|
Seventh-day Adventist Church In Tonga
The Seventh-day Adventist Church in Tonga, ( to, Siasi ʻAhofitu) is one of the smaller religious groups in the South Pacific island state of Tonga with a reported 3,853 members as of June 30, 2020, Retrieved June 4, 2021 started by missionaries from the United States who visited in 1891 and settled in 1895. They set up schools but made very little progress in conversion, handicapped by dietary rules that prohibited popular local foods such as pork and shellfish, and that also banned tobacco, alcohol and . The church was revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh-day Adventist Church
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventist Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the seventh day of the week in the Christian (Gregorian) and the Hebrew calendar, as the Sabbath, and its emphasis on the imminent Second Coming (advent) of Jesus Christ. The denomination grew out of the Millerite movement in the United States during the mid-19th century and it was formally established in 1863. Among its co-founders was Ellen G. White, whose extensive writings are still held in high regard by the church. Much of the theology of the Seventh-day Adventist Church corresponds to common evangelical Christian teachings, such as the Trinity and the infallibility of Scripture. Distinctive post-tribulation teachings include the unconscious state of the dead and the doctrine of an investigative judgment. The church places an emphasis on diet and health, including adhering to Kosher food laws, advocating vegetarianism, and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Hilliard
Edward Hilliard (3 April 1851 – 18 September 1936) was a Seventh-day Adventist missionary from America who worked in Australia, India and Tonga. He was the first resident Seventh-day Adventist missionary on Tonga, and founded the Seventh-day Adventist Church in Tonga. Missionary Edward Hilliard was born on 3 April 1851 in Madrid, St. Lawrence County, New York. His parents were converted to Adventism when he was a child, and he was brought up in that faith. He became an Adventist pastor. In 1895 the Mission Board sent him to Tonga, then called the Friendly Islands, as a missionary. Adventists on the schooner ''Pitcairn'' had first visited Tongatapu, the main island of the Kingdom of Tonga, in 1891. Hilliard arrived at Tongatapu on 30 August 1895 with his wife Ida Hilliard and their two-year-old daughter Alta. They lived in temporary quarters while Edward Hilliard built a four-room cottage. Around November 1895 Ida Hilliard began to teach school, first in their temporary h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vavaʻu
Vavau is an island group, consisting of one large island ( ʻUtu Vavaʻu) and 40 smaller ones, in Tonga. It is part of Vavaʻu District, which includes several other individual islands. According to tradition, the Maui god created both Tongatapu and Vavau, but put a little more effort into the former. Vavau rises above sea level at Mount Talau. The capital is Neiafu, situated at the Port of Refuge (Puatalefusi or Lolo-a-Halaevalu). History Myths and legends In Polynesia, it is said that the islands were created by the god Maui, who reached into the bottom of the sea with his magic hook, caught something on it, and pulled it up to the sea surface, and it became the islands of Vavau. Recorded history Don Francisco Mourelle de la Rúa, commanding the Spanish frigate ''Princesa'', was the first European to come to Vavau, which he did on 4 March 1781. He charted Vavaʻu as ''Martín de Mayorga'', naming it after the man who was the Viceroy of New Spain at that time. Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
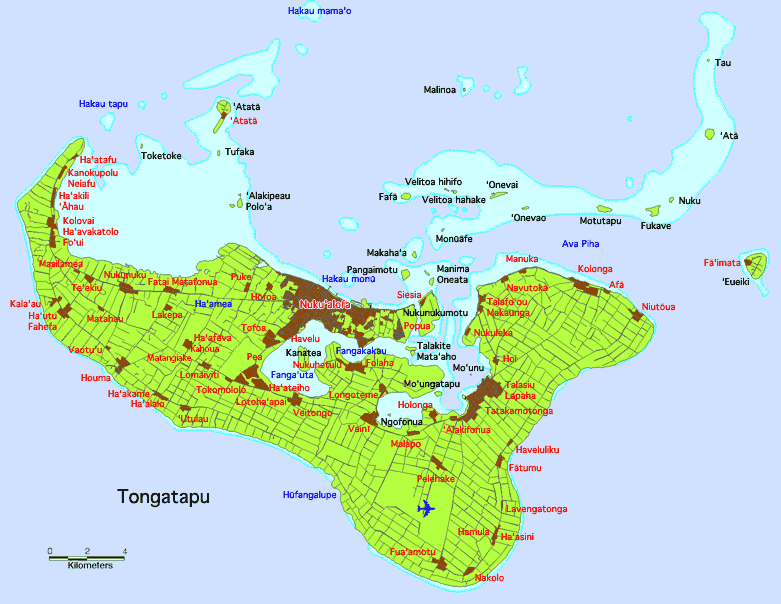
Tongatapu
Tongatapu is the main island of Tonga and the site of its capital, Nukualofa. It is located in Tonga's southern island group, to which it gives its name, and is the country's most populous island, with 74,611 residents (2016), 70.5% of the national population, on . Based on Google Earth Pro, its maximum elevation is at least above sea level along Liku Road at 21 degrees 15 minutes and 55.7 seconds south 175 degrees 08 minutes 06.4 seconds west, but could be even higher somewhere else. Tongatapu is Tonga's centre of government and the seat of its monarchy. Tongatapu has experienced more rapid economic development than the other islands of Tonga, and has thus attracted many internal migrants from them. Geography The island is (or including neighbouring islands) and rather flat, as it is built of coral limestone. The island is covered with thick fertile soil consisting of volcanic ash from neighbouring volcanoes. At the steep coast of the south, heights reach an average of , an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haʻapai
Haʻapai is a group of islands, islets, reefs, and shoals in the central part of Tonga. It has a combined land area of . The Tongatapu island group lies to its south, and the Vavaʻu group lies to its north. Seventeen of the Haʻapai islands are inhabited. Their combined population is 5,419. The highest point in the Ha‘apai group, and in all of Tonga, is on Kao, which rises almost above sea level. The administrative capital village of Haʻapai District is Pangai, which is located on Lifuka. Geography Haʻapai comprises 51 islands that lie directly west of the Tonga Trench. They constitute a chain of both volcanic and coral islands, including Kao, the highest point in the kingdom, which stands high. Farther to the east are the coral islands, which are inhabited. The Haʻapai archipelago lies north of Tongatapu and south of Vavaʻu. Seventeen of the islands are inhabited, including the main islands of Lifuka and Foa. The two main villages in the archipelago are Pangai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merritt Kellogg
Merritt Gardner Kellogg (28 March 1832 – December 20 1921) was a Seventh-day Adventist (SDA) carpenter, missionary, pastor and doctor who worked in Northern California, the South Pacific, and Australia. He designed and built several medical facilities. Kellogg was involved in the controversy about which day should be observed as the Sabbath on Tonga, which lies east of the 180° meridian but west of the International Date Line. Early years Merritt Gardner Kellogg was born in Hadley, Massachusetts on the Connecticut River on 28 March 1832. He attended the Battle Creek Sabbath School. He converted to Seventh-day Adventism at the age of twenty. Kellogg was the half-brother of John Harvey Kellogg. He married Louisa Rawson (1832–94) and they had a child Charles Merritt Kellogg (1856–89). The Kelloggs made the westward journey to California in 1859, where they were probably the first Seventh-day Adventists in the state. In 1861 Kellogg gave a series of Bible lectures in San Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin Butz
Edwin Sebastian Butz (1864 – July 1956) was a Seventh-day Adventist (SDA) missionary who was active in Oceania and in Australia. Missionary career Edwin Sebastian Butz was born in 1864 in the United States. In 1895 he came to the South Pacific with his wife Florence and daughter Alma on the third voyage of the SDA schooner ''Pitcairn''. They served first on Pitcairn Island, then in the early days of the Adventist mission in Tonga. They arrived in Tonga on 29 September 1896 with Sarah and Maria Young, two nursing trainees from Pitcairn Island. There they joined the first SDA missionaries, Edward Hilliard and his wife Ida, who had arrived the previous year. The Butz's initially had difficulty being accepted, as they were Americans and most Europeans in Tonga were British. This was eased by Florence Butz's provision of medical services. The Butz's tried to establish a permanent mission, but were mainly limited to working with the small ''papalagi'' (European) colony. They m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosalind Amelia Young
Rosalind Amelia Young (13 August 1853 – 1 February 1924) was a historian from Pitcairn Islands. Early life Young was born in 1853 on Pitcairn Island to Simon Young and Mary Buffett Christian. She was also the great-granddaughter of John Adams, one of the mutineers of . As a young child she was part of a migration to Norfolk Island Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together wit ... but returned in 1864. Her father led the return of several families to the Pitcairn Islands and became magistrate in 1849. Career From a young age she began recording the history of the Pitcairn Islands, specifically that of Elizabeth Mills, daughter of a ''Bounty'' mutineer. She shared the history of the islands through letters, collecting historical information and personal stories. She also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongan Language
Tongan (English pronunciation: or ; ') is an Austronesian language of the Polynesian branch native to the island nation of Tonga. It has around 187,000 speakers. It uses the word order verb–subject–object. Related languages Tongan is one of the multiple languages in the Polynesian branch of the Austronesian languages, along with Hawaiian, Māori, Samoan and Tahitian, for example. Together with Niuean, it forms the Tongic subgroup of Polynesian. Tongan is unusual among Polynesian languages in that it has a so-called ''definitive accent''. As with all Polynesian languages, Tongan has adapted the phonological system of proto-Polynesian. # Tongan has retained the original proto-Polynesian *h, but has merged it with the original *s as . (The found in modern Tongan derives from *t before high front vowels). Most Polynesian languages have lost the original proto-Polynesian glottal stop ; however, it has been retained in Tongan and a few other languages including Rapa Nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region—the area governed by Auckland Council—which includes outlying rural areas and the islands of the Hauraki Gulf, and which has a total population of . While Europeans continue to make up the plurality of Auckland's population, the city became multicultural and cosmopolitan in the late-20th century, with Asians accounting for 31% of the city's population in 2018. Auckland has the fourth largest foreign-born population in the world, with 39% of its residents born overseas. With its large population of Pasifika New Zealanders, the city is also home to the biggest ethnic Polynesian population in the world. The Māori-language name for Auckland is ', meaning "Tāmaki desired by many", in refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocesan School For Girls, Auckland
, type = Private, Girls, Composite (Year 1–13) with boarding facilities , denomination = Anglican , established = 1903; years ago , motto_translation = That we may serve , address = Clyde StreetEpsomAucklandNew Zealand. , coordinates = , principal = Heather McRae , roll = () , decile = 10 , MOE = 67 , homepage diocesan.school.nzDiocesan School for Girls (Dio) is a private girls' school in Epsom, Auckland, New Zealand. It is consistently a top-achieving school nationally. The school is Anglican-based and was established in 1903. It caters to international students and has accommodation for 50 boarders at Innes House. The school elected to offer students the option of International Baccalaureate diplomas, as an alternative to the national NCEA qualification, from 2008. History Bishop Moore Richar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sālote Tupou III
Sālote Tupou III (born Sālote Mafile‘o Pilolevu; 13 March 1900 – 16 December 1965) was Queen of Tonga from 1918 to her death in 1965. She reigned for nearly 48 years, longer than any other Tongan monarch. She was well known for her height, standing 6 ft 3 in (1.91 metres) tall in her prime. Early life Sālote (Charlotte) was born on 13 March 1900 in Tonga as the eldest daughter and heir of King George Tupou II of Tonga and his first wife, Queen Lavinia Veiongo. She was baptized and named after her great-grandmother Sālote Mafile‘o Pilolevu (daughter of George Tupou I). She was not popular, as she was perceived as being born from the 'wrong mother' because of her mother's lower rank and was disliked so much that it was not safe for her to go outside the palace. Her mother, Queen Lavinia, died from tuberculosis on 25 April 1902. After her death, the Chiefs in Tonga urged King George Tupou II for many years to remarry to produce a male heir. On 11 November 1909, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_p225_AUCKLAND%2C_NEW_ZEALAND.jpg)
.jpg)
