|
Rusidava
Rusidava (or Zusidava) was a Dacian town mentioned in Tabula Peutingeriana between Acidava and Pons Aluti, today's Drăgășani, Vâlcea County, Romania. See also * Dacian davae * List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia * Dacia Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ... * Roman Dacia References Ancient * * Modern * Dacian towns {{Europe-archaeology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine. A Dacian Kingdom of variable size existed between 82 BC until the Roman conquest in AD 106, reaching its height under King Burebista. As a result of the two wars with Emperor Trajan, the population was dispersed and the central city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans, but was rebuilt by the latter to serve as the capital of the Roman province of Dacia. The Free Dacians, living the territory of modern-day Northern Romania disappeared with the start of the Migration Period. Nomenclature The Dacians are first mentioned in the writings of the Ancient Greeks, in Herodotu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dava (Dacian)
''Dava'' (Latinate plural ''davae'') was a Geto-Dacian name for a city, town or fortress. Generally, the name indicated a tribal center or an important settlement, usually fortified. Some of the Dacian settlements and the fortresses employed the Murus Dacicus traditional construction technique. Most of these towns are attested by Ptolemy, and therefore date from at least the 1st century CE. The "''dava''" towns can be found as south as Sandanski and Plovdiv. Strabo specified that the Daci are the Getae. The Dacians, Getae and their kings were always considered as Thracians by the ancients ( Dio Cassius, Trogus Pompeius, Appian, Strabo, Herodotus and Pliny the Elder), and were both said to speak the same Thracian language. Etymology Many city names of the Dacians were composed of an initial lexical element (often the tribe name) affixed to ''-dava'', ''-daua'', ''-deva'', ''-deba'', ''-daba'' or ''-dova'' (''*dʰeh₁-'' "to set, place"). Therefore, ''dava'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
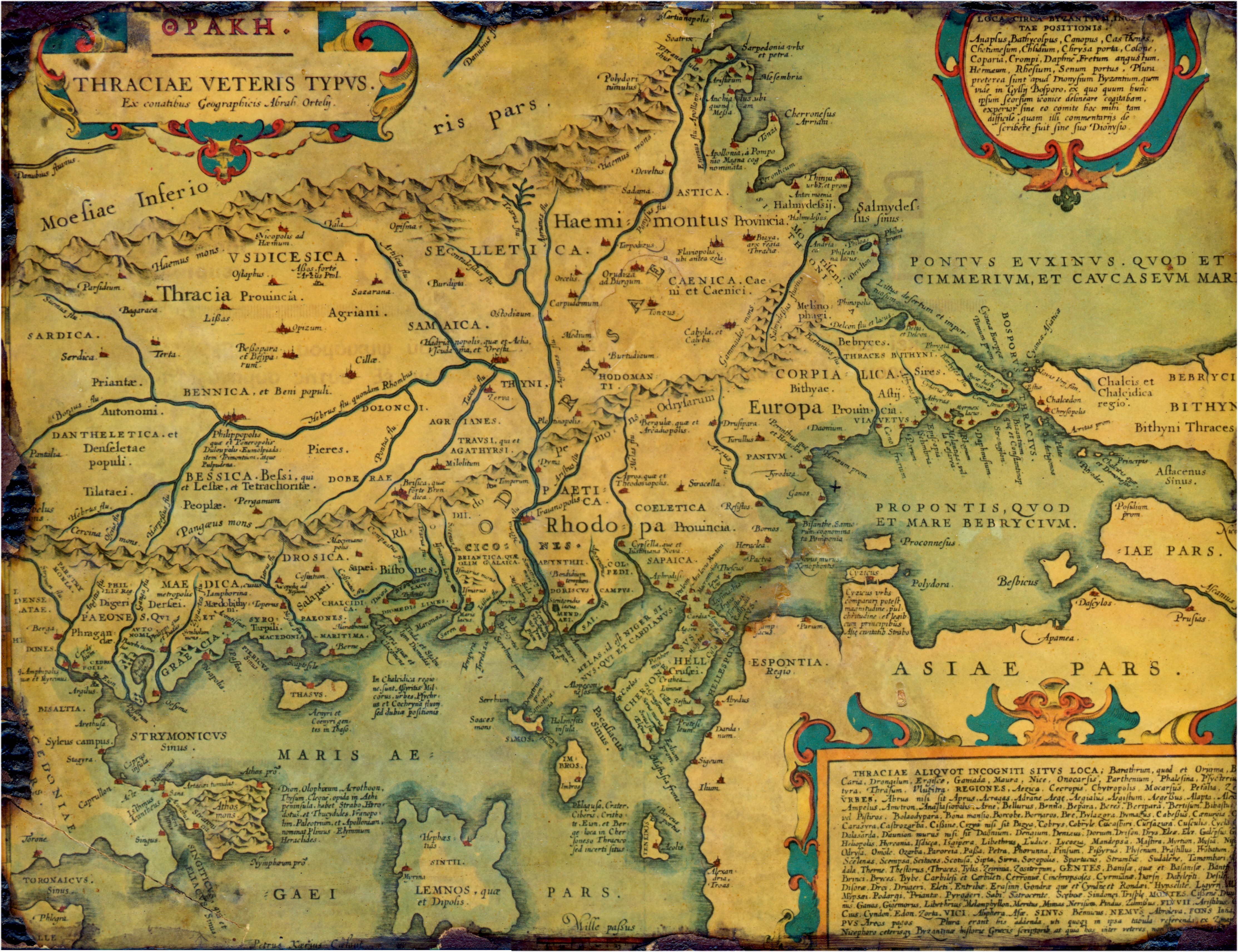
List Of Ancient Cities In Thrace And Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidava
Acidava (''Acidaua'') was a Dacian and later Roman fortress on the Olt river near the lower Danube. The settlements remains are located in today's Enoşeşti, Olt County, Oltenia, Romania. History After the Roman conquest of Dacia by Roman Emperor Trajan, Acidava became a civilian and military center, with castra being built in the area. Acidava was part of the Limes Alutanus, a line of fortifications built under emperor Hadrian running north–south along the ''Alutus'' – the Olt river. The function of the lines was to monitor the Roxolani to the east and deter any possible attacks. Acidava is depicted in the Tabula Peutingeriana between Romula and Rusidava. The same document depicts a second Acidava, between Cedoniae and Apula, but some authors believe it is actually a copy error and the correct name is Sacidava, another Dacian town. See also * Acidava (castra) * Dacia * Roman Dacia * List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia * Dacian davae Notes Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drăgășani
Drăgășani () is a city in Vâlcea County, Romania, near the right bank of the Olt river, and on the railway between Caracal and Râmnicu Vâlcea. The city is well known for the vineyards on the neighboring hills that produce some of the best Wallachian wines. The city administers four villages: Capu Dealului, Valea Caselor, Zărneni and Zlătărei. It is situated in the historical region of Oltenia. History Drăgășani stands on the site of the Daco-Roman ''Rusidava''. On 19 June 1821, during the Greek War of Independence, the Ottomans routed the Filiki Eteria troops of Alexander Ypsilantis near the city in the Battle of Dragashani. There Tudor Vladimirescu fought with his Panduri, revolutionary fighters consisting mainly of peasants and not armed with firepower, against the Turks. Notable people * Florin Costea * Mihai Costea * Alexandru Dandea * Mugur Isărescu * Gib Mihăescu * Adrian Păun Adrian Constantin Alexandru Păun (; born 1 April 1995) is a Romani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabula Peutingeriana
' (Latin for "The Peutinger Map"), also referred to as Peutinger's Tabula or Peutinger Table, is an illustrated ' (ancient Roman road map) showing the layout of the '' cursus publicus'', the road network of the Roman Empire. The map is a 13th-century parchment copy of a possible Roman original. It covers Europe (without the Iberian Peninsula and the British Isles), North Africa, and parts of Asia, including the Middle East, Persia, and India. According to one hypothesis, the existing map is based on a document of the 4th or 5th century that contained a copy of the world map originally prepared by Agrippa during the reign of the emperor Augustus (27 BC – AD 14). However, Emily Albu has suggested that the existing map could instead be based on an original from the Carolingian period. The map was likely stolen by the renowned humanist Conrad Celtes, who bequeathed it to his friend, the economist and archaeologist Konrad Peutinger, who gave it to Emperor Maximilian I, as part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pons Aluti
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus.Saladin Kenneth S.(2007) Anatomy & physiology the unity of form and function. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill Structure The pons is in the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata, and in front of the cerebellum. A separating groove between the pons and the medulla is the inferior pontine sulcus. The superior pontine sulcus separates the pons from the midbrain. The pons can be broadly divided into two parts: the basilar part of the pons (vent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vâlcea County
Vâlcea County (also spelt ''Vîlcea''; ) is a county (județ) of Romania. Located in the historical regions of Oltenia and Muntenia (which are separated by the Olt River), it is also part of the wider Wallachia region. Its capital city is Râmnicu Vâlcea. Demographics In 2011, it had a population of 355,320 and the population density was 61.63/km2. * Romanians - over 98% * Roma, others - 2% Geography This county has a total area of . The North side of the county is occupied by the mountains from the Southern Carpathians group - The Făgăraș Mountains in the east with heights over , and the Lotru Mountains in the west with heights over . They are separated by the Olt River valley - the most accessible passage between Transylvania and Muntenia. Along the Olt River Valley there are smaller groups of mountains, the most spectacular being the . Towards the South, the heights decrease, passing through the sub-carpathian hills to a high plain in the West side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a predominantly temperate-continental climate, and an area of , with a population of around 19 million. Romania is the twelfth-largest country in Europe and the sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Its capital and largest city is Bucharest, followed by Iași, Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara, Constanța, Craiova, Brașov, and Galați. The Danube, Europe's second-longest river, rises in Germany's Black Forest and flows in a southeasterly direction for , before emptying into Romania's Danube Delta. The Carpathian Mountains, which cross Romania from the north to the southwest, include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Settlement in what is now Romania began in the Lower Paleolithic, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last one which is split between Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after Trajan's Dacian Wars, two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |