|
Single-tier Banking System
A single-tier banking system is a policy framework under which all credit institutions coexist without distinction about the quality of their liabilities, or in other words, there is no distinction between central bank money and broad money. This setting is generally associated with communist economic systems. An extreme version of single-tier banking system is the monobank system in which a single institution centralizes all financial intermediation. The alternative to a single-tier system is a two-tier banking system, in which the central bank is singled out and entrusted with monetary policy, as is presently the case in nearly all of the world's jurisdictions. The move from single-tier to two-tier banking systems has been a key feature of post-communist transitions or, in the case of China, post-Mao economic reform. References to tiering in the banking sector also exist in other contexts. For example, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority in the 1980s implemented what it calls a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Bank Money
In economics, the monetary base (also base money, money base, high-powered money, reserve money, outside money, central bank money or, in the UK, narrow money) in a country is the total amount of money created by the central bank. This includes: * the total currency circulating in the public, * plus the currency that is physically held in the vaults of commercial banks, * plus the commercial banks' reserves held in the central bank. The monetary base should not be confused with the money supply, which consists of the total currency circulating in the public plus certain types of non-bank deposits with commercial banks. Management Open market operations are monetary policy tools which directly expand or contract the monetary base. The monetary base is manipulated during the conduct of monetary policy by a finance ministry or the central bank. These institutions change the monetary base through open market operations: the buying and selling of government bonds. For examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banque Commerciale Pour L'Europe Du Nord – Eurobank
Banque Commerciale pour l’Europe du Nord (BCEN) or Banque Commerciale pour l'Europe du Nord – Eurobank (BCEN-Eurobank) was a Soviet-controlled bank in Paris,The piratization of Russia: Russian reform goes awry. Marshall I. Goldman. founded in 1921 by wealthy Russian emigres and supported by Leonid Krasin who, in 1925, sold their stakes to the USSR. It maintained correspondent accounts with Western banks to secure lines of credit for facilitating Soviet imports into that country in which the correspondent account is located. Also, these correspondent accounts performed foreign currency exchange for the Kremlin. History During the 1920s and 1930s, Soviet and numerous foreign sources referred to this bank as the Aero Bank (russian: «Аеробанк») or Airbank in Paris (russian: «Эйробанк» в Париже) and not the Aero-Bank SA which was a branch of the German bank ''Aerobank'', which was known as the Bank der Deutschen Luftfahrt AG (BDL), and established in Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Bank
Viking Bank is a Russian regional bank headquartered in Saint-Petersburg. Their corporate name is Commercial Bank "Viking" Closed Joint Stock Company. Viking Bank is a part of Russian Banking System and is governed by the applicable law of the Russian Federation, regulatory acts of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and the Charter. General Banking License No. 2 is issued by the State Bank of USSR on August 26, 1988. The Bank functions on the financial market as a universal credit institution. History In August 1988, the USSR had begun the period when state banks of industry-specific branches were transformed into the commercial banks. During that period the first private commercial bank - Viking Bank - was established as an experiment (at the beginning the Bank's name was "Patent"). At that time there was no law regulating banking activity and the first Charter of the bank was developed on the basis of the Cooperation Act. Viking Bank was given the General Banking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ... to Kazakhstan–Russia border, the north and west, China to China–Kazakhstan border, the east, Kyrgyzstan to Kazakhstan–Kyrgyzstan border, the southeast, Uzbekistan to Kazakhstan–Uzbekistan border, the south, and Turkmenistan to Kazakhstan–Turkmenistan border, the southwest, with a coastline along the Caspian Sea. Its capital is Astana, known as Nur-Sultan from 2019 to 2022. Almaty, Kazakhstan's largest city, was the country's capital until 1997. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country, the largest and northernmost Muslim world, Muslim-majority cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shymkent
Shymkent (; Шымкент, Şymkent), known until 1993 as Chimkent ( uz, Çımkent, چىمكېنت; Yañalif: Çimkent ()); russian: Чимкент, translit=Chimkent (), is a city in Kazakhstan. It is near the border with Uzbekistan. It is one of three Kazakh cities which have the status equal to that of a region (“city of republican significance”). It is the third-most populous city in Kazakhstan, behind Almaty and Astana, with an estimated population of 1,002,291 . According to regional and city officials, the millionth resident of Shymkent was born on 17 May 2018. It is a regional cultural centre. Shymkent is situated west of Almaty and south of Astana. It is also to the north of Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Etymology The name Chimkent comes from two Sogdian words, ''chim'' (meaning 'turf') and ''kent'' (or ''kand'') (meaning 'city') (also found in the name of nearby Toshkent); thus, it literally means "the city in the grass/turf." After Kazakhstan gained independence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
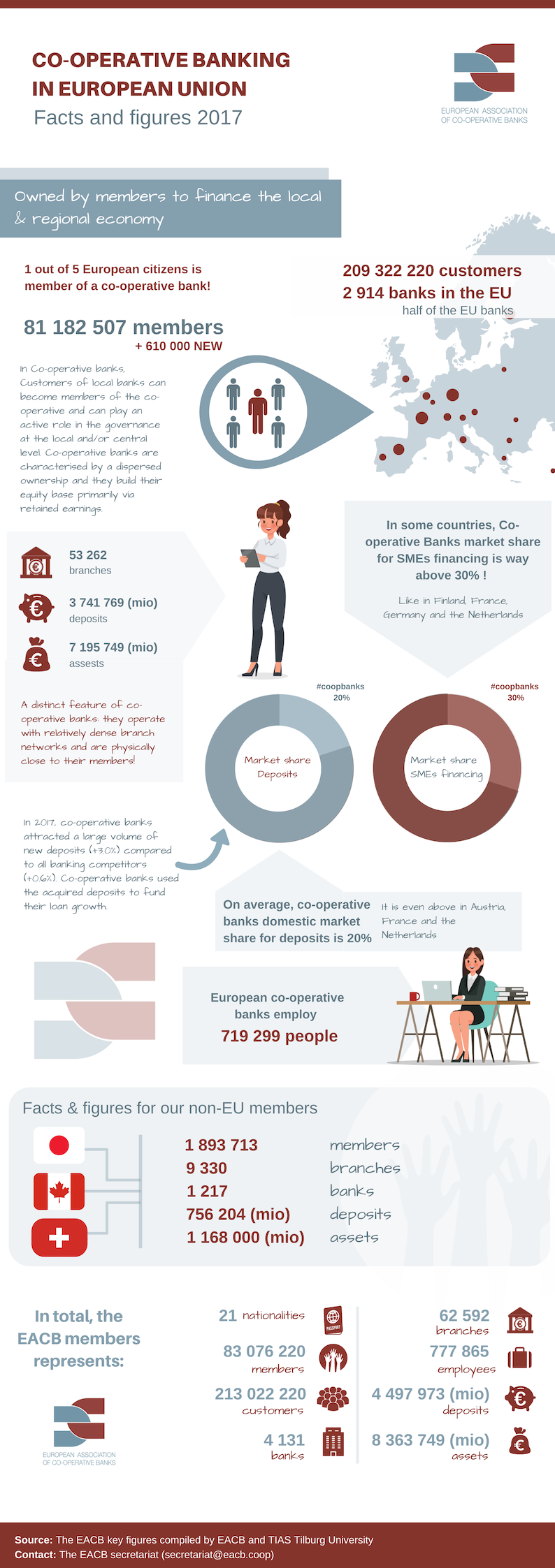
Cooperative Bank
Cooperative banking is retail and commercial banking organized on a cooperative basis. Cooperative banking institutions take deposits and lend money in most parts of the world. Cooperative banking, as discussed here, includes retail banking carried out by credit unions, mutual savings banks, building societies and cooperatives, as well as commercial banking services provided by mutual organizations (such as cooperative federations) to cooperative businesses. A 2013 report by ILO concluded that cooperative banks outperformed their competitors during the financial crisis of 2007–2008. The cooperative banking sector had 20% market share of the European banking sector, but accounted for only 7% of all the write-downs and losses between the third quarter of 2007 and first quarter of 2011. Cooperative banks were also over-represented in lending to small and medium-sized businesses in all of the 10 countries included in the report. Credit unions in the US had five times low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perestroika
''Perestroika'' (; russian: links=no, перестройка, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg) was a political movement for reform within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s widely associated with CPSU general secretary Mikhail Gorbachev and his glasnost (meaning "openness") policy reform. The literal meaning of perestroika is "reconstruction", referring to the restructuring of the Soviet political and economic system, in an attempt to end the Era of Stagnation. Perestroika allowed more independent actions from various ministries and introduced many market-like reforms. The alleged goal of perestroika, however, was not to end the command economy but rather to make socialism work more efficiently to better meet the needs of Soviet citizens by adopting elements of liberal economics. The process of implementing perestroika added to existing shortages, and created political, social, and economic tensions within the Soviet Union. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing dynasty, Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the Russian Empire Census, 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, Lëtzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duché de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Großherzogtum Luxemburg is a small landlocked country in Western Europe. It borders Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembourg, is one of the four institutional seats of the European Union (together with Brussels, Frankfurt, and Strasbourg) and the seat of several EU institutions, notably the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority. Luxembourg's culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its French culture, French and German culture, German neighbors; while Luxembourgish is legally the only national language of the Luxembourgers, Luxembourgish people, French language, French and German language, German are also used in administrative and judicial ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East-West United Bank
East-West United Bank is a bank based in Luxembourg, owned by Sistema. The bank offers private banking and corporate financing. East-West United Bank was established on 12 June 1974 as a "daughter" bank of the Soviet Union's Central Bank. History With the support of Mr. Pierre Werner, who was the Prime Minister of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, on 12 June 1974, the East-West United Bank (EWUB) (Luxembourg) was formed with both the State Bank of the USSR or Gosbank and after the end of the Soviet Union, the Central Bank of Russia, and Russia's Foreign Trade Bank Vneshtorgbank (VTB) as the main shareholders from founding until 1992. From 1992 to 2000, Imperial Bank had a major stake in EWUB of 49% and Tokobank held a 28% stake in EWUB in 1998, but, on 17 April 2000, Imperial Bank was dissolved. Imperial Bank focused on oil and natural gas supplies to East Germany and later to Germany including the oil-for-pipes program. When VTB had a major stake in EWUB from 2000 to 2007, EWUB wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donau Bank
Donau Bank AG was a controlled bank in Vienna, Austria controlled by the Soviet Union and later, after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, by Russia. It was acquired by Russian VTB Bank in 2000. In 2006 the name was changed to VTB Bank (Austria) AG. On December 29, 2017, VTB Group completerestructuringof its European operations. VTB Bank (Austria) AG, VTB Bank (Deutschland) AG und VTB Bank (France) SA, were merged into the newly created VTB Bank (Europe) SE (Frankfurt), which operates under a single banking license. Since that restructuring, VTB Bank (Europe) SE has the branch in Austria. History *1974 - Donau Bank AG is jointly founded in Vienna by the USSR State Bank and the USSR Foreign Trade Bank. *1992 - The Central Bank of the Russian Federation acquires 99.97% of the bank, the remaining 0.03% is retained by the Foreign Trade Bank (Vneshtorgbank). *1997 - VTB acquires a 51% majority share in Donau Bank AG. *2005 - VTB acquires 100% interest in Donau Bank AG. *2006 - In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |