|
Soft Gamma Repeaters
A soft gamma repeater (SGR) is an astronomy, astronomical object which emits large bursts of gamma-rays and X-rays at irregular intervals. It is conjectured that they are a type of magnetar or, alternatively, neutron stars with fossil Accretion disk, disks around them. History On March 5, 1979 a powerful gamma-ray burst was noted. As a number of receivers at different locations in the Solar System saw the burst at slightly different times, its direction could be determined, and it was shown to originate from near a supernova remnant in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Over time it became clear that this was not a normal gamma-ray burst. The photons were less energetic in the soft gamma-ray and hard X-ray range, and repeated bursts came from the same region. Astronomer Chryssa Kouveliotou of the Universities Space Research Association (USRA) at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center decided to test the hypothesis that soft gamma repeaters were magnetars. According to the hypothesis, the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauss (unit)
The gauss (symbol: , sometimes Gs) is a unit of measurement of magnetic induction, also known as magnetic flux density. The unit is part of the Gaussian units, Gaussian system of units, which inherited it from the older centimetre–gram–second system of units#Electromagnetic units .28EMU.29, centimetre–gram–second electromagnetic units (CGS-EMU) system. It was named after the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1936. One gauss is defined as one maxwell (unit), maxwell per square centimetre. As the centimetre–gram–second system of units (cgs system) has been superseded by the International System of Units (SI), the use of the gauss has been deprecated by the standards bodies, but is still regularly used in various subfields of science. The SI unit for magnetic flux density is the Tesla (unit), tesla (symbol T), which corresponds to . Name, symbol, and metric prefixes Although not a component of the International System of Units, the usage of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR 0501+4516
SGR 0501+4516 is a magnetar that is a soft gamma repeater (SGR). Currently, the phenomena of SGRs and the related anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXP) are explained as arising from magnetars. SGR 0501+4516 is located approximately 15,000 light years from Earth and has a magnetic field 100 trillion times stronger than the Earth's. SGR 0501+4516 is remarkable in that it has been the first SGR to have been discovered after ten years without SGR detections. It has been suggested that SGR 0501+4516, together with 1E 1547.0-5408, should be considered as tools for a final unification of SGRs, AXPs and the “transient AXPs (TAXPs)” into a single class of “magnetars candidates”. Discovery Its existence was reported on August 22, 2008, by NASA's Swift satellite, which reported numerous blasts of radiation from the object. The eruptions were subsequently studied in-depth using the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton and International Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory (INTEGRAL) s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as '' spacetime''. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. In the 19th and 20th centuries mathematicians began to examine geometries that are non-Euclidean, in which space is conceived as '' curved'', rather than '' flat'', as in the Euclidean space. According to Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, space around gravitational fields deviates from Euclidean space. Experimental tests of general relativity have confirmed that non-Euclidean geometries provide a bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR J1550−5418
SGR J1550−5418 is a soft gamma repeater (SGR), the sixth to be discovered, located in the constellation Norma. Long known as an X-ray source, it was noticed to have become active on 23 October 2008, and then after a relatively quiescent interval, became much more active on 22 January 2009. It has been observed by the Swift satellite, and by the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, launched in 2008, as well as in X-ray and radio emission. It has been observed to emit intense bursts of gamma rays at a rate of up to several per minute. At its estimated distance of 30,000 light years (~10 kpc), the most intense flares equal the total energy emission of the Sun in ~20 years. The underlying object is believed to be a rotating neutron star, of the type known as ''magnetar A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (~109 to 1011 T, ~1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR 1627−41
SGR 1627−41, is a soft gamma repeater (SGR), located in the constellation of Ara. It was discovered June 15, 1998, using the Burst and transient Source Experiment ( BATSE) and was the first soft gamma repeater to be discovered since 1979. During a period of 6 weeks, the star bursted approximately 100 times, and then went quiet. The measured bursts lasted an average of 100 milliseconds but ranged from 25 ms to 1.8 seconds. SGR 1627−41 is a persistent X-ray source. It is located at a distance of 11 kpc in the radio complex CTB 33, a star forming region that includes the supernova remnant G337.0-0.1. This object is believed to be a neutron star that undergoes random outbursts of hard and soft X-rays. This may be caused by the loss of angular momentum of a highly magnetized neutron star, or magnetar A magnetar is a type of neutron star with an extremely powerful magnetic field (~109 to 1011 T, ~1013 to 1015 G). The magnetic-field decay powers the emission of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is composed of a layer of gas mixture that surrounds the Earth's planetary surface (both lands and oceans), known collectively as air, with variable quantities of suspended aerosols and particulates (which create weather features such as clouds and hazes), all retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere serves as a protective buffer between the Earth's surface and outer space, shields the surface from most meteoroids and ultraviolet solar radiation, keeps it warm and reduces diurnal temperature variation (temperature extremes between day and night) through heat retention (greenhouse effect), redistributes heat and moisture among different regions via air currents, and provides the chemical and climate conditions allowing life to exist and evolve on Earth. By mole fraction (i.e., by quantity of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other trace gases (see Composition below ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR 1806−20
SGR 1806−20 is a magnetar, a type of neutron star with a very powerful magnetic field, that was discovered in 1979 and identified as a soft gamma repeater. SGR 1806−20 is located about 13 kiloparsecs (42,000 light-years) from Earth on the far side of the Milky Way in the constellation of Sagittarius. It has a diameter of no more than and rotates on its axis every 7.5 seconds ( rotation speed at the equator on the surface). , SGR 1806-20 is the most highly magnetized object ever observed, with a magnetic field of over 1015 gauss (G) (1011 tesla) intensity (compared to the Sun's 1–5 G and Earth's 0.25–0.65 G). Explosion Forty-two thousand years after a starquake occurred on the surface of SGR 1806-20, the radiation from the resultant explosion reached Earth on December 27, 2004 ( GRB 041227). In terms of gamma rays, the burst had an absolute magnitude of around −29. It was the brightest event known to have been sighted on this planet from an origin outside t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SGR 0525−66
SGR may refer to: * Heart Colchester and Heart Ipswich, radio stations in Suffolk, England both once known as SGR * Sagittarius (constellation) abbreviation * '' Scary Go Round'', a webcomic * Scientists for Global Responsibility, a United Kingdom group that promotes the ethical practice and use of science and technology * Segar LRT station in Bukit Panjang, Singapore (LRT station abbreviation) * Select Graphic Rendition (ANSI), an ANSI X3.64 escape sequence * Service Général du Renseignement et de la Sécurité, the French name of the Belgian General Information and Security Service * SGR (band), a ska band from New Jersey, United States * Shale Gouge Ratio, a mathematical algorithm aiming to predict the fault rock types for simple fault zones * The Shaw Group, a company which formerly used as its ticker symbol * Slade Green railway station in London, England (National Rail station code) * Smart Green Resilient (planning concept) abbreviation * Societa' di Gestione del ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
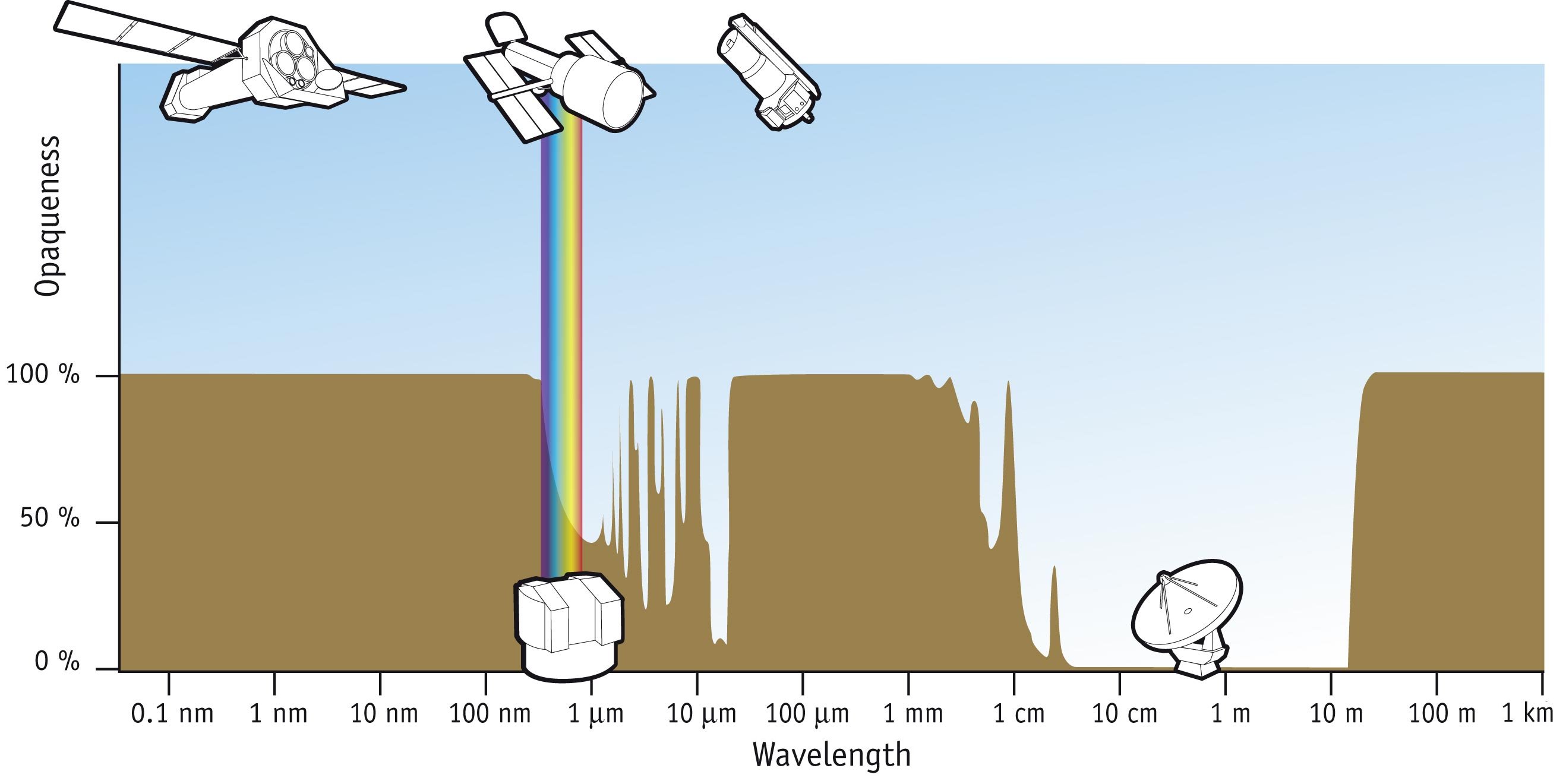
X-ray Astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by Balloon-borne telescope, balloons, sounding rockets, and X-ray astronomy satellite, satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot. X-ray generation, X-ray emission is expected from astronomical objects that contain extremely hot gases at temperatures from about a million kelvin (K) to hundreds of millions of kelvin (MK). Moreover, the maintenance of the E-layer of ionized gas high in the Earth's thermosphere also suggested a strong extraterrestrial source of X-rays. Although theory predicted that the Sun and the stars would be prominent X-ray sources, there was no way to verify this because Earth's atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |