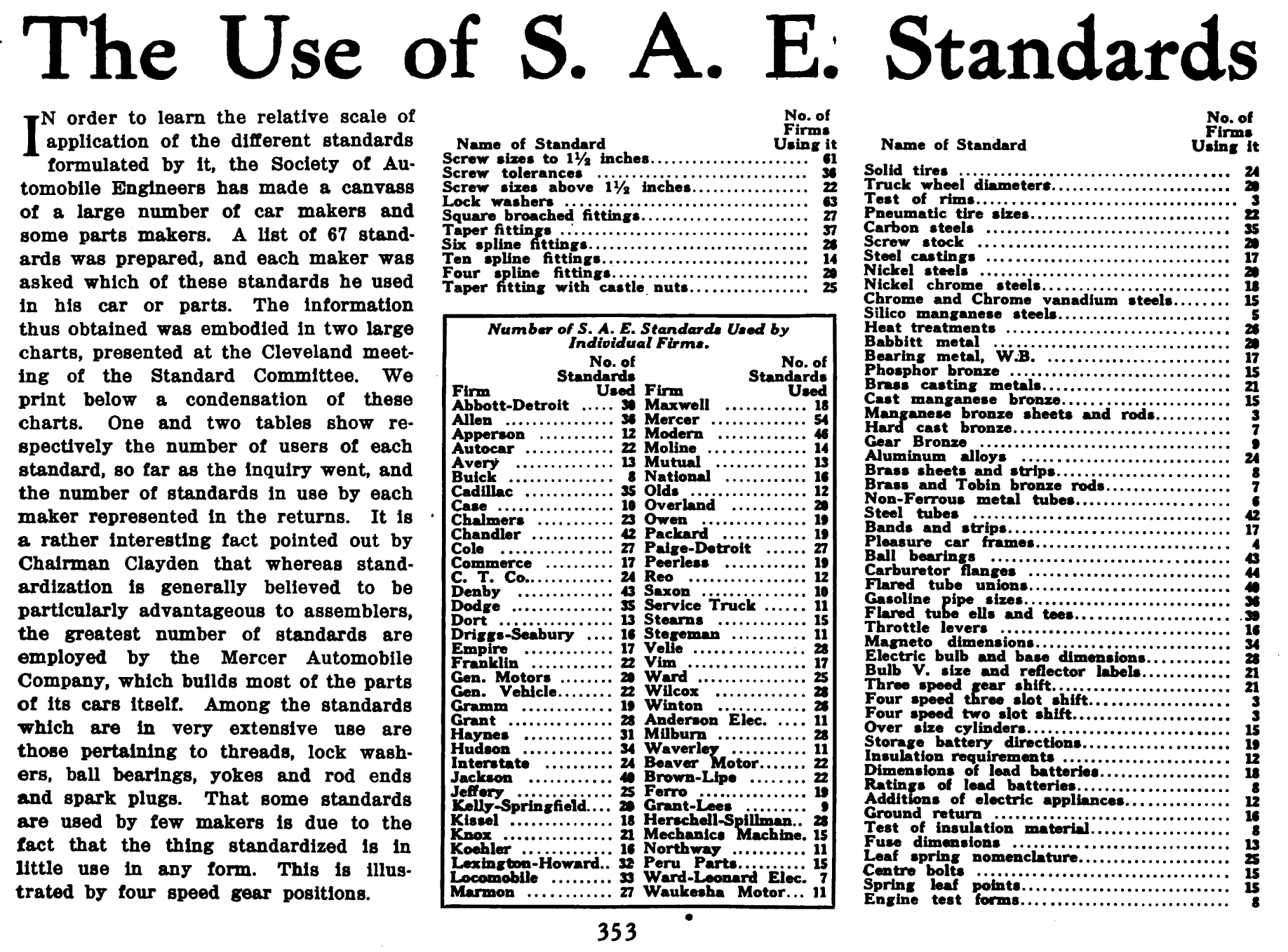
|
Sarich Orbital Engine
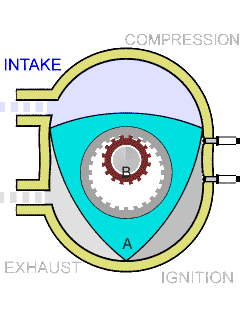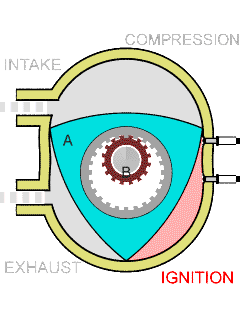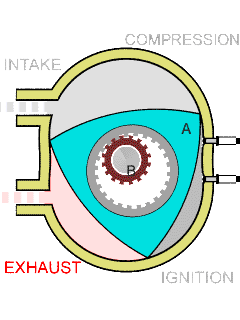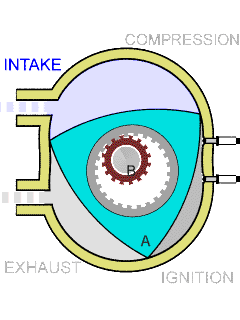
The Sarich orbital engine is a type of internal combustion engine, invented in 1972 by Ralph Sarich, an engineer from Perth, Australia, which features orbital rather than reciprocating motion of its central piston. It differs from the conceptually similar Wankel engine by using a generally prismatic shaped piston that orbits the axis of the engine, without rotation, rather than the rotating trilobular rotor of the Wankel. Overview The engine promised to be about one third the size and weight of conventional piston engines due to the compact arrangement of the combustion chambers. Another advantage is that there is no high-speed contact area with the engine walls, unlike in the Wankel engine in which edge wear is a problem. However, the combustion chambers are divided by vanes which do have contact with both the walls and the orbiting piston and are more difficult to seal due to the eight corners of the combustion chamber. In the patent, the engine is described as two stroke in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons (reciprocating engine, piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a Wankel engine, rotor (Wankel engine), or a propulsive nozzle, nozzle (jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance. This process transforms chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. The first commercially successful internal combustion engines were invented in the mid-19th century. The first modern internal combustion engine, the Otto engine, was designed in 1876 by the German engineer Nicolaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Sarich
Ralph Tony Sarich (born 10 December 1938 in Baskerville, Western Australia) is an Australian automotive engineer, inventor, and businessman who developed the orbital engine and the orbital combustion process engine. Sarich founded the Orbital Engine Company, which developed the orbital combustion process (OCP) engine, based on the two-stroke concept. Early life Sarich was born on 10 December 1938 in Baskerville, Western Australia, to an Austrian and Croatian family. His parents arrived in Australia before the Great Depression of the 1930s. Sarich began an apprenticeship as a fitter and turner, studying high school years 11 and 12 subjects part-time at Midland Technical School. He qualified with top achievement at the completion of his apprenticeship, during and after which he did engineering units one day per week, night classes, and by correspondence. Career His working career encompassed being a fitter and turner and trainee engineer with the Western Australian Governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perth
Perth () is the list of Australian capital cities, capital city of Western Australia. It is the list of cities in Australia by population, fourth-most-populous city in Australia, with a population of over 2.3 million within Greater Perth . The Extremes on Earth#Other places considered the most remote, world's most isolated major city by certain criteria, Perth is part of the South West Land Division of Western Australia, with most of Perth metropolitan region, Perth's metropolitan area on the Swan Coastal Plain between the Indian Ocean and the Darling Scarp. The city has expanded outward from the original British settlements on the Swan River (Western Australia), Swan River, upon which its #Central business district, central business district and port of Fremantle are situated. Perth was founded by James Stirling (Royal Navy officer), Captain James Stirling in 1829 as the administrative centre of the Swan River Colony. The city is situated on the traditional lands of the Whadju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wankel Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an eccentric (mechanism), eccentric Pistonless rotary engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. The concept was proven by German engineer Felix Wankel, followed by a commercially feasible engine designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor spins inside a figure-eight-like epitrochoidal housing around a fixed gear. The midpoint of the rotor moves in a circle around the output shaft, rotating the shaft via a Cam (mechanism), cam. In its basic gasoline-fuelled form, the Wankel engine has lower thermal efficiency and higher exhaust emissions relative to the Four-stroke engine, four-stroke reciprocating engine. This thermal inefficiency has restricted the Wankel engine to limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, many disadvantages have mainly been overcome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAE International
SAE International is a global professional association and standards organization based in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, United States. Formerly the Society of Automotive Engineers, the organization adopted its current name in 2006 to reflect both its international membership and the increased scope of its activities beyond automotive engineering and the automotive industry to include aerospace and other transport industries, as well as commercial vehicles including autonomous vehicles such as self-driving cars, trucks, surface vessels, drones, and related technologies. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. History In the early 1900s there were dozens of automobile manufacturers in the United States, and many more w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyota Kijang
The Toyota Kijang is a series of pickup trucks, station wagons and light commercial vehicles produced and marketed mainly in Southeast Asia, Taiwan, India and South Africa by Toyota between 1976 and 2007 under various other names. The vehicle first entered production in the Philippines as the Toyota Tamaraw in December 1976. It was then introduced in Indonesia in June 1977 as the Kijang, after its unnamed prototype model was showcased in Jakarta in mid-1975. The first two generations were produced from factory as pickup trucks, conversions to other body styles were conducted by local third-party companies. Availability of the model was expanded to more markets since the third-generation model, such as Africa and Taiwan. The Kijang was relatively affordable in the markets where it was sold when compared to the four-wheel drive vehicles (it is predominantly rear-wheel drive) and had high seating capacity, high ground clearance and rugged suspension, popular features in an area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki Karimun
The Suzuki Karimun is a nameplate of city cars produced by the Japanese automaker Suzuki and marketed in Indonesia between September 1999 and 2021 by Suzuki Indomobil Motor, an Indonesian subsidiary of Suzuki. It is named after Great Karimun (''Karimun Besar''), a group of islands in Karimun Regency, Riau Islands, although the subsidiary also said the Karimun name was coined from the phrase "carry to the moon". The Karimun models are based on a kei car Kei car is the smallest category of Japanese expressway-legal motor vehicles. The term ''kei'' is a shortening of , (kanji: ), which translates to English as "light vehicle" (). With restricted dimensions and engine specifications, owners ... platform of Wagon R models and derivatives: * First generation (SL410R, 1999–2006): a locally built first-generation Wagon R-Wide/+. * Second generation (MF31S, 2007–2013): a Maruti Zen Estilo imported from India and rebadged as the Karimun Estilo. This model is a restyled fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford Festiva
The Ford Festiva is a four passenger, three-door, front-drive subcompact car manufactured in South Korea by Kia, under license from Mazda and marketed by Ford for model years 1986–2002 over three generations in Japan, the Americas, and Australia as the Festiva and as the Aspire in North America during its second generation. Designed by Mazda using the DA platform and B series straight-four engines, the Festiva was manufactured in South Korea by Kia, under license. Kia began marketing the first generation in South Korea under license — as the Kia Pride. Australasia and Europe received the first version between 1987 and 1991 as the " Mazda 121". After 1991, Australasian sales began under the "Ford Festiva" name, while European sales continued as the "Kia Pride". Kia ended production of the Pride in 2000. Ongoing production of the first generation overlapped its second generation, introduced in 1993 and marketed as the Ford Aspire in North America and as the Kia Avella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratified Charge Engine
A stratified charge engine describes a certain type of internal combustion engine, usually spark ignition (SI) engine that can be used in trucks, automobiles, portable and stationary equipment. The term "stratified charge" refers to the working fluids and fuel vapors entering the cylinder. Usually the fuel is injected into the cylinder or enters as a fuel rich vapor where a spark or other means are used to initiate ignition where the fuel rich zone interacts with the air to promote complete combustion. A stratified charge can allow for slightly higher compression ratios without " knock," and leaner air/fuel ratio than in conventional internal combustion engines. Conventionally, a four-stroke (petrol or gasoline) Otto cycle engine is fueled by drawing a mixture of air and fuel into the combustion chamber during the intake stroke. This produces a homogeneous charge: a homogeneous mixture of air and fuel, which is ignited by a spark plug at a predetermined moment near the top of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Corporation
Orbital Corporation Limited (), formerly Orbital Engine Corporation Limited pioneered by Ralph Sarich, is an Australian company based in Balcatta, Western Australia, that aims to provide clean engine technologies and alternative fuel systems with reduced environmental impact from gas emissions and improved fuel economy. Consulting services Design, manufacturing, development and testing facilities have been established at the Balcatta facility. Orbital has developed infrastructure in engine design and modelling, numerical analysis, computational fluid dynamics, combustion and fuel system development, rapid-turn-around prototyping, and engine-management system software and hardware design. Autogas systems Orbital Autogas Systems, a former subsidiary of Orbital Corporation, used to produce a retrofit LPG system applicable to a range of vehicles. Orbital Liquid LPG injection (LLi) is claimed to be the latest generation in automotive LPG fuel systems, promising substantial f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |