|
Simon II (High Priest)
Simon II (219–199 BCE) was a Jewish High Priest during the Second Temple period. He was the son of Onias II. Some identify him with Simeon the Just. Mentioned extensively by Jesus son of Eleazar, son of Sirach of Jerusalem, also known as Ben Sira, in chapter 50 of Ben Sira/Sirach in a hymn of Hebrew parallel verse: "The leader of his brothers and the pride of his people was the high priest, Simon son of Onias, who in his life repaired the house, and in his time fortified the temple. He laid the foundations for the high double walls, the high retaining walls for the temple enclosure. In his days a water cistern was dug, a reservoir like the sea in circumference. He considered how to save his people from ruin, and fortified the city against siege. How glorious he was, surrounded by the people, as he came out of the house of the curtain. Like the morning star upon the clouds, like the full moon at the festal season, like the sun shining on the temple of the Most High, like the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon I Symon Filius Onye (titel Op Object) Liber Chronicarum (serietitel), RP-P-2016-49-24-1
Simon may refer to: People * Simon (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name Simon * Simon (surname), including a list of people with the surname Simon * Eugène Simon, French naturalist and the genus authority ''Simon'' * Tribe of Simeon, one of the twelve tribes of Israel Places * Şimon ( hu, links=no, Simon), a village in Bran Commune, Braşov County, Romania * Șimon, a right tributary of the river Turcu in Romania Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Simon'' (1980 film), starring Alan Arkin * ''Simon'' (2004 film), Dutch drama directed by Eddy Terstall Games * ''Simon'' (game), a popular computer game * Simon Says, children's game Literature * ''Simon'' (Sutcliff novel), a children's historical novel written by Rosemary Sutcliff * Simon (Sand novel), an 1835 novel by George Sand * ''Simon Necronomicon'' (1977), a purported grimoire written by an unknown author, with an introduction by a man identified only as "Sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
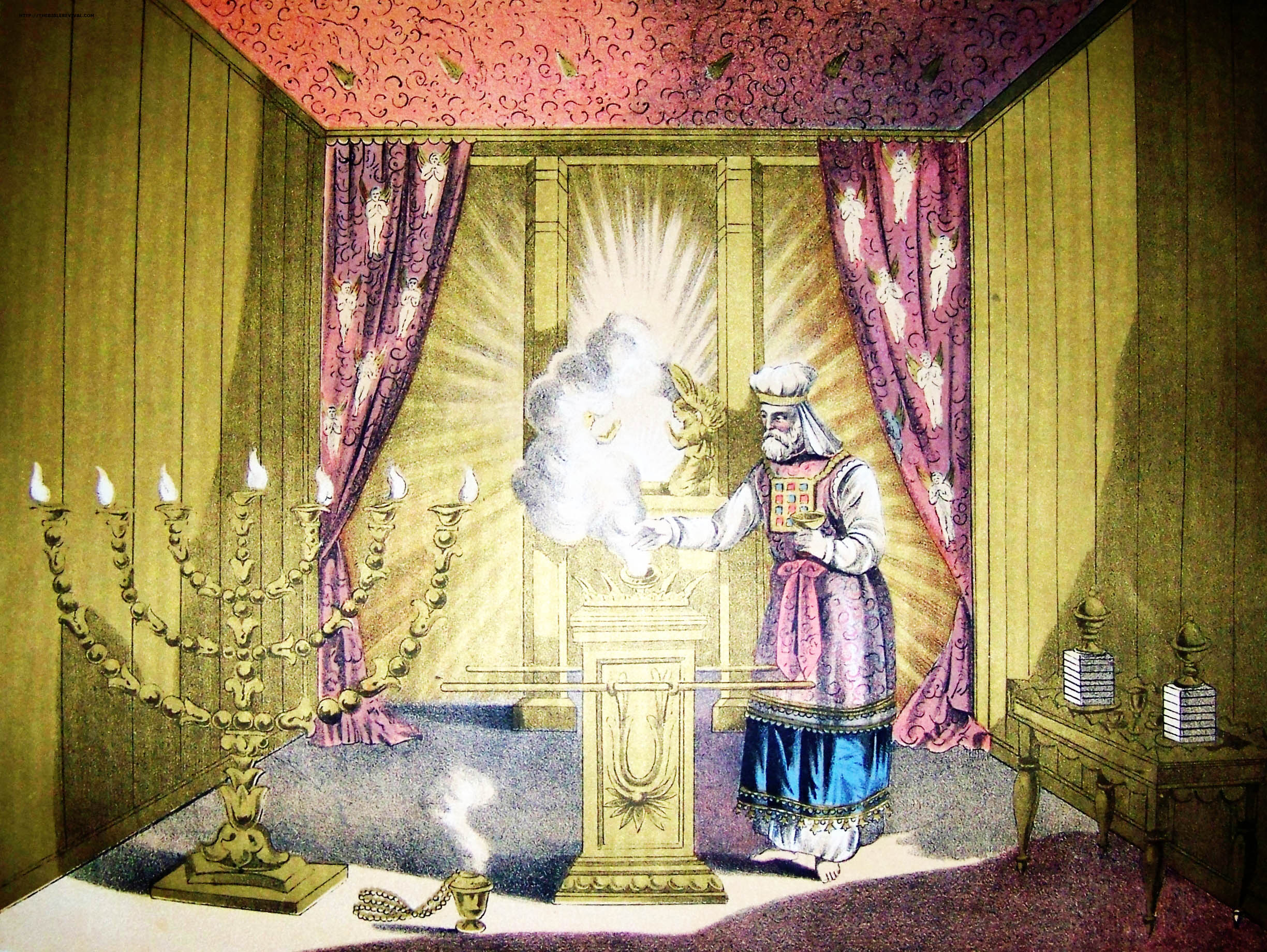
Kohen Gadol
High Priest ( he, כהן גדול, translit=Kohen Gadol or ; ) was the title of the chief religious official of Judaism from the early post- Exilic times until the destruction of the Second Temple in Jerusalem by the Romans in 70 CE. Previously, in the Israelite religion, including during the time of the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, other terms were used to designate the leading priests; however, as long as a king was in place, the supreme ecclesiastical authority lay with him. The official introduction of the term "high priest" went hand-in-hand with a greatly enhanced ritual and political significance bestowed upon the chief priest of the Israelites in the post-Exilic period, especially from 411 BCE onward due to the religious transformations brought about during the time of the Babylonian captivity and due to the lack of a Jewish king and kingdom. The high priests belonged to the Jewish priestly families that trace their paternal line back to Aaron—the first high pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Temple Period
The Second Temple period in Jewish history lasted approximately 600 years (516 BCE - 70 CE), during which the Second Temple existed. It started with the return to Zion and the construction of the Second Temple, while it ended with the First Jewish–Roman War and the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 CE. In 587/6 BCE, the Kingdom of Judah was conquered by the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The Judeans lost their independence and monarchy, and their holy city was destroyed. Part of the Judean population was exiled to Babylon; it was eventually allowed to return following a proclamation by the Persian king Cyrus the Great that was issued after the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenid Empire. Under Persian provincial governance ( 539 – 332 BCE), the returned Jewish population in Judah was allowed to self-govern and rebuild the Temple in Jerusalem. In 332 BCE, Judea was conquered by Alexander the Great, and later incorporated into the Ptolemaic Kingdom (c. 301-200 BCE) and the Seleucid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onias II
Onias II (Hebrew: חוֹנִיּוֹ ''Ḥōniyyō'' or ''Honio'' or ''Honiyya ben Shimon''; Greek: ''Onias Simonides'') was the son of Simon I. He was still a minor when his father died, so that his uncle Eleazar, and after him the latter's uncle Manasseh, officiated as high priests before he himself succeeded to that dignity. According to Josephus, he was a covetous man and of limited intelligence, whose refusal to pay the twenty talents of silver which every high priest was required to pay to the King of Egypt threatened to imperil both the high priest and the people; but at this juncture Joseph, the clever son of Tobias and nephew of Onias, succeeded in pacifying Ptolemy III Euergetes (reigned 246 to 222 BC). Onias is said to have died, almost simultaneously with his nephew Joseph, during the reign of Seleucus IV Philopator (reigned 187 BC to 175 BC), hence about 181 BC.Josephus''Ant.'' xii. 4. § 10. His successor in office was Simon II. Patrilineal ancestry References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeon The Just
Simeon the Righteous or Simeon the Just ( he, שִׁמְעוֹן הַצַדִּיק ''Šīməʿōn haṢadīq'') was a Jewish High Priest during the Second Temple period. He is also referred to in the Mishnah, where he is described as one of the last members of the Great Assembly. Biography Simeon the Righteous is either Simon I (310–291 or 300–273 BCE), son of Onias I, and grandson of Jaddua, or Simon II (219–199 BCE), son of Onias II. Many statements concerning him are variously ascribed by scholars, ancient and modern, to four different persons who bore the same name: Simeon I (by Fränkel and Grätz); Simeon II (by Krochmal in the 18th century, Brüll in the 19th, and Moore and Zeitlin in the 20th); Simon Maccabeus (by Löw); or Simeon the son of Gamaliel (by Weiss). The scholarly consensus of the late 20th century has fallen on Simon II. The Talmud, Josephus (who identifies him as Simon I), and Sirach all contain accounts of him. He was termed "the Righteous" be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Sira
Ben Sira also known as Shimon ben Yeshua ben Eliezer ben Sira (שמעון בן יהושע בן אליעזר בן סירא) or Yeshua Ben Sirach (), was a Hellenistic Jewish scribe, sage, and allegorist from Seleucid-controlled Jerusalem of the Second Temple period. He is the author of '' Sirach'', also known as the "Book of Ecclesiasticus". He wrote his work in Hebrew, possibly in Alexandria in Egypt in the Ptolemaic Kingdom c. 180–175 BCE, where he is thought to have established a school. While Ben Sira is sometimes claimed to be a contemporary of Simeon the Just, it is more likely that his contemporary was High Priest Simon II (219–199 BCE) and this is due to confusion with his father, Yeshua'. A medieval text, the '' Alphabet of Sirach'', was falsely attributed to him. Name In the Koine Greek text of the Book of Sirach, the author's father is called "Jesus the son of Sirach of Jerusalem". Jesus is the Anglicized form of the Greek name Ἰησοῦς, the equivale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirach
The Book of Sirach () or Ecclesiasticus (; abbreviated Ecclus.) is a Jewish work, originally in Hebrew, of ethical teachings, from approximately 200 to 175 BC, written by the Judahite scribe Ben Sira of Jerusalem, on the inspiration of his father Joshua son of Sirach, sometimes called Jesus son of Sirach or Yeshua ben Eliezer ben Sira. In Egypt, it was translated into Greek by the author's unnamed grandson, who added a prologue. This prologue is generally considered the earliest witness to a canon of the books of the prophets, and thus the date of the text is the subject of intense scrutiny. The book itself is the largest wisdom book from antiquity to have survived. Canonical status Sirach is accepted as part of the canon by Catholics, Eastern Orthodox, and most Oriental Orthodox Christians. The Anglican tradition considers Sirach (which was published with other Greek Jewish books in a separate section of the King James Bible) among the apocryphal books, and read them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3 Maccabees
3 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Γ´, translit=Makkabaíōn 3 also called the Third Book of Maccabees, is a book written in Koine Greek, likely in the 1st century BC in Roman Egypt. Despite the title, the book has nothing to do with the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleucid Empire described in 1 Maccabees and 2 Maccabees. Instead it tells the story of persecution of the Jews under Pharaoh Ptolemy IV Philopator (222–205 BC) in Ptolemaic Egypt, some decades before the Maccabee uprising in Judea. The story purports to explain the origin of a Purim-like festival celebrated in Egypt. 3 Maccabees is somewhat similar to the Book of Esther, another book which describes how a king is advised to annihilate the Diaspora Jews in his territory, yet is thwarted by God. In 3 Maccabees, King Ptolemy IV Philopator attempts to enter the Second Temple in Jerusalem, but is rebuffed by divine power. He grows to hate Jews, and orders the Jews of Egypt assembled in his hippodrome to be execu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of High Priests Of Israel
This article gives a list of the High Priests (''Kohen Gadol'') of Ancient Israel up to the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 AD. Because of a lack of historical data, this list is incomplete and there may be gaps. High Priests of Israel The High Priests, like all Levitical priests, belonged to the Aaronic line. The Bible mentions the majority of high priests before the Babylonian captivity, but does not give a complete list of office holders. Lists would be based on various historical sources. In several periods of gentile rule, high priests were appointed and removed by kings. Still, most high priests came from the Aaronic line. One exception is Menelaus, who may not have been from the Tribe of Levi at all, but from the Tribe of Benjamin. From the Exodus to Solomon's Temple The following section is based on information found in the various books of the Bible, including the genealogies given in First Book of Chronicles and the Book of Ezra, the works of Josephus a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onias III
Onias III ( he, חוֹנִיּוֹ ''Ḥōnīyyō''), son of Simon II, was Jewish High Priest during the Second Temple period. He is described in scriptures as a pious man who opposed the Hellenization of Judea. He was succeeded by his brother Jason in 175 BCE. Politics of the office The Seleucid Empire controlled Jerusalem during Onias' tenure and Seleucus IV Philopator (reigned 187–175 BCE) was friendly to the Jews and defrayed all expenses connected with their sanctuary. According to 2 Maccabees, a Hellenizing official of the Temple, Simon, a member of the Tribe of Benjamin, induced Seleucus through his official Heliodorus to plunder the Temple. The attempt was unsuccessful and the court never forgave the High Priest. When Antiochus IV Epiphanes became king in 175 BCE, Onias was obliged to yield to his own brother, Jason, a Hellenizer. According to Josephus, Jason became high priest after the death of Onias, the latter's son being then a minor. Josephus strangely identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BCE High Priests Of Israel
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 ( CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




