|
Sulfonanilide
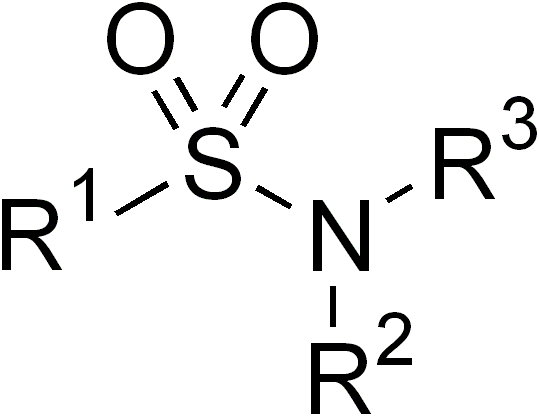
In organic chemistry, a sulfonanilide group is a functional group found in certain organosulfur compounds. It possesses the chemical structure , and consists of a sulfonamide group () where one of the two nitrogen substituents (R' or R") is a phenyl group (). It can be viewed as a derivative of aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ... ().Wujiang Zhenze Xinmin Chemical Auxiliaries Factory"Product name — 2-Aminophenol-4-(2-carboxy)sulfonanilide"Intermediates for Dyes and Pesticides — Products. (2006). References Functional groups Sulfonamides {{organic-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonanilide
In organic chemistry, a sulfonanilide group is a functional group found in certain organosulfur compounds. It possesses the chemical structure , and consists of a sulfonamide group () where one of the two nitrogen substituents (R' or R") is a phenyl group (). It can be viewed as a derivative of aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ... ().Wujiang Zhenze Xinmin Chemical Auxiliaries Factory"Product name — 2-Aminophenol-4-(2-carboxy)sulfonanilide"Intermediates for Dyes and Pesticides — Products. (2006). References Functional groups Sulfonamides {{organic-chemistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organosulfur Compound
Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is vital for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two ( cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries. Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium, and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium, and carbon–tellurium compounds. A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together, and can be represented using structural formulae and by molecular models; complete electronic structure descriptions include specifying the occupation of a molecule's molecular orbitals. Structure determination can be applied to a range of targets from very simple molecules (e.g., diatomic oxygen or nitrogen), to very complex ones (e.g., such as protein or DNA). Background Theories of chemical structure were first developed by August Kekulé, Archibald Scott Couper, and Aleksandr Butlerov, among others, from about 1858. These theories were first to state that chemical compounds are not a random cluster of atoms and functional groups, but rather had a definite or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonamide (chemistry)
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. Because of the rigidity of the functional group, sulfonamides are typically crystalline; for this reason, the formation of a sulfonamide is a classic method to convert an amine into a crystalline derivative which can be identified by its melting point. Many important drugs contain the sulfonamide group. A sulfonamide (compound) is a chemical compound that contains this group. The general formula is or , where each R is some organic group; for example, "methanesulfonamide" (where R = methane, R' = R" = hydrogen) is . Any sulfonamide can be considered as derived from a sulfonic acid by replacing a hydroxyl group () with an amine group. In medicine, the term "sulfonamide" is sometimes used as a synonym for sulfa drug, a derivative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyl Group
In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6 H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. Phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. Phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring. Nomenclature Usually, a "phenyl group" is synonymous with C6H5− and is represented by the symbol Ph or, archaically, Φ. Benzene is sometimes denoted as PhH. Phenyl groups are generally attached to other atoms or groups. For example, triphenylmethane (Ph3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derivative (chemistry)
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone to oxidation: while freshly purified aniline is an almost colorless oil, exposure to air results in gradual darkening to yellow or red, due to the formation of strongly colored, oxidized impurities. Aniline can be diazotized to give a diazonium salt, which can then undergo var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Groups
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the rest of the molecule's composition. This enables systematic prediction of chemical reactions and behavior of chemical compounds and the design of chemical synthesis. The reactivity of a functional group can be modified by other functional groups nearby. Functional group interconversion can be used in retrosynthetic analysis to plan organic synthesis. A functional group is a group of atoms in a molecule with distinctive chemical properties, regardless of the other atoms in the molecule. The atoms in a functional group are linked to each other and to the rest of the molecule by covalent bonds. For repeating units of polymers, functional groups attach to their nonpolar core of carbon atoms and thus add chemical character to carbon chains. Funct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |