Honerkamp patented a toroidal fan, and Rene Louis Marlet patented a toroidal aircraft propeller. The marine propeller was patented again in the late 1960s by Australian enginee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Expansion Joint
A Toroidal expansion joint is a metallic assembly that consists of a series of toroidal convolutions which are circular tubes wrapped around pipe ends or weld ends and have a gap at the inside diameter to allow for axial stroke while absorbing changes in expansion or contraction of the pipe line. Convolutions are the portion of the bellows that allow it to be flexible. The convolutions are formed around reinforcing bands so that only the concave portion of the torus allows for flexibility. Toroidal expansion joints are typically used in high pressure applications, where little movement is required, and generally used for heat exchangers. Usually, they are hydraulically formed, but others are free formed. These expansion joints are also referred to as "Omega" bellows due to their shape resembling the Greek letter, Omega. References External links * Expansion Joint Manufacturers Association EJMA http://www.ejma.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Toroidal Expansion Joint Structural connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroid
In mathematics, a toroid is a surface of revolution with a hole in the middle. The axis of revolution passes through the hole and so does not intersect the surface. For example, when a rectangle is rotated around an axis parallel to one of its edges, then a hollow rectangle-section ring is produced. If the revolved figure is a circle, then the object is called a torus. The term ''toroid'' is also used to describe a toroidal polyhedron. In this context a toroid need not be circular and may have any number of holes. A ''g''-holed ''toroid'' can be seen as approximating the surface of a torus having a topological genus, ''g'', of 1 or greater. The Euler characteristic χ of a ''g'' holed toroid is 2(1−''g''). The torus is an example of a toroid, which is the surface of a doughnut. Doughnuts are an example of a solid torus created by rotating a disk, and are not toroids. Toroidal structures occur in both natural and synthetic materials. Equations A toroid is specified by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Engine
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder". Many swing-piston engines have been proposed, but none have been successful. Two attempts in about 2010 are the prototype American-made MYT engine and prototype Russian ORE for use in the Yo-Mobile hybrid car. Both claimed high fuel efficiency and high power-to-weight ratio, but there have been no successful demonstrations of claimed efficiency or that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toroidal Polyhedron
In geometry, a toroidal polyhedron is a polyhedron which is also a toroid (a -holed torus), having a topology (Mathematics), topological Genus (mathematics), genus () of 1 or greater. Notable examples include the Császár polyhedron, Császár and Szilassi polyhedron, Szilassi polyhedra. Variations in definition Toroidal polyhedra are defined as collections of polygons that meet at their edges and vertices, forming a manifold as they do. That is, each edge should be shared by exactly two polygons, and at each vertex the edges and faces that meet at the vertex should be linked together in a single cycle of alternating edges and faces, the link (geometry), link of the vertex. For toroidal polyhedra, this manifold is an orientability, orientable surface. Some authors restrict the phrase "toroidal polyhedra" to mean more specifically polyhedra topologically equivalent to the (genus 1) torus. In this area, it is important to distinguish embedding, embedded toroidal polyhedra, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |